Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
SSH Perl
Загружено:
kazИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SSH Perl
Загружено:
kazАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Here's an example that uses the ssh program to connect to a remote host.
Because the ssh program reads and writes to its controlling terminal, the IO::Pty modul e is used to create a new pseudo terminal for use by ssh. A new Net::Telnet obje ct is then created to read and write to that pseudo terminal. To use the code be low, substitute "changeme" with the actual host, user, password, and command pro mpt. ## Main program. { my ($pty, $ssh, @lines); my $host = "changeme"; my $user = "changeme"; my $password = "changeme"; my $prompt = '/changeme:~> $/'; ## Start ssh program. $pty = &spawn("ssh", "-l", $user, $host); # spawn() defined below ## Create a Net::Telnet object to perform I/O on ssh's tty. use Net::Telnet; $ssh = new Net::Telnet (-fhopen => $pty, -prompt => $prompt, -telnetmode => 0, -cmd_remove_mode => 1, -output_record_separator => "\r"); ## Login to remote host. $ssh->waitfor(-match => '/password: ?$/i', -errmode => "return") or die "problem connecting to host: ", $ssh->lastline; $ssh->print($password); $ssh->waitfor(-match => $ssh->prompt, -errmode => "return") or die "login failed: ", $ssh->lastline; ## Send command, get and print its output. @lines = $ssh->cmd("who"); print @lines; exit; } # end main program sub spawn { my(@cmd) = @_; my($pid, $pty, $tty, $tty_fd); ## Create a new pseudo terminal. use IO::Pty (); $pty = new IO::Pty or die $!; ## Execute the program in another process. unless ($pid = fork) { # child process die "problem spawning program: $!\n" unless defined $pid; ## Disassociate process from existing controlling terminal. use POSIX (); POSIX::setsid or die "setsid failed: $!";
## Associate process with a new controlling terminal. $tty = $pty->slave; $tty_fd = $tty->fileno; close $pty; ## Make stdio use the new controlling terminal. open STDIN, "<&$tty_fd" or die $!; open STDOUT, ">&$tty_fd" or die $!; open STDERR, ">&STDOUT" or die $!; close $tty; ## Execute requested program. exec @cmd or die "problem executing $cmd[0]\n"; } # end child process $pty; } # end sub spawn
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Test Help StatДокумент18 страницTest Help Statthenderson22603Оценок пока нет
- Vol 17 No 3 and No 4 Fort Laramie and The Sioux War of 1876Документ19 страницVol 17 No 3 and No 4 Fort Laramie and The Sioux War of 1876Лазар СрећковићОценок пока нет
- ADMS 2510 Week 13 SolutionsДокумент20 страницADMS 2510 Week 13 Solutionsadms examzОценок пока нет
- 03 Zero Emissions and Eco-Town in KawasakiДокумент21 страница03 Zero Emissions and Eco-Town in KawasakiAlwi AmarОценок пока нет
- Ranbaxy Acquisition by DaiichiДокумент9 страницRanbaxy Acquisition by Daiichirupe59Оценок пока нет
- HSTE User GuideДокумент26 страницHSTE User GuideAnca ToleaОценок пока нет
- 02 - STD - Bimetal Overload Relay - (2.07 - 2.08)Документ2 страницы02 - STD - Bimetal Overload Relay - (2.07 - 2.08)ThilinaОценок пока нет
- Pca - STATAДокумент17 страницPca - STATAAnonymous U5RYS6NqОценок пока нет
- Defining The Audiovisual IndustryДокумент20 страницDefining The Audiovisual IndustryAyoub Ait MahmoudОценок пока нет
- Brick Bonding AssignmentДокумент4 страницыBrick Bonding AssignmentNija AsifОценок пока нет
- Cronbach's AlphaДокумент4 страницыCronbach's AlphaHeide Orevillo Apa-apОценок пока нет
- Excel Tips TricksДокумент26 страницExcel Tips Tricksskondra12Оценок пока нет
- Revised Procedural Manual On Hazardous Waste Management (Revised DAO 04-36) I CONTENTS Chapter Page PDFДокумент53 страницыRevised Procedural Manual On Hazardous Waste Management (Revised DAO 04-36) I CONTENTS Chapter Page PDFdennisОценок пока нет
- Am Bio PhonicsДокумент21 страницаAm Bio PhonicsLaura Nataly VillaОценок пока нет
- SANAKO Study700 V 500 BrochureДокумент4 страницыSANAKO Study700 V 500 BrochureDwi PrihantoroОценок пока нет
- Daily Activities List - TCF3 (Safety Aramco) : Work Description Date LocationДокумент2 страницыDaily Activities List - TCF3 (Safety Aramco) : Work Description Date LocationSheri DiĺlОценок пока нет
- Dahua Video Conferencing SolutionДокумент16 страницDahua Video Conferencing SolutionDennis DubeОценок пока нет
- Ultrajet 376 Installation Data: Ultra Dynamics Marine, LCC Ultra Dynamics LimitedДокумент2 страницыUltrajet 376 Installation Data: Ultra Dynamics Marine, LCC Ultra Dynamics LimitedhaujesОценок пока нет
- Electronics World 1962 11Документ114 страницElectronics World 1962 11meisterwantОценок пока нет
- LTE ID RNP StandardizationДокумент9 страницLTE ID RNP Standardizationahdanizar100% (1)
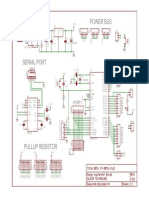
- 8051 Development Board Circuit DiagramДокумент1 страница8051 Development Board Circuit DiagramRohan DharmadhikariОценок пока нет
- Lamaran NongyiДокумент12 страницLamaran NongyiTonoTonyОценок пока нет
- PSA Technology-More Than A Hydrogen Purifier: TOBIAS KELLER and GOUTAM SHAHANI, Linde EngineeringДокумент2 страницыPSA Technology-More Than A Hydrogen Purifier: TOBIAS KELLER and GOUTAM SHAHANI, Linde EngineeringChem.EnggОценок пока нет
- Final Report Air ConditioningДокумент42 страницыFinal Report Air ConditioningAzmi Matali73% (11)
- Blurring Borders Collusion Between Anti-Immigrant Groups and Immigration Enforcement AgentsДокумент9 страницBlurring Borders Collusion Between Anti-Immigrant Groups and Immigration Enforcement AgentsJill HolslinОценок пока нет
- Minimalist CV ResumeДокумент1 страницаMinimalist CV ResumeSijith MathewОценок пока нет
- MetasploitДокумент9 страницMetasploitDhamlo KheralaОценок пока нет
- Tugas-MPSI-P1-P14 - Kelompok 2 - 19.4A.04Документ29 страницTugas-MPSI-P1-P14 - Kelompok 2 - 19.4A.04gilang putraОценок пока нет
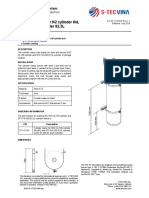
- Cylinder Clamp For N2 Cylinder 84L and FM-200 Cylinder 82.5LДокумент1 страницаCylinder Clamp For N2 Cylinder 84L and FM-200 Cylinder 82.5LNguyễn Minh ThiệuОценок пока нет
- Ap Human Geography Unit 5Документ4 страницыAp Human Geography Unit 5api-287341145Оценок пока нет