Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Supplementary Table 1: The NICE Traffic Light System For Assessing The Risk of Serious Illness in Children With Fever
Загружено:
Alex Cárdenas ValdiviesoИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Supplementary Table 1: The NICE Traffic Light System For Assessing The Risk of Serious Illness in Children With Fever
Загружено:
Alex Cárdenas ValdiviesoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
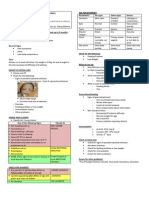
Supplementary table 1: The NICE Traffic light system for assessing the risk of serious illness in children with
fever1
Green-low risk Normal colour of skin , lips, and tongue Responds normally to social cues Content/smiles Stays awake or awakens quickly Strong normal cry/not crying Respiratory Amber-intermediate risk Pallor reported by parent/carer Red-high risk Pale/mottled/ashen blue
Colour
Activity
Not responding normally to social cues Wakes only with prolonged stimulation Decreased activity No smile
No response to social cues Appears ill to a healthcare professional Does not wake or if roused does not stay awake Weak/high pitched/continuous cry Grunting Tachypnoea: RR >60 breaths /min
Nasal flaring Tachypnoea: RR >50breaths/min, age 6-12 months RR >40 breaths /min, age >12 months Oxygen saturation 95% in air Crackles
Moderate or severe chest indrawing
Hydration
Normal skin and eyes Moist mucous membranes
Dry mucous membrane Poor feeding in infants CRT 3 s Reduced urine output Fever for 5 days
Reduced skin turgor
Other
None of the amber or red symptoms or signs
Swelling of limb or joint Non-weight bearing limb or not using an extremity
A new lump >2 cm CRT, capillary refill time; RR respiratory rate. Children with features in the red column are at high risk of serious illness. Children with any features in the amber column and none in the red column are at intermediate risk of serious illness. Those with features in the green column, and none in the amber or red columns, are at low risk. Reference 1. National Collaborating Centre for Women's and Children's Health. Feverish illness in children: assessment and initial management in children younger than five years. London: RCOG Press, 2007:http://www.nice.org.uk/CG047fullguideline.
Age 0-3 months, temperature 380C Age 3-6 months, temperature 390C Non blanching rash Bulging fontanelle Neck stiffness Status epilepticus Focal neurological signs Focal seizures Bile stained vomiting
Вам также может понравиться
- Pediatric EmergenciesДокумент79 страницPediatric Emergenciesأحمد سعد الديوه جيОценок пока нет
- PaediatricДокумент423 страницыPaediatricmuntaserОценок пока нет
- The Normal Newborn: Assessment and CareДокумент71 страницаThe Normal Newborn: Assessment and CareElla Maica RacmanОценок пока нет
- Danger Signs in NewbornДокумент8 страницDanger Signs in NewbornPrabhu MagudeeswaranОценок пока нет
- NewbornДокумент109 страницNewbornnrraman99100% (1)
- Approach To Fever and AntibioticsДокумент13 страницApproach To Fever and Antibioticsasraf amirullahОценок пока нет
- DehydrationДокумент19 страницDehydrationIlyes FerenczОценок пока нет
- NephrocystinosisДокумент31 страницаNephrocystinosisEmily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Management of Critically Ill ChildДокумент36 страницManagement of Critically Ill ChildSibi AntonyОценок пока нет
- Lapkas Marasmus-Down SyndromeДокумент37 страницLapkas Marasmus-Down SyndromeKURBULDKОценок пока нет
- Sepsis in PediatricsДокумент48 страницSepsis in PediatricsCecile Maramba-LazarteОценок пока нет
- Skin Lichen Planus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandSkin Lichen Planus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- NEWBORN ExaminationДокумент38 страницNEWBORN ExaminationEslam HamadaОценок пока нет
- 9 Peds SOAP NotesДокумент17 страниц9 Peds SOAP Notesamber reichelОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент59 страницUntitledRobin KeaneОценок пока нет
- ABO Incompatibility in NeonateДокумент27 страницABO Incompatibility in NeonatemarshalitaОценок пока нет
- Newborn Assessment and CareДокумент79 страницNewborn Assessment and CareStephen Gabriel TitoОценок пока нет
- Down SyndromeДокумент37 страницDown SyndromeBenita DavidОценок пока нет
- Final Practicum - Soap Note 1Документ16 страницFinal Practicum - Soap Note 1api-49464347867% (3)
- Newborn Physical Assessment by Ms. Mevelle L. AsuncionДокумент91 страницаNewborn Physical Assessment by Ms. Mevelle L. AsuncionRizzamwah CatagueОценок пока нет
- Croup: Youtube VidoeДокумент12 страницCroup: Youtube VidoeJEMY JOSEОценок пока нет
- Script Pedia 1Документ38 страницScript Pedia 1Jessy Arcaina BañagaОценок пока нет
- Weebly Head To Toe AssessmentДокумент3 страницыWeebly Head To Toe Assessmentapi-608265381Оценок пока нет
- Trisomy 21Документ32 страницыTrisomy 21Alexandru EsteraОценок пока нет
- Case 1 Pedia Henoch Schonlein PurpuraДокумент45 страницCase 1 Pedia Henoch Schonlein PurpuraJefferson Gumiran100% (1)
- Enterobiasis CaseДокумент4 страницыEnterobiasis CaseKimm Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Pediatric AssessmentДокумент54 страницыPediatric AssessmentThetnaungsoeОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Danger SignsДокумент6 страницNeonatal Danger Signsmarkus_danusantosoОценок пока нет
- Pedia II.19imci Part 2Документ2 страницыPedia II.19imci Part 2Aileen Valdez-ManicsicОценок пока нет
- Fever - MSF Medical GuidelinesДокумент6 страницFever - MSF Medical GuidelinesUmarОценок пока нет
- Prepared By:: Nisha Ghimire Sushmita Poudel Aliza Poudel Devi Rana Namuna KarkiДокумент33 страницыPrepared By:: Nisha Ghimire Sushmita Poudel Aliza Poudel Devi Rana Namuna KarkiPerry BearОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Cardio-Respiratory AssessmentДокумент9 страницPediatric Cardio-Respiratory AssessmentRicky SpideyОценок пока нет
- Docucare TemplateДокумент5 страницDocucare TemplateKassandra AvilaОценок пока нет
- 3.15 Febrile Child Under 5 Years Without A FocusДокумент8 страниц3.15 Febrile Child Under 5 Years Without A Focusiffi82Оценок пока нет
- Final Practicum - Soap Note 3Документ17 страницFinal Practicum - Soap Note 3api-494643478100% (2)
- Final Theoretical Exam in Pediatrics " Set A ": Choose The Most Appropriate ResponseДокумент54 страницыFinal Theoretical Exam in Pediatrics " Set A ": Choose The Most Appropriate ResponseYousif AlaaОценок пока нет
- Dehydration AssessmentДокумент2 страницыDehydration AssessmentzaheerbdsОценок пока нет
- ?pediatric Case Report.Документ14 страниц?pediatric Case Report.Female calmОценок пока нет
- Preeclampsia Case PresentationДокумент26 страницPreeclampsia Case PresentationLohrhen Lheighh Cahreeniyow100% (2)
- KB Viva GuideДокумент21 страницаKB Viva GuideRenuka deviОценок пока нет
- BPJ 45 Pneumonia Pages 25-29Документ5 страницBPJ 45 Pneumonia Pages 25-29Sharon AldaveОценок пока нет
- Final Assessment Soap NoteДокумент13 страницFinal Assessment Soap Noteapi-494643478100% (3)
- Sore ThroatДокумент10 страницSore Throatapi-551073862Оценок пока нет
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromeДокумент4 страницыNeonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromePahw BaluisОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome in A Premature BabyДокумент29 страницRespiratory Distress Syndrome in A Premature BabyVissalini JayabalanОценок пока нет
- Description: Kawasaki Disease (Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome) Is A Form of VasculitisДокумент4 страницыDescription: Kawasaki Disease (Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome) Is A Form of VasculitishamporkОценок пока нет
- Physical Examination in PaediatricsДокумент162 страницыPhysical Examination in PaediatricsUsman Ali100% (1)
- Pediatrics RemarksДокумент62 страницыPediatrics RemarksGÖKSU SAYGILIОценок пока нет
- PediatricsДокумент14 страницPediatricsJohn Christopher LucesОценок пока нет
- 1) BroncholitisДокумент25 страниц1) Broncholitisyaser773arfat2025Оценок пока нет
- Pediatric Assessment Triangle EditДокумент31 страницаPediatric Assessment Triangle EditAlbert Gunawan100% (1)
- Written Output PRIME 3 - Cara, Mariel DanicaДокумент3 страницыWritten Output PRIME 3 - Cara, Mariel DanicaMariel Danica CaraОценок пока нет
- Categorial Intuition SokolowskiДокумент61 страницаCategorial Intuition SokolowskiJake BrownОценок пока нет
- Approach To Fever in Opd PraciceДокумент55 страницApproach To Fever in Opd PraciceAbhijitОценок пока нет
- Newborn ExaminationДокумент65 страницNewborn Examinationst45cyahОценок пока нет
- Course: Emergency Procedures and Patient Care Lecture-4Документ27 страницCourse: Emergency Procedures and Patient Care Lecture-4saba ramzanОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of The New Born InfantДокумент37 страницNursing Care of The New Born Infantnila_sarichandraОценок пока нет
- Morbili: Oleh: Rostika Ayu Fhany EL SharaДокумент30 страницMorbili: Oleh: Rostika Ayu Fhany EL Sharadian febriana yasmarОценок пока нет
- HIGH RISK NEWBORN 13 Student VersionДокумент43 страницыHIGH RISK NEWBORN 13 Student VersionsimmyvashishtОценок пока нет