Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Comparing Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Загружено:
diybookloverИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Comparing Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Загружено:
diybookloverАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bot2010 9/7/2012 What are the similarities and differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
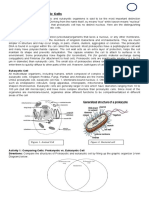
Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles like eukaryotic cells do, and just like the later, the former have cell walls (although the walls of an eukaryotic cell would be composed of cellulose while prokaryotic cell walls would be composed of a substance called murein). Both kinds of cells possess membrane and may or may not have flagella. Prokaryotic flagella are composed of flagellin and eukaryotic flagella are made out of tubulin. There is no prokaryotic cilium and when eukaryotic cells have it, it is made of tubulin. Eukaryotic plant cells are notoriously autotrophic (able to create their own food) while prokaryotic types can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic (having to get their nutrition from another organism). Chloroplasts are organelles necessary for the photosynthetic process, they abound in many eukaryotic plant cells but they are never found on prokaryotes (because, like stated before, prokaryotes do not have membrane-bound organelles like chloroplasts). The two kinds of cells are capable of respiration, which is the process in which glucose is burned to release energy, and reproduction: eukaryotes go through a process called mitosis in contrast to the process of binary fusion, which is carried by prokaryotes. The formers form of sexual reproduction is atypical.
Вам также может понравиться
- Classification and evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsДокумент7 страницClassification and evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsjodeoiraluis josonОценок пока нет
- rDNA TechДокумент20 страницrDNA TechJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidОценок пока нет
- Medical BiotechnologyДокумент34 страницыMedical Biotechnologyalfi alfathanaОценок пока нет
- 7a. Antibacterial AgentsДокумент32 страницы7a. Antibacterial AgentsNiala AlmarioОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology BasicsДокумент24 страницыCell Biology BasicsGeoffrey100% (1)
- Pages From LehningerДокумент3 страницыPages From Lehningerapi-3733156100% (3)
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Gene Structure PDFДокумент2 страницыEukaryotic and Prokaryotic Gene Structure PDFAnthony0% (1)
- XII Biology Biotechnology: Principles and Pro0Cesses: Recombinant DNA TechnologyДокумент8 страницXII Biology Biotechnology: Principles and Pro0Cesses: Recombinant DNA TechnologyNobisuke NobiОценок пока нет
- Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsДокумент18 страницDifferences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellssalahuddin_md5935100% (1)
- Polymerase Chain ReactionДокумент22 страницыPolymerase Chain ReactionPoornaBasuri100% (1)
- Bio 106 Lecture 5 Chemical Basis of Heredit1Документ16 страницBio 106 Lecture 5 Chemical Basis of Heredit1Evan Jane JumamilОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsДокумент31 страницаProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranОценок пока нет
- Enzymes and Their Functions - Activity SheetsДокумент20 страницEnzymes and Their Functions - Activity SheetsHazel Ann Oseña MaderaОценок пока нет
- ImmunoglobulinДокумент39 страницImmunoglobulinReguird AllaeinniОценок пока нет
- Gregor MendelДокумент3 страницыGregor MendelhdОценок пока нет
- Anti Viral DrugsДокумент70 страницAnti Viral DrugsDereje DZ100% (2)
- Lecture 9-GS1 1112-Mitochondria & ChloroplastДокумент37 страницLecture 9-GS1 1112-Mitochondria & ChloroplastHa LuongОценок пока нет
- Controlling Micriobial GrowthДокумент47 страницControlling Micriobial GrowthasiОценок пока нет
- StudentДокумент4 страницыStudentapi-241703778Оценок пока нет
- 1 IntroДокумент5 страниц1 IntroJeanjayannseptoemanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Recombinant DNA TechnologyДокумент39 страницChapter 3 Recombinant DNA TechnologyAnirudh Acharya0% (1)
- Adaptive Immunity - Humoral ImmunityДокумент21 страницаAdaptive Immunity - Humoral ImmunityDaniel AtiehОценок пока нет
- HE Iving ELL AND TS Omponents: T L C I CДокумент54 страницыHE Iving ELL AND TS Omponents: T L C I CMary Ann Marapao GanzonОценок пока нет
- Bio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionДокумент24 страницыBio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionMarmorn ArborshateОценок пока нет
- Cilia and Flagella Structure and FunctionДокумент10 страницCilia and Flagella Structure and FunctionEr Purushottam PalОценок пока нет
- Lecture - Microbial Diversity The Eukaryotic Microbes - Chapter 4 - BSEDДокумент5 страницLecture - Microbial Diversity The Eukaryotic Microbes - Chapter 4 - BSEDMaden betoОценок пока нет
- Q1 Module 1 The Cell TheoryДокумент29 страницQ1 Module 1 The Cell TheoryKathy BaynosaОценок пока нет
- CSIR-NET Cell Biology NotesДокумент32 страницыCSIR-NET Cell Biology NotesSrinivas Nakka100% (1)
- Biochemistry of Cancer Biochemistry of Cancer: DR Madiha Soban BiochemistryДокумент36 страницBiochemistry of Cancer Biochemistry of Cancer: DR Madiha Soban BiochemistryTalha MohsinОценок пока нет
- SPM Biology Cell StructureДокумент12 страницSPM Biology Cell StructureNurfatin JamaludinОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Biotechnology 1Документ16 страницIntroduction To Biotechnology 1Ramesh BeniwalОценок пока нет
- History of BiotechДокумент29 страницHistory of BiotechEL PEPE100% (1)
- Concept of GeneДокумент30 страницConcept of GeneSubhapam KunduОценок пока нет
- Stem Cell Research EssayДокумент7 страницStem Cell Research Essayapi-286667026Оценок пока нет
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellДокумент7 страницCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verОценок пока нет
- Nucleosome Model PDFДокумент26 страницNucleosome Model PDFpenny singhОценок пока нет
- Nucleus - Morphology and FunctionsДокумент25 страницNucleus - Morphology and FunctionsVytheeshwaran Vedagiri96% (24)
- Gastrointestinal DrugsДокумент107 страницGastrointestinal DrugsRezzmah Alicia Tomon KhadrawyОценок пока нет
- Immune System WebquestДокумент4 страницыImmune System WebquestScott ThomasОценок пока нет
- BacteriophageДокумент34 страницыBacteriophagesharkkzz17Оценок пока нет
- BIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and ObjectivesДокумент24 страницыBIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and Objectivescheramae ancesОценок пока нет
- Ribosomes and Protein SynthesisДокумент12 страницRibosomes and Protein SynthesisSulfeekker AhamedОценок пока нет
- Cell NucleusДокумент17 страницCell NucleusAsad Aly100% (8)
- Paper Template Formatting GuideДокумент3 страницыPaper Template Formatting GuideShrinivas Saptalakar0% (1)
- Bacteriology PDFДокумент19 страницBacteriology PDFDarshana Juvekar0% (1)
- Chapter 14 Mutation and CancerДокумент43 страницыChapter 14 Mutation and CancerCharlieHuangОценок пока нет
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismДокумент10 страницNucleic Acid MetabolismIvy AggabaoОценок пока нет
- Classification of The VertebratesДокумент15 страницClassification of The VertebratesMichelle GarciaОценок пока нет
- Microbial Staining TechniquesДокумент10 страницMicrobial Staining TechniquesJohn Emmanuel TayagОценок пока нет
- Gene Therapy: Course InstructorДокумент28 страницGene Therapy: Course InstructorSamiul Alam RajibОценок пока нет
- 07 Gastrulation BiologyДокумент22 страницы07 Gastrulation BiologyKashif JamalОценок пока нет
- Cell Division PDFДокумент11 страницCell Division PDFMrinal SharmaОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCДокумент69 страницBiomolecules and Cells:: Mr. Derrick Banda MSC, BSCAmon Sangulube100% (1)
- CHAPTER XI - Gene TherapyДокумент4 страницыCHAPTER XI - Gene TherapyKeannoОценок пока нет
- Recombinant DNA and Genetic Experimentation: Proceedings of a Conference on Recombinant DNA, Jointly Organised by the Committee on Genetic Experimentation (COGENE) and the Royal Society of London, Held at Wye College, Kent, UK, 1-4 April, 1979От EverandRecombinant DNA and Genetic Experimentation: Proceedings of a Conference on Recombinant DNA, Jointly Organised by the Committee on Genetic Experimentation (COGENE) and the Royal Society of London, Held at Wye College, Kent, UK, 1-4 April, 1979Оценок пока нет
- Eukaryotic and ProkaryoticДокумент1 страницаEukaryotic and ProkaryoticdiybookloverОценок пока нет
- Cell Types Cornell Filled inДокумент2 страницыCell Types Cornell Filled innariciobandigan0823Оценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsДокумент2 страницыProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsSerena Adeline RiveraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellДокумент10 страницChapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKylie VillafloresОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive Voice of Future Continuous Tense - Passive Voice Tips-1Документ5 страницActive and Passive Voice of Future Continuous Tense - Passive Voice Tips-1Kamal deep singh SinghОценок пока нет
- Environment ManagerДокумент234 страницыEnvironment ManagerAbhishek kumarОценок пока нет
- Furnace ITV Color Camera: Series FK-CF-3712Документ2 страницыFurnace ITV Color Camera: Series FK-CF-3712Italo Rodrigues100% (1)
- APC Smart-UPS 1500VA LCD 230V: Part Number: SMT1500IДокумент3 страницыAPC Smart-UPS 1500VA LCD 230V: Part Number: SMT1500IDesigan SannasyОценок пока нет
- Machine Spindle Noses: 6 Bison - Bial S. AДокумент2 страницыMachine Spindle Noses: 6 Bison - Bial S. AshanehatfieldОценок пока нет
- NPV Irr ArrДокумент16 страницNPV Irr ArrAnjaliОценок пока нет
- USA V BRACKLEY Jan6th Criminal ComplaintДокумент11 страницUSA V BRACKLEY Jan6th Criminal ComplaintFile 411Оценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word 2000 IntroductionДокумент72 страницыMicrosoft Word 2000 IntroductionYsmech SalazarОценок пока нет
- Single-Phase Induction Generators PDFДокумент11 страницSingle-Phase Induction Generators PDFalokinxx100% (1)
- Huawei WCDMA Primary Scrambling Code PlanningДокумент22 страницыHuawei WCDMA Primary Scrambling Code PlanningZeljko Vrankovic90% (31)
- Vidura College Marketing AnalysisДокумент24 страницыVidura College Marketing Analysiskingcoconut kingcoconutОценок пока нет
- Learning Stations Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыLearning Stations Lesson Planapi-310100553Оценок пока нет
- Suband Coding in MatlabДокумент5 страницSuband Coding in MatlabZoro Roronoa0% (1)
- Emergency Room Delivery RecordДокумент7 страницEmergency Room Delivery RecordMariel VillamorОценок пока нет
- AAU5243 DescriptionДокумент30 страницAAU5243 DescriptionWisut MorthaiОценок пока нет
- Digital Communication Quantization OverviewДокумент5 страницDigital Communication Quantization OverviewNiharika KorukondaОценок пока нет
- sl2018 667 PDFДокумент8 страницsl2018 667 PDFGaurav MaithilОценок пока нет
- Arduino Guide using MPU-6050 and nRF24L01Документ29 страницArduino Guide using MPU-6050 and nRF24L01usmanОценок пока нет
- ASTM D256-10 - Standard Test Methods For Determining The Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of PlasticsДокумент20 страницASTM D256-10 - Standard Test Methods For Determining The Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of PlasticsEng. Emílio DechenОценок пока нет
- Programming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferenceДокумент16 страницProgramming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferencekrishnamarajublrОценок пока нет
- Micropolar Fluid Flow Near The Stagnation On A Vertical Plate With Prescribed Wall Heat Flux in Presence of Magnetic FieldДокумент8 страницMicropolar Fluid Flow Near The Stagnation On A Vertical Plate With Prescribed Wall Heat Flux in Presence of Magnetic FieldIJBSS,ISSN:2319-2968Оценок пока нет
- Basf Masterseal 725hc TdsДокумент2 страницыBasf Masterseal 725hc TdsshashiОценок пока нет
- SEO Design ExamplesДокумент10 страницSEO Design ExamplesAnonymous YDwBCtsОценок пока нет
- Budget ControlДокумент7 страницBudget ControlArnel CopinaОценок пока нет
- Assessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyДокумент4 страницыAssessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyVijay KumarОценок пока нет
- Amana PLE8317W2 Service ManualДокумент113 страницAmana PLE8317W2 Service ManualSchneksОценок пока нет
- Condy LatorДокумент11 страницCondy LatorrekabiОценок пока нет
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings PDFДокумент11 страницDeep Groove Ball Bearings PDFArpit VermaОценок пока нет
- MSDS FluorouracilДокумент3 страницыMSDS FluorouracilRita NascimentoОценок пока нет
- SEMICONDUCTORS AssignmentДокумент8 страницSEMICONDUCTORS AssignmentMaryam MuneebОценок пока нет