Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Vtu III & IV Sem Syllabus 22-5-8
Загружено:
manjunatha tАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Vtu III & IV Sem Syllabus 22-5-8
Загружено:
manjunatha tАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
S.
No
Subject Code
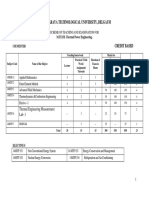
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION III SEMESTER Mechanical (Common to ME/IP/IM/AU/MA/AE) Teaching hours /week Teaching Title Dept. Th. Pr. Engg. Mathematics-III Material Science & Metallurgy/Mechanical Measurements & Metrology Basic Thermodynamics Mechanics of Materials Manufacturing Process-I Computer Aided Machine Drawing/ Fluid Mechanics Metallography & Material Testing Laboratory/ Mechanical Measurements & Metrology Laboratory Foundry & Forging Laboratory/ Machine Shop Mathematics ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE 4 4 ---
Examination I.A. Max. Mark s 25 25 Th. / Pr. 100 100 Total Mark s 125 125
Duration 03 03
1 2*
06 MAT31 06 ME32A/ 06 ME32B 06ME33 06ME34 06ME35 06ME36A/ 06ME36B 06MEL37A/ 06MEL37B 06MEL38A/ 06MEL38B
3 4 5 6 7*
4 4 4 1 --
---03 03
03 03 03 03 03
25 25 25 25 25
100 100 100 100 50
125 125 125 125 75
8*
---
03
03
25
50 700
75 900
Total 21 09 24 200 *Note: Students opted for subjects with code A in III Semester, opt for subjects with code B in IV Semester.
S. No 1 2*
Subject Code 06MAT41 06ME42A/ 06ME42B 06ME43 06ME44 06ME45 06ME46A/ 06ME46B 06MEL47A/ 06MEL47B 06MEL48A/ 06MEL48B
SCHEME OF TEACHING AND EXAMINATION IV SEMESTER Mechanical (Common to ME/IP/IM/AU/MA/AE) Teaching hours /week Teaching Title Dept. Th. Pr. Engg. Mathematics-IV Material Science & Metallurgy/ Mechanical Measurements & Metrology Applied Thermodynamics Kinematics of Machines Manufacturing Process-II Computer Aided Machine Drawing/ Fluid Mechanics Metallography & Material Testing Laboratory/ Mechanical Measurements & Metrology Laboratory Foundry & Forging Laboratory/ Machine Shop Mathematics ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE ME/IP/IM/AU/ MA/MI/AE 4 4 ---
Examination Duration 03 03 I.A. Max. Marks 25 25 Th./ Pr. 100 100 Total Marks 125 125
3 4 5 6 7*
4 4 4 4 --
-----03
03 03 03 03 03
25 25 25 25 25
100 100 100 100 50
125 125 125 125 75
8* Total
--24
03 06
03 24
25 200
50 700
75 900
*Note: Students opted for subjects with code A in III Semester, opt for subjects with code B in IV Semester.
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS III Sub Code Hrs/ Week Total Hrs. : : : 06MAT31 04 52 PART A UNIT 1: Fourier Series Periodic functions, Fourier expansions, Half range expansions, Complex form of Fourier series, Practical harmonic analysis. 7 Hours UNIT 2: Fourier Transforms Finite and Infinite Fourier transforms, Fourier sine and consine transforms, properties. Inverse transforms. 6 Hours UNIT 3: Partial Differential Equations (P.D.E) Formation of P.D.E Solution of non homogeneous P.D.E by direct integration, Solution of homogeneous P.D.E involving derivative with respect to one independent variable only (Both types with given set of conditions) Method of separation of variables. (First and second order equations) Solution of Lagranges linear P.D.E. of the type P p + Q q = R. 6 Hours UNIT 4: Applications of P.D.E Derivation of one dimensional wave and heat equations. Various possible solutions of these by the method of separation of variables. DAlemberts solution of wave equation. Two dimensional Laplaces equation various possible solutions. Solution of all these equations with specified boundary conditions. (Boundary value problems). 7 Hours IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : : : 25 03 100
PART B UNIT 5: Numerical Methods Introduction, Numerical solutions of algebraic and transcendental equations:Newton-Raphson and Regula-Falsi methods. Solution of linear simultaneous equations : - Gauss elimination and Gauss Jordon methods. Gauss - Seidel iterative method. Definition of eigen values and eigen vectors of a square matrix. Computation of largest eigen value and the corresponding eigen vector by Rayleighs power method. 6 Hours UNIT 6: Finite differences (Forward and Backward differences) Interpolation, Newtons forward and backward interpolation formulae. Divided differences Newtons divided difference formula. Lagranges interpolation and inverse interpolation formulae. Numerical differentiation using Newtons forward and backward interpolation formulae. Numerical Integration Simpsons one third and three eighths value, Weddles rule. (All formulae / rules without proof) 7 Hours UNIT 7: Calculus of Variations Variation of a function and a functional Extremal of a functional, Variational problems, Eulers equation, Standard variational problems including geodesics, minimal surface of revolution, hanging chain and Brachistochrone problems. 6 Hours UNIT 8: Difference Equations and Z-transforms Difference equations Basic definitions. Z-transforms Definition, Standard Z-transforms, Linearity property, Damping rule, Shifting rule, Initial value theorem, Final value theorem, Inverse Z-transforms. Application of Z-transforms to solve difference equations. 7 Hours
Text Book: Higher Engineering Mathematics by Dr. B.S. Grewal (36th Edition Khanna Publishers) Unit No. I II III Chapter No. 10 22 17, 18 Article Numbers 10.1 to 10.7, 10.10 and 10.11 22.4, 22.5 17.1 to 17.5, 18.2 Page Nos. 375 400 716 722 541 547 562 564 564 578 580 582 820 826 829 840 843 845 846, 847 857 862 871 878 881 887 1018 1025 888, 889 899 913
IV
18
18.4, 18.5, 18.7
24
24.1, 24.2, 24.4 to 24.6, 24.8
VI
25
25.1, 25.5, 25.12 to 25.14, 25.16
VII VIII
30 26
30.1 to 30.5 26.1, 26.2, 26.9 to 26.15, 26.20, 26.21
Reference Books: Higher Engineering Mathematics by B.V. Ramana (Tata-Macgraw Hill). Advanced Modern Engineering Mathematics by Glyn James Pearson Education. Note: 1. 2. One question is to be set from each unit. To answer Five questions choosing atleast Two questions from each part.
MATERIAL SCIENCE & METALLURGY Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 32 A/ 06 ME 42A : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
PART A UNIT 1: Structure of crystalline solids: Fundamental concepts of unit cell space lattice, Bravaias space lattices, unit cells for cubic structure & HCP, study of stacking of layers of atoms in cubic structure & HCP, calculations of radius, Coordination Number and Atomic Packing Factor for different cubic structures. Crystal imperfections-point, line, surface & volume defects. Diffusion, Diffusion Mechanism, Ficks laws of diffusion. 7 Hours UNIT 2: Concepts of stress & strain, tensile properties, true stress & strain, Hardness, Rockwell, Vickess & Brinell Hardness testing. Plastic deformation, slip & twinning. 6 Hours UNIT 3: Fracture: types, stages in cup & cone fracture, Griffiths criterion. Fatigue: fatigue tests, S-N curves, Factors affecting fatigue life and protection methods. Creep: The creep curves, Mechanisms of creep. Creep-resistant materials. 7 Hours UNIT 4: Solid solutions, Types, Rules of governing the formation of solids solutions. Phase diagrams: Basic terms, phase rule, cooling curves, construction of phase diagrams, interpretation of equilibriums diagrams, Types of phase diagrams. Lever rule. 6 Hours
PART B UNIT 5: Iron carbon equilibrium Diagram, phases in the FeC system, Invariant reactions, critical temperatures, Microstructure of slowly cooled steels, effect of alloying elements on the Fe-C diagram, ferrite & Austenite stabilizers. The TTT diagram, drawing of TTT diagram, TTT diagram for hypo-& hypereutectoid steels, effect of alloying elements, CCT diagram. 7 Hours UNIT 6: Annealing, and its types, normalizing, hardening, tempering, martemering, austempering, surface hardening like case hardening, carburizing, cyaniding, nitriding Induction hardening, hardenabilty, Jominy end-quench test, Age hardening of Al & Cu alloys. 6 Hours UNIT 7: Engineering Alloys: Properties, composition and uses of low carbon, mild medium & high carbon steels. Steel designation & AISI SAE designation. Cast irons, gray CI, white CI, malleable CI, SC iron. Microstructures of cast iron. The light alloys, Al & Mg & Titaniu m alloys. Copper & its alloys: brasses & bronzes. 7 Hours UNIT 8: Corrosion & Its Prevention: Galvanic Cell, The Electrode Potentials, Polarization, Passivation, General methods of Corrosion Prevention, Cathodic Protection, Coatings, Corrosion Prevention by Alloying, Stress Corrosion Cracking. 6hrs Text Books: 1. Materials Science & Engineering- An Introduction, William D.Callister Jr. Wiley India Pvt. Ltd. 6th Edition, 2006, New Delhi. 2. Essentials of Materials For Science And Engineering, Donald R. Askeland, Pradeep P.Phule Thomson-Engineering, 2006. Reference Books: 1. Introduction to Material Science for Engineering, 6th edition James F. Shackel ford. Pearson, Prentice Hall, New Jersy, 2006. nd 2. Physical Metallurgy, Principles & Practices, V Raghavan.PHI 2 Edition 2006, New Delhi. 3. Foundation of Material Science and Engineering, Smith, 3rd Edition McGraw Hill, 1997.
Scheme of Examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
MECHANICAL MEASUREMENTS AND METROLOGY Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 32 B/ 06 ME 42 B : 04 : 52 PART A UNIT 1: Standards of measurement: Definition and Objectives of metrology, Standards of length - International prototype meter, Imperial standard yard, Wave length standard, subdivision of standards, line and end standard, comparison, transfer from line standard to end standard, calibration of end bars (Numerical), Slip gauges, Wringing phenomena, Indian Standards (M81, M-112), Numerical problems on building of slip gauges. 6 Hours UNIT 2: System of limits, Fits, Tolerances and gauging: Definition of tolerance, Specification in assembly, Principle of inter changeability and selective assembly limits o size, Indian standards, concept of limits of size and f tolerances, compound tolerances, accumulation of tolerances, definition of fits, types of fits and their designation (IS 919 -1963), geometrical tolerance, positional - tolerances, hole basis system, shaft basis of system, classification of gauges, brief concept of design of gauges (Taylor's principles), Wear allowance on gauges, Types of gauges -plain plug gauge, ring Gauge, snap gauge, limit gauge and gauge materials. 7 Hours IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
Comparators and Angular measurement: Introduction to Comparator, Characteristics, classification of comparators, mechanical comparators Johnson Mikrokator, Sigma Comparators, dial indicator, Optical Comparators -principles, Zeiss ultra optimeter, Electric and Electronic Comparators -principles, LVDT, Pneumatic Comparators, back pressure gauges, Solex Comparators. Angular measurements, Bevel Protractor, Sine Principle and. use of Sine bars, Sine center, use of angle gauges, (numericals on building of angles) Clinometers. 7 Hours UNIT 3: Interferometer and Screw thread gear measurement : Interferometer Principle of interferometery, autocollimator. Optical flats. Terminology of screw threads, measurement of major diameter, minor diameter pitch, angle and effective diameter of screw threads by 2-wire and 3-wire methods, Best size wire. Toolmakers microscope, gear terminology, use of gear tooth Vernier caliper and gear tooth micrometer 6 Hours PART B UNIT 4: Measurements and Measurement systems: Definition, Significance of measurement, generalized measurement system, definitions and concept of accuracy, precision, calibration, threshold, sensitivity, hystersis, repeatability, linearity, loading effect, system response-times delay. Errors in Measurements, Classification of Errors. Transducers, Transfer efficiency, Primary and Secondary transducers, electrical, Mechanical, electronic transducers, advantages of each type transducers. 7 Hours
UNIT 5: Intermediate modifying and terminating devices: Mechanical systems, inherent problems, Electrical intermediate modifying devices, input circuitry, ballast, ballast circuit, electronic amplifiers and telemetry. Terminating devices, Mechanical, Cathode Ray Oscilloscope, Oscillographs, X-Y Plotters. 6 Hours
UNIT 6: Measurement of Force and Torque, pressure: Principle, analytical balance, platform balance, proving ring, Torque measurement, Prony brake, hydraulic dynamometer. Pressure Measurements, Principle, use of elastic members, Bridgeman gauge, Mcloed gauge, Pirani Gauge. 6 Hours UNIT 7: Temperature and strain measurement: Resistance thermometers, thermocouple, law of thermocouple, materials used for construction, pyrometer, Optical Pyrometer. Strain Measurements, Strain gauge, preparation and mounting of strain gauges, gauge factor, methods of strain measurement 7 Hours Text Books: 1. 2. Mechanical measurements by Beckwith Marangoni and Lienhard, Pearson Education, 6th Ed., 2006 Engineering Metrology by R.K.Jain, Khanna Publishers, 1994.
Reference Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. Engineering Metrology by I.C.Gupta, Dhanpat Rai Publications, Delhi Mechanical measurements by R.K.Jain Industrial Instrumentation Alsutko, Jerry. D.Faulk, Thompson Asia Pvt. Ltd.2002 Measurement Systems Applications and Design by Ernest O, Doblin, McGRAW Hill Book Co.
Scheme of Examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
10
BASIC THERMODYNAMICS Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 33 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
PART-A UNIT 1: Fundamental Concepts & Definitions: Thermodynamics; definition and scope. Microscopic and Macroscopic approaches. Engineering Thermodynamics Definition, some practical applications of engineering thermodynamic. System (closed system) and Control Volume (open system); Characteristics of system boundary and control surface, examples. Thermodynamic properties; definition and units, intensive and extensive properties. Thermodynamic state, state point, state diagram, path and process, quasi-static process, cyclic and non-cyclic processes; Thermodynamic equilibrium; definition, mechanical equilibrium; diathermic wall, thermal equilibrium, chemical equilibrium Zeroth law of thermodynamics, Temperature; concepts, scales, measurement. Internal fixed points. 7 Hours UNIT 2: Work & Heat: Mechanics, definition of work and its limitations. Thermodynamic definition of work; examples, sign convention. Displacement work; at part of a system boundary, at whole of a system boundary, expressions for displacement work in various processes through pv diagrams. Shaft work; Electrical work. Other types of work. Heat; definition, units and sign convention, what heat is not. 6 Hours UNIT 3: First Law of Thermodynamics: Joules experiments, equivalence of heat and work. Statement of the First law of thermodynamics, extension of the First law to non -cyclic processes, energy, energy as a property, modes of energy, pure substance; definition, two-property rule, Specific heat at constant volume, enthalpy, specific heat at constant pressure. Extension of the First law to control volume; steady state-steady flow energy equation, important applications, analysis of unsteady processes such as filling and evacuation of vessels with and without heat transfer. 6 Hours
11
UNIT 4: Second Law of Thermodynamics: Devices converting heat to work; (a) in a thermodynamic cycle, (b) in a mechanical cycle. Thermal reservoir. Direct heat engine; schematic representation and efficiency. Devices converting work to heat in a thermodynamic cycle; reversed heat engine, schematic representation, coefficients of performance. Kelvin -Planck statement of the Second law of Thermodynamic; PMM I and PMM1I. Clasiu's statement .of Second law of Thermodynamic; Equivalence of the two statements; Reversible and irreversible processes; factors that make a process .irreversible, reversible heat engines, Carnot cycle, Carnot principles. Thermodynamic temperature scale. 7 Hours PART B UNIT 5: Entropy: Clasius inequality; statement, proof, application to a reversible cycle. Q /T as independent of the path. Entropy; definition, a property, R principle of increase of entropy, entropy as a quantitative test for irreversibility, calculation of entropy using Tds relations, entropy as a coordinate. Available and unavailable energy. 7 Hours UNIT 6: Availability and Irreversibility: - Maximum Work, maximum useful work for a system and a control volume, availability of a system and a steadily flowing stream, irreversibility. Second law efficiency. 6 Hours UNIT 7: Pure substances: P-T and P-V diagrams, triple point and critical points. Subcooled liquid, saturated liquid, mixture of saturated liquid and vapor, saturated vapor and superheated vapour states of a pure substance with water as example. Enthalpy of change of phase (Latent heat). Dryness factor (quality), T-S and h-s diagrams, representation of various processes on these diagrams. Steam tables and its use. Throttling calorimeter, separating and throttling calorimeter. 6 Hours
12
UNIT 8: Real and ideal gases: Introduction; Vander Waal's Equation Van der Waal's constants in terms of critical properties, law of corresponding states, compressibility factor; compressibility)" chart. Ideal gas; equation of state, internal energy and enthalpy as functions of temperature only, universal and particular gas constants, specific heats, perfect and semi-perfect gases. Evaluation of heat, work, change in internal energy, enthalpy and entropy in various quasi-static processes. Ideal gas mixture; Dalton's law of additive pressures, Amagat's law of additive volumes, evaluation of properties. Analysis of various processes. 7 Hours Text Books: 1. Basic and Applied Thermodynamics by P .K. Nag, Tata McGraw Hill, 3rd Edi. 2002 2. Thermodynamics an engineering approach, by Yunus A. Cenegal and Michael A. Boles. Tata McGraw hill Pub. 2002 Reference Books: 1. Engineering Thermodynamics. By Rajput, Laxmi Publications pvt ltd., 3rd Edi. 2007. 2. Engineering Thermodynamics by J.B. Jones and G.A.Hawkins, John Wiley and Sons. 3. Thermo Dynamics by S.C.Gupta, Pearson Edu. Pvt. Ltd., 1st Ed. 2005. Scheme of Examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
13
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 34 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
PART A UNIT 1: Simple stress and strain: Introduction, stress, strain, mechanical properties of materials, Linear elasticity, Hookes Law and Poissons ratio, Stress-Strain relation behaviour in Tension for Mild steel and non ferrous metals. Extension / Shortening of a bar, bars with cross sections varying in steps, bars with continuously varying cross sections (circular and rectangular), Elongation due to self weight, Principle of super position. 7 Hours UNIT 2: Stress in composite section: Volumetric strain, expression for volumetric strain, elastic constants, simple shear stress, shear strain, temperature stresses (including compound bars). 6 Hours UNIT 3: Compound stresses: Introduction, plane stress, stresses on inclined sections, principal stresses and maximum shear stresses, Mohrs circle for plane stress. 7 Hours UNIT 4: Thick and thin cylinders: Stresses in thin cylinders, changes in dimensions of cylinder (diameter, length and volume), Thick cylinders subjected to internal and external pressures (Lames equation), (compound cylinders not included). 6 Hours
14
PART B UNIT 5: Bending moment and Shear force in beams : Introduction, Types of beams, loads and reactions, shear forces and bending moments, rate of loading, sign conventions, relationship between shear force and bending moments, shear force and bending moment diagrams for different beams subjected to concentrated loads, uniform distributed load (udl) and couple for different types of beams. 7 Hours UNIT 6: Bending and shear stresses in beams: Introduction, theory of simple bending, assumptions in simple bending, relationship between bending stresses and radius of curvature, relationship between bending moment and radius of curvature, moment carrying capacity of a section, shearing stresses in beams, shear stress across rectangular, circular, symmetrical I and T sections (composite / fletched beams not included). 7 Hours UNIT 7: Deflection of beams: Introduction, differential equation for deflection, equations for deflections, slope and moments, double integration method for cantilever and simply supported beams for point load, UDL, UVL and Couple, Macaulays method. 6 Hours UNIT 8: Torsion of circular shafts and Elastic stability of columns : Introduction, pure torsion, assumptions, derivation of torsional equations, polar modulus, torsional rigidity / stiffness of shafts, power transmitted by solid and hollow circular shafts. Introduction to columns, Eulers theory for axially loaded elastic long columns, derivation of Eulers load for various end conditions, limitations of Eulers theory, Rankines formula. 6 Hours
15
Text books: 1. 2. Mechanics of Materials by R.C.Hibbeler, Printice Hall, Pearson Edu., 2005 Mechanics of materials, James.M.Gere, Thomson, Fifth edition 2004. Mechanics of materials, S.I. Units, Ferdinand Beer & Russell Johnstan, TATA Mac GrawHill-2003.
3.
Reference books: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Strength of Materials, S.S.Bhavikatti, Vikas publications House Pvt. Ltd., 2nd Ed., 2006. Mechanics of materials K.V. Rao, G.C. Raju, First Edition,2007 Engineering Mechanics of Solids Egor.P. Popov, Pearson Edu. India, 2nd , Edition, 1998. Mechanics of Solids, Mubeen, Pearson Edu. India, 2002 Strength of Materials, W.A. Nash, Sehaums Outline Series, Fourth Edition-2007.
Scheme of examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
MANUFACTURING PROCESS I Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 35 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
PART A CASTING PROCESS UNIT 1: Introduction: Concept of Manufacturing process, its importance. Classification of Manufacturing processes. Introduction to Casting process & steps involved. Varieties of components produced by casting process. Advantages & Limitations of casting process.
16
Patterns: Definition, functions, Materials used for pattern, various pattern allowances and their importance. Classification of patterns. Binder: Definition, Types of binder used in moulding sand. Additives: Need, Types of additives used. 6 Hours UNIT 2: Sand Moulding : Types of base sand, requirement of base sand. Types of sand moulds. Sand moulds: Moulding sand mixture ingredients (base sand, binder & additives) for different sand mixtures. Method used for sand moulding. Cores: Definition, Need, Types. Method of making cores, Binders used. Concept of Gating & Risering. Principle involved. and types. Fettling and cleaning of castings. Basic steps involved. Casting defects causes, features and remedies. Moulding machines : Jolt type, squeeze type, Jolt & Squeeze type and Sand slinger. 7 Hours UNIT 3: Special moulding Process :Study of important moulding processes Green sand, Core sand, Dry sand, Sweep mould, CO2 mould, Shell mould, Investment mould. Metal moulds : Gravity die-casting, Pressure die casting, centrifugal casting, Squeeze Casting, Slush casting, Thixocasting and continuous casting processes. 7 Hours UNIT 4: Melting Furnaces: Classification of furnaces. Constructional features & working principle of Gas fired pit furnace, Resistance furnace, Coreless Induction furnace, Electric Arc Furnace, Cupola furnace. 6 Hours PART B WELDING UNIT 5: Welding process: Definition, Principles, Advantages & limitations of welding.
Classification,
Application,
17
Arc Welding : Principle, Metal Arc welding (MAW), Flux Shielded Metal Arc Welding (FSMAW), Inert Gas Welding (TIG & MIG) Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) and Atomic Hydrogen Welding processes. (AHW)
Gas Welding : Principle, Oxy Acetylene welding, Reaction in Gas welding, Flame characteristics, Gas torch construction & working. Forward and backward welding. 7 Hours UNIT 6: Special type of welding: Resistance welding - principles, Seam welding, Butt welding, Spot welding and projection welding. Friction welding, Explosive welding, Thermit welding, Laser welding and Electron beam welding. 7 Hours UNIT 7: Metallurgical aspect in welding : Structure of welds, Formation of different zones during welding. Heat affected zone (HAZ). Parameters affecting HAZ. Effect of carbon content on structure and properties of steel. Shrinkage in welds & Residual stresses. Concept of electrodes, Filler rod and fluxes. Welding defects Detection causes & remedy. 6 Hours UNIT 8: Principles of soldering & brazing: Parameters involved & Mechanism. Different Types of Soldering & Brazing Methods. Inspection Methods Methods used for Inspection of casting and welding. Visual, Magnetic particle, Fluorescent particle, Ultrasonic, Radiography, Eddy current, Holography methods of Inspection. 6 Hours Text Books: 1. 2. Manufacturing & Technology: Foundry Forming and Welding, P.N.Rao 2nd Ed., Tata McGraw Hill, 2003. Manufacturing Process-I, Dr.K.Radhakrishna, Sapna Book House, 2nd Edition 2007.
18
Reference Books: 1. 2. Manufacturing Technology, Serope Kalpakjain, Steuen.R.Sechmid, Pearson Education Asia, 5th Ed. 2006. Process and Materials of Manufacturing :, Roy A Lindberg, 4th Ed. Pearson Edu. 2006.
Scheme of examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
COMPUTER AIDED MACHINE DRAWING Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 36A/ 06 ME 46A : 04 (1 Hr. Theory & 2 Hrs. Practical) : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
Introduction: Review of graphic interface of the software. Review of basic sketching commands and navigational commands. Starting a new drawing sheet. Sheet sizes. Naming a drawing. Drawing units, grid and snap. 2 Hours PART A UNIT 1: Sections of Solids: Sections of Pyramids, Prisms, Cubes, Tetrahedrons, Cones and Cylinders resting only on their bas es (No problems on, axis inclinations, spheres and hollow solids). True shape of sections. Orthographic views: Conversion of pictorial views into orthographic projections of simple machine parts with or without section. (Bureau of Indian Standards conventions are to be followed for the drawings) Hidden line conventions. Precedence of lines. 8 Hours
19
UNIT 2: Thread forms: Thread terminology, sectional views of threads. ISO Metric (Internal & External) BSW (Internal & External) square and Acme. Sellers thread, American Standard thread. Fasteners: Hexagonal headed bolt and nut with washer (assembly), square headed bolt and nut with washer (assembly) simple assemb ly using stud bolts with nut and lock nut. Flanged nut, slotted nut, taper and split pin for locking, counter sunk head screw, grub screw, Allen screw. 8 Hours PART B UNIT 3: Keys & Joints Parallel key, Taper key, Feather key, Gibhead key and Woodruff key Riveted Joints: single and double riveted lap joints, butt joints with single/double cover straps (Chain and Zigzag, using snap head rivets). cotter joint (socket and spigot), knuckle joint (pin joint) for two rods. 8 Hours UNIT 4: Couplings Split Muff coupling, Protected type flanged coupling, pin (bush) type flexible coupling, Oldhams coupling and universal coupling (Hooks Joint) 8 Hours PART C Assembly Drawings (Part drawings should be given) 1. Plummer block (Pedestal Bearing) 2. Petrol Engine piston 3. I.C. Engine connecting rod 4. Screw jack (Bottle type) 5. Tailstock of lathe 6. Machine vice 7. Tool Head of a shaper 18 Hours
20
Text books 1. A Primer on Computer Aided Machine Drawing-2007, Published by VTU, Belgaum. 2. Machine Drawing, N.D.Bhat & V.M.Panchal 3. Machine Drawing , N. Siddeshwar, P. Kanniah, V.V.S. Sastri,published by Tata Mc GrawHill,2006 Reference Books 4. A Text Book of Computer Aided Machine Drawing, S. Trymbaka Murthy, CBS Publishers, New Delhi, 2007 5. Machine Drawing , K.R. Gopala Krishna, Subhash Publication. 6. Machine Drawing with Auto CAD. Goutam Pohit & Goutham Ghosh, 1st Indian print Pearson Education, 2005 7. Auto CAD 2006, for engineers and designers'. Sham Tickoo. Dream tech 2005 Note Internal assessment: 25 Marks All the sheets should be drawn in the class using software. Sheet sizes should be A3/A4. All sheets must be submitted at the end of the class by taking printouts. Scheme of Examination Two questions to be set from each Part-A, Part -B and Part-C. Student has to answer one question each from Part-A and Part-B for 20 marks each. And one question from Part-C for 60 marks.
i.e.
PART-A 1x20= 20 Marks PART-B 1x20= 20 Marks PART-C 1x60= 60 Marks Total =100 Marks
21
FLUID MECHANICS Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 36B/ 06 ME 46B : 04 : 52 PART A UNIT 1: Properties of Fluids: Introduction, properties of fluids, viscosity, thermodynamic properties, Surface tension and Capillarity, Vapour pressure and Cavitation. 6 Hours UNIT 2: Fluid Statics: Fluid pressure at a point, Pascals law, pressure variation in a static fluid, Absolute, gauge, atmospheric and vacuum pressures, simp le manometers, differential manometers, total pressure and center of pressure, vertical plane surface submerged in liquid, horizontal plane surface submerged in liquid, inclined plane surface submerged in liquid, curved surface submerged in liquid. Buoyancy, center of buoyancy, metacenter and metacentric height, conditions of equilibrium of floating and submerged bodies. 7 Hours Fluid Kinematics: Types of fluid flow, Introduction, continuity equation, continuity equation in three dimensions (Cartesian co-ordinate system only), velocity and acceleration, velocity potential function and stream function. 7 Hours UNIT 3: Dimensional Analysis: Introduction, derived quantities, dimensions of physical quantities, dimensional homogeneity, Buckinghams p theorem, Raleighs method, dimensionless numbers, similitude, types of similitudes. 6 Hours IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
22
PART B UNIT 4: Fluid Dynamics: Introduction, equations of motion, Eulers equation of motion, Bernoullis equation from Eulers equation, Bernoullis equation for real fluids. 6 Hours UNIT 5: Fluid flow measurements: Introduction, venturimeter, orifice meter, Pitot tube. Flow through pipes: Frictional loss in pipe flow, Darcy- Equation for loss of head due to friction in pipes, Chezys equation for loss of head due to friction in pipes, hydraulic gradient and total energy line. 7 Hours UNIT 6: Laminar flow and viscous effects: Reynolds number, critical Reynolds number, Laminar flow through circular pipe-Hagen poiseulles equation, Laminar flow between parallel and stationery plates. 6 Hours UNIT 7: Flow past immersed bodies: Drag, Lift, expression for lift and drag, pressure drag and friction drag, boundary layer concept, displacement thickness, momentum thickness and energy thickness. Introduction to compressible flow: Velocity of sound in a fluid, Mach number, Propagation of pressure waves in a compressible fluid. 7 Hours Text Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fluid Mechanics by Oijush K.Kundu, IRAM COCHEN, EL SEVIER 3rd Ed. 2005. Fluid Mechanics by Dr. Bansal.R.K, Lakshmi Publications, 2004. Fluid Mechanics and hydraulics, Dr. Jagadishlal: Metropolitan Book Co-Ltd., 1997. Fluid Mechanics (SI Units), Yunus A. Cingel John M. Oimbala. Tata MaGrawHill,2006.
23
Reference books: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fluid Mechanics, Fundamental & applications, by Yunus A, Cenegel, John M,Cimbala, Tata MacGraw Hill, 2006. Fluid Mechanics by John F.Douglas, Janul and M.Gasiosek and john A. Swaffield, Pearson Education Asia, 5th ed., 2006 Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power Engineering, Kumar.D.S, Kataria and Sons.,2004. Fluid Mechanics R.K.Hegde, Niranjana Murthy Spana Book House, 2005.
Scheme of examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
METALLOGRAPHY AND MATERIAL TESTING LABORATORY Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 MEL 37A / 06 MEL 47A : 03 : 42 PART A 1. Preparation of specimen for Metallograpic examination of different engineering materials. Identification of microstructures of plain carbon steel, tool steel, gray C.I, SG iron, Brass, Bronze & composites. Heat treatment: Annealing, normalizing, hardening and tempering of steel. Hardness studies of heat-treated samples. To study the wear characteristics of ferrous, non-ferrous and composite materials for different parameters. Non-destructive test experiments like, (a). Ultrasonic flaw detection (b). Magnetic crack detection (c). Dye penetration testing, to study the defects of Casted and Welded specimens IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 50
2. 3. 4.
24
PART B
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Tensile, shear and compression tests of metallic and non metallic specimens using a Universal Testing Machine Torsion tests Bending Test on metallic and nonmetallic specimens. Izod and Charpy tests on M.S. Specimen. Brinell, Rockwell and Vickerss Hardness test. Fatigue Test.
Scheme of Examination: ONE question from part -A: ONE question from part -B: Viva -Voice: Total: 20 Marks 20 Marks 10 Marks 50 Marks
MECHANICAL MEASUREMENTS AND METROLOGY LABORATORY Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 MEL 37 B / 06 MEL 47 B : 03 : 42 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 50
PART-A: MECHANICAL MEASUREMENTS 1. Calibration of Pressure Gauge 2. Calibration of Thermocouple 3. Calibration of LVDT 4. Calibration of Load cell 5. Determination of modulus of elasticity of a mild steel specimen using strain gauges.
25
PART-B: METROLOGY 6. 7. 8. 9. Measurements using Optical Projector / Toolmaker Microscope. Measurements of angle using Sine Center / Sine bar / bevel protractor Measurements of alignment using Autocollimator / roller set Measurements of cutting tool forces using a) Lathe tool Dynamometer b) Drill tool Dynamometer. Measurements of Screw thread Parameters using two wire or three-wire method. Measurements of Surface roughness. Using Tally surf/mechanical Comparator. Measurements of gear tooth profile using gear tooth vernier /gear tooth micrometer. Calibration of micrometer using slip gauges Measurement using Optical Flats
10. 11. 12. 13. 14.
Scheme of Examination: ONE question from Metrology (part -A) ONE question from Instrumentation (part -B) Viva Voce Total 20 Marks 20 Marks 10 Marks 50 Marks
FOUNDRY AND FORGING LABORATORY Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 MEL 38A / 06 MEL 48A : 03 : 42 PART A 1. Testing of Moulding sand and Core sand Preparation of sand specimens and conduction of the following tests: 1 Compression, Shear and Tensile tests on Universal Sand Testing Machine. 2 3 4 5 6 Permeability test Core hardness & Mould hardness tests. Grain fineness number test (Sive Analysis test) Clay content test. Moisture content test. IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 50
26
PART B 2. Foundry Practice Use of foundry tools and other equipments. Preparation of moulds using two moulding boxes using patterns or without patterns. (Split pattern, Match plate pattern and Core boxes). Preparation of one casting (Aluminum or cast iron-Demonstration only) PART C 3. Forging Operations Preparing minimum three forged models involving upsetting, drawing and bending operations. Out of these three models, at least one model is to be prepared by using Power Hammer. Scheme of Examination: One question is to be set from Part-A: One question is to be set from either Part-B or Part -C: Viva-Voce: Total: 30 marks 10 marks. 50 marks. 10 marks
MACHINE SHOP Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 MEL 38 B / 06 MEL 48 B : 03 : 42 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 50
PART A Preparation of three models on lathe involving Plain turning, Taper turning, Step turning, Thread cutting, Facing, Knurling, Drilling, Boring, Internal Thread cutting and Eccentric turning. PART B Cutting of V Groove/ dovetail / Rectangular groove using Shaping and Cutting of Gear Teeth using Milling Machine.
27
Scheme of Examination: One Model from Part A One Model from Part B Viva Voce Total 30 marks 10 marks 10 marks 50 marks
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS - IV Sub Code Hrs/ Week Total Hrs. : : : 06MAT41 04 52 PART A UNIT 1: Numerical Methods Numerical solutions of first order and first degree ordinary differential equations Taylors series method, Modified Eulers method, Runge Kutta method of fourth order, Milnes and Adams -Bashforth predictor and corrector methods (All formulae without Proof). 6 Hours UNIT 2: Complex Variables Function of a complex variable, Limit, Continuity Differentiability Definitions. Analytic functions, Cauchy Riemann equations in cartesian and polar forms, Properties of analytic functions. Conformal Transformation 2 Definition. Discussion of transformations: W = z , W = ez, W = z + (I/z), z ? 0 Bilinear transformations. 7 Hours UNIT 3: Complex Integration Complex line integrals, Cauchys theorem, Cauchys integral formula. Taylors and Laurents series (Statements only) Singularities, Poles, Residues, Cauchys residue theorem (statement only). 6 Hours IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : : : 25 03 100
28
UNIT 4: Series solution of Ordinary Differential Equations and Special Functions Series solution Frobenius method, Series solution of Bessels D.E. leading to Bessel function of fist kind. Equations reducible to Bessels D.E., Series solution of Legendres D.E. leading to Legendre Polynomials. Rodirgues formula. 7 Hours PART B UNIT 5: Statistical Methods 2 Curve fitting by the method of least squares: y = a + bx, y = a + bx + cx , b x bx y = ax y = ab , y = ae , Correlation and Regression. Probability: Addition rule, Conditional probability, Multiplication rule, Bayes theorem. 6 Hours UNIT 6: Random Variables (Discrete and Continuous) p.d.f., c.d.f. Binomial, Poisson, Normal and Exponential distributions. 7 Hours UNIT 7: Sampling, Sampling distribution, Standard error. Testing of hypothesis for means. Confidence limits for means, Students t distribution, Chi-square distribution as a test of goodness of fit. 7 Hours UNIT 8: Concept of joint probability Joint probability distribution, Discrete and Independent random variables. Expectation, Covariance, Correlation coefficient. Probability vectors, Stochastic matrices, Fixed points, Regular stochastic matrices. Markov chains, Higher transition probabilities. Stationary distribution of regular Markov chains and absorbing states. 6 Hours
29
Text Book: Higher Engineering Mathematics by Dr. B.S. Grewal (36th Edition Khanna Publishers) Unit No. I Chapter No. 27 Article Numbers 27.1, 27.3, 27.5, 27.7, 27.8 Page Nos. 914, 916 922 924, 933 630 650 652 658 661 671 507 514, 521 523 526 529 20 25 755 762, 765 768 776 776 780 783 798 791 816
II III
20 20
20.1 to 20.10 20.12 to 20.14, 20.16 to 20.19
IV
16
16.1 to 16.6, 16.10, 16.13, 16.14
1 23
1.12 to 1.14 23.9, 23.10, 23.11, 23.14, 23.16 to 23.18 23.19 to 23.22, 23.26 to 23.30
VI
23
VII
23
23.31 to 23.37
Unit VIII: Text book: Probability by Seymour Lipschutz (Schaums series) Chapters 5 & 7 Reference Books: 1. Higher Engineering Mathematics by B.V. Ramana (Tata-Macgraw Hill). 2. Advanced Modern Engineering Mathematics by Glyn James Pearson Education. Note: 1. One question is to be set from each unit. 2. To answer Five questions choosing atleast Two questions from each part.
30
APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 43 : 04 : 52 PART A IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
UNIT 1: Combustion thermodynamics: Theoretical (Stoichiometric) air for combustion of fuels. Excess air, mass balance, actual combustion. Exhaust gas analysis. A/F ratio. Energy balance for a chemical reaction, enthalpy of formation, enthalpy and internal energy of combustion. Combustion efficiency. 7 Hours UNIT 2: Gas Power Cycles: Air standard cycles; Carnot, Otto, Diesel, Dual and Stirling cycles, P-v and T diagrams, description, efficiencies and mean -s effective pressures. Comparison of Otto and Diesel cycles. 6 Hours UNIT 3: Gas turbines and Jet Propulsion: Classification of Gas Turbines, Analysis of open cycle gas turbine cycle. Advantages and Disadvantages of closed cycle. Methods to improve thermal efficiency. Jet propulsion and Rocket propulsion. 6 Hours UNIT 4: Vapour Power Cycles: -Carnot vapour power cycle, drawbacks as a reference cycle. Simple Rankine cycle; description, T s diagram, analysis for performance. Comparison of Carnot and Rankine cycles. Effects of pressure and temperature on Rankine cycle performance. Actual vapour power cycles. Ideal and practical regenerative Rankine cycles, open and closed feed water heaters. Reheat Rankine cycle. 7 Hours
31
PART B UNIT 5: Reciprocating Compressors: - Operation of a single stage reciprocating compressors. Work input through P v diagram and steady state steady flow analysis. Effect of clearance and volumetric efficiency. Adiabatic, isothermal and mechanical efficiencies. Multi-stage compressor, Saving in work, optimum intermediate pressure, inter-cooling, minimum work for compression. 7 Hours UNIT 6: Refrigeration: -Vapour compression refrigeration system; description, analysis, refrigerating effect, capacity, power required, units of refrigeration, COP. Refrigerants and their desirable properties. Air cycle refrigeration; reversed Carnot cycle, reversed Brayton cycle. Vapour absorption refrigeration system. Steam jet refrigeration. 7 Hours UNIT 7: Psychrometrics: - Atmospheric air and psychrometric properties; Dry bulb temperature, wet bulb temperature, dew point temperature; partial pressures, specific and relative humidifies and the relation between the two Enthalpy and adiabatic saturation temperature. Construction and Use of psychrometric chart. Analysis of various processes; heating, cooling, dehumidifying and humidifying. Adiabatic mixing of stream of moist air. Summer and winter air - conditioning. 6 Hours UNIT 8: I.C. Engines: Testing of two-stroke and four-stroke Sl and CI engines for performance, related numerical problems, heat balance, Morse test. 6 Hours Text Books: 1. Basic and Applied Thermodynamics by P.K.Nag, Tata McGraw Hill Pub. Co., 2002. 2. Fundamental of Classical Thermodynamics by G.J. Van Wylen and R.E.Sonntag, Wiley Eastern.
32
Reference Books: 1. 2. Thermodynamics -An Engineering Approach by Yunus, A.Cenegal and Michael A.Boles, Tata McGraw Hill Pub. Co., 2002 Applied Thermodynamics by R.K.Hegde and Niranjan Murthy, Sapna Book House, 2005.
Scheme of Examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
KINEMATICS OF MACHINES Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 44 : 04 : 52 PART A UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION: DEFINITIONS: Link or element, kinematic pairs, degrees of freedom, Grublers criterion (without derivation), Kinematic chain, Mechanism, structure, Mobility of Mechanism, Inversion, Machine. KINEMATIC CHAINS AND INVERSIONS: Inversions of Four bar chain; Single slider crank chain and Double slider crank chain. 7 Hours UNIT 2: MECHANISMS: Quick return motion mechanisms -Drag link mechanism, Whitworth mechanism and Crank and slotted lever Mechanism. Straight line motion mechanisms Peaucelliers mechanism and Roberts mechanism. Intermittent Motion mechanisms Geneva mechanism and Ratchet and Pawl mechanism. Toggle mechanism, Pantograph, Ackerman steering gear mechanism. 7 Hours IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
33
UNIT 3: VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION ANALYSIS OF MECHANISMS (GRAPHICAL METHODS) Velocity and acceleration analysis of Four Bar mechanism slider crank , mechanism and Simple Mechanisms by vector polygons: Relative velocity and acceleration of particles in a common link, relative velocity and accelerations of coincident Particles on separate links- Coriolis component of acceleration. Angular velocity and angular acceleration of links, velocity of rubbing. 7 Hours UNIT 4: VELOCITY ANALYSIS BY INSTANTANEOUS CENTER METHOD: Definition, Kennedys Theorem, Determination of linear and angular velocity using instantaneous center method KLEINS CONSTRUCTION: Analysis of velocity and acceleration of single slider crank mechanism. 6 Hours PART B UNIT 5: VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION ANALYSIS OF MECHANISMS (ANALYTICAL METHODS): Analysis of four bar chain and slider crank chain using analytical expressions. (use of complex algebra and vector algebra) 6 Hours UNIT 6: SPUR GEARS: Gear terminology, law of gearing, Characteristics of involute action, Path of contact, Arc of contact, Contact ratio, Interference in involute gears, Methods of avoiding interference, Back lash, Comparison of involute and cycloidal teeth. 6 Hours UNIT 7: GEAR TRAINS: Simple gear trains, Compound gear trains for large speed reduction, Epicyclic gear trains, Algebraic and tabular methods of finding velocity ratio of epicyclic gear trains. Tooth load and torque calculations in epicyclic gear trains. 7 Hours
34
UNIT 8: CAMS: Types of cams, Types of followers, Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration time curves for cam profiles. Disc cam with reciprocating follower having knife -edge, roller and flat-faced follower, Disc cam with oscillating roller follower, Follower motions including SHM, Uniform velocity, uniform acceleration and retardation and Cycloidal motion. 7 Hours Text Books: 1. 2. Theory of Machines, Rattan S.S, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Ltd., New Delhi, and 2nd edition -2005. Theory of Machines, Sadhu Singh, Pearson E ducation (Singapore) Pvt. Ltd., Indian Branch, New Delhi, 2ND Edi. 2006.
Reference books: 1. 2. Theory of Machines & Mechanisms , Shigley. J. V. and Uickers, J.J., OXFORD University press.2004 Theory of Machines -I, by A.S.Ravindra, Sudha Publications, Revised 5th Edi. 2004.
Scheme of Examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 question from part B. Graphical Solutions may be obtained either on the Graph Sheets or on the Answer Book itself. MANUFACTURING PROCESS II Sub Code Hrs/week Total Lecture Hrs : 06 ME 45 : 04 : 52 IA Marks Exam Hours Exam Marks : 25 : 03 : 100
PART A UNIT 1: Theory of Metal Cutting : Single point cutting tool nomenclature, geometry, Merchants circle diagram and analysis, Ernst Merchants solution, shear angle relationship, problems of Merchants analysis, tool wear and tool failure, tool life, effects of cutting parameters on tool life, tool failure criteria, Taylors tool life equation, problems on tool life evaluation. 7 Hours
35
UNIT 2: Cutting tool materials: Desired properties, types of cutting tool materials HSS, carbides coated carbides, ceramics cutting fluids. Desired properties, types and selection. Heat generation in metal cutting, factors affecting heat generation. Heat distribution in tool and W/P. Measurement of tool tip temperature. 7 Hours UNIT 3: Turning (Lathe), Shaping and planning machines: Classification, constructional features of turret and capstan lathe, tool layout, shaping m/c, planning m/c, driving mechanisms of lathe, shaping and planning machines, operations on lathe, shaping machine and planning machine. 6 Hours UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. 6 Hours PART B UNIT 5: Milling machines: Classification, constructional features, milling cutters nomenclature, milling operations, up milling and down milling concepts. Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular indexing calculations. Simple problems on simple and compound indexing. 7 Hours UNIT 6: Grinding machines: Types of abrasives, bonding process, classification, constructional features (cylindrical and surface grinding), selection of grinding wheel. 6 Hours UNIT 7: Laping and Honing machines: Principles of operation, construction, applications. 7 Hours
36
UNIT 8: Non-traditional machining processes : Principle, need, equipment, operation and LBM, plasma arc machining, Electro chemical machining, ultrasonic machining, abrasive let machining, water jet machining. 6 Hours Text Books: 1. 2. 3. Workshop Technology by Hazara Choudhry, Vol-II, Media Promoters & Publishers Pvt. Ltd. 2004 Production Technology by R.K.Jain, Khanna Publications, 2003. Production technology by HMT, Tata MacGraw Hill, 2001.
Reference Books: 1. 2. Manufacturing Science by Amitabha Ghosh and Mallik, affiliated East West Press, 2003. Fundamentals of Metal Machining and Machine Tools by G. Boothroyd, McGraw Hill, 2000.
Scheme of examination: One Question to be set from each chapter. Students have to answer any FIVE full questions out of EIGHT questions, choosing at least 2 questions from part A and 2 questions from part B.
*********
37
Вам также может понравиться
- Optical Technology in Current MeasurementДокумент2 страницыOptical Technology in Current MeasurementAnoop Ravi50% (2)
- RGPV 7th Sem Scheme CSE.Документ1 страницаRGPV 7th Sem Scheme CSE.Ankit AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Softwsre Engineering Lesson Plan For Teaching StaffДокумент1 страницаSoftwsre Engineering Lesson Plan For Teaching StaffRajesh KannaОценок пока нет
- Proggramming Visual Basic 2010Документ15 страницProggramming Visual Basic 2010shbaguseОценок пока нет
- ProblemStatement For t4 TrackДокумент4 страницыProblemStatement For t4 TrackSoorya PrashanthОценок пока нет
- A Gentle Introduction To The Chi-Squared Test For Machine LearningДокумент17 страницA Gentle Introduction To The Chi-Squared Test For Machine Learningyuvaraj raj0% (2)
- OOSE IMP Questions&Question Bank (III Year I Sem)Документ52 страницыOOSE IMP Questions&Question Bank (III Year I Sem)sai tejasОценок пока нет
- PHD FAQДокумент15 страницPHD FAQMunivel EllappanОценок пока нет
- Java Execption HandlingДокумент13 страницJava Execption HandlingSirisha KurakulaОценок пока нет
- Scheme - G Third Semester (Ej, Et, En, Ev, Ex, Is, Ic, Iu, De, Mu, Ie, Ed, Ei)Документ39 страницScheme - G Third Semester (Ej, Et, En, Ev, Ex, Is, Ic, Iu, De, Mu, Ie, Ed, Ei)digisagarОценок пока нет
- Asimov ModelДокумент5 страницAsimov ModelharimugutkarОценок пока нет
- Ieee 13 Node Test Feeder: Digsilent PowerfactoryДокумент9 страницIeee 13 Node Test Feeder: Digsilent PowerfactorypouyanОценок пока нет
- 5th Sem Dbms Lab ProgramsДокумент22 страницы5th Sem Dbms Lab ProgramsPrajwal R Prasad33% (3)
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Laboratory ManualДокумент52 страницыDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Laboratory ManualMECHANICAL SMCETОценок пока нет
- Solid Modelling Practical ManualДокумент188 страницSolid Modelling Practical Manualajaysurya9245Оценок пока нет
- PLCs and AutomationДокумент2 страницыPLCs and AutomationKhaja JamalОценок пока нет
- DS 18CS652 IA1-QPaperДокумент2 страницыDS 18CS652 IA1-QPaperPuneet MittalОценок пока нет
- Machine Learning AssignmentДокумент55 страницMachine Learning AssignmentAkashОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Viva Amit RawatДокумент12 страницComprehensive Viva Amit RawatAmit RawatОценок пока нет
- Automation of Ac System Employing PLC and ScadaДокумент10 страницAutomation of Ac System Employing PLC and Scadaeyob feshaОценок пока нет
- Compiler Design Model Lab QuestionsДокумент4 страницыCompiler Design Model Lab QuestionsKisan SakthiОценок пока нет
- NPHSAT Project PresentationДокумент23 страницыNPHSAT Project PresentationAdarshОценок пока нет
- B.SC (CS) Real SyllabusДокумент75 страницB.SC (CS) Real SyllabusPeaky BlindersОценок пока нет
- Python Interview QuestionsДокумент13 страницPython Interview QuestionsNanda KumarОценок пока нет
- Gtu Micro Processor PracticalДокумент79 страницGtu Micro Processor Practicalbaba100% (1)
- Java8 InnardsДокумент4 страницыJava8 InnardsAbhishek KumarОценок пока нет
- Tcs Aspire Java1Документ5 страницTcs Aspire Java1Anagha WalimbeОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Dos NewДокумент44 страницыLab Manual Dos NewAdira HayatОценок пока нет
- Question 1Документ18 страницQuestion 1Datta RajendraОценок пока нет
- MCQsДокумент19 страницMCQsbyrisetty sruthiОценок пока нет
- Servlets Mock Test IДокумент11 страницServlets Mock Test IMark225userОценок пока нет
- New Scheme Engg Nep V6Документ22 страницыNew Scheme Engg Nep V6Dr-Bharath Vedashantha MurthyОценок пока нет
- MEE1045 - MECHATRONICS-SYSTEMS-DESIGN - EPJ - 1.0 - 49 - MEE1045 Mechatronics Systems Design PDFДокумент2 страницыMEE1045 - MECHATRONICS-SYSTEMS-DESIGN - EPJ - 1.0 - 49 - MEE1045 Mechatronics Systems Design PDFSathish SatОценок пока нет
- Ee6602 Embedded SystemsДокумент3 страницыEe6602 Embedded SystemsNO R100% (1)
- FM Lab Mark Split UpДокумент1 страницаFM Lab Mark Split UpbalajimeieОценок пока нет
- Co-Po Big Data AnalyticsДокумент41 страницаCo-Po Big Data AnalyticssuniОценок пока нет
- 8 Bit Microcontroller: Vishal V.Panchbhai, Asst. Prof. E & T DeptДокумент41 страница8 Bit Microcontroller: Vishal V.Panchbhai, Asst. Prof. E & T DeptSagar DhapkeОценок пока нет
- Pd9211-Quality Concepts in Design 2Документ2 страницыPd9211-Quality Concepts in Design 2Vignesh VickyОценок пока нет
- Additive Manufacturing R16 Oct 2019 PDFДокумент4 страницыAdditive Manufacturing R16 Oct 2019 PDFrajuОценок пока нет
- Vtu Mechanical EngineeringДокумент175 страницVtu Mechanical Engineeringsbhalesh40% (5)
- Cad Cam Previous Paper JntukДокумент4 страницыCad Cam Previous Paper JntukMD KHALEELОценок пока нет
- Operations Research (17ME81) Notes and Video Links From Sadashiv BellubbiДокумент2 страницыOperations Research (17ME81) Notes and Video Links From Sadashiv BellubbiAmogh TerdalОценок пока нет
- DBMS Module-2-Notes - NormalizationДокумент18 страницDBMS Module-2-Notes - NormalizationRupak DuttaОценок пока нет
- Com OrgДокумент39 страницCom OrgDouaa M. AliОценок пока нет
- Aucr2004 PDFДокумент37 страницAucr2004 PDFSenthilkumar PalanisamyОценок пока нет
- Azure Virtual MachinesДокумент3 страницыAzure Virtual Machineskrishna.vukkalaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Mechatronics Short CourseДокумент3 страницыFundamentals of Mechatronics Short CourseAamir Hasan KhanОценок пока нет
- VTU SEM 1 Scheme of Evaluation and SyllabusДокумент13 страницVTU SEM 1 Scheme of Evaluation and SyllabusAdilHEngineerОценок пока нет
- Syllabus - CSEДокумент110 страницSyllabus - CSESIETDOC100% (5)
- Srtmu Fe Syllabus 2Документ34 страницыSrtmu Fe Syllabus 2shriraj0786Оценок пока нет
- M.tech Machine SyllabusДокумент41 страницаM.tech Machine SyllabusSyed Faiz Quadri0% (1)
- FEM SyllabusДокумент2 страницыFEM SyllabuskumarОценок пока нет
- Course DiaryДокумент66 страницCourse DiaryAishwarya RaviОценок пока нет
- S Y B Tech (Mechanical Engg) SyllabusДокумент30 страницS Y B Tech (Mechanical Engg) SyllabusBhavesh JainОценок пока нет
- M.E.Mech. HEAT POWERДокумент37 страницM.E.Mech. HEAT POWERKapil KotangaleОценок пока нет
- 3rd Sem Course DiaryДокумент61 страница3rd Sem Course DiaryShafiq Ahmed ShahbazОценок пока нет
- Aeronautical Syllabus-Shivaji University - R.H.B. RamamurthyДокумент36 страницAeronautical Syllabus-Shivaji University - R.H.B. RamamurthyZachary GuerraОценок пока нет
- M.tech Syllabus PDFДокумент51 страницаM.tech Syllabus PDFAnonymous MR8PLYОценок пока нет
- Periyar University Dde MSC Physics SyllabusДокумент30 страницPeriyar University Dde MSC Physics Syllabusபிரபாகரன் பிரபாகரன்Оценок пока нет
- 3rd Sem Aero Syllabus For VTUДокумент8 страниц3rd Sem Aero Syllabus For VTUaeroromeosОценок пока нет
- Multibagger Stock IdeasДокумент16 страницMultibagger Stock Ideaskmrsg7Оценок пока нет
- Policies and Schemes of Central and State Governments For People With DisabilitiesДокумент128 страницPolicies and Schemes of Central and State Governments For People With Disabilitiesmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Preparation For Nba AccreditationДокумент76 страницPreparation For Nba AccreditationKarthikeyan Purusothaman100% (2)
- Minitab DOE Tutorial PDFДокумент32 страницыMinitab DOE Tutorial PDFnmukherjee20100% (3)
- Chi Square 34Документ4 страницыChi Square 34Paul LixfeОценок пока нет
- Amendment of KCSR Recruitment For AICTEДокумент3 страницыAmendment of KCSR Recruitment For AICTEmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Mysore District PDFДокумент13 страницMysore District PDFmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Result - Mtech MaintenanceДокумент2 страницыResult - Mtech Maintenancemanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY AND OVERVIEW OF SMALL-SCALE INDUSTRIES (SSIs) IN INDIAДокумент343 страницыDEVELOPMENT STRATEGY AND OVERVIEW OF SMALL-SCALE INDUSTRIES (SSIs) IN INDIAmanjunatha t100% (2)
- Annual Report of Industries and Commerce KarnatakaДокумент29 страницAnnual Report of Industries and Commerce Karnatakamanjunatha t0% (1)
- Decision Support SystemsДокумент33 страницыDecision Support SystemsJacton OpiyoОценок пока нет
- 03jan Feb SF 2Документ9 страниц03jan Feb SF 2manjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Budget SalaryДокумент1 страницаBudget Salarymanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- VTU - V & VIIIsem Syllabus 23-7-8Документ11 страницVTU - V & VIIIsem Syllabus 23-7-8manjunatha tОценок пока нет
- 2nd SEM M SECTION CAEG RESULTДокумент6 страниц2nd SEM M SECTION CAEG RESULTmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Factor Analysis - SpssДокумент15 страницFactor Analysis - Spssmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Result - Mtech MemДокумент2 страницыResult - Mtech Memmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth Some Empirical StudiesДокумент213 страницEntrepreneurship and Economic Growth Some Empirical Studiesmanjunatha t100% (1)
- Sample Size in Factor Analysis: Why Size Matters Helen C Lingard and Steve RowlinsonДокумент6 страницSample Size in Factor Analysis: Why Size Matters Helen C Lingard and Steve Rowlinsonmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 and 2Документ2 страницыAssignment 1 and 2manjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Measuring IntrapreneurshipДокумент228 страницMeasuring Intrapreneurshipmanjunatha t100% (2)
- Gender Differences in Motivations For Becoming An EntrepreneurДокумент327 страницGender Differences in Motivations For Becoming An Entrepreneurmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Question BankДокумент2 страницыQuestion Bankmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Reciprocating CompressorДокумент3 страницыReciprocating Compressormanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Applied Thermodynamics - Attendance and InternalsДокумент3 страницыApplied Thermodynamics - Attendance and Internalsmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Документ7 страницmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Документ7 страницmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Документ6 страницmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- Iii Sem Camd Attendance and InternalsДокумент4 страницыIii Sem Camd Attendance and Internalsmanjunatha tОценок пока нет
- REVIEW Development of DRsДокумент17 страницREVIEW Development of DRsnozue.tatsuhiro nozueОценок пока нет
- Final Energy Balance-Vizag DT 9-6-18Документ14 страницFinal Energy Balance-Vizag DT 9-6-18SUBHOMOYОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 1Документ9 страницChapter - 1Sahil PatilОценок пока нет
- Thermophysical Properties of Propane, National Bureau of Standars.Документ256 страницThermophysical Properties of Propane, National Bureau of Standars.Ezra E. Rangel AcedoОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of GasesДокумент17 страницKinetic Theory of Gasesyajur bishnoiОценок пока нет
- Performance Specification: Hot Side Cold SideДокумент2 страницыPerformance Specification: Hot Side Cold SideStevan KrstojevicОценок пока нет
- Thermia ATEC Datasheet SRBДокумент2 страницыThermia ATEC Datasheet SRBsloba68Оценок пока нет
- Carrier 30WG 140Документ1 страницаCarrier 30WG 140Stjepan KrpanОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Matters Workbook Chapter 2 Experimental Chemistry AnswersДокумент2 страницыChemistry Matters Workbook Chapter 2 Experimental Chemistry AnswersLim Kew Chong83% (6)
- Chapter 13Документ31 страницаChapter 13DrakzОценок пока нет
- MEC 4205 Exam - May - 2018 - Marking GuideДокумент18 страницMEC 4205 Exam - May - 2018 - Marking GuideBirimumaso DavidОценок пока нет
- Che 471fall HW 7 2008Документ5 страницChe 471fall HW 7 2008HungDoОценок пока нет
- 6 Olander - Fundamental Aspects of Nuclear Reactor Fuel Elements - Termo EstatistДокумент624 страницы6 Olander - Fundamental Aspects of Nuclear Reactor Fuel Elements - Termo EstatistLauri RubertiОценок пока нет
- Mr. Saxena - EP88Документ11 страницMr. Saxena - EP88Umar ShamshiriОценок пока нет
- Capiz State University: Charles' LawДокумент2 страницыCapiz State University: Charles' LawSheila Mae Feguro Halaghay100% (1)
- Phase DiagramДокумент3 страницыPhase DiagramTing TCОценок пока нет
- Hot Water Vs Cold WaterДокумент10 страницHot Water Vs Cold WaterviiolettaОценок пока нет
- VRV System of Air ConditionДокумент15 страницVRV System of Air ConditionRushabh Rajendra YerunkarОценок пока нет
- Le Chatelier's Principle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент7 страницLe Chatelier's Principle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlfred RogerОценок пока нет
- Aquaforce Water-Cooled Liquid Screw Chillers: Product DataДокумент60 страницAquaforce Water-Cooled Liquid Screw Chillers: Product DataOctavio Farid Rossi YumhaОценок пока нет
- CHM1311 Lab#3Документ13 страницCHM1311 Lab#3zaf77Оценок пока нет
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 4Документ33 страницыPhysics Form 4 Chapter 4Eric LengОценок пока нет
- ConvectionДокумент27 страницConvectionVinoth Malaikani100% (2)
- Refresher 2 (Pipe)Документ12 страницRefresher 2 (Pipe)Kira YagamiОценок пока нет
- 270 Boiler Control - One Modulating Boiler and DHWДокумент24 страницы270 Boiler Control - One Modulating Boiler and DHWe-ComfortUSAОценок пока нет
- 2014 Sac Me Spec Ver105Документ61 страница2014 Sac Me Spec Ver105Lawrence Anthony BenitezОценок пока нет
- Q Bank - CHEM - CET-I - III - 2020Документ20 страницQ Bank - CHEM - CET-I - III - 2020Kp ModiОценок пока нет
- K SH SC: T2 ATM Type Temp. UnitДокумент2 страницыK SH SC: T2 ATM Type Temp. UnitjrrguitarОценок пока нет
- EAT Xchanger Esign: 7.1.1 Basic Principle of Heat ExchangersДокумент31 страницаEAT Xchanger Esign: 7.1.1 Basic Principle of Heat ExchangersNoman Aslam100% (1)
- CFD Analysis of Heat Transfer in A Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Using FluentДокумент48 страницCFD Analysis of Heat Transfer in A Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Using FluentManishSharma90% (10)