Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Renal Diseases Pathophysiology
Загружено:
Billy GayadosИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Renal Diseases Pathophysiology
Загружено:
Billy GayadosАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
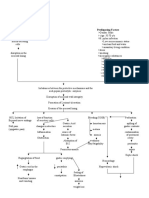
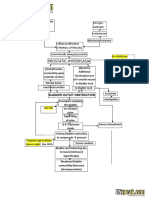
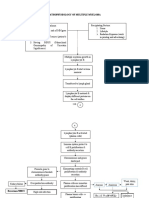
Risk factors: Inability or failure to empty bladder completely Obstructed urinary flow Decreased natural host defenses or immunosuppression
Instrumentation of the urinary tract Inflammation or abrasion of the urethral mucosa Contributing conditions such as: DM, Pregnancy,neurologic disorders, gout.
Loss of integrity of the mucosal lining
Decreased resistance to invading organisms
Bacteria enters the urethra
Attachment & Proliferation of bacteria in the urethra
Irritation of the lining of the bladder
Bacteria Travels from urethra to bladder, attach to and colonize the bladder
Urethrovesical reflux
urethritis
Cystitis Urine stagnation
Urine cultures, Test for WBCs, Test for STDs, CT Scan
Pain Swelling, Discharges accumulation of leukocytes
Ureterovesical Reflux
Cystolithiasis, Pregnancy, Untreated UTI
Acute pain related to infection within the urinary tract Deficient knowledge about factors predisposing the pt. to infection & recurrence, detection, & prevention of recurrence &
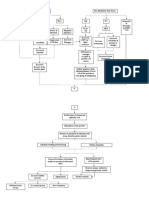
Introduction of bacteria to the ureters
oliguria Passing a cloudy or strong smelling urine pressure on lower abdomen low grade fever
Ureteritis Urinalysis, cystoscopy, Imaging test (ultrasound & x-ray) Infection ascends to the kidneys
Risk for hypertermia
Pyelonephritis
Relieving pain >Antispasmodic agents, Application of heat, Inc. fluid intake, Analgesics, frequent voiding Monitoring & managing potential complications >Using strict aseptic technique in any procedures Frequent inspection of urine,Performing a meticulous perineal care, maintaining a closed system. Promoting Home and community-Based care >Good hygiene, increasing fluid intake, urinating regularly & more frequently.
Ultrasound study or ct scan, iv urogram, measurement of creatinine clearance, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine levels.
poseidon|billy
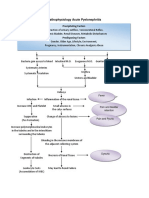
Activation of the immune response
General feeling of being well
Flank Pain Back Pain
Decreased erythropoietin
Release of pyrogens from bacteria
Malaise
Acute Pain
Decreased Stimulation of bone marrows
Release of prostaglandin e2
Irritation of the urinary tract lining/
N&V Hematuria
Decreased Erythropoiesis
Elevation of the body thermostat by the hypothalamus
Dysuria
Decreased RBC production
Vasoconstriction
Reduced heat loss through the skin
Anemia
Shivering Chills ineffective tissue perfusion
Fever
Decrease temperature >loosen clothing
Relieving pain >Increase fluid intake to decrease burning sensation
Adequate tissue perfusion >Monitor v/s, capillary refill, color of skin & mucosa, provide oxygen as needed
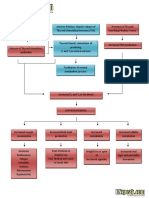
Microorganisms circulate in the blood stream
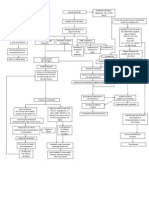
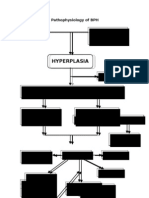
Acute glomerulonephritis
Over production of antibodies
Deposition of antigen-antibody complex in glomerulus
Post infections
Acute inflammation & damage within the nephrons including the glomerulus
poseidon|billy
Increased production of epithelial cells lining the glomerulus
leukocyte infiltration of the glomerulus
thickening of the glomerular infiltration membrane Marked Proteinuria Pitting edema hypoalbuminemia hyperlipidemia fatty cast in the urine
Scarring and loss of glomerular filtration membrane
Decreased GFR Hematuria
Excess fluid volume related to accumulation of fluids in the body
Chronic glomerulonephritis
Repeated episodes of acute Glomerulonephritis
Elevate edematous extremities, change position frequently Encourage bed rest
Cortex shrinks to a layer 1 to 2 mm thick or less
Bands of scar tissue distort the remaining cortex Electron microscopy and immunoflourescent analysis Surface of the kidney rough and irregular Urinalysis, chest x-ray, ECG, CT scan, MRI Numerous glomeruli and their tubules become scarred
Branches of the renal artery are thickened Hypertension elevated BUN & Serum Creatinine vascular changes severe nosebleed pedal edema loss of weight and strength
Branches of the renal artery are thickened
poseidon|billy
Risk for decreased cardiac output
Monitor F&E Give emotional Support Instruction to the patient include explanations and scheduling for follow-up evaluations: BP, and blood studies and creatinine levels
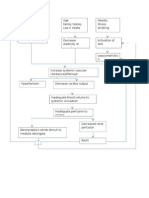
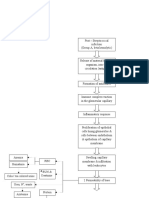
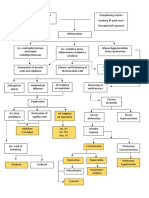
Volume Depletio n:Renal losses
Chronic glomerulonephritis progresses Acute pyelonephritis Acute glomerulonephirtis Renal obstruction
Acute renal Failure Intrarenal Failure
Prerenal failure
Intrarenal Failure
Impaired blood flow
Acute parechymal damage to the glomeruli or kidney tubules
Pressure rises in the kidney
Hypo perfusion
Problem on osmosis
Monitor fluid & Electrolyte balance Reducing metabolic pain: Bed Rest Prevent infection: Asespsis Provide skin care Provide psychosocial support
tubular back leak
Fluid & electrolyte imbalance Impaired skin integrity Formation of cast/ vasoconstriction
Dry skin Drowsiness headache muscle twitching seizure may appear critically ill & lethargic
Decrease GFR
poseidon|billy
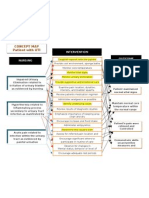
Chronic renal failure
Urinalysis, Blood test, renal ultrasound, Ct/MRI scan, ECG, Renal endoscopy, Renal Biopsy,
Sodium & water
potassium Balance
Elimination of nitrogenous waste
Erythropoeitin production
Acid-Base balance
Hypertension
Hyperkalemia Uremia Edema
Anemia Acidosis
Increased vascular volume
Skeletal buffering Pericarditis Heart failure Coagulopathies
Skin disorder
G.I. Manifestation
Neurologic Manifestation
Sexual Dysfunction
Risk for decreased cardiac output
Disturbed thought process
Osteodystrophies
Assess degree of hypertension Assess level of activity Investigate report of chest pain Hyperparathyroidism Hypocalcemia
Activation of vit. D
Phosphate elimination
END STAGE RENAL DISEASE
Uremic syndrome develops
poseidon|billy
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF RENAL DISEASES
SUbmitted by:Billy Gayados, BSN-III, BLOCK-M SUbmitted to: MR. Dennis ramos
LEGEND:
DIAGNOSTICS SIgns & Symptoms Disease Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Responsibilities
poseidon|billy
Вам также может понравиться
- Moonlight PDFДокумент371 страницаMoonlight PDFFerzada Sajiran100% (2)
- Cholecystitis Concept MapДокумент4 страницыCholecystitis Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (7)
- Topnotch IM For MoonlightersДокумент274 страницыTopnotch IM For Moonlightersmefav7778520100% (2)
- VII. Pathophysiology of PUDДокумент1 страницаVII. Pathophysiology of PUDJehmima Gloriani100% (1)
- Benchmark Capstone Project Change Proposal Week 8Документ15 страницBenchmark Capstone Project Change Proposal Week 8Kerry-Ann Brissett-SmellieОценок пока нет
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapДокумент3 страницыFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of DMДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Hypertension PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaОценок пока нет
- Patho UtiДокумент1 страницаPatho UtiCarl Mayrina de Jesus100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Case Presentation On Urinary Tract InfectionДокумент56 страницCase Presentation On Urinary Tract InfectionJohn Alvin Yoro92% (24)
- تجميعةДокумент168 страницتجميعةRn nadeenОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaKevin Jade Herrera0% (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram PDFДокумент2 страницыBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram PDFgailОценок пока нет
- COPD PathoДокумент1 страницаCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaОценок пока нет
- Copd PathoДокумент2 страницыCopd PathoAlvin RamirezОценок пока нет
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewДокумент7 страницPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Electrolyte Imbalance NCPДокумент6 страницElectrolyte Imbalance NCPjohnart jimenezОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology: Non-Hodgkin's LymphomaДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology: Non-Hodgkin's LymphomaExernest Joever ZausaОценок пока нет
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYofДокумент3 страницыPATHOPHYSIOLOGYofRose Si CheeksОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionДокумент50 страницPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 034Документ19 страницChapter 034Mahmmoud FuqahaОценок пока нет
- Path o PhysiologyДокумент9 страницPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersОценок пока нет
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeДокумент3 страницыAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsОценок пока нет
- Acute Renal Failure PathoДокумент4 страницыAcute Renal Failure PathoGlenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of BPHДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of BPHJerome Matthew Hautea Amorado0% (1)
- Pathophysiology On DementiaДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology On Dementiaiamjulzcurtis50% (2)
- Concept MapДокумент1 страницаConcept MapDon Rieza100% (1)
- Concept MapДокумент5 страницConcept Mapmild_tea100% (1)
- PathophyДокумент2 страницыPathophymharz_astilloОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho Irritable Bowel SyndromeДокумент1 страницаPa Tho Irritable Bowel Syndromekaye0403Оценок пока нет
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTOОценок пока нет
- CHOLANGITISДокумент1 страницаCHOLANGITISKirk Torregosa PañaresОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- V. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableДокумент2 страницыV. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableMary Grace BanezОценок пока нет
- Concept Map AsthmaДокумент4 страницыConcept Map AsthmaAstrid Moreno De LeonОценок пока нет
- PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаPathophysiologyHazel PalomaresОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology BPH Case StudyДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology BPH Case Studyyhanne100% (24)
- Communicating Pathophysiology: Impaired Absorption of The CSF in The Arachnoid SpaceДокумент2 страницыCommunicating Pathophysiology: Impaired Absorption of The CSF in The Arachnoid SpaceAyaBasilioОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factorsleslie_macasaetОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and AnemiaДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and Anemiapa3kmedina100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkRifa'atul MahmudahОценок пока нет
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisДокумент1 страницаPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- BPH Pathophysio 4CДокумент2 страницыBPH Pathophysio 4CPatricia Camille Ponce JonghunОценок пока нет
- Massive AscitesДокумент12 страницMassive Ascitesranitidin100% (1)
- Acute Pyelonephritis PathoДокумент1 страницаAcute Pyelonephritis PathoGlenn Asuncion PagaduanОценок пока нет
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureДокумент3 страницыHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Patho PneumoniaДокумент2 страницыPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisДокумент1 страницаSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaОценок пока нет
- Hyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramДокумент1 страницаHyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramMarielle CabanbanОценок пока нет
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoОценок пока нет
- Hypothyroidism PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаHypothyroidism PathophysiologyCleo Joyce C. CristalОценок пока нет
- Esophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNДокумент20 страницEsophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNAnn SalvatierraОценок пока нет
- EsrdДокумент3 страницыEsrdRonald Lavada RN100% (1)
- Copd PathoДокумент1 страницаCopd PathoRey AngeloОценок пока нет
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedДокумент1 страницаPathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- Pediatric Genitourinary DisordersДокумент40 страницPediatric Genitourinary DisordersGelsey Gelsinator JianОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Pharmacotherapeutics II YrДокумент20 страницUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Pharmacotherapeutics II YrpawannnnОценок пока нет
- Edema in ChildДокумент16 страницEdema in ChildKesava DassОценок пока нет
- Genitourinary InfectionsДокумент36 страницGenitourinary InfectionsMisbah KaleemОценок пока нет
- Urinary EliminationДокумент71 страницаUrinary EliminationFrances LiqueОценок пока нет
- Renal and Urinary DisordersДокумент134 страницыRenal and Urinary Disordersmirmodepon05100% (1)
- UTIs 1Документ38 страницUTIs 1Eduardo Valdez RodríguezОценок пока нет
- Postpartum ComplicationsДокумент37 страницPostpartum ComplicationsNusa KojОценок пока нет
- Chapter 132: Lower Urinary Tract Infection: Where Is The Bathroom? Level I Problem IdentificationДокумент4 страницыChapter 132: Lower Urinary Tract Infection: Where Is The Bathroom? Level I Problem IdentificationReen ChavezОценок пока нет
- NURS 209-Study GuideДокумент22 страницыNURS 209-Study GuideTenzin KelsangОценок пока нет
- BCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)Документ7 страницBCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)biddyusmc100% (1)
- Urine Culture Manual MT - SINAI PDFДокумент15 страницUrine Culture Manual MT - SINAI PDFAvi VermaОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Mellitus - Diabetic KetoacidosisДокумент21 страницаDiabetes Mellitus - Diabetic KetoacidosisJamil Lorca100% (5)
- Safety&InfectiousnclexДокумент83 страницыSafety&InfectiousnclexPrang Ismael BR C. AndigОценок пока нет
- Frequently Asked Questions About Kidney Health (English) : Question: What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Disorder?Документ6 страницFrequently Asked Questions About Kidney Health (English) : Question: What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Disorder?Arjay NeivaОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis ISKДокумент17 страницDiagnosis ISKLestari Amelia AdmОценок пока нет
- Cauda-Uti Eccmid PDFДокумент42 страницыCauda-Uti Eccmid PDFIzaac JdevОценок пока нет
- ISK Pada Anak (Ade Sinta)Документ10 страницISK Pada Anak (Ade Sinta)Ades SundayОценок пока нет
- Renal and Urinary DisordersДокумент11 страницRenal and Urinary DisordersChristian Espanilla100% (4)
- Form Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterДокумент1 страницаForm Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterTeenu JobyОценок пока нет
- Medical AbbreviationДокумент3 страницыMedical AbbreviationWaode FitriОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Infections - Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management 2018 PDFДокумент254 страницыNeonatal Infections - Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management 2018 PDFBao NguyenОценок пока нет
- Three Treasures Manual With Tongue Pictures PDFДокумент214 страницThree Treasures Manual With Tongue Pictures PDFspiraldao100% (4)
- Lab Exercise 11 Urine Specimen CollectionДокумент7 страницLab Exercise 11 Urine Specimen CollectionArianne Jans MunarОценок пока нет
- Aafp Uti GuidelinesДокумент10 страницAafp Uti GuidelinesCess Lagera YbanezОценок пока нет
- Antibiotik: Generik Nama Paten Indikasi Dosis Bumil As. Clavulanat + AmoxycillinДокумент8 страницAntibiotik: Generik Nama Paten Indikasi Dosis Bumil As. Clavulanat + AmoxycillinVeve PujiОценок пока нет
- Keep Safe Everyone. God Bless 2C.: 3. Deadline For This Activity Will Be On Sunday March 29, 2020 11:59PMДокумент10 страницKeep Safe Everyone. God Bless 2C.: 3. Deadline For This Activity Will Be On Sunday March 29, 2020 11:59PMJœnríčk AzueloОценок пока нет
- 2020 Article 479Документ5 страниц2020 Article 479Anida HasnaОценок пока нет
- PlaylistДокумент5 страницPlaylistM.N MesaОценок пока нет
- Backup of ANTIMICROBIALS PRINTABLEДокумент4 страницыBackup of ANTIMICROBIALS PRINTABLEinvading_jam7582100% (1)
- Koss2012, Citologia Del Tracto Urinario-Convertido Traducido Version 2.5Документ142 страницыKoss2012, Citologia Del Tracto Urinario-Convertido Traducido Version 2.5Jaime Enrique Betanzos TeobalОценок пока нет
- MedSurg Chapter 66 OutlineДокумент7 страницMedSurg Chapter 66 OutlineJosephine NavarroОценок пока нет