Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Summary of Reactions
Загружено:
Austin GohОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Summary of Reactions
Загружено:
Austin GohАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
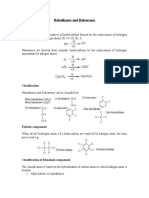
SUMMARY OF REACTIONS
Homologous Series
Alkane
Reaction / Mechanism Free radical substitution 1. Initiation Step 1.1. Homolytic fission of halogens 2. Propagation Step 2.1. Alkane reacts with halogens to produce alkyl radical 2.2. Alkyl radical propagates the chain reaction 3. Termination Step 3.1. Chain reactions stop 3.2. Free radicals combined molecules Electrophilic Substitution 1. Formation of carbocation - + , - ( Induced dipole ) - + attacks the bond 2. Nucleophilic Attack - - ion attacks the electron deficient site ( Carbonium ion)
E.g,Condition,Observation CH3CH3 + Br2 BrCH2CH3 + HBr Brown Bromine is decolourised Steamy fumes is formed
Alkene
Hydrogenation CH2=CH2 + H2 CH3CH3 + Halogen CH2=CH2 + Br2 CH2BrCH2Br + Hydrogen Halides CH2=CH2 + HBr CH3CH2Br + H2O CH2=CH2 + [O] + H2O CH3CH2OH
Oxidation
Combustion CH2=CH2 + 3O2 2CO2 + 2H2O Catalytic Oxidation
Temperature: about 250 - 300C about 15 atmospheres silver
Pressure:
Catalyst:
2CH2=CH2 + O2 2 (Epoxyethane) + H2O CH2OHCH2OH
Reaction with KMnO4 Cold KMnO4 CH2=CH2 + H2O + [O] CH2(OH)CH2(OH) Hot,acidified KMnO4 CH3C(CH3)=CH2 + [O] + H2O CH3C(CH3)(OH)CH2(OH)Ketone/Aldehyde Carboxylic acid Purple colour turns colourless Addition Polymerisation nCH2=CH2 ( CH2-CH2 )
Haloalkane
Nucleophilic Substitution
Hydrolysis CH3CH2Br + NaOH CH3CH2OH + NaBr If carbon bonded >1 halogen atom, 1. CH3CH(Br)2 CH3CH(OH)2 CH3CH=O
Вам также может понравиться
- Oxidation - Reduction (Redox) ReactionДокумент10 страницOxidation - Reduction (Redox) ReactionJa FuentesОценок пока нет
- Reaction KineticsДокумент12 страницReaction KineticsTheresaHangDuongОценок пока нет
- Assignment - 3Документ12 страницAssignment - 3padhiyararpitaОценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbons NotesДокумент13 страницHydrocarbons NotesShivansh Pundir100% (1)
- ChemChapter7 RojasДокумент6 страницChemChapter7 RojasTn F'dzОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsДокумент7 страницNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsSachi Srivastava ; 51 ; 5724Оценок пока нет
- HydrocarbonsДокумент76 страницHydrocarbonsnivitamathsfavouriteОценок пока нет
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesДокумент159 страницPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsДокумент120 страницOrganic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsLoveena Steadman100% (8)
- CH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanДокумент58 страницCH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanpujaОценок пока нет
- Alkyl HalidesДокумент54 страницыAlkyl HalidesSaurabh KumarОценок пока нет
- Chemical Arithmetic and Reactions: ObjectivesДокумент24 страницыChemical Arithmetic and Reactions: Objectivesgoputs6386Оценок пока нет
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 15: HydrocarbonsДокумент12 страницCIE Chemistry A Level: 15: HydrocarbonsAgung Ratana Jayo Silim IPH StudentОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Redox Reactions STDNTДокумент49 страницChapter 8 Redox Reactions STDNTHaziqrosliziОценок пока нет
- NamereactionorganicДокумент13 страницNamereactionorganicdeykrishna654100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Equations-1Документ22 страницыChemical Reactions and Equations-1krithicktcrОценок пока нет
- Complete Organic Chemistry (Brahmastra) Part 2Документ763 страницыComplete Organic Chemistry (Brahmastra) Part 2mohdamaankhan74Оценок пока нет
- Type of Chemical Reaction: Prepared By-Abhay Bohra Guided by - Aakansha LalДокумент8 страницType of Chemical Reaction: Prepared By-Abhay Bohra Guided by - Aakansha LalVishal NandwanaОценок пока нет
- Notes - Alkyl Halides and Aryl HalidesДокумент34 страницыNotes - Alkyl Halides and Aryl HalidesDivya MehtaОценок пока нет
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsДокумент8 страницAakash Institute: NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsSuneethaОценок пока нет
- Permeating & Mechanisms PDFДокумент18 страницPermeating & Mechanisms PDFShabnam Fatima SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions N Equations Q N AnsДокумент11 страницChemical Reactions N Equations Q N AnsDHRUV TEKUMALAОценок пока нет
- Chemical Equation and ReactionsДокумент20 страницChemical Equation and ReactionsdivyeshОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 13 Hydro CarbonДокумент22 страницыChapter - 13 Hydro CarbonManan TyagiОценок пока нет
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-Anil-Hsslive PDFДокумент12 страницHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-Anil-Hsslive PDFAnwar Hashmi67% (3)
- AlkenesДокумент16 страницAlkenesAbhijeetОценок пока нет
- 10th Science Byjus SolutionsДокумент159 страниц10th Science Byjus SolutionsChinmay B PОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsДокумент8 страницNCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equationssamiksha choudharyОценок пока нет
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-azhar TuitionДокумент12 страницHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-azhar Tuitionasharstuition685607Оценок пока нет
- Hsslive Xii CH 6 Haloalkanes AnilДокумент13 страницHsslive Xii CH 6 Haloalkanes AnilUnkown HumanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Alkyl HalidesДокумент32 страницыChapter 5 Alkyl HalidesMohd HanafiahОценок пока нет
- Overview of Alkene ReactionsДокумент11 страницOverview of Alkene ReactionsVickyОценок пока нет
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesДокумент28 страницHaloalkanes and HaloarenesDevansh TiwaryОценок пока нет
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 2 NotesДокумент18 страницAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 2 NotesMuadh Chati100% (2)
- Preparations and Reactions of AlkanesДокумент25 страницPreparations and Reactions of AlkanesCarlo ManguilОценок пока нет
- Alkyl HalidesДокумент54 страницыAlkyl HalidesChandrapal SinghОценок пока нет
- Haloalkanes HaloareneДокумент23 страницыHaloalkanes HaloarenegtfhrfvhwcvfrwdpitОценок пока нет
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NotesДокумент10 страницHaloalkanes and Haloarenes NotesArchanaa PadmavathiОценок пока нет
- 204 Chlorine and ChloratesДокумент2 страницы204 Chlorine and ChloratesM DiОценок пока нет
- Halogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackДокумент23 страницыHalogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackBritney PattersonОценок пока нет
- Halogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackДокумент23 страницыHalogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackBritney PattersonОценок пока нет
- The Chemistry of The Halogens Is Dominated by Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsДокумент5 страницThe Chemistry of The Halogens Is Dominated by Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsMUKUОценок пока нет
- HaloalkanesДокумент13 страницHaloalkanesChingYan TanОценок пока нет
- 10 Sci Chem Unit 1 ChemicalreactionДокумент5 страниц10 Sci Chem Unit 1 ChemicalreactionPranav katariaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 1: Quarter 4: Module 2 Types of Chemical ReactionsДокумент3 страницыChemistry 1: Quarter 4: Module 2 Types of Chemical ReactionsRain AlmsОценок пока нет
- Types of Reactions Guided Tutorial Spring 2015Документ41 страницаTypes of Reactions Guided Tutorial Spring 2015Stefanie CorcoranОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Part 1Документ10 страницElectrochemistry Part 1Shofwa AnnisaaОценок пока нет
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-987978Документ9 страницCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-987978abiniveshofficial4708Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions and Equations VeeДокумент20 страницChemical Reactions and Equations VeeSanjay JagarwalОценок пока нет
- Chm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsДокумент34 страницыChm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsOluwabusolami Akinola100% (1)
- Types of Chemical ReactionsДокумент40 страницTypes of Chemical ReactionschhajuramОценок пока нет
- Jimmy's Combo PDFДокумент9 страницJimmy's Combo PDFRawan Abd ElaatyОценок пока нет
- H +CL 2Hcl 3bacl +al (So) 2alcl +3baso 2Na+2H O 2Naoh+H: QuestionsДокумент98 страницH +CL 2Hcl 3bacl +al (So) 2alcl +3baso 2Na+2H O 2Naoh+H: Questionsakky81Оценок пока нет
- Types of Chemical ReactionsДокумент31 страницаTypes of Chemical ReactionsJoshua ManalacОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Unit 2Документ13 страницOrganic Chemistry Unit 2ABDULLAH SHAHZADОценок пока нет
- F332 Notes (Elements From The Sea)Документ11 страницF332 Notes (Elements From The Sea)Becky Tenney100% (1)
- Aldehydes, Ketones TheoryДокумент28 страницAldehydes, Ketones Theoryshilpa sakhareОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОценок пока нет