Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
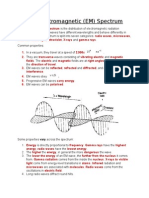
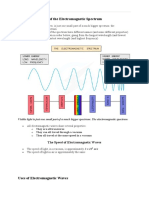
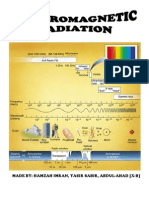
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Загружено:
Shamoose AlaaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Загружено:
Shamoose AlaaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
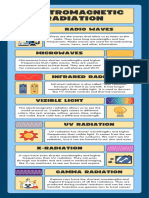
GAMMA RAY:
Gamma Radiation cannot be seen or felt, it mostly passes through skin and tissue but some of it is absorbed by cells. Gamma waves have a very high frequency. We use Gamma Radiation for to sterilise surgical instruments and to kill harmful bacteria in food. In general, exposure to Gamma Radiation is dangerous as it can make cells cancerous.
X-RAYS:
X-Rays are like Gamma Rays as they cannot be seen or felt. X-Rays mostly pass through skin and soft tissue but they dont easily pass through bone or metal. This makes them suitable for medical imaging, for checking for metal components and welds for cracks or other damage.
ULTRAVIOLET:
Ultraviolet radiation is found naturally in sunlight. We cannot see or feel it, but our skin responds to it by turning darker. Ultraviolet radiation is used in sun beds, security pens and
in fluorescent lights. Coatings inside the tube or bulb absorb the ultraviolet light and re-emit it as visible light.
VISIBLE LIGHT:
All the light we can see fits in here. To remember the colours in order of wavelength think of a rainbow. Violet has the shortest and red has the longest wavelengths in the visible spectrum. If we keep stretching the wavelength of visible red light we get to infrared.
INFRARED:
Infrared is an invisible radiation. Infrared is absorbed by the skin and we feel it as heat. It is used in heaters, grills and toasters. It is also used for television remote controls and in optical fibre communications.
MICROWAVES:
Microwave radiation has even longer wavelengths. Water in food can absorb microwave radiation, which is how food heats up in a microwave oven. Microwave radiation is also used to transmit mobile phone signals. Microwave transmitters and receivers on buildings and masts communicate with the mobile telephones in their range.
RADIO WAVES:
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths of all, which means they have the lowest frequencies too. They are used to transmit television and radio programmes. Some wavelengths of radio waves are diffracted by the ground, which means they can be received behind hills, and some radio transmissions can be reflected off a layer of the atmosphere called the ionosphere. This means radio signals can be sent around the world without using satellites.
Вам также может понравиться
- Electromagnetic Spectrum:: Common Properties of em WavesДокумент3 страницыElectromagnetic Spectrum:: Common Properties of em Wavesgwen_frenz2500Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент11 страницElectromagnetic SpectrumamyrulerzОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Applications of EM WavesДокумент28 страницModule 2 - Applications of EM WavesMariane HinanibanОценок пока нет
- RadiacionДокумент1 страницаRadiacionEduardo HerreraОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент2 страницыScienceLorin Louise P. AquinoОценок пока нет
- Elctronic RadiationДокумент4 страницыElctronic RadiationTia WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Science PT 2nd QRTR 1Документ29 страницScience PT 2nd QRTR 1Rayver Chris VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- THE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilДокумент10 страницTHE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilHannah Joy DulayОценок пока нет
- Em SpectrumДокумент24 страницыEm SpectrumFender CoomstoneОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Module 2Документ2 страницыUnit 2 Module 2heide100% (1)
- PhysicsДокумент2 страницыPhysicsGayathri GirishОценок пока нет
- Uses of EM WavesДокумент3 страницыUses of EM WavesPallika DhingraОценок пока нет
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент10 страницThe Electromagnetic SpectrumTharanya LinganathanОценок пока нет
- Science 10 Lesson2 EM Waves ApplicationsДокумент32 страницыScience 10 Lesson2 EM Waves ApplicationsJean LaguitanОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic WavesДокумент11 страницElectromagnetic WavesSherazОценок пока нет
- Light EnergyДокумент2 страницыLight EnergyMa Catherine DiazОценок пока нет
- EM SpectrumДокумент6 страницEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Radio WavesДокумент4 страницыRadio WavesSophia Nicole ZaraОценок пока нет
- Radiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyДокумент42 страницыRadiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyChristine Marielle Claroniño ApoОценок пока нет
- Introduction To EM SpectrumДокумент8 страницIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattОценок пока нет
- Untitled DocumentДокумент6 страницUntitled DocumentMichaela CuarteroОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic RadiationДокумент5 страницElectromagnetic Radiationangelagranada.workОценок пока нет
- 1..radio Waves 2.gamma Waves 3.red 4. Violet 5.. Infrared 6.. X-Ray 7..gamma RaysДокумент1 страница1..radio Waves 2.gamma Waves 3.red 4. Violet 5.. Infrared 6.. X-Ray 7..gamma RaysJackielyn A. LunaОценок пока нет
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Документ7 страницThe Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Nur-shima SakilinОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент40 страницElectromagnetic Spectrumtripathiansh447Оценок пока нет
- Complete Waves o Level 2023Документ26 страницComplete Waves o Level 2023Absar KhaskheliОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент40 страницElectromagnetic Spectrummike ebioОценок пока нет
- Concept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesДокумент4 страницыConcept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesLunaОценок пока нет
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Документ15 страницScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaОценок пока нет
- Radio and Television Signlas: Radio Waves Are Used For Communication Such As Broadcasting Television and RadioДокумент4 страницыRadio and Television Signlas: Radio Waves Are Used For Communication Such As Broadcasting Television and RadioPA-MAHINAY, Joven O.Оценок пока нет
- Applications of EM of WavesДокумент9 страницApplications of EM of WavesashleynicolecalinawanОценок пока нет
- Parts & Properties of Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент3 страницыParts & Properties of Electromagnetic SpectrumFaiq IrfanОценок пока нет
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент4 страницы3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDhanBahadurОценок пока нет
- Types of Electromagnetic WavesДокумент15 страницTypes of Electromagnetic Wavesphoebecruz636Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент13 страницElectromagnetic Spectrumehan.ilrnestersОценок пока нет
- The EM Spectrum RecapДокумент10 страницThe EM Spectrum RecapYusuf AlamОценок пока нет
- Sci 10 PPT - em WavesДокумент27 страницSci 10 PPT - em WavesDioscora S. GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Waves Reading PassageДокумент2 страницыWaves Reading PassagedavidОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент13 страницElectromagnetic SpectrumMaryam ShahidОценок пока нет
- 27-Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент43 страницы27-Electromagnetic Spectrumtouch grassОценок пока нет
- EM WavesДокумент11 страницEM WavesHomok Noki100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum 20232024Документ15 страницElectromagnetic Spectrum 20232024WowОценок пока нет
- Nature of LightДокумент25 страницNature of LightPremnath KrishnasamyОценок пока нет
- By NaanaДокумент29 страницBy Naanajuicypine14Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент33 страницыElectromagnetic Waves and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDanae Forrester100% (1)
- Vibration and Waves: Electromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент43 страницыVibration and Waves: Electromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumrancesОценок пока нет
- Industrial Application of Gamma RaysДокумент3 страницыIndustrial Application of Gamma RaysJephte MantalabaОценок пока нет
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент15 страницThe Electromagnetic SpectrumJohnRenzoMolinarОценок пока нет
- Waves of The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент4 страницыWaves of The Electromagnetic SpectrumVanessa CaballeroОценок пока нет
- Em Wave and em SpectrumДокумент22 страницыEm Wave and em Spectrummilk teaОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент34 страницыElectromagnetic SpectrumShinpay doodles100% (1)
- Made By: Hamzah Imran, Yasir Sabir, Abdul-Ahad (X-B)Документ12 страницMade By: Hamzah Imran, Yasir Sabir, Abdul-Ahad (X-B)Hamza ImranОценок пока нет
- LESSON 1. Electromagnetic Sgypectrum NOTESДокумент38 страницLESSON 1. Electromagnetic Sgypectrum NOTESRyan Aint simpОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент33 страницыElectromagnetic SpectrumReynald AntasoОценок пока нет
- 1 - Forms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumДокумент3 страницы1 - Forms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumMisha WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic WavesДокумент21 страницаElectromagnetic WavesCrisanta GanadoОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент43 страницыElectromagnetic SpectrumRin Kiyoshi Hazumi-FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Sim 10Документ13 страницSim 10Denver CarriagaОценок пока нет
- Table 6.2. Acidity of Some Hydrocarbons: Entry Hydrocarbon Cs (CHA) Cs (THF) K (DMSO)Документ1 страницаTable 6.2. Acidity of Some Hydrocarbons: Entry Hydrocarbon Cs (CHA) Cs (THF) K (DMSO)panda biruОценок пока нет
- AMMAN Is Hiring!Документ1 страницаAMMAN Is Hiring!Mine 77Оценок пока нет
- Myritol® 318Документ4 страницыMyritol® 318hadjer djemiliОценок пока нет
- FiltrasiДокумент4 страницыFiltrasiRusydinaОценок пока нет
- Study On Mechanical Properties of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Short Columns Under Different Curing TemperaturesДокумент12 страницStudy On Mechanical Properties of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Short Columns Under Different Curing TemperaturesTJPRC PublicationsОценок пока нет
- Engineering Physics Questions and AnswersДокумент95 страницEngineering Physics Questions and AnswersSheambom Nelson100% (1)
- QC Chart - Graphite AAS - DRAFTДокумент13 страницQC Chart - Graphite AAS - DRAFTConsultant JerocasОценок пока нет
- SAF 2205 DatasheetДокумент11 страницSAF 2205 DatasheetNitinОценок пока нет
- Wonderloy PC 540Документ2 страницыWonderloy PC 540Phung LucОценок пока нет
- Hazardous Waste ManagementДокумент20 страницHazardous Waste ManagementYuki SalemОценок пока нет
- Low Temp Separation Unit PDFДокумент2 страницыLow Temp Separation Unit PDFMaribel Apaza MamaniОценок пока нет
- New Formulations and Test Comparison For The Classification of PVC Cables Under EU Regulation N° 305/2011 For Construction ProductsДокумент29 страницNew Formulations and Test Comparison For The Classification of PVC Cables Under EU Regulation N° 305/2011 For Construction ProductsTien Dung PhanОценок пока нет
- Dangerous Goods Hazmat Material Training Cat-10Документ24 страницыDangerous Goods Hazmat Material Training Cat-10Claudio GonzalezОценок пока нет
- DNV Software: Chapter 2: Performing A Worst-Case AnalysisДокумент36 страницDNV Software: Chapter 2: Performing A Worst-Case AnalysisprashantОценок пока нет
- Some Basic ConceptsДокумент5 страницSome Basic ConceptsebooksufiОценок пока нет
- User Guide Absorber Kit System - ENДокумент12 страницUser Guide Absorber Kit System - ENMichel SpelierОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Science and Engineering of Materials 7Th Edition Askeland Wright 1305076761 978130507676 Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницSolution Manual For Science and Engineering of Materials 7Th Edition Askeland Wright 1305076761 978130507676 Full Chapter PDFjerrod.hunter322100% (11)
- MSC Analytical Chemistry SyllabusДокумент49 страницMSC Analytical Chemistry SyllabusAjay Sharma ShankyanОценок пока нет
- General Physics CH 01 PDFДокумент75 страницGeneral Physics CH 01 PDFAnonymous 0rIj5j1iОценок пока нет
- Engineering Thermodynamics - A Computer Approach (SI Units Version) - R. K. Rajput PDFДокумент431 страницаEngineering Thermodynamics - A Computer Approach (SI Units Version) - R. K. Rajput PDFShahzad Ali RanaОценок пока нет
- Goulds e SH Stainless Steel Pumps Technical Brochure BeSH R2Документ60 страницGoulds e SH Stainless Steel Pumps Technical Brochure BeSH R2Daniel Ortiz GonzálezОценок пока нет
- MSDS - HK SivekДокумент8 страницMSDS - HK SivekNoor HafidlullahОценок пока нет
- Phy MCQДокумент20 страницPhy MCQSaima ShahОценок пока нет
- International Maritime Dangerous Goods CodeДокумент45 страницInternational Maritime Dangerous Goods Codequanghoa18121973100% (2)
- Hafiz Rehan: Technical ResponsibilitiesДокумент8 страницHafiz Rehan: Technical ResponsibilitiesAdnan AhmedОценок пока нет
- Cantesto MSDSДокумент11 страницCantesto MSDSLuis ErnestoОценок пока нет
- What Is Buoyancy and Stability of Submerged Bodies.Документ14 страницWhat Is Buoyancy and Stability of Submerged Bodies.Odama KhanОценок пока нет
- Magna 55 BrazingДокумент2 страницыMagna 55 BrazingLee Chong EeОценок пока нет
- BIO307 Lecture 3 (Introduction To Enzymes)Документ13 страницBIO307 Lecture 3 (Introduction To Enzymes)Phenyo MmerekiОценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницDetailed Lesson PlanFelipe Jimenez91% (11)