Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
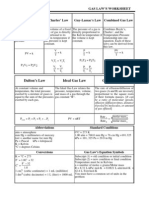
Dalton's Law Worksheet
Загружено:
Irni BeyИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dalton's Law Worksheet
Загружено:
Irni BeyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chemistry: Daltons Law of Partial Pressure Directions: Solve each of the following problems.
Show your work, including proper units. 1. Container A (with volume 1.23 dm3) contains a gas under 3.24 atm of pressure. Container B (with volume 0.93 dm3) contains a gas under 2.82 atm of pressure. Container C (with volume 1.42 dm3) contains a gas under 1.21 atm of pressure. If all of these gases are put into Container D (with volume 1.51 dm3), what is the pressure in Container D?
2. Container A (with volume 1.56 L) contains a gas under 185.3 kPa of pressure. Container B has 1/3 the volume of Container A, but its gas is under twice the pressure as that of Container A. If the gases from A and B are combined into Container C (with volume 0.95 L), what is the pressure in Container C?
3. Container A (with volume 150 mL) contains a gas under an unknown pressure. Container B (with volume 250 mL) contains a gas under 628 mm Hg of pressure. Container C (with volume 350 mL) contains a gas under 437 mm Hg of pressure. If all of these gases are put into Container D (with volume 300 mL),giving it 1439 mm Hg of pressure, find the original pressure of the gas in Container A.
4. The gases of three identical containers A, B, and C are under pressures of 1.44 atm, 3.16 atm, and 2.52 atm, respectively. These gases are then combined into Container D (with a volume of 3.92 L) so that the pressure in Container D is 4.38 atm. Containers A, B, and C have the same volume. Find that volume.
Answers: 1. 5.51 atm 2. 507.1 kPa 3. 812 mm Hg 4. 2.41 L
Вам также может понравиться
- Scioly Green Generation NotesДокумент2 страницыScioly Green Generation NotesApril Lovely100% (1)
- Https - Scholar - Vt.edu - Access - Content - Group - Practice Tests - Coming Soon - Practice Test 4 PDFДокумент12 страницHttps - Scholar - Vt.edu - Access - Content - Group - Practice Tests - Coming Soon - Practice Test 4 PDFEmmett GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Chemistry-Gas Laws Multiple ChoiceДокумент5 страницChemistry-Gas Laws Multiple ChoiceGeorge Isaac McQuilesОценок пока нет
- GLWS9Документ6 страницGLWS9Vince HernándezОценок пока нет
- 13 Partial Pressures of GasesДокумент6 страниц13 Partial Pressures of GasesTanisha Marie100% (1)
- Rock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsДокумент4 страницыRock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsBhawana SinghОценок пока нет
- Unit Weight of AggregatesДокумент5 страницUnit Weight of AggregatesMayolites33% (3)
- Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure: ChemistryДокумент3 страницыDalton's Law of Partial Pressure: ChemistryJhudy PhotОценок пока нет
- All Gas LawДокумент5 страницAll Gas LawdasaОценок пока нет
- Taller de GasesДокумент20 страницTaller de GasesAle Cruz DОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Practice ProblemsДокумент16 страницCH 5 Practice Problemsjaskaran singhОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Документ4 страницыGas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Leighton RowlandОценок пока нет
- Test Ch. 12 (The Gas Laws) PracticeДокумент4 страницыTest Ch. 12 (The Gas Laws) Practiceliza1207Оценок пока нет
- Test Gas LawsДокумент5 страницTest Gas LawsCenando BodanioОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 5.2-5.5Документ4 страницыChemistry 5.2-5.5Arthur AguijonОценок пока нет
- 2 Part Gas Law Practice!!Документ28 страниц2 Part Gas Law Practice!!ahix123Оценок пока нет
- Gas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Документ3 страницыGas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Nikhil Singh100% (1)
- Assignment Gaseous State JH Sir-2621Документ38 страницAssignment Gaseous State JH Sir-2621Noob Iplay100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Gases Homework1Документ3 страницыChapter 5 Gases Homework1Mary JewelОценок пока нет
- Sheet-1-Gaseous StateДокумент3 страницыSheet-1-Gaseous StateHarshit SinghОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - GasesДокумент22 страницыChapter 5 - GasesTony Ansah100% (1)
- Practice Questions For Ch. 5: Name: - Class: - Date: - Id: AДокумент23 страницыPractice Questions For Ch. 5: Name: - Class: - Date: - Id: APrem MehrotraОценок пока нет
- Gases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryДокумент20 страницGases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryAshley Marie ChildersОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Homework 2Документ4 страницыChapter 5 Homework 2Mary JewelОценок пока нет
- Chemistry (Practice Test) Name - Chapter 12 (The Gas Laws)Документ4 страницыChemistry (Practice Test) Name - Chapter 12 (The Gas Laws)Cenando BodanioОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Examples Example 1Документ2 страницыChapter 12 Examples Example 1Neil BrazaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 AssignmentДокумент6 страницUnit 1 Assignment7qyv7chzkcОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRTДокумент5 страницGas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRTJose Barrera GaleraОценок пока нет
- Tutorial - 4Документ1 страницаTutorial - 4useyourvoice125Оценок пока нет
- 18 Tugas Sifat Sifat Gas CH 1Документ19 страниц18 Tugas Sifat Sifat Gas CH 1Fadhillah AnsyariОценок пока нет
- Combined Gas Law:: T Cons T PVДокумент4 страницыCombined Gas Law:: T Cons T PVAsru RojamОценок пока нет
- 1694771313-FlattenedДокумент14 страниц1694771313-Flattenedaarushigusain25Оценок пока нет
- Chapter Test in Grade 10Документ8 страницChapter Test in Grade 10Maestro de Grapico100% (3)
- Gas Laws Review WS ANSWERSДокумент3 страницыGas Laws Review WS ANSWERSAlyssa ColeОценок пока нет
- Worksheet On General ChemistryДокумент2 страницыWorksheet On General ChemistryMay Conde AguilarОценок пока нет
- ANSWER KEY For More Gas Law Practice ProДокумент6 страницANSWER KEY For More Gas Law Practice ProyoyiyyiiyiyОценок пока нет
- POPДокумент16 страницPOPzaneОценок пока нет
- Gaseous State: Single Correct Option (+3,-1)Документ4 страницыGaseous State: Single Correct Option (+3,-1)Aakash GoelОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios de La Primera Ley de TermodinámicaДокумент12 страницEjercicios de La Primera Ley de TermodinámicaGissela BTОценок пока нет
- Unit Practice Test: Gas Laws: Multiple ChoiceДокумент8 страницUnit Practice Test: Gas Laws: Multiple Choiceanj pianoОценок пока нет
- Science Quest Reviewer Gas LawsДокумент5 страницScience Quest Reviewer Gas LawsEva esperaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ25 страницChapter 5roxy8marie8chanОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Gaseous StateДокумент6 страницChemistry Gaseous Stateraghavendra jОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ25 страницChapter 5batraz79Оценок пока нет
- States of Matter - GasДокумент81 страницаStates of Matter - GasRaymond Godfrey DagwasiОценок пока нет
- Gases Practice Quest 2013 AnswersДокумент5 страницGases Practice Quest 2013 Answersethanwong3412Оценок пока нет
- Key Homework 3 11th Gas LawДокумент5 страницKey Homework 3 11th Gas LawTai PanОценок пока нет
- Worksheet GasesДокумент6 страницWorksheet GasesakladffjaОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws AssignmentДокумент5 страницGas Laws AssignmentShweta SharmaОценок пока нет
- Ebook Chemistry 3Rd Edition Burdge Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент40 страницEbook Chemistry 3Rd Edition Burdge Test Bank Full Chapter PDFricinussquabash.46iz9100% (13)
- Gas LawsДокумент42 страницыGas LawsCharmy Delos Reyes AtabayОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 3rd Edition Burdge Test BankДокумент19 страницChemistry 3rd Edition Burdge Test Bankcleopatrasang611py100% (27)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Drdo KanchanbaghДокумент4 страницыKendriya Vidyalaya Drdo Kanchanbaghyash rajОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Xi (Chapter 2)Документ14 страницChemistry Xi (Chapter 2)MoonОценок пока нет
- Exercise GasesДокумент4 страницыExercise GasesAri AdiantariОценок пока нет
- 38 1 THE PROPERTIES OF GASES Discussion PDFДокумент3 страницы38 1 THE PROPERTIES OF GASES Discussion PDFZakirОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Gases III Answers 1Документ5 страницWorksheet Gases III Answers 1Emilio JacintoОценок пока нет
- Quiz1 2ndquarter GasesДокумент1 страницаQuiz1 2ndquarter GasesAlgem Cris CrusisОценок пока нет
- Activity 2.2Документ1 страницаActivity 2.2kc bpОценок пока нет
- Gases Sample Questions PDFДокумент25 страницGases Sample Questions PDFKhay Nochefranca100% (1)
- Problem Set 1 SolutionsДокумент5 страницProblem Set 1 SolutionsFeredun AzariОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- DLL Q4 G5 Sci Week 1Документ6 страницDLL Q4 G5 Sci Week 1Virgie Anne ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Other Relevant Laws Codes and Standards in The Energy and Power IndustryДокумент69 страницOther Relevant Laws Codes and Standards in The Energy and Power IndustryVanvan BitonОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic TestДокумент17 страницDiagnostic TestRynCalasagsagОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Physics IgcseДокумент9 страницNuclear Physics IgcseMuhammad asifОценок пока нет
- Rate of Reaction AssignmentДокумент7 страницRate of Reaction AssignmentJoaquin SolanoОценок пока нет
- DLP Science 6Документ6 страницDLP Science 6Tim Lopez IIОценок пока нет
- Ilovepdf MergedДокумент91 страницаIlovepdf MergedBaritugo, Raghnall Paul G.Оценок пока нет
- DSL TrainingДокумент96 страницDSL TrainingAnonymous 47Qe2KuuHyОценок пока нет
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics BasicsДокумент46 страницChemical Engineering Thermodynamics Basicsdppriya1984Оценок пока нет
- Aluminium Chemical PropertieДокумент9 страницAluminium Chemical PropertieShreenivas ThakurОценок пока нет
- Stratigraphy MCQs With AnswerДокумент10 страницStratigraphy MCQs With Answerkumar Harsh67% (3)
- Carnot Cycle For I.C Engine and Its LimitationsДокумент27 страницCarnot Cycle For I.C Engine and Its Limitationsmsshahenter0% (1)
- Summative Test No. 1 in Science 5 Fourth Quarter.Документ3 страницыSummative Test No. 1 in Science 5 Fourth Quarter.BALETEОценок пока нет
- Thesis - Maisarah Binti Zaharudin - KH17059Документ52 страницыThesis - Maisarah Binti Zaharudin - KH17059LogamalarОценок пока нет
- 2018 BookДокумент477 страниц2018 Bookbrahim chalhoub100% (2)
- 62BДокумент2 страницы62BJamie SchultzОценок пока нет
- Solid Waste management-IECДокумент54 страницыSolid Waste management-IECjohn frits gerard mombayОценок пока нет
- Bamboo Reinforced ConcreteДокумент14 страницBamboo Reinforced ConcreteharisankarОценок пока нет
- Physical Constants: N Z N ZДокумент56 страницPhysical Constants: N Z N ZVARSHITHОценок пока нет
- Wettability of ClaysДокумент6 страницWettability of ClaysMackarenna Paz Bla BlaОценок пока нет
- Safety Disaster Risk Management: CHAPTER 1: The Fundamentals of Disaster and Disaster Risk What Is Disaster?Документ4 страницыSafety Disaster Risk Management: CHAPTER 1: The Fundamentals of Disaster and Disaster Risk What Is Disaster?Andry LladocОценок пока нет
- Block 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityДокумент70 страницBlock 5: Atomic Physics: #Thenuclearatom #RadioactivityMac Justine JimenezОценок пока нет
- Introduction To ChemistryДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To ChemistryCharles MintahОценок пока нет
- Salient Features Karnali Chisapani SHEP 2 PagerДокумент2 страницыSalient Features Karnali Chisapani SHEP 2 PagerBidur Gautam100% (2)
- Lbe Diskusi 16 Tambahan FixДокумент4 страницыLbe Diskusi 16 Tambahan FixRayhan Al FaiqОценок пока нет
- The Environment Rephrasing KeyДокумент2 страницыThe Environment Rephrasing KeyPatricia CapaceОценок пока нет
- Answer Keys Aiits 2 - XiДокумент4 страницыAnswer Keys Aiits 2 - XiAnimesh PaliwalОценок пока нет