Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Propanolol and Spironolactone Drug Study
Загружено:
Lisette CastilloИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Propanolol and Spironolactone Drug Study
Загружено:
Lisette CastilloАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
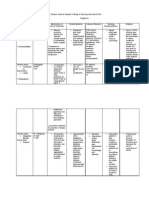
Name Spironolactone 75mg/tab
Classification Aldosterone Antagonist Potassiumsparing diuretic
Action Completely blocks the effects of aldosterone in the renal tubule, causing loss of sodium and water and retention of potassium
Indication Diagnosis and maintenance of primary hyperaldosteronism Treatment of hypokalemia or prevention of hypokalemia in patients who would be at high risk if hypokalemia occurred: Digitalized patients, patients with cardiac arrhythmias Essential hypertension, usually in combination with other drugs
Contraindication Contraindicated with allergy to spironolactone, hyperkalemia, renal disease, anuria, amiloride or triamterene use. Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation
Adverse action CNS: Dizziness, headache, drowsiness, fatigue , ataxia, confusion Dermatologic: Rash,urticaria GI: Cramping, diarrhea, dry mouth, thirst, vomiting. GU: Impotence, irregular menses, amenorrhea, postmenopausal bleeding
Nursing consideration Record alternate-day therapy on a calendar, or prepare dated envelopes. Take the drug early because of increased urination. Weigh yourself on a regular basis, at the same time and in the same clothing, and record the weight on your calendar. Avoid foods that are rich in potassium (fruits,Sanka).
These side effects may occur: Increased volume and frequency of urination; dizziness, confusion, feeling faint on arising, drowsiness (avoid rapid position changes, hazardous activities: driving, using Hematologic: Hyper alcohol); increased thirst (suck on kalemia, sugarless lozenges; use frequent hyponatremia, mouth care); changes in menstrual agranulocytosis cycle, deepening of the voice, impotence, enlargement of the Other: breasts can occur (reversible). Carcinogenic in animals, deepening Report weight change of more than of the voice, 3 lb in one day, swelling in your hirsutism, ankles or fingers, dizziness, gynecomastia trembling, numbness, fatigue, enlargement of breasts, deepening of voice, impotence, muscle weakness or cramps.
Name Propanolol 20 mg/tab Q8
Classification Antianginal, Antiarrythmic, Antihypertensiv e, non selective beta-adrenergic blocker
Action Competitively blocks betaadrenergic receptors in the heart and juxtaglomerular apparatus, decreasing the influence of the sympathetic nervous system o n these tissues, the excitability of the heart, cardiac workload and oxygen consumption, an d the release of rennin and lowering BP; has membranestabilizing(local anesthetic) effects that contribute to its antiarrhthmic action; acts in the CNS to reduce sympathetic outflow and vasoconstrictor tone.
Indication a. Hypertension alone or with other drugs, expecially diuretics. b. Angina pectoris caused by coronary atherosclerosis c. Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis to manage associated stress-induced angina, palpitations and syncope. d. Cardiac arrhythmias especially supraventricular tachycardia, and ventricular tachycardias induced by digitalis or catecholamines. e. Prevention if reinfarction in clinically stable patients5-21 days after MI f. Pheochromocytoma, an adjunctive therapy after treatment with an alpha adrenergic blocker to manage the tachycardia before or during surgery or if the pheochromocytoma is inoperable g. Phrophylaxis for migraine headache h. Treatment of essential tremor, familial or hereditary
Contraindication a.Allergy to betablocking agents R: It may induce allergic reactions b. Sinus bradycardia R: It may further contribute to the decreased heart rate of the client c. Pregnancy R: It may cause neonatal bradycardia d. Apnea R: It may further cause relaxation of the respiratory muscles, thus inhibiting respiration
Adverse action Adverse Effects: a. Fever, rashes, pruritus, shortness of breath R: Hypersensitivity reactions to the drug b. Bradycardia, heartfailure R: Reduced cardiac oxygen in the heart. Drug-Drug a. Aminophylline, theophylline R: May act antagonistically reducing the effects of one or both drugs. May reduce theophylline elimination b. Amiodarone, fluconazole, isoniazid R: May increase propranolol level c. Amobarbital, Phenobarbital R: May reduce propranolol effects. Increase beta blocker dose. d. Cemetidine R: May increase pharmacologic effects of beta blocker. e. Epinephrine R: May cause an initial hypertensive episode followed by bradycardia. f. Oral antibiotics R: May alter requirements for these drugs in previously stabilized diabetic patients
Nursing consideration 1.) Monitor the vital signs of the client. 2.) Encourage eat in small frequent feedings if there are episodes of vomiting. 3.) May offer ice chips to reduce nausea. 4.) TSB for fever 5.) Instruct client not to get up on bed immediately to reduce the occurrence of dizziness. 6.) May be given with food if GI upsets occurs 7.) Provide environment conducive for rest
Вам также может понравиться
- Drug StudyДокумент23 страницыDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetОценок пока нет
- Bumetanide (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыBumetanide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse68880% (1)
- AmilorideДокумент1 страницаAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- PropranololДокумент2 страницыPropranololChristine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Atorvastatin (LIPITOR)Документ2 страницыAtorvastatin (LIPITOR)Kristine Young100% (1)
- DigoxinДокумент1 страницаDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Atorvastatin Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыAtorvastatin Drug StudyJustine May Gervacio0% (1)
- Drug Study - NitroglycerinДокумент1 страницаDrug Study - Nitroglycerinchriscustodio100% (1)
- Drug Study Calcium GluconateДокумент1 страницаDrug Study Calcium GluconateLarah Mae AndogОценок пока нет
- Drug Study VALSARTANДокумент1 страницаDrug Study VALSARTANThrizia Salas100% (1)
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Документ1 страницаEnoxaparin (Lovenox)EОценок пока нет
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingДокумент3 страницыBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesДокумент1 страницаGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonОценок пока нет
- CaptoprilДокумент2 страницыCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Name of Drug FinalДокумент7 страницName of Drug FinalJaessa FelicianoОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneДокумент4 страницыDRUG STUDY - SpironolactoneMarianne Claire P. Bartolome50% (2)
- Codeine Phosphate (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыCodeine Phosphate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (2)
- Drug Study LosartanДокумент2 страницыDrug Study LosartanIris BalinoОценок пока нет
- Drug Levothyroxine SodiumДокумент2 страницыDrug Levothyroxine SodiumSrkocher0% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыDrug Studyunkown userОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)Документ2 страницыDrug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)mikErlh80% (5)
- Clopidogrel Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыClopidogrel Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie CayetanoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - MidazolamДокумент8 страницDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityДокумент2 страницыRepublic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityRosemarie EustaquioОценок пока нет
- Furosemide Drug SyudyДокумент1 страницаFurosemide Drug SyudyallenininiОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент9 страницDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- Doxazosin MesylateДокумент2 страницыDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Drug Study of FurosemideДокумент5 страницDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Atropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Документ3 страницыAtropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- DORMICUMДокумент1 страницаDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsДокумент3 страницыClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEОценок пока нет
- Captopril Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаCaptopril Drug Studyiammkrissa33% (3)
- Heparin InjectionДокумент2 страницыHeparin InjectiongagandipkSОценок пока нет
- 10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateДокумент2 страницы10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateamitОценок пока нет
- DiovanДокумент2 страницыDiovanianecunar100% (1)
- Drug AnalysisДокумент18 страницDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateДокумент2 страницыDRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- Arixtra Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыArixtra Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- Bisoprolol Fumarate (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыBisoprolol Fumarate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse688867% (6)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaОценок пока нет
- Ramipril Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- 7 Drug StudyДокумент17 страниц7 Drug StudyMa. Mechile MartinezОценок пока нет
- Benztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыBenztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyHamimah Bint AliОценок пока нет
- Clonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыClonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse688875% (4)
- CaptoprilДокумент2 страницыCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaОценок пока нет
- Atenolol Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыAtenolol Drug StudyFranz.thenurse6888100% (2)
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsДокумент4 страницыGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- FurosemideДокумент2 страницыFurosemideIvanne HisolerОценок пока нет
- Captopril (Drug Study)Документ3 страницыCaptopril (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (3)
- MetoprololДокумент1 страницаMetoprololjchowking100% (1)
- Drug RationaleДокумент77 страницDrug RationaleYolanda WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Drug and NCPДокумент15 страницDrug and NCPgeelawlietОценок пока нет
- CVA Drug StudyДокумент51 страницаCVA Drug StudyKarel LuОценок пока нет
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureДокумент31 страницаOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420Оценок пока нет
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MДокумент9 страницMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент10 страницDrug StudyHelen ReonalОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент9 страницDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug 25Документ17 страницDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- DrugsДокумент6 страницDrugsMillet RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneДокумент28 страницAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeОценок пока нет
- American GeographyДокумент7 страницAmerican GeographyLisette CastilloОценок пока нет
- Theoretical FrameworkДокумент2 страницыTheoretical FrameworkLisette CastilloОценок пока нет
- NCM 107 ControllingДокумент31 страницаNCM 107 ControllingLisette Castillo100% (1)
- Gentamicin Sulfate-Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыGentamicin Sulfate-Drug StudyDaisy Palisoc82% (11)
- Anatomy and Physiology CardiovascularДокумент5 страницAnatomy and Physiology CardiovascularLisette CastilloОценок пока нет
- BiopsyДокумент3 страницыBiopsyLisette CastilloОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology CardiovascularДокумент5 страницAnatomy and Physiology CardiovascularLisette CastilloОценок пока нет
- UTI PathoДокумент3 страницыUTI PathoLisette CastilloОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент10 страницDrug StudyLisette CastilloОценок пока нет
- Koch PostulatesДокумент1 страницаKoch PostulatescdumenyoОценок пока нет
- PTB Case-StudyДокумент64 страницыPTB Case-StudyBeverly DatuОценок пока нет
- HYPERALDOSTERONISMДокумент7 страницHYPERALDOSTERONISMMarnee Justine ColladoОценок пока нет
- Brown Tumor - WikipediaДокумент11 страницBrown Tumor - WikipediaDr. Prashant VermaОценок пока нет
- Screenshot 2021-10-27 at 13.19.13Документ74 страницыScreenshot 2021-10-27 at 13.19.13Kenny MgulluОценок пока нет
- BurnsДокумент27 страницBurnsThao TranОценок пока нет
- FDA Marijuana Negative Monograph RejectionДокумент7 страницFDA Marijuana Negative Monograph RejectionMarijuana MomentОценок пока нет
- Viral Gastroenteritis-1Документ17 страницViral Gastroenteritis-1Abdus SubhanОценок пока нет
- DFP40182 Software Requirement and DesignДокумент3 страницыDFP40182 Software Requirement and DesignTiyah BahariОценок пока нет
- Vertigo and Dizziness in The ElderlyДокумент6 страницVertigo and Dizziness in The ElderlyCarmen DélanoОценок пока нет
- General Paper September 2020Документ26 страницGeneral Paper September 2020Kumah Wisdom100% (1)
- Anal AbscessДокумент5 страницAnal AbscessFernia StevaniОценок пока нет
- MalariaДокумент21 страницаMalariayusak tapakedingОценок пока нет
- Alemnesh MandeshДокумент94 страницыAlemnesh MandeshDОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Head Trauma: PathophysiologyДокумент5 страницPediatric Head Trauma: Pathophysiologyherman76Оценок пока нет
- s8. Partograph. ExerciseДокумент44 страницыs8. Partograph. ExerciseAngel ReyesОценок пока нет
- Contoh Perhitungan ABCДокумент5 страницContoh Perhitungan ABCAndini SetiawatiОценок пока нет
- SOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) and PELOD (Pediatric LogisticДокумент5 страницSOFA (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment) and PELOD (Pediatric LogisticvidyahamzahОценок пока нет
- Comm Dent MCQДокумент8 страницComm Dent MCQoss-20502745Оценок пока нет
- Experimental Design in Clinical TrialsДокумент18 страницExperimental Design in Clinical Trialsarun_azamОценок пока нет
- Program and Proceedings - 11th International Regional "Stress and Behavior" Neuroscience and Biopsychiatry Conference (North America), June 22-24, 2017, Miami Beach, FL, USAДокумент49 страницProgram and Proceedings - 11th International Regional "Stress and Behavior" Neuroscience and Biopsychiatry Conference (North America), June 22-24, 2017, Miami Beach, FL, USAISBS_SocietyОценок пока нет
- Passive MovementДокумент16 страницPassive MovementNaemah Ansari100% (1)
- Ca BladderДокумент11 страницCa Bladdersalsabil aurellОценок пока нет
- 60 Revision MCQs For ProsДокумент9 страниц60 Revision MCQs For ProsUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Name of Pharmacy: ................................. CityДокумент1 страницаName of Pharmacy: ................................. Cityravi sheladiyaОценок пока нет
- Providing First Aid and Emergency ResponseДокумент161 страницаProviding First Aid and Emergency ResponseTHE TITANОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis Management Hepatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis Dan Penatalaksanaan Ensefalopati HepatikДокумент21 страницаDiagnosis Management Hepatic Encephalopathy Diagnosis Dan Penatalaksanaan Ensefalopati HepatikKadek Rudita YasaОценок пока нет
- Pfizer Drug R&D Pipeline As of July 31, 2007Документ19 страницPfizer Drug R&D Pipeline As of July 31, 2007anon-843904100% (1)
- Jason Case StudyДокумент2 страницыJason Case StudyLLLJJJОценок пока нет
- CH-UH Media Statement Re Healthcare 11-30-2020Документ2 страницыCH-UH Media Statement Re Healthcare 11-30-2020WKYC.comОценок пока нет