Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
AM & FM Radio Transmission Techniques
Загружено:
Jangshik BaboИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AM & FM Radio Transmission Techniques
Загружено:
Jangshik BaboАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1.
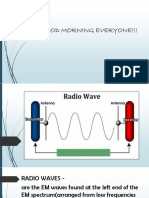
Both AM and FM radio programs are transmitted over the air via radio waves, which are
part of a broad range of electromagnetic waves that include visible light, X-rays, gamma rays and others. Electromagnetic waves are all around us in different frequencies. Radio waves are similar to light waves but are at a frequency our eyes are not sensitive to. Electromagnetic waves are generated by alternating current (AC), the electrical power used to run every appliance in our homes from washing machines to televisions. Alternating current in the US is 120 volts at 60Hz, which means that the current alternates or changes direction in the wire 60 times per second. Other countries use 50Hz as the standard. Both 50 and 60Hz are relatively low frequencies, but even 60Hz alternating current generates some level of electromagnetic radiation, meaning that some of the electricity escapes the wire and is transmitted into air. The higher the frequency of the electricity, the more electricity escapes the wire and into space. Thus, electromagnetic radiation can be described as 'electricity in the air'.
2. Amplitude modulation (AM) is a technique used in electronic communication, most
commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent. For example, changes in signal strength may be used to specify the sounds to be reproduced by aloudspeaker, or the light intensity of television pixels. Contrast this with frequency modulation, in which the frequency is varied, and phase modulation, in which the phase is varied in accordance to the modulating signal. frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. (Compare with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier wave varies, while the frequency remains constant.)
Вам также может понравиться
- Antenna BasicsДокумент125 страницAntenna Basicssamadhan1187Оценок пока нет
- Aerials & Radio Frequency PropagationДокумент30 страницAerials & Radio Frequency Propagationjoeven64Оценок пока нет
- 062 - Radio Navigation - AnswersДокумент86 страниц062 - Radio Navigation - AnswersEASA ATPL Question Bank100% (1)
- 1a. Review Radio TheoryДокумент46 страниц1a. Review Radio TheoryRhonny AlbertoОценок пока нет
- UNIT5 Fundamentals of Communication EngineeringДокумент20 страницUNIT5 Fundamentals of Communication EngineeringUpender Rao Sunkishala100% (4)
- Communication - Systems Rammohan MudgalДокумент27 страницCommunication - Systems Rammohan MudgalRammohan MudgalОценок пока нет
- Wireless FM TransmitterДокумент16 страницWireless FM TransmitterAntonio Herrera CabriaОценок пока нет
- Hawk Bags About: FoundedДокумент8 страницHawk Bags About: FoundedJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- RAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010Документ45 страницRAN Radio Theory: By: Zuliana Ismail, 2010zulianaОценок пока нет
- Radio-Frequency Wave PropagationДокумент42 страницыRadio-Frequency Wave PropagationChris Jomarie ObraОценок пока нет
- PUPCET 2014 Application GuideДокумент2 страницыPUPCET 2014 Application Guidephilippines2Оценок пока нет
- Carmen's Best Ice CreamДокумент3 страницыCarmen's Best Ice CreamJangshik Babo100% (1)
- PresentationДокумент38 страницPresentationAnonymous C09uQydeB100% (1)
- Types of Signals and Radio Modulation TechniquesДокумент13 страницTypes of Signals and Radio Modulation TechniquesNarasimman DonОценок пока нет
- FM Radio: Inventor - Definition - Difference With AM Radio Frequency Modulated RadioДокумент7 страницFM Radio: Inventor - Definition - Difference With AM Radio Frequency Modulated RadioDaniella Pasilbas SabacОценок пока нет
- Boundless Physics: Radio WavesДокумент29 страницBoundless Physics: Radio WavesYollyОценок пока нет
- FM AM RadioДокумент17 страницFM AM RadioKathrine AlbanoОценок пока нет
- Discover the History and Uses of Radio WavesДокумент28 страницDiscover the History and Uses of Radio WavesRyoshipukuОценок пока нет
- q 3 Electronics.m1 2Документ4 страницыq 3 Electronics.m1 2Che RishОценок пока нет
- L.N - Ra&i - Unit - 1Документ12 страницL.N - Ra&i - Unit - 1FIGHTER WINGS AVIATION COLLEGEОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic WaveДокумент32 страницыElectromagnetic WaveClrs BchnОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Avionics & Autopilot System - : Midterm CoverageДокумент75 страницAircraft Avionics & Autopilot System - : Midterm CoverageSantos MaineОценок пока нет
- CH 16Документ31 страницаCH 16Mizanur RahmanОценок пока нет
- VHF 2003Документ98 страницVHF 2003reachbibhu88Оценок пока нет
- RadioДокумент30 страницRadiomusicontherocksОценок пока нет
- G10 Science Q2 W5 Effects of ElectromagneticДокумент43 страницыG10 Science Q2 W5 Effects of ElectromagneticAndrew VidezОценок пока нет
- Lehigh University Summer Workshop on Wireless CommunicationsДокумент97 страницLehigh University Summer Workshop on Wireless CommunicationsryanhaОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Radio Communication: 1.1.1 Electromagnetic SignalДокумент9 страниц1.1 Radio Communication: 1.1.1 Electromagnetic SignalMonalisa PalОценок пока нет
- G10 Science Q2 - W5 - Effects of ElectromagneticДокумент43 страницыG10 Science Q2 - W5 - Effects of ElectromagneticKarina GentonОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Radio Communication: 1.1.1 Electromagnetic SignalДокумент2 страницы1.1 Radio Communication: 1.1.1 Electromagnetic SignalMonalisa PalОценок пока нет
- Electronics Quarter 3 - Module 1: Amplitude and Frequency ModulationДокумент20 страницElectronics Quarter 3 - Module 1: Amplitude and Frequency ModulationBangtan SonyeodanОценок пока нет
- Air Cadet Publication: CommunicationsДокумент50 страницAir Cadet Publication: CommunicationsMarcus DragoОценок пока нет
- Communication SystemsДокумент9 страницCommunication Systemsmaria.rehmanОценок пока нет
- Electronics Notes 1 OvjДокумент13 страницElectronics Notes 1 OvjanuОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент50 страницElectromagnetic SpectrumMisty Vito100% (1)
- CH 03Документ31 страницаCH 03engaydiОценок пока нет
- FM TransmitterДокумент5 страницFM TransmitterLiaqat Hussain BhattiОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Spectrum NotesДокумент5 страницElectromagnetic Spectrum NotesRalph Kerd AbapoОценок пока нет
- Understanding electronics and information and communication systems through electromagnetic waves and radio communicationДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding electronics and information and communication systems through electromagnetic waves and radio communicationFidaОценок пока нет
- Modulation 1Документ6 страницModulation 1Tamiranashe Tammie NyunguОценок пока нет
- Reading 34: Frequency Modulation What Is Frequency Modulation?Документ15 страницReading 34: Frequency Modulation What Is Frequency Modulation?Mustafa IbrahimОценок пока нет
- AC Fundamentals ExplainedДокумент10 страницAC Fundamentals Explainedanand011100% (1)
- Etymology: Radio WavesДокумент3 страницыEtymology: Radio WavesAmir DanialОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Spectrum GuideДокумент9 страницElectromagnetic Spectrum GuideGeorcelle CarcillarОценок пока нет
- Radio Waves Transmission ReceptionДокумент1 страницаRadio Waves Transmission ReceptionRandy PerosoОценок пока нет
- TV VHF and UHF Propagation: MultipathДокумент6 страницTV VHF and UHF Propagation: MultipathNiraj ShresthaОценок пока нет
- ECS-IntroductionДокумент48 страницECS-IntroductionMac Kelly JandocОценок пока нет
- PCS Unit 1Документ22 страницыPCS Unit 1sham411202Оценок пока нет
- AM-LAB 1 - Amplitude ModulationДокумент18 страницAM-LAB 1 - Amplitude ModulationDanny OxinaОценок пока нет
- Good Morning Everyone!!!Документ14 страницGood Morning Everyone!!!Jerrick arcegono SENPAIОценок пока нет
- Physics Research AssignmentДокумент7 страницPhysics Research AssignmentMimi HuynhОценок пока нет
- Frequency Modulation: For Frequency Modulation As Used in Digital Coding, See Differential Manchester Encoding - SignalДокумент2 страницыFrequency Modulation: For Frequency Modulation As Used in Digital Coding, See Differential Manchester Encoding - Signalprashanth fernandesОценок пока нет
- Antenna Report Update 1.0Документ23 страницыAntenna Report Update 1.0Shambhavi KОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Waves GuideДокумент7 страницElectromagnetic Waves GuideEvefel Ruth SanchezОценок пока нет
- 1 - Basic PrinciplesДокумент37 страниц1 - Basic Principlessoo chiОценок пока нет
- FM Transmitter Project 2km CHAPTER 1Документ3 страницыFM Transmitter Project 2km CHAPTER 1Jubril Akinwande80% (5)
- Electronics: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Amplitude and Frequency ModulationДокумент19 страницElectronics: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Amplitude and Frequency ModulationSheryl Mae BalanaОценок пока нет
- Amplitude Modulation (AM) Transmitter: Engineering and Technology DivisionДокумент9 страницAmplitude Modulation (AM) Transmitter: Engineering and Technology Divisioner denice catamoraОценок пока нет
- BroadcastingДокумент2 страницыBroadcastingabidansarialiОценок пока нет
- ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMSДокумент48 страницELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMSRaymond Cruzin100% (3)
- Perceptions - ANOVA CompleteДокумент61 страницаPerceptions - ANOVA CompleteJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- FinalДокумент6 страницFinalJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Thesis QuestionnaireДокумент7 страницThesis QuestionnaireJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Curriculum VitaeДокумент3 страницыCurriculum VitaeJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- C-13 With AnimationsДокумент12 страницC-13 With AnimationsJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Proposed BudgetДокумент2 страницыProposed BudgetJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Gantt Chart for Pre-Operating Activities of a Food BusinessДокумент1 страницаGantt Chart for Pre-Operating Activities of a Food BusinessJangshik Babo100% (1)
- What Is Gender ?: - Gender Is The Range of Physical, Biological, Mental andДокумент2 страницыWhat Is Gender ?: - Gender Is The Range of Physical, Biological, Mental andJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Baltar, Joanna Marie D.Документ3 страницыBaltar, Joanna Marie D.Jangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- OverloadДокумент2 страницыOverloadJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- College of Accountancy Sta. Mesa Manila: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesДокумент1 страницаCollege of Accountancy Sta. Mesa Manila: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Accounting Information Systems and The Accountants (FINISHED)Документ13 страницChapter 1 - Accounting Information Systems and The Accountants (FINISHED)Jangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- QuestionnaireДокумент8 страницQuestionnaireJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Two Criteria For A Powerful Vision StatementДокумент3 страницыTwo Criteria For A Powerful Vision StatementJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- CSRДокумент7 страницCSRJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- MDH Sustainability Report 2011Документ52 страницыMDH Sustainability Report 2011Jangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- MacbethДокумент13 страницMacbethJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- © Association For Scientific Research: Mathematical and Computational Applications, Vol. - , No. - , Pp.Документ12 страниц© Association For Scientific Research: Mathematical and Computational Applications, Vol. - , No. - , Pp.Jangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Bond Valuation FundamentalsДокумент5 страницBond Valuation FundamentalsJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- TMC09ARДокумент43 страницыTMC09ARJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Load Central Product CodesДокумент41 страницаLoad Central Product CodesObed AndalisОценок пока нет
- Transportation Problem 1Документ26 страницTransportation Problem 1catchsachitaОценок пока нет
- Bengar IndustrialДокумент4 страницыBengar IndustrialJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- ContactsДокумент1 страницаContactsJangshik BaboОценок пока нет
- Your NameДокумент1 страницаYour Namekarencook21Оценок пока нет
- POM Samplech01Документ24 страницыPOM Samplech01Jangshik BaboОценок пока нет