Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
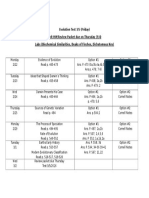
TRB Chapter 01
Загружено:
api-235160519Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TRB Chapter 01
Загружено:
api-235160519Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
ANSWERS --CHAPTER 1 PREPARING FOR THE AP EXAM MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following events has increased the impact of humans on the environment? I Advances in technology II Reduced human population growth III Use of tools for hunting (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2. I only I and II only II and III only I and III only I, II, and III
As described in this chapter, environmental indicators (a) always tell us what is causing an environmental change. (b) can be used to analyze the health of natural systems. (c) are useful only when studying large-scale changes. (d) do not provide information regarding sustainability. (e) take into account only the living components of ecosystems. Which statement regarding a global environmental indicator is not correct? (a) Concentrations of atmospheric carbon dioxide have been rising quite steadily since the Industrial Revolution. (b) World grain production has increased fairly steadily since 1950, but worldwide production of grain per capita has decreased dramatically over the same period. (c) For the past 130 years, average global surface temperatures have shown an overall increase that seems likely to continue. (d) World population is expected to be between 8.1 billion and 9.6 billion by 2050. (e) Some natural resources are available in finite amounts and are consumed during a onetime use, whereas other finite resources can be used multiple times through recycling. Figure 1.8 (on page 10) shows atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations over time. The measured concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is an example of (a) a sample of air from over the Antarctic. (b) an environmental indicator. (c) replicate sampling. (d) calculating an ecological footprint. (e) how to study seasonal variation in Earths temperatures. In science, which of the following is the most certain? (a) Hypothesis (b) Idea (c) Natural law (d) Observation (e) Theory
3.
4.
5.
BFW Publishers
Chapter 1: Studying The State of Our Earth
15
6.
All of the following would be exclusively caused by anthropogenic activities except (a) combustion of fossil fuels. (b) overuse of resources such as uranium. (c) forest clearing for crops. (d) air pollution from burning oil. (e) forest fires. Use figure 1.6 (on page 9) to calculate the approximate rate of change in world grain production per person between 1950 and 2000. (a) 10 percent (b) 20 percent (c) 30 percent (d) 40 percent (e) 50 percent The populations of some endangered animal species have stabilized or increased in numbers after human intervention. An example of a species that is still endangered and needs further assistance to recover is the (a) American bison. (b) peregrine falcon. (c) bald eagle. (d) American alligator. (e) snow leopard.
7.
8.
Questions 9 and 10 refer to the following experimental scenario: An experiment was performed to determine the effect of caffeine on the pulse rate of five healthy 18year-old males. Each was given 250 mL of a beverage with or without caffeine. The men had their pulse rates measured before they had the drink (time 0 minutes) and again after they had been sitting at rest for 30 minutes after consuming the drink. The results are shown in the following table. Subject Beverage Caffeine content (mg/serving) 1 2 3 4 5 Water Caffeine-free soda Caffeinated soda Coffee, decaffeinated Coffee, regular 0 0 10 3 45 Pulse rate 0 minutes 60 55 58 62 58 Pulse rate 30 minutes 59 56 68 67 81
16
Friedland & Relyea Environmental Science for AP*
BFW Publishers
9.
Before the researchers began the experiment, they formulated a null hypothesis. The best null hypothesis for the experiment would be that caffeine (a) has no observable effect on the pulse rate of an individual. (b) will increase the pulse rates of all test subjects. (c) will decrease the pulse rates of all test subjects. (d) has no observable effects on the pulse rates of 18-year-old males. (e) from a soda will have a greater effect on pulse rates than caffeine from coffee. After analyzing the results of the experiment, the most appropriate conclusion would be that caffeine (a) increased the pulse rates of the 18-year old males tested. (b) decreased the pulse rates of the 18-year-old males tested. (c) will increase the pulse rate of any individual that is tested. (d) increases the pulse rate and is safe to consume. (e) makes drinks better than decaffeinated beverages.
10.
FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS
1. Your neighbor has fertilized her lawn. Several weeks later, she is alarmed to see that the surface of her ornamental pond, which sits at the bottom of the sloping lawn, is covered with a green layer of algae. (a) Suggest a feasible explanation for the algal bloom in the pond. (2 points)
It is most likely that too much fertilizer was applied to the lawn. When it rained some of the run-off flowed down the sloping lawn and entered the ornamental pond. This increased the nutrient supply in the pond and resulted in an algal bloom a few weeks later. (b) Design an experiment that would enable you to validate your explanation. (7 points) Include and label in your answer: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) a testable hypothesis. (2 points) the variable that you will be testing. (1 point) the data to be collected. (1 point) a description of the experimental procedure. (2 points) a description of the results that would validate your hypothesis. (1 point)
An example experiment could be: The experiment will test the hypothesis that fertilizer will promote the growth of pond algae in water. The variable that will be tested is the amount of fertilizer that will be added to each experimental group. The data that will be collected is the amount of algae growth in each of the experimental groups. The experiment will be performed using the following procedure: A sample of the pond water is obtained and filtered through a paper towel. The algae left on the paper towel is transferred to a container of distilled water (1L) and mixed thoroughly.
BFW Publishers
Chapter 1: Studying The State of Our Earth
17
50 mL of the diluted algae solution is measured into five identical small clear glass containers. The following amounts of fertilizer are put into the containers and mixed thoroughly: 0.00 g into container 1 0.25g into container 2 0.50g into container 3 0.75g into container 4 1.00g into container 5 The above steps are repeated another three times to use up all of the 1L of the algae mixture and providing a total of four experimental groups. That is, the experiment is repeated four times. The containers with no (0g of) fertilizer represent the control group. Each of the labeled glass containers is placed on a sunny windowsill and monitored on a daily basis. The glass containers are compared for algal growth by assessing the green coloration of each container. (This could be done qualitatively as described above and/or compared to the color of 50ml of water taken directly from the surface of the pond with the algal bloom OR quantitatively by using a colorimeter if one is available). It is expected that between 3 and 7 days, depending on the amount of sunlight, more algal growth will be evident in the containers that have fertilizer added to them. The amount of algae will depend on the amount of fertilizer that was added-the more fertilizer, the more algae. This result validates the hypothesis that fertilizer will promote the growth of pond algae in water. This also helps to validate the explanation in (a) above. (c) Based on the data from your experiment and your explanation of the problem, think of, and suggest, one action that your neighbor could take to help the pond recover. (1 point) It may be difficult to get the pond to recover immediately due to the high level of fertilizer that was added to the lawn. The algae growth may continue until all the fertilizer has runoff from the lawn. The neighbor should NOT apply any more fertilizer to the lawn. She needs to use a soil test kit and assess the nutrient levels of the lawn. Using a mulching lawn mower will help restore nutrient levels naturally. The algae in the pond could be harvested or scooped off when it is in a quantity that enables this to occur. This could also be done in conjunction with drawing down the level of the pond water and replacing it with freshwater. This will help dilute the nutrient level in the pond. She could also plant vegetation on the side of the pond that is facing up the slope. This will help reduce nutrient input from runoff water when it rains, as the plants will take up the nutrients before runoff enters the pond.
2.
The study of environmental science sometimes involves examining the overuse of environmental resources. (a) Identify one general effect of overuse of an environmental resource. (3 points) Possible answers could include cutting down trees, which leads to massive erosion. Other answers could be loss of soil, which caused food production to decrease and overuse of needed water resources.
18
Friedland & Relyea Environmental Science for AP*
BFW Publishers
(b) For the effect you listed above, describe a more sustainable strategy for resource utilization. (3 points) Possible answers could include any of the sustainable development ideas from page 12. For example, practices such as conserving and finding alternatives to nonrenewable resources as well as protecting the capacity of the environment to continue to supply renewable resources. Recycling and reuse are other possible answers with a suitable discussion of the strategy. (c) Describe how past events from Easter Island can indicate environmental issues on Earth today. (4 points) Answers can include a discussion of how environmental scientists believe that there are limits to the supply of clean air and water, nutritious foods, and other life-sustaining resources our environment provides. They also feel there is a point at which Earth will no longer be able to maintain a stable climate.
MEASURING YOUR IMPACT
Exploring Your Footprint Make a list of the activities you did today and attempt to describe their impact on the five global environmental indicators described in this chapter. For each activity, such as eating lunch or traveling to school, make as complete a list as you can of the resources and fuels that went into the activity and try to determine the impacts of using those resources. After completing your inventory, visit the Web site of the Global Footprint Network (www.footprintnetwork.org) and complete the personal footprint calculator. Compare the impacts you described with the impacts you are asked to identify in the personal footprint calculator. A student could mention many ideas here. Possible answers might include driving to school, eating lunch, taking a shower, washing dishes, taking out the trash, talking on a cell phone, etc. For each activity students are to list the resources and fuels that went into that activity. If a student mentioned washing dishes, he or she might say that water, coal, and soap were resources and fuels that went into that activity. If the student said eating lunch, he or she could list all the foods that are found in that lunch, where those came from (vegetables, meat, etc.) and the bag that holds it. Fuel was used to transport the food to and from the store as well as in the processing of that food. After completing the personal footprint calculator, the student should think of other activities that they didnt include before. Examples include the fact that students live in a home, drive to school, have electricity, and eat items that are not grown locally. The footprint calculator also has students think about things like how many miles per gallon their car gets, how large their house is, and how many people live in that home. Chances are the student didnt include many of these in his or her daily activities.
CHAPTER 1 PREPARED QUIZ AND TEST
To save paper and reduce waste, we have placed the prepared quiz for this chapter on the Teachers Resource CD. It may also be downloaded from the password protected Teachers side of the Book Companion Web site: www.bfwpub.com/highschool/FriedlandAPES
BFW Publishers
Chapter 1: Studying The State of Our Earth
19
Вам также может понравиться
- Earth Science: Water Resources: Waste Generation and ManagementДокумент38 страницEarth Science: Water Resources: Waste Generation and ManagementCK BernalОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Biofilter Treatment of Aquaculture Water For Reuse ApplicationsДокумент12 страницBiofilter Treatment of Aquaculture Water For Reuse ApplicationsDavid BorgesОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2020Документ27 страницCBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2020ved bhaskerОценок пока нет
- Periphyton: Functions and Application in Environmental RemediationОт EverandPeriphyton: Functions and Application in Environmental RemediationОценок пока нет
- Gek1522t - Gek1522t s2 - 2013 - End Term Q&AДокумент10 страницGek1522t - Gek1522t s2 - 2013 - End Term Q&AraynimohdОценок пока нет
- Biology Class 12 NCERT Solutions Chapter 16 Environmental IssuesДокумент13 страницBiology Class 12 NCERT Solutions Chapter 16 Environmental IssuesV A Prem KumarОценок пока нет
- The Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualОт EverandThe Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualОценок пока нет
- Biology - Freeman 3E - Ecology Chapter 54 QuizДокумент14 страницBiology - Freeman 3E - Ecology Chapter 54 QuizEtoileCamelliaОценок пока нет
- SECTION I. USE OF ENGLISH (35 X 1 35 Points) Choose The Most Suitable Alternatives To Complete The Following Texts. Text 1Документ11 страницSECTION I. USE OF ENGLISH (35 X 1 35 Points) Choose The Most Suitable Alternatives To Complete The Following Texts. Text 1ergunesozlmОценок пока нет
- BC Provincial Exam - Sample AДокумент46 страницBC Provincial Exam - Sample AmaxbwОценок пока нет
- Biology Paper 2 by Andy Tse: InstructionsДокумент8 страницBiology Paper 2 by Andy Tse: InstructionsnonameОценок пока нет
- How Substances Impact the EnvironmentДокумент10 страницHow Substances Impact the EnvironmentArjan BhargavaОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 40Документ8 страницSample Paper: Time: 90 Minutes Max. Marks: 40Absar AlamОценок пока нет
- Biology Sample Test PDFДокумент45 страницBiology Sample Test PDFCj CaoОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 10 Science Previous Year Question Paper 2020Документ174 страницыCBSE Class 10 Science Previous Year Question Paper 2020RITESH RajОценок пока нет
- Paket 4 Text 1 1.e 6.d 11.b 2.b 7.a 12.b 3.c 8.c 13.b 4.d 9.b 14.b 5.e 10.d 15.dДокумент4 страницыPaket 4 Text 1 1.e 6.d 11.b 2.b 7.a 12.b 3.c 8.c 13.b 4.d 9.b 14.b 5.e 10.d 15.dIndah LestariОценок пока нет
- Activity 4-BORREДокумент4 страницыActivity 4-BORRELara Mae Felizardo BorreОценок пока нет
- Science CFA - Energy TransferДокумент6 страницScience CFA - Energy TransferHelina AmbayeОценок пока нет
- K G K SCH Z21va3Vzc2lja0BidWZmYWxvc2Nob29scy5vcmc Human Impact BellworkДокумент7 страницK G K SCH Z21va3Vzc2lja0BidWZmYWxvc2Nob29scy5vcmc Human Impact Bellwork9200 shotsОценок пока нет
- Our Environment Class X QuestionsДокумент7 страницOur Environment Class X Questionscontacts2021allОценок пока нет
- APES Aquatic Ecology TestДокумент10 страницAPES Aquatic Ecology Testasoni98Оценок пока нет
- APES Chapters 1&2 Study GuideДокумент7 страницAPES Chapters 1&2 Study GuideAlan PeckОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 QuizДокумент3 страницыChapter 2 QuizIvaОценок пока нет
- Ap Practice Exam With FRQДокумент41 страницаAp Practice Exam With FRQVanessa LuoОценок пока нет
- HKDSE Biology Exercise Vol1Документ9 страницHKDSE Biology Exercise Vol1Alexey Yagudin Wong0% (1)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityДокумент2 страницыGujarat Technological Universitykapiljoshi007Оценок пока нет
- Eutrophication ExperimentsДокумент6 страницEutrophication ExperimentsBiancaОценок пока нет
- Section D: Ecology and The Environment: EcosystemsДокумент5 страницSection D: Ecology and The Environment: EcosystemsMD MotinОценок пока нет
- Class 10 (2022-23) Environment TestДокумент2 страницыClass 10 (2022-23) Environment TestThe Dragon sniper gamingОценок пока нет
- BSC1060 Practice Quiz Chapter 1Документ9 страницBSC1060 Practice Quiz Chapter 1jproyaleОценок пока нет
- 1.018/7.30J Ecology 1: The Earth System Problem Set 2, Fall 2009 Assigned: Ses #9 Due: Ses #13 at The Beginning of ClassДокумент4 страницы1.018/7.30J Ecology 1: The Earth System Problem Set 2, Fall 2009 Assigned: Ses #9 Due: Ses #13 at The Beginning of ClassMovie Scene BankОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Environment The Science Behind The Stories 4th Edition WithgottДокумент15 страницTest Bank For Environment The Science Behind The Stories 4th Edition WithgottLawrence Walker100% (35)
- Integral FisicoQuimicaДокумент5 страницIntegral FisicoQuimicaMarco LegnameОценок пока нет
- Simple Electrometric Methods For Estimating Microbial Activity in Aquaculture PondsДокумент11 страницSimple Electrometric Methods For Estimating Microbial Activity in Aquaculture PondsPriscilla CelesОценок пока нет
- Australian Biology Olympiad 2008Документ31 страницаAustralian Biology Olympiad 2008Science Olympiad BlogОценок пока нет
- English Worksheet For Class 10Документ4 страницыEnglish Worksheet For Class 10DhrubОценок пока нет
- Injso 2015 QPДокумент22 страницыInjso 2015 QPTonya CruzОценок пока нет
- Climate Change Module LessonsДокумент14 страницClimate Change Module Lessonsserry gupit0% (1)
- IMSO 2009 Problem Set For Theory 2Документ16 страницIMSO 2009 Problem Set For Theory 2Marilyn CitadelОценок пока нет
- Association of Teachers in Biological Sciences: National Standard Examination in Biology 2012-2013Документ17 страницAssociation of Teachers in Biological Sciences: National Standard Examination in Biology 2012-2013Mrinal ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- SBI Clerk Mains Model Question Paper Set 5Документ77 страницSBI Clerk Mains Model Question Paper Set 5anand kumarОценок пока нет
- Nicolas Arturo Jaramillo Garrido - Cycles2Документ2 страницыNicolas Arturo Jaramillo Garrido - Cycles2Nicolas arturo Jaramillo GarridoОценок пока нет
- Carbon Decomposition in An Organic Farming SystemДокумент30 страницCarbon Decomposition in An Organic Farming SystemAndrae GenusОценок пока нет
- Technologies For Domestic Wastewater Recycling: B. Je Erson, A. Laine, S. Parsons, T. Stephenson, S. JuddДокумент8 страницTechnologies For Domestic Wastewater Recycling: B. Je Erson, A. Laine, S. Parsons, T. Stephenson, S. JuddTan TanОценок пока нет
- 2021 Biological Treatment of Saline Domestic Wastewater by Using A Down-Flow Hanging Sponge ReactorДокумент7 страниц2021 Biological Treatment of Saline Domestic Wastewater by Using A Down-Flow Hanging Sponge ReactorEddie D SouzaОценок пока нет
- Biogas Productionfrom Algae Biomass Harvestedat Wastewater TreaДокумент5 страницBiogas Productionfrom Algae Biomass Harvestedat Wastewater TreaNitin PatilОценок пока нет
- ACT Biology-Dr. Rehab Final Revision 1Документ10 страницACT Biology-Dr. Rehab Final Revision 1m.mansoor3377Оценок пока нет
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionДокумент4 страницыMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionVedavatyBadaravadaОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Assessment Task AnalysisДокумент3 страницыModule 3 Assessment Task AnalysisHans Ivan MañuscaОценок пока нет
- Answer 1:: Wastes Generated at HomeДокумент8 страницAnswer 1:: Wastes Generated at HomeMax SmithОценок пока нет
- Kibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 FinalДокумент15 страницKibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 Finalmins.succesorОценок пока нет
- FINAL-Greywater Edited Feb 9Документ35 страницFINAL-Greywater Edited Feb 9Jomaica Mabanag TuayonОценок пока нет
- Civil Questions and Answers-Other-Major-TopicsДокумент39 страницCivil Questions and Answers-Other-Major-TopicsAkd Deshmukh100% (1)
- Skema Jawapan Solaf 2 SainsДокумент10 страницSkema Jawapan Solaf 2 SainsFidaОценок пока нет
- Seed GerminationДокумент37 страницSeed GerminationAlyОценок пока нет
- BAB 7. Restating SentenceДокумент5 страницBAB 7. Restating SentenceLentera DakwahОценок пока нет
- Le Review Calendar2016Документ2 страницыLe Review Calendar2016api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Unit 7 Hw914sheet2015Документ3 страницыUnit 7 Hw914sheet2015api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Feeding The World Health Toxicology 1545076398844 TCДокумент11 страницFeeding The World Health Toxicology 1545076398844 TCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Feeding The World Health Toxicology 1545076400199 SCДокумент9 страницFeeding The World Health Toxicology 1545076400199 SCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Evolutionhwpacket 2016Документ9 страницEvolutionhwpacket 2016api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Unit12nutexcresphw Sheet Miller2016Документ1 страницаUnit12nutexcresphw Sheet Miller2016api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- 2015nutrespexc ReviewpacketanswerkeyДокумент6 страниц2015nutrespexc Reviewpacketanswerkeyapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Millercircimmunehw SheetДокумент2 страницыMillercircimmunehw Sheetapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- CircimmhwpacketДокумент8 страницCircimmhwpacketapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- 2016nutexcresp HW PacketДокумент6 страниц2016nutexcresp HW Packetapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Air Pollution Climate Change TCДокумент12 страницAir Pollution Climate Change TCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Evolution Test 3/5 (Friday) Unit HW/Review Packet Due On Thursday (3/4) Labs (Biochemical Similarities, Beaks of Finches, Dichotomous Key)Документ1 страницаEvolution Test 3/5 (Friday) Unit HW/Review Packet Due On Thursday (3/4) Labs (Biochemical Similarities, Beaks of Finches, Dichotomous Key)api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- 2015nutrespexc ReviewpacketДокумент7 страниц2015nutrespexc Reviewpacketapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Air Pollution Climate Change SCДокумент11 страницAir Pollution Climate Change SCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Evolution Reviewpacketanswer KeyДокумент5 страницEvolution Reviewpacketanswer Keyapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Water Resources Water Pollution TCДокумент7 страницWater Resources Water Pollution TCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- RevewipacketanswerkeyrevisedДокумент5 страницRevewipacketanswerkeyrevisedapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Water Resources Water Pollution SCДокумент6 страницWater Resources Water Pollution SCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- 2016 ProteinsynthesishwsheetДокумент1 страница2016 Proteinsynthesishwsheetapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- 2015proteinsynthesishw PacketДокумент7 страниц2015proteinsynthesishw Packetapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- ModerngeneticshwmillerДокумент1 страницаModerngeneticshwmillerapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Genetics Review Packe2016answerkeyДокумент5 страницGenetics Review Packe2016answerkeyapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Geneticengineeringhwpacket 2016Документ5 страницGeneticengineeringhwpacket 2016api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- HintДокумент4 страницыHintapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- 2016 ProteinsynthesishwsheetДокумент1 страница2016 Proteinsynthesishwsheetapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- 2015proteinsynthesishw PacketДокумент7 страниц2015proteinsynthesishw Packetapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Geology and Nre TCДокумент7 страницGeology and Nre TCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Review Packetmeiosisgeneticsanswerkey2015Документ5 страницReview Packetmeiosisgeneticsanswerkey2015api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Geology and Nre SCДокумент6 страницGeology and Nre SCapi-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Reviewpacket 2015Документ6 страницReviewpacket 2015api-235160519Оценок пока нет
- Litz Wire Termination GuideДокумент5 страницLitz Wire Termination GuideBenjamin DoverОценок пока нет
- The German eID-Card by Jens BenderДокумент42 страницыThe German eID-Card by Jens BenderPoomjit SirawongprasertОценок пока нет
- PA2 Value and PD2 ValueДокумент4 страницыPA2 Value and PD2 Valueguddu1680Оценок пока нет
- War, Rivalry An State Building in Latin AmericaДокумент16 страницWar, Rivalry An State Building in Latin AmericaPablo Andrés Garrido GonzálezОценок пока нет
- RoutineHub - R Download - iOS 13, 14, 15, 2Документ1 страницаRoutineHub - R Download - iOS 13, 14, 15, 2Gabriell AnjosОценок пока нет
- Template - Time in ManufacturingДокумент2 страницыTemplate - Time in ManufacturingVero RoaОценок пока нет
- Recent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVAДокумент7 страницRecent Developments in Ultrasonic NDT Modelling in CIVAcal2_uniОценок пока нет
- Grade 4 DLL Quarter 2 Week 2 Sir Bien CruzДокумент47 страницGrade 4 DLL Quarter 2 Week 2 Sir Bien CruzRonel Fillomena0% (1)
- Videocon ProjectДокумент54 страницыVideocon ProjectDeepak AryaОценок пока нет
- CE ProblemДокумент5 страницCE ProblemJho FОценок пока нет
- Samuel Vizcaino: Professional ProfileДокумент3 страницыSamuel Vizcaino: Professional ProfileVizcaíno SamuelОценок пока нет
- Expt 1 Yarn Formation (Sherley Trash Analyser)Документ7 страницExpt 1 Yarn Formation (Sherley Trash Analyser)Yashdeep Sharma0% (1)
- Process of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeДокумент5 страницProcess of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeSantosh Kumar MahtoОценок пока нет
- Current Developments in Testing Item Response Theory (IRT) : Prepared byДокумент32 страницыCurrent Developments in Testing Item Response Theory (IRT) : Prepared byMalar VengadesОценок пока нет
- Ownership and Governance of State Owned Enterprises A Compendium of National Practices 2021Документ104 страницыOwnership and Governance of State Owned Enterprises A Compendium of National Practices 2021Ary Surya PurnamaОценок пока нет
- Snorkeling: A Brief History and Guide to This Underwater AdventureДокумент3 страницыSnorkeling: A Brief History and Guide to This Underwater AdventureBernadette PerezОценок пока нет
- Kanavos Pharmaceutical Distribution Chain 2007 PDFДокумент121 страницаKanavos Pharmaceutical Distribution Chain 2007 PDFJoao N Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- Reasons Why Coca Cola Has A Large Market Share in Kenya and The WorldДокумент9 страницReasons Why Coca Cola Has A Large Market Share in Kenya and The WorldAludahОценок пока нет
- Leica CS10 CS15 GSSensors QG v3.0.1 en PDFДокумент16 страницLeica CS10 CS15 GSSensors QG v3.0.1 en PDFMohammad Saiful AzamОценок пока нет
- Italian Painters 02 MoreДокумент450 страницItalian Painters 02 Moregkavvadias2010Оценок пока нет
- Explanation of Four Ahadeeth From Imaam Al-Bukhaaree's Al-Adab-Ul-MufradДокумент4 страницыExplanation of Four Ahadeeth From Imaam Al-Bukhaaree's Al-Adab-Ul-MufradMountainofknowledgeОценок пока нет
- Graphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasДокумент11 страницGraphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasMargie Tirado JavierОценок пока нет
- T Cells & Autoimmunity, s3Документ21 страницаT Cells & Autoimmunity, s3LiaAriestaОценок пока нет
- Ceeshsworkingstudents Abm Group2Документ18 страницCeeshsworkingstudents Abm Group2kzz9c5hqrwОценок пока нет
- Magnets Catalog 2001Документ20 страницMagnets Catalog 2001geckx100% (2)
- Department of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityДокумент2 страницыDepartment of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityRica Tano50% (2)
- Oreilly Design For Voice InterfacesДокумент37 страницOreilly Design For Voice InterfacesHarmony JordenОценок пока нет
- How To Oven and Sun Dry Meat and ProduceДокумент12 страницHow To Oven and Sun Dry Meat and ProduceLes BennettОценок пока нет
- Bahasa InggrisДокумент8 страницBahasa InggrisArintaChairaniBanurea33% (3)
- Delhi Mumbai Award Status Mar 23Документ11 страницDelhi Mumbai Award Status Mar 23Manoj DoshiОценок пока нет
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterОт EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterОценок пока нет
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersОт EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersОценок пока нет
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastОт EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (31)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityОт EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesОт EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (21)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosОт EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (8)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeОт EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- The Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and VaporОт EverandThe Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and VaporРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)
- Ruthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterОт EverandRuthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (11)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeОт EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersОт EverandA Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (111)
- The Story of Stuff: How Our Obsession with Stuff is Trashing the Planet, Our Communities, and Our Health-and a Vision for ChangeОт EverandThe Story of Stuff: How Our Obsession with Stuff is Trashing the Planet, Our Communities, and Our Health-and a Vision for ChangeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (37)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (111)
- The Finest Hours: The True Story of the U.S. Coast Guard's Most Daring Sea RescueОт EverandThe Finest Hours: The True Story of the U.S. Coast Guard's Most Daring Sea RescueРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)