Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Glucocorticoids
Загружено:
BigBoostingАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Glucocorticoids
Загружено:
BigBoostingАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
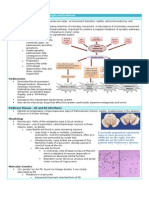
DRUG STUDY AND INFORMATION FORM Generic Name: Glucocorticoids Trade Name: Prednisone, Dexamethasone Drug Class: Glucocorticoids
Structure/Chemistry: Prednisone Dexamethasone
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of Action: Glucocorticoids act through their binding to a specific physiological receptor that translocates to the nucleus and induces anti-proliferative and apoptotic responses in sensitive cells.
Pharmacologic Effects: Cytotoxic agents due to their lympholytic effects and their ability to suppress mitosis in lymphocytes
Drug Resistance or Tolerance: Remissions occur more frequently than with anti-metabolites (therefore, glucocorticoids are usually coupled with anti-metabolites often followed by an anthracycline or methotrexate and L-asparaginase). Acute changes in dexamethasone dosage can lead to a rapid recrudescence of symptoms.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Prednisone is given orally in doses as high as 60-100 mg or even higher for the first few days but gradually reduced to around 20-40 mg/day. Dexamethasone is given orally Distribution:
Elimination: Dexamethasone t1/2 of 36-54 hours. Prednisone t1/2 of 1 hour.
Metabolism:
Adverse Side Effects/Toxicity: Drug Interactions: Used in combination with radiotherapy to prevent edema in critical areas (brain)
Therapeutic uses: Acute leukemia in children and malignant lymphoma in children and adults. A valuable component for curative regimens of other malignancies (Hodgkins disease, nonHodgkins lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia). Helpful in controlling auto-immune hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia associated with CLL. Provides temporary restoration of neurological function from cerebral metastases (do not discontinue dexamethasone in patients with brain metastases). Dexamethasone is preferred for multiple myeloma remission, in combination with melphalan, anthracyclines, vincristine, bortezomib, or thalidomide. Miscellaneous:
Вам также может понравиться
- Obgyn Abbreviations For RotationДокумент2 страницыObgyn Abbreviations For RotationBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- The Mental Status ExaminationДокумент16 страницThe Mental Status Examinationeloisa.abcedeОценок пока нет
- GI NotesДокумент19 страницGI NotesBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerДокумент14 страницPsychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Bone Cancer Chart 2012Документ8 страницBone Cancer Chart 2012BigBoostingОценок пока нет
- GI High YieldДокумент1 страницаGI High YieldBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Lectura 1 PDFДокумент73 страницыLectura 1 PDFgroudon_18Оценок пока нет
- The Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDДокумент4 страницыThe Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Neurologic Presentations of HIV/AIDSДокумент23 страницыNeurologic Presentations of HIV/AIDSBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Psychosomatic MedicineДокумент14 страницPsychosomatic MedicineGiuseppe RutiglianiОценок пока нет
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionДокумент9 страницGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionДокумент9 страницGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Neoplasias TableДокумент3 страницыNeoplasias TableBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Cross Sections of Upper LimbДокумент12 страницCross Sections of Upper LimbBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Triangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryДокумент6 страницTriangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- ProcarbazineДокумент2 страницыProcarbazineBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- NervesДокумент139 страницNervesBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Blue Boxes For MusculoskeletalДокумент16 страницBlue Boxes For MusculoskeletalBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- ThalidomideДокумент2 страницыThalidomideBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Neuro Phase Notes MS-1Документ43 страницыNeuro Phase Notes MS-1BigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Cranial Nerve TractsДокумент2 страницыCranial Nerve TractsBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- Muscles NervesДокумент3 страницыMuscles NervesBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- CNS PharmДокумент16 страницCNS PharmBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- RituximabДокумент2 страницыRituximabBigBoosting100% (2)
- TretinoinДокумент2 страницыTretinoinBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- OfatumumabДокумент2 страницыOfatumumabBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- VincristineДокумент2 страницыVincristineBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- NilotinibДокумент2 страницыNilotinibBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- S Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationДокумент2 страницыS Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- MercaptopurineДокумент2 страницыMercaptopurineBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)