Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
How To Make Series and Parallel Connections of An SCR
Загружено:
Rana Israr AhmadИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
How To Make Series and Parallel Connections of An SCR
Загружено:
Rana Israr AhmadАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Abstract: Thyristors are connected in series for high voltage applications.
Their On and Off
state characteristics are differ due to turn on time , turn off time and leakage currents in forward and reverse directions. This deviation results in many problems. For series connection resistance R is used to limit the capacitor discharge current and RC circuit is also used as a Snubber circuit.
How to make series connections of an SCR ?
In many power control applications the required voltage and current ratings exceed the voltage and current that can be provided by a single SCR. Under such situations the SCRs are required to be connected in series or in parallel to meet the requirements. Sometimes even if the required rating is available, multiple connections are employed for reasons of economy and easy availability of SCRs of lower ratings. Like any other electrical equipment, characteristics/properties of two SCRs of same make and ratings are never same and this leads to certain problems in the circuit.
Series Connection of an SCR
SCR Series Connection
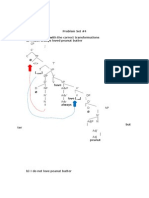
When the required voltage rating exceeds the SCR voltage rating, a number of SCRs are required to be connected in series to share the forward and reverse voltage. As it is not possible to have SCRs of completely identical characteristics, deviation in characteristics lead to the following two major problems during series connections of the SCRs: (i) Unequal distribution of voltage across SCRs. (ii) Difference in recovery characteristics. Care must be taken to share the voltage equally. For steady-state conditions, voltage sharing is achieved by using a resistance or a Zener diode in parallel with each SCR. For transient voltage sharing a low non-inductive resistor and capacitor in series are placed across each SCR, as shown in figure. Diodes D1 connected in parallel with resistor Rl, helps in dynamic stabilisation. This circuit reduces differences between blocking voltages of the two devices within permissible limits. Additionally the R-C circuit can also serve the function ofsnubber circuit. Values of R1 and C1 can primarily be calculated for snubber circuit and a check can be made for equalization. If Q is the difference in recovery charge of two devices arising out of different recovery current for different time and V is the permissible difference in blocking voltage then C1 = Q/ V. The value of resistance Rx should be sufficient to over damp the circuit. Since the capacitor C1 can discharge through the SCR during turn-on, there can be excessive power dissipation, but the switching current from C1 is limited by the resistor R1 This resistance also serves the purpose of damping out ringing which is oscillation of C1 with the circuit inductance during commutation. All the SCRs connected in series should be turnedon at the same time when signals are applied to their gates simultaneously.
ID2 = ID3 = IDn and ID1 < ID2 ID2 = ID3 = IDn The off-state current spread is given by DID where DID = ID2 - ID1 DID = (IT - I2) - (IT - I1)
DID = I1 - I2 therefore I2 = I1 - DID The voltage drop across thyristor T1 is given by VD1 where, VD1 = RI1 Vs = VD1 + (ns - 1)I2R = VD1 + (ns - 1)(I1 - DID)R Vs = VD1 + (ns - 1)I1R - (ns - 1)DIDR Vs = nsVD1 - (ns - 1)DIDR Solving the above equation for VD1 the voltage across thyristor T1 yields
Obj100
ID1 = 0 and DID = ID2 The voltage across thyristor T1 is now given as VDS(max), where
Obj101
The voltage difference between thyristors T1 and the other thyristors is given by
Obj102
where Q1 is the charge stored by thyristor T1 and Q2 is the charge stored by the other thyristors such that Q2 = Q3 = Qn and Q1 < Q2
The transient voltage across thyristor T1 is given by
Obj103
The worse case transient voltage occurs when Q1 = 0, hence DQ = Q2 and is given by
Obj104
The transient voltage derating factor which is normally used to increase the reliability of the string is given by
Obj105
Вам также может понравиться
- Syntax Ps4Документ6 страницSyntax Ps4blue_child86% (7)
- Crowd Management - Model Course128Документ117 страницCrowd Management - Model Course128alonso_r100% (4)
- Substation Training ModuleДокумент94 страницыSubstation Training ModuleKarthick Rathinasamy100% (8)
- Unit-I 2Документ22 страницыUnit-I 2Federico AldoОценок пока нет
- Series and Parallel Connection of SCRДокумент21 страницаSeries and Parallel Connection of SCRDeepika BairagiОценок пока нет
- Power Control.: SCR Can Be Turned-On Phase ControlДокумент6 страницPower Control.: SCR Can Be Turned-On Phase ControlEric BiscochoОценок пока нет
- Basic Power Electronics Notes 2.1 To 2.3 PDFДокумент8 страницBasic Power Electronics Notes 2.1 To 2.3 PDFEscape From EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Power DiodesДокумент5 страницPower DiodesJahan ZaibОценок пока нет
- Special Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of TechnologyДокумент35 страницSpecial Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of Technologyjay mehtaОценок пока нет
- SCR Power Control CircuitДокумент8 страницSCR Power Control CircuitRyan Joseph BalmacedaОценок пока нет
- Ree601 PDFДокумент9 страницRee601 PDFJ JulietОценок пока нет
- Activity 3 in Industrial ElectronicsДокумент15 страницActivity 3 in Industrial ElectronicsFrancis Valdez Lopez100% (1)
- Series and Parallel Operation of SCRДокумент6 страницSeries and Parallel Operation of SCRNaod FОценок пока нет
- Diac Triac and Quadrac For AC Power ControlДокумент5 страницDiac Triac and Quadrac For AC Power Controlmarcoms75Оценок пока нет
- Power ElectronicsДокумент201 страницаPower Electronicsdream breakerОценок пока нет
- TURN OFF SCR & Protection CKTДокумент13 страницTURN OFF SCR & Protection CKTkavitabhatuОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics: THYRISTOR ProtectionДокумент12 страницPower Electronics: THYRISTOR ProtectionK Lokesh LingaiahОценок пока нет
- RMAE Notes DIAC TRIACДокумент9 страницRMAE Notes DIAC TRIACPriyanka BhateleОценок пока нет
- Pe PPT PDFДокумент268 страницPe PPT PDFtushar agale100% (1)
- Nota Unit 6Документ19 страницNota Unit 6F1036Оценок пока нет
- PE - Mini Project ReportДокумент6 страницPE - Mini Project Reportchemistryraja123Оценок пока нет
- SCR Triggering MethodsДокумент17 страницSCR Triggering MethodssriОценок пока нет
- Dmx5313-Power Electronics and Motor Drives - DS01 - 28.05.2022Документ32 страницыDmx5313-Power Electronics and Motor Drives - DS01 - 28.05.2022Tommba TommyОценок пока нет
- Ser-Par Opr of SCRsДокумент15 страницSer-Par Opr of SCRsashish_rewaОценок пока нет
- Diode and Its ApplicationsДокумент39 страницDiode and Its ApplicationsUsama SidhuОценок пока нет
- EEN-324 Power ElectronicsДокумент53 страницыEEN-324 Power ElectronicsRameshBabuОценок пока нет
- Module 1 NotesДокумент30 страницModule 1 NotesSoxamОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2 PEДокумент13 страницAssignment 2 PEHemkeshОценок пока нет
- Snubber Circuit Design AnalysisДокумент27 страницSnubber Circuit Design Analysisetmatsuda100% (1)
- SCRДокумент53 страницыSCRBharatОценок пока нет
- SCR ProtectionДокумент23 страницыSCR ProtectiontinashechiveroОценок пока нет
- Assessment Checklist WritingДокумент8 страницAssessment Checklist WritingKevin Duvan RoblesОценок пока нет
- Pe FINALДокумент131 страницаPe FINALAnonymous R4WpNxОценок пока нет
- SCR, Traic, Diac ReportДокумент19 страницSCR, Traic, Diac ReportPravin Gareta60% (5)
- Triac Lamp Dimmer Circuit.: DiacsДокумент7 страницTriac Lamp Dimmer Circuit.: DiacsBaquiran John Paul BaquiranОценок пока нет
- Experiment #10-Using SCRS: Hands-On RadioДокумент2 страницыExperiment #10-Using SCRS: Hands-On RadioAnonymous ptCa270Uy2Оценок пока нет
- HV Resonance CollectionДокумент4 страницыHV Resonance CollectionfreiwildОценок пока нет
- Comparison Between FLC and MMC IECON2009 1 PDFДокумент6 страницComparison Between FLC and MMC IECON2009 1 PDFAamir YousufОценок пока нет
- ODD II YR 2 MarksДокумент99 страницODD II YR 2 MarksjesudosssОценок пока нет
- Best of Design Ideas - Volume 2Документ18 страницBest of Design Ideas - Volume 2ableseaman100% (3)
- Power DiodesДокумент20 страницPower DiodesMuhamad Arif AminОценок пока нет
- LicprojectrДокумент5 страницLicprojectrTanmay PatilОценок пока нет
- Series Operation of ThyristorsДокумент12 страницSeries Operation of ThyristorsAastha MandaliaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics 2010-2011Документ68 страницPower Electronics 2010-2011Adnan Younus100% (1)
- Unit - I Power Semi Conductor Devices Syllabus: Semiconductor Power Diodes, Thyristors - Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCR'S) - Triacs, GtosДокумент33 страницыUnit - I Power Semi Conductor Devices Syllabus: Semiconductor Power Diodes, Thyristors - Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCR'S) - Triacs, GtosRAJOLI GIRISAI MADHAVОценок пока нет
- Recombination Time in DiodesДокумент4 страницыRecombination Time in Diodesluis palominoОценок пока нет
- DC To Ac Converter by Using 555 Timer ICДокумент6 страницDC To Ac Converter by Using 555 Timer ICAlfred Adukobirre AdukobillaОценок пока нет
- Gate Firing Circuits For SCR'S R-C Triggering CircuitДокумент3 страницыGate Firing Circuits For SCR'S R-C Triggering CircuitB ANIL KUMARОценок пока нет
- Wi-Fi Home AutomationДокумент23 страницыWi-Fi Home Automationchandru_8Оценок пока нет
- SCR DC Motor Forward/Reverse Control: Experiment #6Документ6 страницSCR DC Motor Forward/Reverse Control: Experiment #6Zeeshan RafiqОценок пока нет
- Automatic Night Light Circuit Using SCR: Semester ProjectДокумент10 страницAutomatic Night Light Circuit Using SCR: Semester ProjectNasheed AhmedОценок пока нет
- Unit 2Документ22 страницыUnit 2SUSHMAGUPTAОценок пока нет
- IECD Capsule NotesДокумент59 страницIECD Capsule NotesANANTHU PRADEEPОценок пока нет
- Over-Under Voltage Cut-Off With On-Time Delay PROJECT REPORTДокумент35 страницOver-Under Voltage Cut-Off With On-Time Delay PROJECT REPORTSumit Agarwal75% (4)
- Exp. No. - 3 Step Response of RLC CircuitДокумент9 страницExp. No. - 3 Step Response of RLC CircuitEsh-war RajОценок пока нет
- CH 5 - AC-AC ConvertersДокумент22 страницыCH 5 - AC-AC ConvertersGebremichael Teklay GebretsadikОценок пока нет
- Pee Lab ManualДокумент77 страницPee Lab ManualRajendraTuraka100% (1)
- The Diac: SCR's TriacsДокумент4 страницыThe Diac: SCR's TriacsZaheer Ahmed100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- AWANA Handbook 2010-2011Документ8 страницAWANA Handbook 2010-2011carriepratchard100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 23-Feb-2024Документ4 страницыAdobe Scan 23-Feb-2024muzwalimub4104Оценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023Документ45 страницFundamentals of Logistics XI - 2023saiyaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ26 страницChapter 3Francis Anthony CataniagОценок пока нет
- Operating Instructions: Vacuum Drying Oven Pump ModuleДокумент56 страницOperating Instructions: Vacuum Drying Oven Pump ModuleSarah NeoSkyrerОценок пока нет
- Rastriya Swayamsewak SanghДокумент60 страницRastriya Swayamsewak SanghRangam Trivedi100% (3)
- BRB Personal Care Cost Effictive Guide Formulation Edition 2019Документ28 страницBRB Personal Care Cost Effictive Guide Formulation Edition 2019Abdulrahman HamdanОценок пока нет
- Instant Download The Practice of Creative Writings 3rd Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEДокумент32 страницыInstant Download The Practice of Creative Writings 3rd Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEbarbara.ward425100% (46)
- Have Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Документ25 страницHave Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Aditya ThakurОценок пока нет
- Library SectionsДокумент4 страницыLibrary SectionsGello Sotnuiq100% (4)
- Maxdb Backup RecoveryДокумент44 страницыMaxdb Backup Recoveryft1ft1Оценок пока нет
- Boomer L2 D - 9851 2586 01Документ4 страницыBoomer L2 D - 9851 2586 01Pablo Luis Pérez PostigoОценок пока нет
- JIS-G3455 - Carbon Steel Pipes For High Pressure ServiceДокумент27 страницJIS-G3455 - Carbon Steel Pipes For High Pressure ServiceHoang Tan100% (1)
- UBO - Lecture 07 - Implementing and Managing Organisational ChangeДокумент0 страницUBO - Lecture 07 - Implementing and Managing Organisational ChangeShahNooraniITОценок пока нет
- PriceDoxy 09 September 2011Документ56 страницPriceDoxy 09 September 2011Elena OltuОценок пока нет
- EL2 - Raise Organic Small RuminantsДокумент62 страницыEL2 - Raise Organic Small RuminantsButch Demayo100% (1)
- File Server Resource ManagerДокумент9 страницFile Server Resource ManagerBùi Đình NhuОценок пока нет
- Bilge Günsel TEL531E Detection and Estimation Theory W #1-2Документ25 страницBilge Günsel TEL531E Detection and Estimation Theory W #1-2ahmetОценок пока нет
- Memo For Completed RubricДокумент3 страницыMemo For Completed Rubricnisev2003Оценок пока нет
- Part-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanДокумент4 страницыPart-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanTechi Son taraОценок пока нет
- 3250-008 Foundations of Data Science Course Outline - Spring 2018Документ6 страниц3250-008 Foundations of Data Science Course Outline - Spring 2018vaneetОценок пока нет
- TCC Number 153-4-4Документ1 страницаTCC Number 153-4-4jeremie gamonОценок пока нет
- Design and Fabrication of Light Electric VehicleДокумент14 страницDesign and Fabrication of Light Electric VehicleAshish NegiОценок пока нет
- AADE Review of Lost Circulation Materials and Treatments With An Updated ClassificationДокумент9 страницAADE Review of Lost Circulation Materials and Treatments With An Updated ClassificationMuhamad IrfanОценок пока нет
- Unit 9 TelephoningДокумент14 страницUnit 9 TelephoningDaniela DanilovОценок пока нет
- CSMP77: en Es FRДокумент38 страницCSMP77: en Es FRGerson FelipeОценок пока нет
- HimediaДокумент2 страницыHimediaWiwit MarianaОценок пока нет
- 5G, 4G, Vonr Crash Course Complete Log AnaylsisДокумент11 страниц5G, 4G, Vonr Crash Course Complete Log AnaylsisJavier GonzalesОценок пока нет