Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Why Do Grignard Reagents React With Carbonyl Compounds?
Загружено:
shehdilanun0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
32 просмотров2 страницыGrignard reagents react with carbonyl compounds because the carbon-magnesium bond in Grignard reagents is polar, giving the carbon atom a slight negative charge that allows it to act as a nucleophile. As a nucleophile, the negatively charged carbon attacks the positively charged carbon in carbonyl compounds. This reaction occurs because of the electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged carbon in the Grignard reagent and the positively charged carbon in the carbonyl compound.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
R-Mg-X
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документGrignard reagents react with carbonyl compounds because the carbon-magnesium bond in Grignard reagents is polar, giving the carbon atom a slight negative charge that allows it to act as a nucleophile. As a nucleophile, the negatively charged carbon attacks the positively charged carbon in carbonyl compounds. This reaction occurs because of the electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged carbon in the Grignard reagent and the positively charged carbon in the carbonyl compound.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
32 просмотров2 страницыWhy Do Grignard Reagents React With Carbonyl Compounds?
Загружено:
shehdilanunGrignard reagents react with carbonyl compounds because the carbon-magnesium bond in Grignard reagents is polar, giving the carbon atom a slight negative charge that allows it to act as a nucleophile. As a nucleophile, the negatively charged carbon attacks the positively charged carbon in carbonyl compounds. This reaction occurs because of the electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged carbon in the Grignard reagent and the positively charged carbon in the carbonyl compound.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
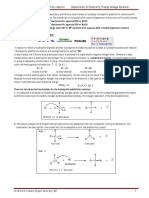
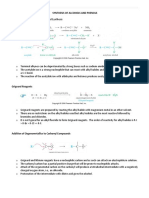
Why do Grignard reagents react with carbonyl
compounds?
The mechanisms for these reactions aren't required in
syllabuses, but you might need to know a little about
the nature of Grignard reagents.
The bond between the carbon atom and the
magnesium is polar. Carbon is more electronegative
than magnesium, and so the bonding pair of electrons
is pulled towards the carbon.
That leaves the carbon atom with a slight negative
charge.
The Grignard reagent can therefore serve as a
nucleophile because of the attraction between the
slight negativeness of the carbon atom in the Grignard
reagent and the positiveness of the carbon in the
carbonyl compound.
A nucleophile is a species that attacks positive (or
slightly positive) centres in other molecules or ions.
http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/haloalkanes/grignard.html
Вам также может понравиться
- Why Do Grignard Reagents React With Carbonyl Compounds?Документ3 страницыWhy Do Grignard Reagents React With Carbonyl Compounds?Anonymous JOOQkGbwoRОценок пока нет
- Diethyl EtherДокумент3 страницыDiethyl EtherRaj VarmanОценок пока нет
- Real Chem 238 LabДокумент78 страницReal Chem 238 Labmaya22scottОценок пока нет
- Unit 4Документ113 страницUnit 4RameshbabuОценок пока нет
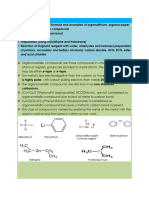
- Rahman S. Z. Saleem: Department of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, SBASSE Lahore University of Management SciencesДокумент22 страницыRahman S. Z. Saleem: Department of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, SBASSE Lahore University of Management Scienceshazyhazy9977Оценок пока нет
- Preparation of Benzoic Acid Using A Grignard Reagent: Experiment 5Документ9 страницPreparation of Benzoic Acid Using A Grignard Reagent: Experiment 5mamadou17diallo17Оценок пока нет
- Organometallic CompoundsДокумент9 страницOrganometallic CompoundsAng JonathanОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Grignard ReagentsДокумент8 страницAn Introduction To Grignard Reagentssafiya_91Оценок пока нет
- Grignard ReagntДокумент18 страницGrignard ReagntSiddarth Singh100% (1)
- KarboanionДокумент13 страницKarboanionHasanulKamilОценок пока нет
- Organometallic Chemistry: B R ThoratДокумент40 страницOrganometallic Chemistry: B R ThoratBapu ThoratОценок пока нет
- The Preparation of A Grignard Reagent Is An Important Laboratory Technique and Is A Required Method in The Synthesis of Numerous Organic MoleculesДокумент1 страницаThe Preparation of A Grignard Reagent Is An Important Laboratory Technique and Is A Required Method in The Synthesis of Numerous Organic MoleculeskhekhyОценок пока нет
- Grignard ReactionДокумент8 страницGrignard ReactionGourav AgrawalОценок пока нет
- AO Brochure GrignardДокумент12 страницAO Brochure GrignardHimanshu RanjanОценок пока нет
- Organometallic Compounds: Guest Lecturer: Prof. Jonathan L. SesslerДокумент40 страницOrganometallic Compounds: Guest Lecturer: Prof. Jonathan L. Sesslerhera hmОценок пока нет
- Grignard ReactionДокумент1 страницаGrignard ReactionSulaiman Al Shidhani100% (2)
- Grignard 3Документ2 страницыGrignard 3elbronОценок пока нет
- Alkenes NotesДокумент7 страницAlkenes NotesIndervir SinghОценок пока нет
- Grignard Reagents: Reagents Such As CHДокумент3 страницыGrignard Reagents: Reagents Such As CHAnthony BasantaОценок пока нет
- Organometallic Chemistry by RajwantДокумент8 страницOrganometallic Chemistry by Rajwantrajwant kaurОценок пока нет
- Cu ZN OrganometallicsДокумент60 страницCu ZN Organometallicsalusia24Оценок пока нет
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosДокумент18 страницNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosAMAN JATОценок пока нет
- Chapter:-Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Department of Chemistry, Pratap College, AmalnerДокумент12 страницChapter:-Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Department of Chemistry, Pratap College, Amalnermilindthakare75Оценок пока нет
- A.D. Chemistry Organometallic CompoundsДокумент11 страницA.D. Chemistry Organometallic Compoundsombiraji122Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 8 Halide RXДокумент84 страницыLecture 8 Halide RXquang trầnОценок пока нет
- Aliphatic N Aromatic SubДокумент48 страницAliphatic N Aromatic SubSahla Thasnim ckОценок пока нет
- Organic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions sn1 and sn2 ReactioДокумент13 страницOrganic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions sn1 and sn2 ReactioDebarjan DattaОценок пока нет
- G R Reduction AlkaneДокумент43 страницыG R Reduction AlkaneManthan HaritashОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7. Organometallic Compounds of Group I and II MetalsДокумент1 страницаChapter 7. Organometallic Compounds of Group I and II MetalsSeungju KangОценок пока нет
- Radical Reaction - IДокумент35 страницRadical Reaction - Ihappy cyenoОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry - Chapter 17 - Organometallic ReactionsДокумент14 страницOrganic Chemistry - Chapter 17 - Organometallic ReactionsSairille ManejaОценок пока нет
- McMurry9e PPT CH10Документ50 страницMcMurry9e PPT CH10emily7876Оценок пока нет
- Radical ReactionsДокумент36 страницRadical ReactionsNimra KhanОценок пока нет
- BhivbnmДокумент8 страницBhivbnmPrachiОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Grignard ReagentsДокумент2 страницыAn Introduction To Grignard ReagentsHang VuongОценок пока нет
- Organic RXN MechanismДокумент24 страницыOrganic RXN MechanismNabin ShresthaОценок пока нет
- 1 - Synthesis of Alcohols and PhenolsДокумент2 страницы1 - Synthesis of Alcohols and PhenolsMohamad AzaniОценок пока нет
- Li MG OrganometallicsДокумент62 страницыLi MG OrganometallicsArish AhmedОценок пока нет
- Organic Chem II Lec 4Документ46 страницOrganic Chem II Lec 4Bình NguyễnОценок пока нет
- 5-Grignard Benzophenone Methyl Benzoate and CO2 Sp17Документ13 страниц5-Grignard Benzophenone Methyl Benzoate and CO2 Sp17yugawad0% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Ethers and EpoxidesДокумент82 страницыChapter 8 - Ethers and EpoxidesCute ni LeynesОценок пока нет
- Review of N GrapheneДокумент14 страницReview of N Graphenedeepakrm74Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions, Stereochemical AspectsДокумент20 страницChemical Reactions, Stereochemical AspectsKalpa DihingiaОценок пока нет
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEДокумент1 страницаHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEUnknownОценок пока нет
- Grignard ReactionДокумент6 страницGrignard ReactionGillary Peña MuñozОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 Halogen DerivativesДокумент11 страницChapter 16 Halogen DerivativesSabina SabaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ57 страницChapter 9Quỳnh Anh TrầnОценок пока нет
- Haloalkanes and Haloarene - NotesДокумент13 страницHaloalkanes and Haloarene - NotesAmythОценок пока нет
- 1Документ13 страниц1Anonymous g7uPednIОценок пока нет
- Org Chem E8 Classification Tests For Organic HalidesДокумент4 страницыOrg Chem E8 Classification Tests For Organic HalidesJustin Victor AngОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions: Lecture by Kalpajyoti Dihingia Department of Chemistry DHSK CollegeДокумент21 страницаChemical Reactions: Lecture by Kalpajyoti Dihingia Department of Chemistry DHSK CollegeKalpa DihingiaОценок пока нет
- Nucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonДокумент46 страницNucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonAhmed AtefОценок пока нет
- Li MG Organometallics1Документ62 страницыLi MG Organometallics1BarshaОценок пока нет
- Freeradicals 171225065343Документ58 страницFreeradicals 171225065343Jawad HussainОценок пока нет
- Grignard ReagentДокумент7 страницGrignard Reagentd anjilappaОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of RadicalsДокумент54 страницыCharacteristics of RadicalsdesyОценок пока нет
- Reasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2Документ8 страницReasoning Qns With Answers - Haloalkanes&Haloarenes 2tanishka0307Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Substitution ReactionДокумент43 страницыChapter 4 Substitution ReactionNahom AmanuelОценок пока нет
- Graphene-based Carbocatalysis: Synthesis, Properties and Applications: Volume 1От EverandGraphene-based Carbocatalysis: Synthesis, Properties and Applications: Volume 1Оценок пока нет
- SK017 Paper2 Sem1 0708Документ3 страницыSK017 Paper2 Sem1 0708shehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Sem1 Unit6 Chemical EquilibriumДокумент3 страницыSem1 Unit6 Chemical Equilibriumshehdilanun100% (1)
- Objektif Q SKO17 Set 3Документ4 страницыObjektif Q SKO17 Set 3shehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Students H8 Buffer SolutionДокумент1 страницаStudents H8 Buffer SolutionshehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Past Year Analysis SK017Документ2 страницыPast Year Analysis SK017shehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Sem1 Unit4 Periodic TableДокумент10 страницSem1 Unit4 Periodic Tableshehdilanun0% (1)
- Sem1 Unit5 Chemical BondingДокумент6 страницSem1 Unit5 Chemical Bondingshehdilanun100% (1)
- Sem1 Unit8 Phase EquilibriaДокумент5 страницSem1 Unit8 Phase EquilibriashehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Sem1 Unit7 Ionic EquilibriaДокумент5 страницSem1 Unit7 Ionic Equilibriashehdilanun50% (2)
- Sem1 Unit3 Atomic StructureДокумент8 страницSem1 Unit3 Atomic Structureshehdilanun100% (1)
- Past Year Analysis Sk017Документ2 страницыPast Year Analysis Sk017shehdilanunОценок пока нет
- How Study Chem ChartДокумент1 страницаHow Study Chem ChartshehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Sem1 Unit2 States of MatterДокумент7 страницSem1 Unit2 States of MattershehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Sem1 Unit1 MatterДокумент9 страницSem1 Unit1 Mattershehdilanun100% (2)
- Set IV Objective Sem IIДокумент6 страницSet IV Objective Sem IIshehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Forecast FiNaL SK 027 0809Документ2 страницыForecast FiNaL SK 027 0809shehdilanunОценок пока нет
- RPH laNUn Tutor Week 15 H8 T46Документ1 страницаRPH laNUn Tutor Week 15 H8 T46shehdilanunОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 OH LaNunДокумент7 страницChapter 16 OH LaNunshehdilanun100% (1)
- RPH laNUn Amali Week 15 H3 P27Документ2 страницыRPH laNUn Amali Week 15 H3 P27shehdilanunОценок пока нет
- RPH laNUn Kuliah SelasaДокумент1 страницаRPH laNUn Kuliah SelasashehdilanunОценок пока нет
- RPH laNUn Amali Week 15 H1 P1Документ1 страницаRPH laNUn Amali Week 15 H1 P1shehdilanunОценок пока нет