Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Revision Quiz Ch13
Загружено:
Sweetygirl_16Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Revision Quiz Ch13
Загружено:
Sweetygirl_16Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
13
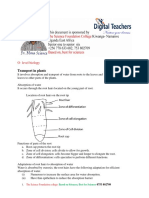
Plant transport
... xylem.
Revision
QUIZ
Use these questions to help you revise
1 These tubes carry water and mineral salts
up the stem. (page 202)
2 These tubes carry dissolved food from the
leaves to the rest of the plant. (p. 202)
... phloem.
3 Where is the xylem and phloem found in a
stem? (p. 203)
... in a ring of vascular bundles.
4 What is cambium? (p. 203) 5 How would you prove that water passes up
the xylem tissue? (p. 203)
... a layer of cells that divides to form new xylem and new phloem. ... stand a plant in dyed water for a few hours. Then cut a section of the stem and find out where the dye is located. ... they have thin cell walls and a large surface area. ... transpiration.
6 How are root hairs adapted for absorbing
water? (p. 204)
7 What do we call the evaporation of water
from the leaves into the air? (p. 205)
8 What do we call the continuous flow of
water from the roots up to the leaves in the xylem? (p. 205)
... the transpiration stream.
9 What happens to young plants if they lose
too much water by transpiration? (p. 206)
... they wilt.
10 What conditions cause the rate of
transpiration to increase? (p. 206)
... windy, dry, warm conditions.
11 What conditions cause the rate of
transpiration to decrease? (p. 206)
... still, humid, cool conditions.
12 What does a potometer measure? (p. 207) 13 What could you do to a potometer to make
conditions a) windy? and b) humid? (p. 207)
... the rate of water uptake. ... a) put the potometer near a fan b) put a polythene bag over the shoot.
14 Some salts enter roots by diffusion but
others are taken up by ... (p. 208)
... active transport.
15 What is translocation? (p. 208)
... the movement of soluble food around the plant in the phloem.
Gareth Williams, 2011
Вам также может понравиться
- Transport in PlantsДокумент26 страницTransport in Plantsliban100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsОценок пока нет
- Transpiration Biology Class X - ICSE (2019-20)Документ22 страницыTranspiration Biology Class X - ICSE (2019-20)the lillyОценок пока нет
- SAT Vocab.Документ6 страницSAT Vocab.Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Transpiration Notes Class 10Документ4 страницыTranspiration Notes Class 10proodootОценок пока нет
- Transport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationДокумент71 страницаTransport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationCarolyn KhooОценок пока нет
- 1 and 2 Term QUESTION BANK - 2020-21 Biology STD ViiДокумент68 страниц1 and 2 Term QUESTION BANK - 2020-21 Biology STD ViiJfifjjfОценок пока нет
- Biology STD 8 Question Bank 2020-21Документ19 страницBiology STD 8 Question Bank 2020-21ShreyashОценок пока нет
- Biology Questions and Answers Form 2Документ41 страницаBiology Questions and Answers Form 2Zubin Jammaa FulaniОценок пока нет
- Transport in Plants O LevelДокумент14 страницTransport in Plants O LevelTatenda ChirobeОценок пока нет
- Transpiration Exercise ExДокумент8 страницTranspiration Exercise ExGraciously meОценок пока нет
- Set B Sample QuestionnaireДокумент14 страницSet B Sample QuestionnairerhonnaОценок пока нет
- Class X Transpiration: Book Name: Selina ConciseДокумент12 страницClass X Transpiration: Book Name: Selina ConciseVansh AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Biology Course Answerbook 22 29Документ8 страницBiology Course Answerbook 22 29Reta SahawnehОценок пока нет
- Transport in Plant Notes Apr13 - 1Документ18 страницTransport in Plant Notes Apr13 - 1Danes WaranОценок пока нет
- Alternative Bio F2 NotesДокумент47 страницAlternative Bio F2 Noteskeith mugerwaОценок пока нет
- Transport in PlantsДокумент20 страницTransport in PlantsLeon XuОценок пока нет
- Plant TestДокумент13 страницPlant TestsubkumquatОценок пока нет
- Final Exam ScienceДокумент14 страницFinal Exam SciencepksingОценок пока нет
- Lab Activity: Plant TranspirationДокумент3 страницыLab Activity: Plant TranspirationOriana RegaladoОценок пока нет
- Lab Activity: Plant TranspirationДокумент3 страницыLab Activity: Plant TranspirationOriana RegaladoОценок пока нет
- Act 22 Water Loss MEMOДокумент1 страницаAct 22 Water Loss MEMOsofi sofiОценок пока нет
- Plants StructureДокумент2 страницыPlants StructureArina KhusnaОценок пока нет
- Transport in Flowering Plants Final VersionДокумент9 страницTransport in Flowering Plants Final VersionJohn MoyoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 YranspirationДокумент27 страницChapter 5 YranspirationDXN LUDHIANAОценок пока нет
- 14 Rectified - WaterДокумент7 страниц14 Rectified - Waterdiyanshud.thakurОценок пока нет
- The Water CycleДокумент3 страницыThe Water CycleRyan NegadОценок пока нет
- A, Level Transport by MR Li - 1Документ107 страницA, Level Transport by MR Li - 1asadukimbugwe20Оценок пока нет
- Transport in PlantsДокумент17 страницTransport in PlantsMichelle HlungwaniОценок пока нет
- X-Questions On Absorption ByrootsДокумент10 страницX-Questions On Absorption ByrootsYashОценок пока нет
- Botany G Sem 4 Ascent of Sap IdasДокумент11 страницBotany G Sem 4 Ascent of Sap IdasgoddonОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 16 WaterДокумент3 страницыChapter - 16 Water8460Оценок пока нет
- The Water CycleДокумент1 страницаThe Water CycleHenry LopezОценок пока нет
- Biology CH 9Документ22 страницыBiology CH 9Faheem UllahОценок пока нет
- Diy Induction CoilДокумент7 страницDiy Induction Coilmr.christianpink.254Оценок пока нет
- Zquestions in Long Answer QuestionsДокумент10 страницZquestions in Long Answer QuestionsyadavaudaysinghОценок пока нет
- Uptake of Water in PlantsДокумент12 страницUptake of Water in PlantsVictoria VirgoОценок пока нет
- (Max 3 or 4 Points) : Difference Between The FollowingДокумент5 страниц(Max 3 or 4 Points) : Difference Between The Following7168 HridyanshОценок пока нет
- MCQs of Plant TransportationДокумент5 страницMCQs of Plant Transportationprofessor zulfi100% (2)
- Project Report On TranspirationДокумент5 страницProject Report On TranspirationSnehal JoshiОценок пока нет
- Biology 11: Kingdom Plantae: Unit TopicsДокумент18 страницBiology 11: Kingdom Plantae: Unit TopicsMariel AnaОценок пока нет
- 8th-Bio-Ch-1-Notes Class8Документ18 страниц8th-Bio-Ch-1-Notes Class8SaumyaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 12 - Questions - Summary S2024Документ6 страницLecture 12 - Questions - Summary S2024sydneepnОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 2 Model Answers PDF 32628Документ3 страницыWorksheet 2 Model Answers PDF 32628samirОценок пока нет
- Class 6 Water - Question AnswerДокумент5 страницClass 6 Water - Question Answerlaxmi sainiОценок пока нет
- 10 Support and Transport Systems in PlantsДокумент50 страниц10 Support and Transport Systems in Plantsapi-202349222Оценок пока нет
- Plant Physio Q & ANSДокумент17 страницPlant Physio Q & ANSVandana MishraОценок пока нет
- Give Two Ways of Determining The Genotypes (Height) of The Pawpaw Plant ShownДокумент246 страницGive Two Ways of Determining The Genotypes (Height) of The Pawpaw Plant ShownAbigail ChepkuruiОценок пока нет
- Core CH 10 TranspirationДокумент12 страницCore CH 10 TranspirationommpОценок пока нет
- 9.1 NewДокумент5 страниц9.1 NewYuvraj GuptaОценок пока нет
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.От EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.Оценок пока нет
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Документ42 страницыForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Marcus LeeОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes - Plant ScienceДокумент8 страницBiology Notes - Plant Sciencesarah_beck100% (1)
- Support and LocomotionДокумент25 страницSupport and LocomotionUV Vïpêr UnïcôrnОценок пока нет
- (Absorption by Roots - Notes) PDFДокумент6 страниц(Absorption by Roots - Notes) PDFthe lillyОценок пока нет
- Topic 8 Transport in Plants: 8.1 Vascular Tissue Functions of Xylem & PhloemДокумент10 страницTopic 8 Transport in Plants: 8.1 Vascular Tissue Functions of Xylem & PhloemMuhammad Hassan TariqОценок пока нет
- Transport System in Plants: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatДокумент20 страницTransport System in Plants: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatAkiela JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Transport Plants QuestionsДокумент2 страницыTransport Plants QuestionsSalvator LevisОценок пока нет
- Transport in PlantsДокумент7 страницTransport in PlantsMasthankhan PatanОценок пока нет
- Flowering: Tennessee Bulbs ForДокумент24 страницыFlowering: Tennessee Bulbs ForPeter ThomasОценок пока нет
- Taxation EuДокумент23 страницыTaxation EuSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Art Terrorism Topic Key WordsДокумент1 страницаArt Terrorism Topic Key WordsSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- New ECA Club OutlineДокумент1 страницаNew ECA Club OutlineSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- VAT Considerations For E-Commerce - International Tax ReviewДокумент6 страницVAT Considerations For E-Commerce - International Tax ReviewSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- International Taxation of Electronic Commerce Income - A ProposalДокумент31 страницаInternational Taxation of Electronic Commerce Income - A ProposalSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- IGCSE Science - Revision WebsitesДокумент1 страницаIGCSE Science - Revision WebsitesSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- 4 Types of Coral ReefsДокумент2 страницы4 Types of Coral ReefsSweetygirl_16100% (1)
- Revision Quiz Ch18Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch18Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Useful Phrases&Complex ConnectivesДокумент3 страницыUseful Phrases&Complex ConnectivesSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch19Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch19Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- 4400 Mark Schemes IGCSE November 2004Документ33 страницы4400 Mark Schemes IGCSE November 2004Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch16Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch16Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch13Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch13Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch17Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch17Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch15Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch15Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch14Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch14Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch11Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch11Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch16Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch16Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch15Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch15Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch12Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch12Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch14Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch14Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch12Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch12Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Control and Coordination: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseДокумент1 страницаControl and Coordination: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch07Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch07Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Support and Movement: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseДокумент1 страницаSupport and Movement: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Revision Quiz Ch10Документ1 страницаRevision Quiz Ch10Sweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет
- Blood and Circulation: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseДокумент1 страницаBlood and Circulation: Use These Questions To Help You ReviseSweetygirl_16Оценок пока нет