Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nursing Care Plan - Spinal Cord Injury
Загружено:
deric92%(36)92% нашли этот документ полезным (36 голосов)
58K просмотров2 страницыSpinal cord injury may result from trauma, vascular disruption, infection, tumor, and other insults. Most common sites of injury are the cervical areas C5, C6, and C7. Patient will demonstrate techniques or behaviors that enable resumption of activity.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Nursingcrib.com Nursing Care Plan - Spinal Cord Injury
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документSpinal cord injury may result from trauma, vascular disruption, infection, tumor, and other insults. Most common sites of injury are the cervical areas C5, C6, and C7. Patient will demonstrate techniques or behaviors that enable resumption of activity.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
92%(36)92% нашли этот документ полезным (36 голосов)
58K просмотров2 страницыNursing Care Plan - Spinal Cord Injury
Загружено:
dericSpinal cord injury may result from trauma, vascular disruption, infection, tumor, and other insults. Most common sites of injury are the cervical areas C5, C6, and C7. Patient will demonstrate techniques or behaviors that enable resumption of activity.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Student Nurses’ Community
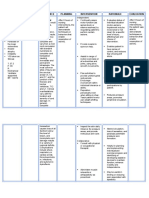
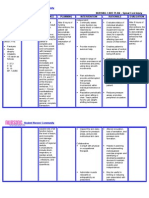
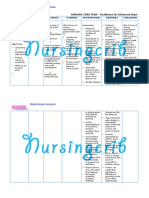
NURSING CARE PLAN – Spinal Cord Injury
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Independent:
SUBJECTIVE: Impaired Spinal cord After 8 hours of • Continually asses • Evaluates status of After 8 hours of
physical injury may result nursing motor function (as individual situation nursing
“Hindi ako mobility related from trauma, interventions, the spinal shock or edema (motor-sensory interventions, the
makagalaw” (I to vascular patient will resolves) by impairment may be patient was able
can’t move) as neuromascular disruption, demonstrate requesting patient to mixed and/ or not to demonstrate
verbalized by the impairment. infection, tumor, techniques or perform certain clear) for a specific techniques or
patient. and other insults. behaviors that actions. level of injury, behaviors that
The injury may be enable affecting type and enable
OBJECTIVE: partial or resumption of choice of intervention. resumption of
complete and activity. activity.
Paralysis vary from a mild • Provide means to • Enables patient to
Muscle cord concussion summon help. have sense of control,
atrophy with transient and reduces fear of
Irritability numbness to being left alone.
V/S taken as complete cord
follows: transaction • Assist in range of • Enhances circulation,
causing motion exercises on all restores or maintains
T: 37.3 immediate and extremities and joints, muscle tone and joint
P: 92 permanent using slow, smooth mobility, and prevent
R: 19 tetraplegia. The movements. disuse contractures
BP: 120/80 most common and muscle atrophy.
sites of injury are
the cervical areas • Plan activities to • Prevents fatigue,
C5, C6, and C7,
provide uninterrupted allowing opportunity
and the junction
rest periods. for maximal efforts or
of the thoracic
Encourage participations by
and lumbar
involvement within patient.
vertebrae, T12
individual tolerance or
and L1. Clinical
ability.
manifestations
• Reposition periodically • Reduces pressure
vary with the
location and even when sitting in areas, promotes
severity of cord chair. Teach patient peripheral circulation.
damage. In how to use weight-
general, complete shifting techniques.
transaction
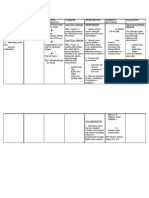
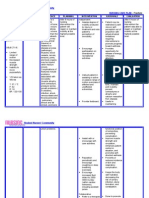
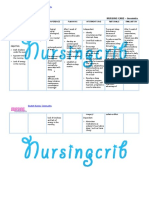
Student Nurses’ Community
causes loss of all • Inspect the skin daily. • Altered circulation,
function below Observe for pressure loss of sensation, and
the level of lesion, areas, and provide paralysis potentiate
and incomplete meticulous skin care. pressure sore
cord damage formation.
results in a
variety of regional Collaborative:
deficits. • Consult with physical • Helpful in planning
Complications or occupational and implementing
include shock, therapist. individualized
respiratory or exercise program and
cardiac arrest, identifying or
thromboembolism developing assistive
, infections, and devices to maintain
autonomic function, enhance
dysreflexia. mobility and
independence.
• Administer muscle • May be useful in
relaxants or limiting or reducing
antispasticity as pain associated with
prescribed. spasticity
Вам также может понравиться
- (NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2Документ2 страницы(NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2roren100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPДокумент2 страницыSpinal Cord Injury NCPEmmanuelRodriguez100% (1)
- 3 Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care PlanДокумент9 страниц3 Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis88% (8)
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPДокумент2 страницыSpinal Cord Injury NCPShengxy Ferrer100% (6)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentДокумент17 страницImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentAileen Lopez83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan for Altered Level of ConsciousnessДокумент8 страницNursing Care Plan for Altered Level of ConsciousnessJeffrey Dela Cruz50% (4)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionДокумент2 страницыDisturbed Sensory Perceptionsuper ahga-once0% (1)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionДокумент4 страницыNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaОценок пока нет
- NCP Risk For InjuryДокумент2 страницыNCP Risk For InjuryAbigail Joy Tabones75% (4)
- NCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionДокумент2 страницыNCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionRene John Francisco50% (4)
- NCP OrifДокумент8 страницNCP Orif2211890001Оценок пока нет
- Parkinson's Disease NCPДокумент1 страницаParkinson's Disease NCPAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado67% (3)
- NCPДокумент3 страницыNCPAlyanna Peñaflorida100% (2)
- Self Care Deficit BahtingДокумент1 страницаSelf Care Deficit BahtingNaj SoliveresОценок пока нет
- Nursing diagnosis impaired mobilityДокумент2 страницыNursing diagnosis impaired mobilityAi Rou100% (1)
- NCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)Документ2 страницыNCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)yanny0350% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Skin Integrity Traction)Документ2 страницыNursing Care Plan Impaired Skin Integrity Traction)deric100% (18)
- Thyroidectomy Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыThyroidectomy Nursing Care PlanRnspeakcom100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For "Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Ruptured Inter Vertebral Disc"Документ9 страницNursing Care Plan For "Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Ruptured Inter Vertebral Disc"jhonroks100% (7)
- NCP - BedriddenДокумент4 страницыNCP - Bedriddenadelaigner_racho589475% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale ResponseДокумент4 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale Responsekhate fonteОценок пока нет
- NXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3Документ2 страницыNXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3marielle_dellaОценок пока нет
- NCP Disturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related To Chemotherapy Evidenced by Visual DistortionДокумент2 страницыNCP Disturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related To Chemotherapy Evidenced by Visual DistortionCamille Grace100% (2)
- NCP AnginaДокумент3 страницыNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPJhel NabosОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For "Disc Surgery"Документ11 страницNursing Care Plan For "Disc Surgery"jhonroks92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan TBIДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan TBIChester Manalo87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionДокумент7 страницNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarctionmariejo95% (125)
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisОценок пока нет
- NCP - Head InjuryДокумент3 страницыNCP - Head Injurykaheliyala94% (33)
- NCP TbiДокумент4 страницыNCP TbiWyen CabatbatОценок пока нет
- NCP ThyroidectomyДокумент2 страницыNCP Thyroidectomykhinayo100% (3)
- ThyroidectomyДокумент2 страницыThyroidectomyYenyen Legas100% (2)
- Nursing Care for Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionДокумент4 страницыNursing Care for Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusionalliahjoyce ignacioОценок пока нет
- NCP PottsДокумент3 страницыNCP PottsFenie Jane Quinlat LapastoraОценок пока нет
- Spinal Injury Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыSpinal Injury Nursing Care PlanPatricia OrtegaОценок пока нет
- CVA Activity IntoleranceДокумент1 страницаCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- Retinal Detachment: Case Report Operating RoomДокумент35 страницRetinal Detachment: Case Report Operating RoomCarlo Joseph Intal Llacer50% (2)
- NCP Impaired Skintissue IntegrityДокумент5 страницNCP Impaired Skintissue IntegrityArt Christian RamosОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterAnonymous NZTQVgjaОценок пока нет
- NCP For Subarachnoid HemorrhageДокумент4 страницыNCP For Subarachnoid HemorrhageJoan Rose Rendon-Hung78% (18)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired AdjustmentДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan Impaired Adjustmentderic100% (2)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionДокумент3 страницыDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJashtine JingcoОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationДокумент3 страницыStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiОценок пока нет
- NCP CSДокумент4 страницыNCP CSJM UncianoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan - FractureДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan - Fracturederic95% (19)
- FractureДокумент1 страницаFractureReechie TeasoonОценок пока нет
- NCP Impaired MobilityДокумент4 страницыNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroОценок пока нет
- NCP NeuroДокумент2 страницыNCP NeuroErryl Justine Advincula100% (1)
- Assessment NeuroДокумент2 страницыAssessment NeurodhagallarteОценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord Injury: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentДокумент17 страницSpinal Cord Injury: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentPreciousmae Talay JavierОценок пока нет
- Assessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentДокумент3 страницыAssessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentKim Glaidyl BontuyanОценок пока нет
- NCP CVA ImmoblityДокумент3 страницыNCP CVA ImmoblityAnalyn FloresОценок пока нет
- Day 3 Activity: Nursing Care Plan: College of Health SciencesДокумент6 страницDay 3 Activity: Nursing Care Plan: College of Health SciencesAngelica Charisse BuliganОценок пока нет
- Geria NCP, Dela CruzДокумент7 страницGeria NCP, Dela CruzStephany Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan FibromyalgiaДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Fibromyalgiaderic90% (10)
- NCPДокумент5 страницNCPKasandra Dawn BerisoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыNursing Care PlanLjae NatinoОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Stroke NCPДокумент11 страницIschemic Stroke NCPJohannah DaroОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPДокумент14 страницNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPДокумент8 страницNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic86% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Answer Key CicДокумент3 страницыAnswer Key Cictiburshoc16Оценок пока нет
- Stunting Kamas Kirim, DR. Dr. Titis Prawitasari, Sp.A (K), 160622Документ51 страницаStunting Kamas Kirim, DR. Dr. Titis Prawitasari, Sp.A (K), 160622Theodora NancyОценок пока нет
- Appointment Letters Independent DirectorsДокумент62 страницыAppointment Letters Independent DirectorsArudra KumarОценок пока нет
- Answers To Exam Practice: Chapter 6 Food and HumansДокумент5 страницAnswers To Exam Practice: Chapter 6 Food and Humansan ChiОценок пока нет
- HPWJ Medical Alert Card SampleДокумент2 страницыHPWJ Medical Alert Card SampleSameer Kumar JubailОценок пока нет
- Medifocus April 2007Документ61 страницаMedifocus April 2007Pushpanjali Crosslay HospitalОценок пока нет
- Fat Burner: Fitzoye Nutrition IntroducingДокумент6 страницFat Burner: Fitzoye Nutrition IntroducingrajeshОценок пока нет
- Liver Cirrhosis: Causes, Complications and ManagementДокумент55 страницLiver Cirrhosis: Causes, Complications and ManagementAnonymous vUEDx8100% (1)
- Pengisian Tanggal3Документ32 страницыPengisian Tanggal3gusrina simamoraОценок пока нет
- What Are The Psychological Benefits of GratitudeДокумент6 страницWhat Are The Psychological Benefits of GratitudebrendaОценок пока нет
- Virtual GriefДокумент1 страницаVirtual GriefWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitОценок пока нет
- Trauma and Stressor-Related DisordersДокумент32 страницыTrauma and Stressor-Related DisordersRay Anne Labra-PepitoОценок пока нет
- Hirarc FoundationДокумент3 страницыHirarc FoundationknabpshoОценок пока нет
- Nutrition and Students Academic PerformanceДокумент10 страницNutrition and Students Academic Performanceapi-222239614Оценок пока нет
- Journal FoodДокумент4 страницыJournal FoodMizaZainalОценок пока нет
- Chronic IllnessДокумент13 страницChronic IllnessAnusha KumarasiriОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ52 страницыModule 1Sarim AliОценок пока нет
- The Paper Test Includes 4 Pages Time Allowance: 40 Minutes Date: 06 June, 2021Документ4 страницыThe Paper Test Includes 4 Pages Time Allowance: 40 Minutes Date: 06 June, 2021Truơng Anh TàiОценок пока нет
- Handbook On Counselling and Psychosocial Care For Children-2018Документ274 страницыHandbook On Counselling and Psychosocial Care For Children-2018Firaol MesfinОценок пока нет
- Winters Ildp Final Review Draft ApprovedДокумент7 страницWinters Ildp Final Review Draft Approvedapi-424954609Оценок пока нет
- Drugs and Magic Remedies Objectionable Advertisements Act 1954Документ9 страницDrugs and Magic Remedies Objectionable Advertisements Act 1954Latest Laws TeamОценок пока нет
- "Unpack" and Share Assumptions: Figure 2.6 Success in Theory of Change ModelsДокумент18 страниц"Unpack" and Share Assumptions: Figure 2.6 Success in Theory of Change ModelsSarniati AniОценок пока нет
- Mdms Meritwise AdmДокумент93 страницыMdms Meritwise AdmAakash SethiОценок пока нет
- Balanced Diet ChartДокумент2 страницыBalanced Diet ChartjosephОценок пока нет
- CMC Vellore Summer Admission Bulletin 2020 Revised 16 Nov 2020Документ58 страницCMC Vellore Summer Admission Bulletin 2020 Revised 16 Nov 2020Allen ChrysoОценок пока нет
- Aunt Minnie Pediatric NeuroДокумент15 страницAunt Minnie Pediatric NeuroRommel OliverasОценок пока нет
- Effects of Drug Abuse on Health and SocietyДокумент9 страницEffects of Drug Abuse on Health and SocietyAditya guptaОценок пока нет
- Understanding the pros and cons of early marriage for teenagersДокумент15 страницUnderstanding the pros and cons of early marriage for teenagersShoba ManoharanОценок пока нет
- Gina Cushenberry Nutrition Resume 2016Документ6 страницGina Cushenberry Nutrition Resume 2016api-308173770Оценок пока нет
- Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride 5 MG Film-Coated Tablet AntihistamineДокумент3 страницыLevocetirizine Dihydrochloride 5 MG Film-Coated Tablet AntihistamineRuel Vincent AsubarОценок пока нет