Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
FCPIT Practical File
Загружено:
Shefali GuptaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
FCPIT Practical File
Загружено:
Shefali GuptaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
FCPIT Practical File
Submitted To :Miss Rajwinder Kaur
Submitted By :Name :- Harshvir Roll No :- 20 Class :- B.Tech ME 1 (A)
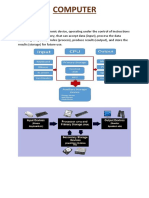
Experiment 1 Title: - Basics of Keyboard, Motherboard, RAM, Hard Disk, Different Printers. Objective: - 1 Software Requirements: - Operating System Hardware Requirements: - Keyboard, Mouse, CPU, RAM, Hard Disk, Printers. Theory:Ram:- Random Access Memory Random-access memory (RAM) is a form of computer data storage. Today, it takes the form of integrated circuits that allow stored data to be accessed in any order with a worst case performance of constant time
Types Of RAM The two main forms of modern RAM are static RAM (SRAM) and dynamic RAM. In static RAM, a bit of data is stored using the state of a flip-flop. This form of RAM is more expensive to produce, but is generally faster and requires less power than DRAM and, in modern computers, is often used as cache memory for the CPU Keyboard:In computing, a keyboard is a typewriter-style keyboard, which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. Following the decline of punch cards and paper tape, interaction via teleprinter-style keyboards became the main input device for computers.
Types Of Keyboard 1) Standard 2) Laptop Sized 3) Thumb Sized
Laptop Sized Keyboard: - Keyboards on laptops and notebook computers usually have a shorter travel distance for the keystroke and a reduced set of keys. They may not have a numerical keypad, and the function keys may be placed in locations that differ from their placement on a standard, full-sized keyboard. Standard Sized Keyboard: - Standard "full-travel" alphanumeric keyboards have keys that are on three-quarter inch centers (0.750 inches, 19.05 mm), and have a key travel of at least 0.150 inches (3.81 mm). Desktop computer keyboards, such as the 101-key US traditional keyboards or the 104-key Windows keyboards, include alphabetic characters, punctuation symbols, numbers and a variety of function keys. Thumb Sized Keyboard: - Smaller keyboards have been introduced for laptops (mainly nettops), PDAs, smartphones, or users who have a limited workspace. A thumb keyboard (thumbboard) is used in some personal digital assistants such as the Palm Treo and BlackBerry and some UltraMobile PCs such as the OQO. Printers: In computing, a printer is a peripheral which produces a text and/or graphics of documents stored in electronic form, usually on physical print media such as paper or transparencies. Many printers are primarily used as local peripherals, and are attached by a printer cable or, in most new printers, a USB cable to a computer which serves as a document source. Some printers, commonly known as network printers, have built-in network interfaces, typically wireless and/or
Ethernet based, and can serve as a hard copy device for any user on the network.
Types of Printers 1) Impact Printers 2) Non Impact Printers Impact Printers: - The Printers Which print the Sheet by coming in full Physical Contact with the sheet Non Impact Printers: - The type of printers which print the sheet by no contact with the sheet Further Divisions of Printers 1) Laser Printer 2) Dot matrics Printer 3) Inkjet Printer Laser Printer: A laser printer is a common type of computer printer that rapidly produces high quality text and graphics on plain paper. As with digital photocopiers and multifunction printers (MFPs), laser printers employ a xerographic printing process, but differ from analog photocopiers in that the image is produced by the direct scanning of a laser beam across the printer's photoreceptor. Dot Matrics Printer: A dot matrix printer or impact matrix printer is a type of computer printer with a print head that runs back and forth, or in an up and down motion, on the page and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper, much like the print mechanism on a typewriter. However, unlike a typewriter or daisy wheel printer, letters are drawn out of a dot matrix, and thus, varied fonts and arbitrary graphics can be produced. Because the printing involves mechanical pressure, these printers can create carbon copies and carbonless copies.
Inkjet: An inkjet printer is a type of computer printer that creates a digital image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper. Inkjet printers are the most commonly used type of printer[1]and range from small inexpensive consumer models to very large professional machines, that can cost up to thousands of dollars CPU: The central processing unit (CPU) is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, and is the primary element carrying out the functions of the computer or other processing device. It carries out each instruction of the program in sequence, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. In other words, the CPU plays a role analogous to the brain in the computer.
ALU (Arithmetic and Logical Unit) : In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a digital circuit that performs arithmetic and logical operations. The ALU is a fundamental building block of the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer, and even the simplest microprocessors contain one for purposes such as maintaining timers. The processors found inside modern CPUs and graphics processing units (GPUs) accommodate very powerful and very complex ALUs; a single component may contain a number of ALUs CU (Control Unit) : A control unit in general is a central (or sometimes distributed but clearly distinguishable) part of the machinery that controls its operation, provided that a piece of machinery is complex and organized enough to contain any such unit. One domain in which the term is specifically used is the area of computer design. In the automotive industry, the control unit helps maintain various functions of the motor vehicle Hard Disk: -
A hard disk drive (HDD; also hard drive or hard disk)[2] is a non-volatile, random access digital data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motordriven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the platters.
Mouse: In computing, a mouse is a pointing device that functions by detecting two-dimensional motion relative to its supporting surface. Physically, a mouse consists of an object held under one of the user's hands, with one or more buttons. It sometimes features other elements, such as "wheels", which allow the user to perform various system-dependent operations, or extra buttons or features that can add more control or dimensional input. The mouse's motion typically translates into the motion of a cursor on a display, which allows for fine control of a graphical user interface.
Вам также может понравиться
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)Документ5 страницCentral Processing Unit (CPU)EllaОценок пока нет
- Portfolio in Robotics (1st Quarter)Документ29 страницPortfolio in Robotics (1st Quarter)No NameОценок пока нет
- ICT BookДокумент9 страницICT Booksenzoc1Оценок пока нет
- Basic Hardware Units of A ComputerДокумент12 страницBasic Hardware Units of A ComputerRobinson JoshuaОценок пока нет
- Complete CP NotesДокумент91 страницаComplete CP NotesAnonymous 1HlNy6nОценок пока нет
- CpfdfileДокумент27 страницCpfdfileSukhpal KaurОценок пока нет
- 1 Computers FundamentalsДокумент13 страниц1 Computers Fundamentalsdevil's doubleОценок пока нет
- (Ict) Computer BasicsДокумент51 страница(Ict) Computer BasicsmwelimkhaliphiОценок пока нет
- Basic Power PointДокумент10 страницBasic Power PointPaul Anthony Gerona JacerОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)Документ32 страницыBasic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)abhi_txt90Оценок пока нет
- ComputerДокумент8 страницComputerBeth AlcontinОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ21 страницаUnit 1Mr Sathesh Abraham Leo CSEОценок пока нет
- Computer and Its ComponentsДокумент4 страницыComputer and Its ComponentsIsmail MswОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computers Notes OUTPUT DevicesДокумент20 страницIntroduction To Computers Notes OUTPUT Devicesmunaxemimosa8Оценок пока нет
- Learning Activity Sheet # 1 TITLE: Assemble Computer HardwareДокумент6 страницLearning Activity Sheet # 1 TITLE: Assemble Computer HardwareAngelo VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- 1) Introduction To ComputerДокумент50 страниц1) Introduction To ComputerSajalОценок пока нет
- Basics of The Computer System: Presented By: Sumit Pachauri Student: Mba Iiird SemДокумент33 страницыBasics of The Computer System: Presented By: Sumit Pachauri Student: Mba Iiird SemrajasekarkalaОценок пока нет
- Computer: Made by Surbhi JainДокумент25 страницComputer: Made by Surbhi JainniveshjainОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of It and ProgrammingДокумент6 страницFundamentals of It and ProgrammingRavi Mohan BhattОценок пока нет
- Lesson A Hardware SoftwareДокумент46 страницLesson A Hardware SoftwareSitsiritsit AlibangbangОценок пока нет
- Types & Components of A Computers SystemДокумент12 страницTypes & Components of A Computers Systemmr_ndlelaОценок пока нет
- IT NotesДокумент3 страницыIT NotesMuzamil LoneОценок пока нет
- Computer Basics: Basic Parts of A Desktop ComputerДокумент10 страницComputer Basics: Basic Parts of A Desktop ComputerManuel PachekoОценок пока нет
- 01 Notes Hardware ConceptsДокумент11 страниц01 Notes Hardware ConceptsAbhinav AnandОценок пока нет
- BayehДокумент11 страницBayehTEWODROS TADDESEОценок пока нет
- Class 9 - Computer System OverviewДокумент35 страницClass 9 - Computer System OverviewMonicaОценок пока нет
- Office Automation Tools NotesДокумент75 страницOffice Automation Tools NotesthedrealityyОценок пока нет
- Disk DriveДокумент8 страницDisk DrivemarckentulangОценок пока нет
- Computers 1st Sem NotesДокумент26 страницComputers 1st Sem NotesSugandha Agarwal88% (26)
- Basics of The Computer System: Presented By: Sumit Pachauri Student: Mba Iiird SemДокумент33 страницыBasics of The Computer System: Presented By: Sumit Pachauri Student: Mba Iiird SemVipul PartapОценок пока нет
- IT p1Документ6 страницIT p1Muzamil LoneОценок пока нет
- Section1 Notes (Grd-9)Документ6 страницSection1 Notes (Grd-9)Moody GauchoОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Basic Computer Concept Part 2Документ37 страницModule 1 Basic Computer Concept Part 2Manilyn NunezОценок пока нет
- Unit1-The Computer SystemДокумент14 страницUnit1-The Computer SystemLen CumminsОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)Документ32 страницыBasic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)poo235Оценок пока нет
- (OS) Operating SystemДокумент21 страница(OS) Operating SystemSa Kh AauОценок пока нет
- Basics of The Computer System: Presented By: Sumit Pachauri Student: Mba Iiird SemДокумент33 страницыBasics of The Computer System: Presented By: Sumit Pachauri Student: Mba Iiird SemsanaОценок пока нет
- IT ConceptsДокумент11 страницIT ConceptsMohammed Sumaila Sawadugu Action-90Оценок пока нет
- Computer NotesДокумент16 страницComputer Notesmunaxemimosa8Оценок пока нет
- Concept of ComputerДокумент47 страницConcept of ComputerAbdullah ShoaibОценок пока нет
- Components of ComputerДокумент4 страницыComponents of ComputerSheikh Hammad Bin KhalidОценок пока нет
- Computer 1: (Introduction To Computer Concepts and Software)Документ32 страницыComputer 1: (Introduction To Computer Concepts and Software)Cristin Porcadilla AranteОценок пока нет
- DCA 101 NotesДокумент95 страницDCA 101 NoteswesiteguidesОценок пока нет
- Coa Lab ManualДокумент33 страницыCoa Lab ManualSENTHIL RОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two:-: Computer SystemДокумент134 страницыChapter Two:-: Computer SystemTolera TamiruОценок пока нет
- DC 102 Module 1 Lesson 1Документ12 страницDC 102 Module 1 Lesson 1jerome paulinesОценок пока нет
- TLE-ICT-CHS - Operating System (July 27,2018)Документ2 страницыTLE-ICT-CHS - Operating System (July 27,2018)Marvin GoОценок пока нет
- Scanner: How Scanners WorkДокумент14 страницScanner: How Scanners WorkInderjeet KaurОценок пока нет
- PDF Inggris GabunganДокумент135 страницPDF Inggris GabunganRiadhi RaznanОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 2Документ134 страницыChapter - 2elias asefaОценок пока нет
- BCA3RDPC Assembly TroubleshootingДокумент62 страницыBCA3RDPC Assembly TroubleshootingARTIST Urban sahilОценок пока нет
- Pre Grade Computer Book 5 - 7 Introduction To Computers. Book Vol Ume - 1Документ21 страницаPre Grade Computer Book 5 - 7 Introduction To Computers. Book Vol Ume - 1andsenОценок пока нет
- Parts of Computer and Input and Output DevicesДокумент27 страницParts of Computer and Input and Output Devicesdua tanveerОценок пока нет
- GEE2Документ15 страницGEE2Ronimarie Nicole ZapataОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 CompleteДокумент17 страницChapter 2 CompleteappawashОценок пока нет
- UNIT-1: Computer DefinitionДокумент35 страницUNIT-1: Computer DefinitionPathivadaSantoshNaiduОценок пока нет
- ICT G10 - Chapter 1Документ17 страницICT G10 - Chapter 1tonet enteaОценок пока нет
- Installation, User's, and Maintenance Guide - IBM System Storage DS3400Документ166 страницInstallation, User's, and Maintenance Guide - IBM System Storage DS3400Si PhuОценок пока нет
- List IndexДокумент10 страницList IndexBorad Madan BarkacharyОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12Документ16 страницCambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12Mr. TigerОценок пока нет
- Toshiba Satellite E205 ManualДокумент243 страницыToshiba Satellite E205 ManualJose PerezОценок пока нет
- Dahua UsermanualДокумент498 страницDahua UsermanualBurim QehajaОценок пока нет
- LESSON 5 - Conducting TestsДокумент12 страницLESSON 5 - Conducting TestsCharis VasquezОценок пока нет
- Access Control Software User Manual ZK SoftwareДокумент93 страницыAccess Control Software User Manual ZK SoftwareJovany SalazarОценок пока нет
- Latitude 7.0 System Specifications 24 Sep 2015Документ7 страницLatitude 7.0 System Specifications 24 Sep 2015Hansel Manuel Torres EyssericОценок пока нет
- Lecture 10: Memory System - Memory Technology: CSE 564 Computer Architecture Summer 2017Документ44 страницыLecture 10: Memory System - Memory Technology: CSE 564 Computer Architecture Summer 2017Richu GuptaОценок пока нет
- Huawei Flash StorageДокумент97 страницHuawei Flash StorageRasika Kumara SudasingheОценок пока нет
- HP Storageworks Arrays: Enterprise Midrange Entry LevelДокумент30 страницHP Storageworks Arrays: Enterprise Midrange Entry Levelstashokkumar@gmail.comОценок пока нет
- Practical Error-Correction Design For Engineers 2ed 1991Документ495 страницPractical Error-Correction Design For Engineers 2ed 1991Fernando Adan Serrano OrozcoОценок пока нет
- Team Update #1: General NoticesДокумент5 страницTeam Update #1: General NoticesWilliam MerchantОценок пока нет
- HP LaserJet Enterprise M607 M608 M609 Repair Manual PDFДокумент2 258 страницHP LaserJet Enterprise M607 M608 M609 Repair Manual PDFBadara DIALLO50% (4)
- The First Operating System Was Introduced in The Early 1950's, It Was Called GMOS and Was Created by General Motors For IBM's Machine The 701.Документ19 страницThe First Operating System Was Introduced in The Early 1950's, It Was Called GMOS and Was Created by General Motors For IBM's Machine The 701.MuhammadNaveedОценок пока нет
- ORICO 95RU3 Series - Manual (9528RU3 - 9548RU3 - 9558RU3)Документ20 страницORICO 95RU3 Series - Manual (9528RU3 - 9548RU3 - 9558RU3)huy tranОценок пока нет
- Exceed ZX-A88M2: AMD A6 7480 2-Core 2-Thread 3.5-3.8ghzДокумент3 страницыExceed ZX-A88M2: AMD A6 7480 2-Core 2-Thread 3.5-3.8ghzJoranne GregorioОценок пока нет
- AWS NotesДокумент81 страницаAWS NotesHUGUES ADDIH100% (1)
- Ds Eternus dx8900 s4 WW enДокумент7 страницDs Eternus dx8900 s4 WW enmerkavaОценок пока нет
- The Ultimate Guide For Anonymous and Secure Internet UsageДокумент52 страницыThe Ultimate Guide For Anonymous and Secure Internet Usagekeijo242100% (1)
- Xi Ip 2013-14Документ136 страницXi Ip 2013-14Ravi JhaОценок пока нет
- 02 HeiTel CamControl LITE Tds English Lores PDFДокумент2 страницы02 HeiTel CamControl LITE Tds English Lores PDFAndres Arias C.Оценок пока нет
- HP Compaq 6200 Series Pro Desktop PC Quick SpecsДокумент65 страницHP Compaq 6200 Series Pro Desktop PC Quick SpecsDunat DobricaОценок пока нет
- Intelligent Disk SubsystemsДокумент69 страницIntelligent Disk SubsystemsjohnОценок пока нет
- Technology and Livelihood EducationДокумент56 страницTechnology and Livelihood EducationDerick B. PicardoОценок пока нет
- Instruction Manual: FD2005 USB3.0 Dual SATA HDD Docking Station With Offline Clone FunctionДокумент26 страницInstruction Manual: FD2005 USB3.0 Dual SATA HDD Docking Station With Offline Clone FunctionvaleriОценок пока нет
- Smart. Safe. Secure. Seagate Surveillance-Specialised StorageДокумент4 страницыSmart. Safe. Secure. Seagate Surveillance-Specialised StorageSureerat KaewkeereeОценок пока нет
- Playstation 4 Basic Repair GuideДокумент4 страницыPlaystation 4 Basic Repair GuideMauricio Trujillo PazОценок пока нет
- IBM 3650 RedbookДокумент37 страницIBM 3650 RedbookRiyaz HussainОценок пока нет
- Hard Disk Formatting and CapacityДокумент3 страницыHard Disk Formatting and CapacityVinayak Odanavar0% (1)