Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
HW 3
Загружено:
Fathi MusaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
HW 3
Загружено:
Fathi MusaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CSCI4211 Spring 2011 Assignment #3 Due date: April 12, 2011 (Tuesday) 1.
IP Fragmentation and Reassembly: An IP packet originally has a size of 6000 bytes including 20-byte header and 5980-byte payload. To reach the destination, the route goes through three networks, A, B, and C. Network A is the one where the sender is directly connected, and Network C is where the receiver is connected. Network A has an MTU of 5000 bytes. Network B has an MTU of 2000 bytes. Network C has an MTU of 800 bytes. (a) How is fragmentation done when the original IP packet enters Network B from Network A? Draw a graph to indicate the outcome of fragmentation. (b) When these fragments enter Network C from Network B, how are the fragmentations done? Draw a graph to show the results for each fragment from (a).
C
receiver
MTU=800 Bytes
A
sender
MTU=2000 Bytes
MTU=5000 Bytes
2. A router has the following (CIDR) entries in its routing table: Address/mask Next hop 135.46.56.0/22 Interface 0 135.46.60.0/22 Interface 1 192.53.40.0/23 Router 1 default Router 2 For each of the following IP address, what does the router do if packets with the following addresses arrives? (a) 135.46.63.10 (b) 135.46.57.14 (c) 135.46.52.2 (d) 192.53.40.7 (e) 192.53.56.7
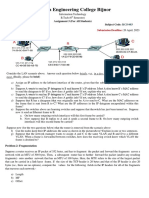
3. Consider the network shown below. ISP B provides national backbone service to regional ISP A. ISP C provides national backbone service to regional ISP D. B and C are peering with each other in two places using BGP. Consider the traffic going from A to D. B would prefer to hand that traffic over to C on the West Coast (so that C would have to absorb the cost of carrying the traffic cross-country), while C would prefer to get the traffic via its East coast peering point with B (so that B would have carried the traffic across-country). What BGP mechanism might C use, so that B would hand over A-to-D traffic at their East Coast peering point? N ISP A W S ISP B E
ISP C
ISP D
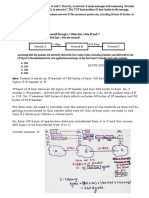
4. Reverse path forwarding. Consider the network topology and link costs shown below. Suppose that node E is the multicast source. Using arrows like those shown in Figure 4.44 in the textbook to indicate links over which packets will be forwarded using RPF and links over which packets will not be forwarded given that node E is the source. A
3 3
3
3
4 5
3
C
3
B
3
2
3
1 2 D 1 2
Вам также может понравиться
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxОт EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsОт EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqОценок пока нет
- BGP Configuration and Troubleshooting Exam QuestionsДокумент16 страницBGP Configuration and Troubleshooting Exam Questionsromeo821100% (5)
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesОт EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesОценок пока нет
- CCNAv3 – New Questions ReviewДокумент276 страницCCNAv3 – New Questions Reviewdufreine100% (1)
- ComNet MiniExam2 SolutionДокумент5 страницComNet MiniExam2 SolutionMohammed HoushanОценок пока нет
- 60617-3 1996Документ24 страницы60617-3 1996Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Homework 2 (due Nov. 26) - MP3 datagrams, distance vector routing, link state routing, address allocation, BGP traffic engineeringДокумент4 страницыHomework 2 (due Nov. 26) - MP3 datagrams, distance vector routing, link state routing, address allocation, BGP traffic engineeringAndario0% (1)
- HW 2Документ5 страницHW 2Kastuv Mani TuladharОценок пока нет
- Quiz 4 Chapter 5Документ4 страницыQuiz 4 Chapter 5Cokelat Smarties0% (1)
- CSE 323 - Homework - 3 - Fall 2013 - CДокумент2 страницыCSE 323 - Homework - 3 - Fall 2013 - CnikovnikovОценок пока нет
- Spanning Tree and RBF Flooding PDFДокумент4 страницыSpanning Tree and RBF Flooding PDFbekojanОценок пока нет
- ôn tập tự luận NWC203cДокумент6 страницôn tập tự luận NWC203cJi HoonОценок пока нет
- EE3204 Nov 01Документ6 страницEE3204 Nov 01Bryan WongОценок пока нет
- Exercises 3Документ6 страницExercises 3dassoumenn50% (2)
- Chapter 4: P4 P10 P19 P26 P28 P38 P46 P49 Chapter 5: P6 P15 P18 P22 P26 P29 Chapter 7: P19 P21Документ21 страницаChapter 4: P4 P10 P19 P26 P28 P38 P46 P49 Chapter 5: P6 P15 P18 P22 P26 P29 Chapter 7: P19 P21Abdelhakim KhlifiОценок пока нет
- CN Assignment 3 2022-23Документ4 страницыCN Assignment 3 2022-23SANDEEP KUMARОценок пока нет
- Assignment 5Документ3 страницыAssignment 5dono_Aja7814100% (1)
- Assignment I - IT Summer 2022Документ2 страницыAssignment I - IT Summer 2022Estifanos Endalew100% (1)
- Computer Network by Kanodia PublicationДокумент30 страницComputer Network by Kanodia PublicationNeha BhavsarОценок пока нет
- CS 421 Final Exam: Computer Networks QuestionsДокумент5 страницCS 421 Final Exam: Computer Networks QuestionsedeОценок пока нет
- Communication Networks II Ethernet Exercise 1Документ8 страницCommunication Networks II Ethernet Exercise 1Giang NguyenОценок пока нет
- ChutiyaДокумент6 страницChutiyaramОценок пока нет
- ACN Assign 05 SolutionДокумент11 страницACN Assign 05 SolutionFarrukh Tahir100% (1)
- CEG3185 Past Final - Docx - 1438983146678Документ6 страницCEG3185 Past Final - Docx - 1438983146678TurabОценок пока нет
- B.E. 6th Semester Computer Network ExamДокумент19 страницB.E. 6th Semester Computer Network Examshyjuother9773Оценок пока нет
- CPIT370 Final Spring2020.Docx 2Документ4 страницыCPIT370 Final Spring2020.Docx 2LinaОценок пока нет
- 200-120 AsnwerДокумент46 страниц200-120 AsnwernestorchueОценок пока нет
- EC 504 End Semester QPДокумент3 страницыEC 504 End Semester QPVinod PrakashОценок пока нет
- Birla Institute of Technology & Science Computer Networks Exam QuestionsДокумент4 страницыBirla Institute of Technology & Science Computer Networks Exam QuestionsChaitanyaLukkaОценок пока нет
- Network and Communication Important QuestionДокумент9 страницNetwork and Communication Important QuestionShadab AlamОценок пока нет
- Homework - 1 - 2017Документ4 страницыHomework - 1 - 2017Ackeema JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Fragmentation PDFДокумент6 страницFragmentation PDFDibyendu PaulОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks Test Questions (A1-G1)Документ11 страницComputer Networks Test Questions (A1-G1)RammurtiRawatОценок пока нет
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Документ3 страницыQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Shri Varsha100% (1)
- Computer Networksfinal Exam 2019Документ12 страницComputer Networksfinal Exam 2019binaОценок пока нет
- Midterm SolutionДокумент5 страницMidterm SolutionsyhonaaОценок пока нет
- CAU HOI ON TAP PE NWC203c SUMMER 2021Документ4 страницыCAU HOI ON TAP PE NWC203c SUMMER 2021Dang Phuong Anh (K15 HCM)Оценок пока нет
- Cisco: Question & AnswersДокумент13 страницCisco: Question & AnswersdaraОценок пока нет
- UGC NET CS Computer Networks Test 1 QuestionsДокумент3 страницыUGC NET CS Computer Networks Test 1 QuestionsSanthini KaОценок пока нет
- Final ExamДокумент3 страницыFinal Examjohn francisОценок пока нет
- Midterm2 cp372 SolutionДокумент8 страницMidterm2 cp372 SolutionbottbottОценок пока нет
- Model Question Paper-MC0075Документ20 страницModel Question Paper-MC0075Guy StimulatorОценок пока нет
- Question Paper: Bms College of EngineeringДокумент2 страницыQuestion Paper: Bms College of EngineeringcjdcjwvdfjdОценок пока нет
- 16b Practise Questions PDFДокумент5 страниц16b Practise Questions PDFHung XОценок пока нет
- Exam QuestionДокумент28 страницExam QuestionNay OoОценок пока нет
- Review Questions On Network and CommunicationsДокумент6 страницReview Questions On Network and CommunicationsAdmas MamoОценок пока нет
- Exam: 350-020 Title: CCIE SP Optical Qualification Ver: 06-22-09Документ80 страницExam: 350-020 Title: CCIE SP Optical Qualification Ver: 06-22-09George GeorgescuОценок пока нет
- Network Selected QuestionsДокумент13 страницNetwork Selected Questionsmisho_16100% (1)
- CS 168 Homework 2: Addressing, IP Fragmentation, Distance Vector RoutingДокумент5 страницCS 168 Homework 2: Addressing, IP Fragmentation, Distance Vector RoutingHerman DuquerronetteОценок пока нет
- CCNAv3 – New Questions ReviewДокумент238 страницCCNAv3 – New Questions ReviewSunda100% (1)
- Metropolitan Area Networks: 13.1 Review QuestionsДокумент2 страницыMetropolitan Area Networks: 13.1 Review QuestionsOso PolОценок пока нет
- ELEN 4017 - Network Fundamentals Tutorial No. 4: InstructionsДокумент3 страницыELEN 4017 - Network Fundamentals Tutorial No. 4: Instructionsasadmehmud5934Оценок пока нет
- Which Action Is Taken by A Switch Port Enabled For Poe Power Classification Override?Документ16 страницWhich Action Is Taken by A Switch Port Enabled For Poe Power Classification Override?Ghazwan SalihОценок пока нет
- Sub Module 5.4Документ22 страницыSub Module 5.4ISHTIAQОценок пока нет
- COMSATS University Data Communication Networks AssignmentДокумент2 страницыCOMSATS University Data Communication Networks AssignmentSaleem IqbalОценок пока нет
- GOtta'Документ11 страницGOtta'laxmimeenaОценок пока нет
- Air University Final Examination: Summer, 2008Документ5 страницAir University Final Examination: Summer, 2008Mahnoor SalmanОценок пока нет
- Analog in Output ModulesДокумент2 страницыAnalog in Output ModulesFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Literature Approaches To Teaching LiteratureДокумент14 страницLiterature Approaches To Teaching LiteratureFathi Musa100% (1)
- Why Should Literature Be Used in The Language Classroom?: Nina Daskalovska, Violeta DimovaДокумент5 страницWhy Should Literature Be Used in The Language Classroom?: Nina Daskalovska, Violeta DimovaFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Presentation by Omar AlTurki - English PoetryДокумент14 страницPresentation by Omar AlTurki - English PoetryFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Iic DK EX55 Oi SQ HM 8 Dkiz QL T6 yДокумент12 страницIic DK EX55 Oi SQ HM 8 Dkiz QL T6 yFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Busbar SpecificationsДокумент2 страницыBusbar SpecificationsFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Product Data Sheet 6ES7232-4HA30-0XB0Документ2 страницыProduct Data Sheet 6ES7232-4HA30-0XB0Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Soft Start and Star Delta Trip Class by Application ChartДокумент2 страницыSoft Start and Star Delta Trip Class by Application ChartFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- PROFIBUS Guideline AssemblingДокумент132 страницыPROFIBUS Guideline AssemblingSrikala VenkatesanОценок пока нет
- LV1 3RP15Документ6 страницLV1 3RP15Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- LAD9R1Документ1 страницаLAD9R1Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Built-In Panel PC CP65xx: Installation and Operating Instructions ForДокумент25 страницBuilt-In Panel PC CP65xx: Installation and Operating Instructions ForFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- 74LS93Документ11 страниц74LS93cocoxo13marОценок пока нет
- PLC or DCS PDFДокумент12 страницPLC or DCS PDFsafvanshaikhОценок пока нет
- 74 Ls 47Документ3 страницы74 Ls 47Joelo D' CartonОценок пока нет
- Prolific PL2303HX Driver SettingsДокумент11 страницProlific PL2303HX Driver SettingsFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Siemens PLC Connection Manual for GP-PRO/PBIIIДокумент52 страницыSiemens PLC Connection Manual for GP-PRO/PBIIIFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- PL 2303Документ11 страницPL 2303Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Price of OilДокумент1 страницаPrice of OilFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Production LevelsДокумент4 страницыProduction LevelsT-money SloanОценок пока нет
- Low-Cost HDTV Satellite Set-Top Box Decoder For Microsoft VC-1, H.264 and MPEG-2Документ4 страницыLow-Cost HDTV Satellite Set-Top Box Decoder For Microsoft VC-1, H.264 and MPEG-2Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- 41310Документ14 страниц41310Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- DATASHEETДокумент4 страницыDATASHEETFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Op Toc Rev7.1Документ5 страницOp Toc Rev7.1Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- Counter HEF4510BДокумент10 страницCounter HEF4510BnnguyenQuangBa100% (1)
- DATASHEETДокумент4 страницыDATASHEETFathi MusaОценок пока нет
- 170343626Документ6 страниц170343626Fathi MusaОценок пока нет
- ASR 1fДокумент4 страницыASR 1fMadison MadisonОценок пока нет
- ERX Cable Pinouts GuideДокумент8 страницERX Cable Pinouts Guidedenilson.rodr1357Оценок пока нет