Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Static Kramer Drive
Загружено:
Swagat PradhanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Static Kramer Drive
Загружено:
Swagat PradhanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Static Kramer Drive
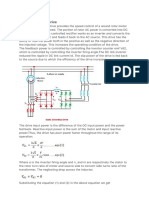
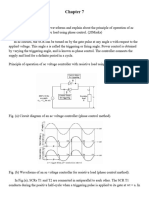
A static kramer drive is a method to obtain an injected voltage that is in phase with the rotor current. The schematic circuit for a static kramer drive is shown below
The voltage at the slip rings is forced to be in phase with the rotor currents by the diode rectifier. The magnitude of the slip ring voltage is set by the DC link voltage, which is in turn set by the inverter connected back to the AC supply. In the diagram above and the analysis presented, the inverter used is a thyristor converter. However, a PWM inverter can also be used. Simple Analysis This simple analysis of the static kramer drive illustrates the operation of the drive. It neglects the voltage drops in the drive and any possible commutation overlap in the diode rectifier. The voltage at the input to the diode rectifier is given by
and the dc link voltage can be found from the diode input line-line voltage as
Considering the thyristor converter, this circuit can be thought of as a thyristor rectifier connected in reverse, and the DC link voltage is related to the line-line inverter voltage as
Substituting the above expressions, the voltage injected into the rotor can be calculated as
In the case that the inverter line-line voltage is connected to the supply through a transformer, as shown in the diagram above, the injected voltage can be related to the supply voltage as
Using this simplified analysis together with the slip energy recovery torque equations, the thyristor firing angle required for a particular torque at a particular speed can be found. If necessary, more detailed analysis can be carried out by repeating the above process, but including device voltages and commutation overlap. Torque-Speed Because the slip ring voltage is derived using a diode bridge, the torque speed curve for a motor operated using a static kramer drive does not produce a negative torque as soon as the speed exceeds the no-load speed. If the slip is too low for a given injected voltage, the voltage induced in the rotor circuit by the stator will have a lower magnitude than the DC link voltage. As a result, no rotor current will flow and the torque will be zero. Torque speed curves for different injected voltages are animated below
Вам также может понравиться
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Рейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (3)
- Static Scherbius DriveДокумент5 страницStatic Scherbius Driveanandlm710Оценок пока нет
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОт EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Speed Control of DC MotorsДокумент27 страницSpeed Control of DC MotorsBabuKannanОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОт EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetОценок пока нет
- Answer QB 2Документ22 страницыAnswer QB 2Goud SannyОценок пока нет
- The Simplified Circle DiagramДокумент5 страницThe Simplified Circle DiagramPradeep RajasekeranОценок пока нет
- Motor PDFДокумент9 страницMotor PDFAbhishek SurinОценок пока нет
- Motor Drives BY K .Sunil Kumar Griet-Power ElectronicsДокумент4 страницыMotor Drives BY K .Sunil Kumar Griet-Power ElectronicsKalyan KumarОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryДокумент6 страницExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalОценок пока нет
- EM Assignment 2Документ7 страницEM Assignment 2M.Vijaya VarshiniОценок пока нет
- Inverters For Ac Motor DriveДокумент17 страницInverters For Ac Motor DriveAslam SdОценок пока нет
- No Load and Block Rotor Test: Premier Trading CorporationДокумент11 страницNo Load and Block Rotor Test: Premier Trading CorporationKsr Akhil100% (1)
- 25-Feb-2020 11B Converter Fed and Chopper Fed DC DrivesДокумент16 страниц25-Feb-2020 11B Converter Fed and Chopper Fed DC DrivesATULYA ALOK 17BEE0065Оценок пока нет
- PSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Документ8 страницPSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Vishal BhatОценок пока нет
- 06533563Документ8 страниц06533563MadhavanIceОценок пока нет
- DC Motors Starters and Breaking MethodsДокумент25 страницDC Motors Starters and Breaking MethodsRukkuArunОценок пока нет
- PWM and DC Motor ControlДокумент9 страницPWM and DC Motor ControlYimy GarciaОценок пока нет
- Em 1 TestingДокумент13 страницEm 1 TestingAravindОценок пока нет
- An Application of Matlab/Simulink For Speed Control of DC Series Motor Using Buck ConverterДокумент5 страницAn Application of Matlab/Simulink For Speed Control of DC Series Motor Using Buck ConverterArghya MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Induction Motor Analysis For Start-Up ProtectionДокумент11 страницInduction Motor Analysis For Start-Up ProtectionAnonymous 1AAjd0Оценок пока нет
- Electrial Machines Second ReportДокумент7 страницElectrial Machines Second ReportMohamed YahiaОценок пока нет
- Electric Machines Lab: Open Ended Lab ReportДокумент8 страницElectric Machines Lab: Open Ended Lab ReportSaadОценок пока нет
- Experiment N0 - 2Документ4 страницыExperiment N0 - 2Hapijul SanfuiОценок пока нет
- Ed Lab ManualДокумент27 страницEd Lab ManualBonnieОценок пока нет
- DC Motors Starters and Breaking MethodsДокумент25 страницDC Motors Starters and Breaking Methodskrishnareddy_chintalaОценок пока нет
- AEEE 352 Assignment 3Документ10 страницAEEE 352 Assignment 3mchris91Оценок пока нет
- Electric Drives ControlДокумент29 страницElectric Drives ControlNebyou DanielОценок пока нет
- Dynamic and Transient Behavior of A DC-motorДокумент10 страницDynamic and Transient Behavior of A DC-motorYosua SuitellaОценок пока нет
- Lab 07 - DC MotorsДокумент9 страницLab 07 - DC MotorsChamila SumathiratnaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Application in DC Motor Drives - Case Study - ss03595 - Sarwan Shah PDFДокумент6 страницPower Electronics Application in DC Motor Drives - Case Study - ss03595 - Sarwan Shah PDFMehdi Raza KhorasaniОценок пока нет
- Regenerative Braking of Induction MotorДокумент27 страницRegenerative Braking of Induction MotorcoolkannaОценок пока нет
- Speed DC MotorДокумент35 страницSpeed DC MotorDienar Adiose AljahezОценок пока нет
- DC Brush Motor TheoryДокумент7 страницDC Brush Motor Theoryjfsmenezes4534Оценок пока нет
- PROJCTДокумент32 страницыPROJCTSwati Agarwal100% (1)
- DC Drives - ConstructionДокумент10 страницDC Drives - ConstructionSuyog ShingareОценок пока нет
- 142 No Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor DolДокумент15 страниц142 No Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor DolgettinОценок пока нет
- Investigate The DC Motor CharacteristicДокумент7 страницInvestigate The DC Motor CharacteristicAhmar KhanОценок пока нет
- AC Drives and Soft Starter Application Guide - AllenBradleyCoДокумент5 страницAC Drives and Soft Starter Application Guide - AllenBradleyCojoyama100% (1)
- PWM Stepper Motor: 2-Pole Permanent Magnet MotorДокумент4 страницыPWM Stepper Motor: 2-Pole Permanent Magnet MotorSahil VoraОценок пока нет
- Basic of ElectricalДокумент10 страницBasic of ElectricalAbdul RazzakОценок пока нет
- Speed Control and Starting of A DC MotorДокумент56 страницSpeed Control and Starting of A DC MotorCarlos Arias LuyandoОценок пока нет
- Fig. 2 (A) Self Excited Induction GeneratorДокумент7 страницFig. 2 (A) Self Excited Induction GeneratorLaxmikant BagaleОценок пока нет
- Theory Em2 LabДокумент2 страницыTheory Em2 Labbalaji1986Оценок пока нет
- Unit Ii Drive ChaacteristicsДокумент26 страницUnit Ii Drive Chaacteristicssaravanakmar vОценок пока нет
- Assignment Elecrical DriveДокумент7 страницAssignment Elecrical DriveTaufik AdhaОценок пока нет
- Synchronous Motor Drives: Open Loop V/F Control of Synchronous MotorДокумент11 страницSynchronous Motor Drives: Open Loop V/F Control of Synchronous MotorSaish Dalvi100% (1)
- AVR'sДокумент3 страницыAVR'sMeghanath AdkonkarОценок пока нет
- Starting and Braking of Induction MotorДокумент15 страницStarting and Braking of Induction MotorSOURABH MONGRAОценок пока нет
- Induction Motor Braking - Regenerative, Plugging &+ PDFДокумент8 страницInduction Motor Braking - Regenerative, Plugging &+ PDFTechnical boxОценок пока нет
- Kreatryx Koncept Pock PDFДокумент8 страницKreatryx Koncept Pock PDFTechnical boxОценок пока нет
- Ied Unit VДокумент8 страницIed Unit VRudra Kumar MishraОценок пока нет
- DC2-4 Quadrant Single Phase RectifireДокумент5 страницDC2-4 Quadrant Single Phase RectifireAman SinghОценок пока нет
- Electrical Machines I: Week 13: Ward Leonard Speed Control and DC Motor BrakingДокумент15 страницElectrical Machines I: Week 13: Ward Leonard Speed Control and DC Motor Brakingmansoor.ahmed100Оценок пока нет
- Unit V: DC MotorsДокумент28 страницUnit V: DC Motorskrishnareddy_chintalaОценок пока нет
- DC MotorДокумент8 страницDC Motorven_avv3382Оценок пока нет
- Synchronous MotorДокумент5 страницSynchronous Motornaga531Оценок пока нет
- Task 4: Figure 1 Speed-Torque Curve For Ideal DC MotorДокумент19 страницTask 4: Figure 1 Speed-Torque Curve For Ideal DC MotoraqeelОценок пока нет
- IEC Exam 2023Документ15 страницIEC Exam 2023Phyo KoОценок пока нет
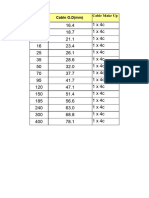
- Cable TrayДокумент12 страницCable TraySwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Cables: Welcome To Presentation OnДокумент63 страницыCables: Welcome To Presentation OnSwagat Pradhan0% (1)
- Comprehensive Design Tool For Sizing Solar Water Pumping System in EgyptДокумент12 страницComprehensive Design Tool For Sizing Solar Water Pumping System in EgyptSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- O-t-CO-T-CO: What Is O-0.3s-CO-3min-CO For A Circuit Breaker?Документ1 страницаO-t-CO-T-CO: What Is O-0.3s-CO-3min-CO For A Circuit Breaker?Swagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- 5003 PDFДокумент7 страниц5003 PDFamitbheltbgОценок пока нет
- Cable DiaДокумент1 страницаCable DiaSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Sec Floor TrayДокумент13 страницSec Floor TraySwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Sizing of PV Array For Water Pumping Application: June 2016Документ7 страницSizing of PV Array For Water Pumping Application: June 2016Swagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Improving Your Collaboration With Colleagues From Different CulturesДокумент4 страницыImproving Your Collaboration With Colleagues From Different CulturesSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Ensure The Successful Diffusion of InnovationДокумент2 страницыEnsure The Successful Diffusion of InnovationSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Results in Physics: M. Benghanem, K.O. Daffallah, A. AlmohammediДокумент6 страницResults in Physics: M. Benghanem, K.O. Daffallah, A. AlmohammediSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Ensure The Successful Diffusion of Your InnovationДокумент2 страницыEnsure The Successful Diffusion of Your InnovationSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Competency Certification in Creativity - 20073793Документ1 страницаCompetency Certification in Creativity - 20073793Swagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Boost Group Creativity: A Strong LinkДокумент2 страницыBoost Group Creativity: A Strong LinkSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Leading A Brainstorming Session: Main Principles of BrainstormingДокумент2 страницыLeading A Brainstorming Session: Main Principles of BrainstormingSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- ZJIV005 en-US PDFДокумент1 страницаZJIV005 en-US PDFSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Design A Great Customer ExperienceДокумент2 страницыDesign A Great Customer ExperienceSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Expressing Frustrations in A Constructive Manner (The Desc Method)Документ2 страницыExpressing Frustrations in A Constructive Manner (The Desc Method)Swagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- When Can The ABC Game Help Your Team Be More United and Creative?Документ1 страницаWhen Can The ABC Game Help Your Team Be More United and Creative?Swagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Analyzing A Complex Problem by Using An Issue TreeДокумент2 страницыAnalyzing A Complex Problem by Using An Issue TreeSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- How To Get Out of The Rescuer Role in ConflictДокумент1 страницаHow To Get Out of The Rescuer Role in ConflictSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Leading A Brainstorming Session: Main Principles of BrainstormingДокумент2 страницыLeading A Brainstorming Session: Main Principles of BrainstormingSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Dealing With Interpersonal Crisis: 1. in A Crisis Situation, It's Crucial To Do Something!Документ3 страницыDealing With Interpersonal Crisis: 1. in A Crisis Situation, It's Crucial To Do Something!Swagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Ensure The Successful Diffusion of Your InnovationДокумент2 страницыEnsure The Successful Diffusion of Your InnovationSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Find Creative SolutionsДокумент2 страницыFind Creative SolutionsSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Expressing Frustrations in A Constructive Manner (The Desc Method)Документ2 страницыExpressing Frustrations in A Constructive Manner (The Desc Method)Swagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Get Yourself Into A Creative Frame of Mind: Clarify Your Creative ProblemДокумент2 страницыGet Yourself Into A Creative Frame of Mind: Clarify Your Creative ProblemSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Look at A Problem Creatively: Clarify Your Creative ProblemДокумент2 страницыLook at A Problem Creatively: Clarify Your Creative ProblemSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Boost Self-Development and Innovation With Exploration DaysДокумент2 страницыBoost Self-Development and Innovation With Exploration DaysSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Boost Group Creativity: A Strong LinkДокумент2 страницыBoost Group Creativity: A Strong LinkSwagat PradhanОценок пока нет
- Flymotion Mach3 Usb Motion Card Installation ManualДокумент34 страницыFlymotion Mach3 Usb Motion Card Installation ManualdaocongdablОценок пока нет
- Industrial Ups 3phase Enertonic I 01Документ8 страницIndustrial Ups 3phase Enertonic I 01kylegazeОценок пока нет
- 太陽能光伏系統安裝指南 Guidance Notes for Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System InstallationДокумент36 страниц太陽能光伏系統安裝指南 Guidance Notes for Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System InstallationRaymond LamОценок пока нет
- SEW AC Motoren CatalogДокумент692 страницыSEW AC Motoren CatalogandreiwlОценок пока нет
- HCPL 7840 000e DatasheetДокумент10 страницHCPL 7840 000e DatasheetMikael BogrenОценок пока нет
- MR Service ManualДокумент42 страницыMR Service ManualYuwarath SuktrakoonОценок пока нет
- Design of High Efficiency Electrical Motors For A Hybrid Electric VehicleДокумент14 страницDesign of High Efficiency Electrical Motors For A Hybrid Electric Vehicleapi-3709675100% (1)
- Https - WWW - Solaredge.com - Sites - Default - Files - Se P Series Commercial Add On Power Optimizer Datasheet PDFДокумент4 страницыHttps - WWW - Solaredge.com - Sites - Default - Files - Se P Series Commercial Add On Power Optimizer Datasheet PDFvimallambaОценок пока нет
- User Manual: DTSU666-H 100 A and 250 A Smart Power SensorДокумент27 страницUser Manual: DTSU666-H 100 A and 250 A Smart Power SensorAitor LarrenОценок пока нет
- MGDG chpt1-1Документ17 страницMGDG chpt1-1Kishor ShekokareОценок пока нет
- Delta VFD Ms30estesiДокумент40 страницDelta VFD Ms30estesiClaudio GonzalezОценок пока нет
- FR500D Elevator Drive Manual V1.1Документ47 страницFR500D Elevator Drive Manual V1.1adam okbiОценок пока нет
- HCPL J312Документ24 страницыHCPL J312Sergiu BadalutaОценок пока нет
- Homework #8 November 4, 2005Документ3 страницыHomework #8 November 4, 2005Asmaa WajeahОценок пока нет
- PSCAD Power Electronics Lab ManualДокумент26 страницPSCAD Power Electronics Lab Manualyugendraraokn0% (1)
- 212 PTM05 Electrical Power SystemsДокумент31 страница212 PTM05 Electrical Power SystemsMuktasid Sakib RahmanОценок пока нет
- Siemens AG Epiepmel1: Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaДокумент154 страницыSiemens AG Epiepmel1: Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaMendes OffShoreОценок пока нет
- Partially Owned by Ansaldo Sistemi Industriali S.p.A.: Answer Drives S.R.LДокумент14 страницPartially Owned by Ansaldo Sistemi Industriali S.p.A.: Answer Drives S.R.LMohamed AlkharashyОценок пока нет
- Multi V IV - HP - 380V - Manual - Service - 20130710 PDFДокумент138 страницMulti V IV - HP - 380V - Manual - Service - 20130710 PDFElson CumaruОценок пока нет
- Couse File Documents23Документ73 страницыCouse File Documents23vijay patilОценок пока нет
- 06 Makdessi Georges Kako OFAEnR DFBEEДокумент17 страниц06 Makdessi Georges Kako OFAEnR DFBEEFazila KhanОценок пока нет
- Riello PWP Tech UPSДокумент36 страницRiello PWP Tech UPSGoran StosevskiОценок пока нет
- Finalreport SwetasinghДокумент19 страницFinalreport Swetasinghsaurav kumarОценок пока нет
- B5X Motion Control System (B51 B55 B57 B58 ManualДокумент88 страницB5X Motion Control System (B51 B55 B57 B58 Manualgeovanni martinezОценок пока нет
- Design Methodology of Off-Grid PV Solar Powered System - 5!1!2018Документ23 страницыDesign Methodology of Off-Grid PV Solar Powered System - 5!1!2018Matthew Mhlongo0% (1)
- SG350HX: Multi-MPPT String Inverter For SystemДокумент2 страницыSG350HX: Multi-MPPT String Inverter For SystemLeeОценок пока нет
- Design and Analysis of High-Gain Medium-Voltage DC-DC Converters For High-Power PV ApplicationsДокумент5 страницDesign and Analysis of High-Gain Medium-Voltage DC-DC Converters For High-Power PV ApplicationsHussain K. SayedОценок пока нет
- FA - SS2 - AC - Drive - User - Manual - V1.05Документ176 страницFA - SS2 - AC - Drive - User - Manual - V1.05LUATОценок пока нет
- Design Simulation For A 3 Phase Grid Connected PV Inverter in Simulink PDFДокумент9 страницDesign Simulation For A 3 Phase Grid Connected PV Inverter in Simulink PDFNguyen KhoaОценок пока нет