Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
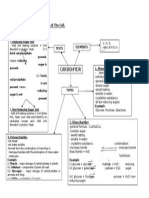
Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind Map
Загружено:
huileng_wongАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind Map
Загружено:
huileng_wongАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
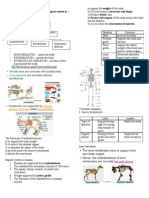
Chapter 4: Chemical Composition of The Cell.
1. Reducing Sugar Test - Add 2ml testing solution + 2ml Benedicts solution. Heat. (i) if brick red precipitate present, means reducing sugar is present. red precipitate present, means sugar is not . (ii) if brick is not reducing present
TESTS
ELEMENTS
- C, H, O. - ratio of H:O is 2:1
CARBOHYDR
TYPES
1. Non-Reducing Sugar Test - Add 2ml testing solution + 1ml dilute HCL. Heat. Cool. Add solid NaHCO to neutralize excess acid. Add 2ml Benedicts solution. Heat.
1. Monosaccharides - basic building blocks of carbohydrate. -general formula : C6H12O6 -simple sugar. -sweet tasting. -soluble in water. -crystalline substance. -all are reducing sugars. Example -Glucose, Fructose, Galactose.
3. Polysaccharides -not sweet -not water soluble. -formed from the combination of more than 2 monosaccharides with the elimination of more water molecules. Example (i) Starch - major storage of carbohydrates in plants. (ii) Cellulose component of plant cell wall. (iii) Glycogen - major storage of carbohydrates in animals and fungi. (iv) Chitin exoskeleton of insects.
2. Disaccharides -general formula : C12H22O11 -complex sugar. - sweet tasting. - soluble in water. - crystalline substance. -monosaccharide + disaccharide + H2O Example (i) glucose + glucose (ii) glucose + galactose (iii) glucose + fructose reducing sugar)
condensation monosaccharide hydrolysis
maltose + H2O Lactose + H2O
reducing sugar
sucrose + H2O (non-
Вам также может понравиться
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4-ProteinДокумент1 страницаBiology Form 4 Chapter 4-ProteinFarain Rashdi75% (4)
- Science Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkaliДокумент38 страницScience Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkalinurafziОценок пока нет
- Sains Form1 Final ExamДокумент10 страницSains Form1 Final ExamNOR SUAKMA BT JAAFARОценок пока нет
- WORKSHEET 11.1 Locomotion and Support in Humans and AnimalsДокумент6 страницWORKSHEET 11.1 Locomotion and Support in Humans and Animalsmiedsassin67% (3)
- Science concepts explainedДокумент8 страницScience concepts explainedCheng NieОценок пока нет
- Science Chapter 2 Form 1Документ23 страницыScience Chapter 2 Form 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Biology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2Документ13 страницBiology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2SanjeefKumrIIОценок пока нет
- Form 1 Science Pendulum ExperimentДокумент2 страницыForm 1 Science Pendulum ExperimentAngie Kong Su Mei0% (1)
- Biology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseДокумент3 страницыBiology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseAlan WangОценок пока нет
- Measure Science with PrecisionДокумент45 страницMeasure Science with PrecisionNurasyikin SaidinОценок пока нет
- Experiment f4 CellДокумент3 страницыExperiment f4 CellAmsyidi AsmidaОценок пока нет
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Документ14 страницTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanОценок пока нет
- RPT Chem Form 4 2020 (DLP)Документ25 страницRPT Chem Form 4 2020 (DLP)WONG KEE PING MoeОценок пока нет
- Cigarette Smoke ExperimentДокумент3 страницыCigarette Smoke ExperimentSarina ShariffОценок пока нет
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Документ4 страницыScience Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Autumn JJ40% (5)
- Malaysia Form 4 Physics Chapter 2Документ1 страницаMalaysia Form 4 Physics Chapter 2lakyn_267% (3)
- Form 4 SPM Biology Chapter 5Документ5 страницForm 4 SPM Biology Chapter 5Janice NgОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Документ5 страницChemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Azsyerrah Jahini67% (3)
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideДокумент39 страницChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideMuhd Rifaie RodzilОценок пока нет
- SC F2 CH1Документ59 страницSC F2 CH1amalina rohaizan50% (2)
- FORM 2 - The Sensory Organs and How We Perceive the WorldДокумент16 страницFORM 2 - The Sensory Organs and How We Perceive the WorldMyName Tiff94% (16)
- Science Form 2Документ4 страницыScience Form 2lembu_sihat77100% (1)
- Teknik Jawab Soalan Bio SPMДокумент5 страницTeknik Jawab Soalan Bio SPMpin21880% (1)
- Matter States and PropertiesДокумент33 страницыMatter States and PropertiesyokekeannОценок пока нет
- STF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section AДокумент8 страницSTF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section AzuaihaОценок пока нет
- SPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Документ4 страницыSPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Felicia LingОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 QuestionДокумент9 страницChapter 3 QuestionShila KaurОценок пока нет
- Reaction of Alkali Metals With Water and OxygenДокумент6 страницReaction of Alkali Metals With Water and Oxygenみゆ マイクロ100% (1)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Документ24 страницыForm 2 Science Chapter 5EeJun LeeОценок пока нет
- Practical 2 Food TestДокумент6 страницPractical 2 Food Testrickyip87100% (1)
- Modul Sains SPM Section CДокумент25 страницModul Sains SPM Section CJaaizah JaafarОценок пока нет
- Science Notes Form 3Документ20 страницScience Notes Form 3Jasmine Kaur KaurОценок пока нет
- Form 1 Science Chapter 5 Part 1Документ21 страницаForm 1 Science Chapter 5 Part 1qq235100% (1)
- Gas Law Problems and SolutionsДокумент4 страницыGas Law Problems and SolutionsAngie Kong Su MeiОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 1 Chemistry F4 Chapter3 Chemical Equation AnswerДокумент2 страницыWorksheet 1 Chemistry F4 Chapter3 Chemical Equation AnswerIpul Catur0% (1)
- Biology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 11Документ7 страницBiology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 11Nik HusnaОценок пока нет
- F2 Chap 3 MCQДокумент5 страницF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell DivisionДокумент7 страницBiology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell Divisionizuaf817Оценок пока нет
- Compilation of Experiments Form 4Документ13 страницCompilation of Experiments Form 4Marzila MohamedОценок пока нет
- PendulumДокумент17 страницPendulumBaoz PingОценок пока нет
- Cell Chemical Composition Chapter 4Документ1 страницаCell Chemical Composition Chapter 4Navindran ChandranОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapДокумент1 страницаChapter 4 Carbohydrate Mind MapNg YieviaОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент7 страницCarbohydratesDanluidQMalintadОценок пока нет
- Biology Paper 3 Guide (As-Level)Документ17 страницBiology Paper 3 Guide (As-Level)XEDGER0986% (7)
- Quantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates I - Lab 4Документ27 страницQuantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates I - Lab 4Noriko Medoruma0% (3)
- Carbohydrates Classification and TestsДокумент11 страницCarbohydrates Classification and TestsSHОценок пока нет
- Biochemical TestsДокумент2 страницыBiochemical TestsJacqueline DavisОценок пока нет
- General Properties of CarbohydratesДокумент3 страницыGeneral Properties of CarbohydratesShine GatilloОценок пока нет
- Detect Non-Reducing Sugars with Benedict's TestДокумент2 страницыDetect Non-Reducing Sugars with Benedict's TestSamer Ehab75% (4)
- Lab 8Документ9 страницLab 8Norjetalexis CabreraОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4Документ3 страницыExperiment 4atiqahОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates Pptxlec2Документ13 страницCarbohydrates Pptxlec2احمد احمدОценок пока нет
- 23 Tests For CarbohydratesДокумент9 страниц23 Tests For CarbohydratespollyОценок пока нет
- Molisch Test and Benedict TestДокумент6 страницMolisch Test and Benedict Testعلاوي البرشلونيОценок пока нет
- Tests For CarbohydratesДокумент9 страницTests For CarbohydratesPanasheMuduzu100% (1)
- Detecting Reducing and Non-Reducing SugarsДокумент6 страницDetecting Reducing and Non-Reducing SugarsShayden LeslieОценок пока нет
- CHARBOHYDRATEДокумент33 страницыCHARBOHYDRATENada hasan100% (1)
- Benedict's Test For Reducing SugarДокумент2 страницыBenedict's Test For Reducing SugarMohammed Parfals100% (2)
- Carbohydrates LabДокумент6 страницCarbohydrates LabMycaela Archivido De AlvaОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Tests Benedict's Reagent Iodine SolutionДокумент3 страницыCarbohydrate Tests Benedict's Reagent Iodine SolutionTomNaccaratoОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell DivisionДокумент7 страницBiology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell Divisiongelgaban67% (3)
- Chapter 6Документ12 страницChapter 6huileng_wongОценок пока нет
- Form 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент7 страницForm 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membranehuileng_wongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ12 страницChapter 6huileng_wongОценок пока нет
- Form 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент7 страницForm 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membranehuileng_wongОценок пока нет
- Form 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneДокумент7 страницForm 4-Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membranehuileng_wongОценок пока нет
- Respiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Документ14 страницRespiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Aisyahumaira_hidayahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Biology Form 4 NotesДокумент2 страницыChapter 3 Biology Form 4 Noteshuileng_wongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Biology Form 4 NotesДокумент2 страницыChapter 3 Biology Form 4 Noteshuileng_wongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Biology Form 4 NotesДокумент2 страницыChapter 3 Biology Form 4 Noteshuileng_wongОценок пока нет
- DTMF Relay and Interworking On CUBE PDFДокумент18 страницDTMF Relay and Interworking On CUBE PDFEngin KartalОценок пока нет
- Albemarle Family YMCA Pool ScheduleДокумент2 страницыAlbemarle Family YMCA Pool ScheduleYMCA of South Hampton RoadsОценок пока нет
- Burnelli AircraftДокумент51 страницаBurnelli Aircraftretread1100% (3)
- 2022 Consumer Trends ReportДокумент29 страниц2022 Consumer Trends Reportadelin litan100% (1)
- Ruibal & Shoemaker 1984 - Osteoders in AnuransДокумент17 страницRuibal & Shoemaker 1984 - Osteoders in AnuransRuivo LucasОценок пока нет
- 4880 AnsiДокумент0 страниц4880 AnsiabualamalОценок пока нет
- Final MTech ProjectДокумент30 страницFinal MTech ProjectArunSharmaОценок пока нет
- Bringing Class to Mass: L'Oreal's Plénitude Line Struggles in the USДокумент36 страницBringing Class to Mass: L'Oreal's Plénitude Line Struggles in the USLeejat Kumar PradhanОценок пока нет
- Shyness and Social AnxietyДокумент22 страницыShyness and Social Anxietybeleanadrian-1Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To AIX Mirror Pools 201009Документ11 страницIntroduction To AIX Mirror Pools 201009Marcus BennettОценок пока нет
- American Cows in Antarctica R. ByrdДокумент28 страницAmerican Cows in Antarctica R. ByrdBlaze CОценок пока нет
- Early Daoist Dietary Practices: Examining Ways To Health and Longevity. by Shawn ArthurДокумент6 страницEarly Daoist Dietary Practices: Examining Ways To Health and Longevity. by Shawn ArthurlsdkОценок пока нет
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesДокумент51 страницаDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesChrystal Khey MendozaОценок пока нет
- Aci 306.1Документ5 страницAci 306.1safak kahramanОценок пока нет
- Why We Can't Stop Obsessing Over CelebritiesДокумент2 страницыWhy We Can't Stop Obsessing Over CelebritiesJoseMa AralОценок пока нет
- Purposive Communication: Republic of The Philippines Province of Ilocos Sur Ilocos Sur Community College Vigan CityДокумент7 страницPurposive Communication: Republic of The Philippines Province of Ilocos Sur Ilocos Sur Community College Vigan CityLes GasparОценок пока нет
- Learning and Teaching in The Clinical EnvironmentДокумент4 страницыLearning and Teaching in The Clinical EnvironmentDaniel Alejandro Lozano MorenoОценок пока нет
- New Life in Christ by Wilson HerreraДокумент18 страницNew Life in Christ by Wilson Herreralesantiago100% (1)
- Cot 1 Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Документ3 страницыCot 1 Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Arlen FuentebellaОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive Cooling Technologies For Thermal Management of AvionicsДокумент10 страницActive and Passive Cooling Technologies For Thermal Management of AvionicsdavidОценок пока нет
- Research Day AbstractsДокумент287 страницResearch Day AbstractsStoriesofsuperheroesОценок пока нет
- Levitator Ino - InoДокумент2 страницыLevitator Ino - InoSUBHANKAR BAGОценок пока нет
- Fuji Synapse PACS Quick GuideДокумент1 страницаFuji Synapse PACS Quick GuideM MОценок пока нет
- Kenya Dieticians License ApplicationДокумент5 страницKenya Dieticians License ApplicationGrace NdutaОценок пока нет
- Earth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsДокумент4 страницыEarth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsJj BarakaОценок пока нет
- 2019-Kubelka-Munk Double Constant Theory of Digital Rotor Spun Color Blended YarnДокумент6 страниц2019-Kubelka-Munk Double Constant Theory of Digital Rotor Spun Color Blended YarnyuОценок пока нет
- Abcd AirtelДокумент12 страницAbcd AirtelPrakhar RatheeОценок пока нет
- FS 3 Technology in The Learning EnvironmentДокумент24 страницыFS 3 Technology in The Learning EnvironmentJayson Gelera CabrigasОценок пока нет
- Frame Fit Specifications 2019 MTB Components Rev CДокумент167 страницFrame Fit Specifications 2019 MTB Components Rev Cpicko 86Оценок пока нет
- Contineous Assessment 2 Group BДокумент11 страницContineous Assessment 2 Group BMasnoon MidhatОценок пока нет