Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ANCHOR BOLT DESIGN - Gulf Publishing - Pressure Vessel Design Manual 3rd Edition 195
Загружено:
Alessio BarboneИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ANCHOR BOLT DESIGN - Gulf Publishing - Pressure Vessel Design Manual 3rd Edition 195
Загружено:
Alessio BarboneАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
182
Pressure Vessel Design Manual
Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolts are governed by one of the three following load cases: 1. Longitudinal load: If Qo > QL, then no uplift occurs, and the minimum number and size of anchor bolts should be used. If Qo < Q L , then uplift does occur:
QL - Qo
. N
= load per bolt
2. Shear: Assume the fNed saddle takes the entire shear load.
FL = shear per bolt
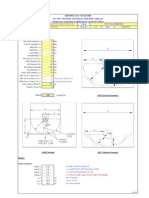
3. Transverse load: This method of determining uplift and overturning is determined from Ref. 21 (see Figure 3-57).
Figure 3-57. Dimensions and loading for base plate and anchor bolt analysis.
M = (0.5Fe or F w ) B M e=Qo
Y3
+ K,Y2 + KzY + K3 = 0
If e < "/6, then there is no uplift. If e 3 %, then proceed with the following steps. This is an iterative procedure for finding the tension force, T, in the outermost bolt. Step 1: Find the effective bearing length, Y. Start by calculating factors K 1 a ,
K i = 3(e - 0.5A) 6nlat Kz = F (f + e)
If not equal to 0, then proceed with Step 3. Step 3: Assume a new value of Y and recalculate the equation in Step 2 until the equation balances out to approximately 0. Once Y is determined, proceed to Step 4. Step 4: Calculate the tension force, T, in the outermost bolt or bolts. I A Y 1
Step 5: From Table 3-28, select an appropriate bolt material and size corresponding to tension-force, T. Step 6: Analyze the bending in the base plate. Distance, x = 0.5A +f - Y Moment, M = Tx 6M Bending stress,fb = -
Step 2: Substitute values of K1-3 into the following equation and assume a value of Y = %A as a first trial.
t"b
Allowable Tension Load on Bolts, Kips, per AlSC
~
Nom. Bolt Dia., in.
Cross-sectional Area, ab, in.' A-307 A-325 Ft=20ksi Ft=44ksi
%
0.3068 6.1 13.5
t
0.4418 8.8 19.4
2 l
0.6013 12.0 26.5
1%
1%
1%
1.485 29.7 65.3
1'h
0.7854 15.7 34.6
0.994 19.9 43.7
1.227 24.5 54.0
1.767 35.3 77.7
Вам также может понравиться
- Zick Analysis For Saddle SupportДокумент8 страницZick Analysis For Saddle Supportfuransu777100% (1)
- Hinge Calculation FormulasДокумент2 страницыHinge Calculation FormulasamaОценок пока нет
- SEISMIC ANALYSIS KazzincДокумент14 страницSEISMIC ANALYSIS KazzincArees KhambattaОценок пока нет
- Steel Design Notes CSAДокумент73 страницыSteel Design Notes CSAAntoine LetendreОценок пока нет
- Studding Outlet Calculation - PV Elite 2016Документ8 страницStudding Outlet Calculation - PV Elite 2016Liu YangtzeОценок пока нет
- PFS FWKO Tank EvaluationДокумент12 страницPFS FWKO Tank EvaluationkoyahassanОценок пока нет
- PV Elite ResultДокумент239 страницPV Elite ResultChaitanya Sai TОценок пока нет
- Baffle Thickness CalculationДокумент22 страницыBaffle Thickness CalculationAdrian Stoicescu100% (1)
- Tailing Lug - 173004-05Документ1 страницаTailing Lug - 173004-05shazan100% (1)
- Horizontal Vessel Stress AnalysisДокумент12 страницHorizontal Vessel Stress AnalysissridharОценок пока нет
- Saddle 1Документ3 страницыSaddle 1RUDHRA DHANASEKARОценок пока нет
- New Storage Tanks Design GuidelinesДокумент6 страницNew Storage Tanks Design GuidelineschrisevabОценок пока нет
- Documents - Tips - Pressure Vessel Design Calc Asme VIII Div 1Документ35 страницDocuments - Tips - Pressure Vessel Design Calc Asme VIII Div 1bainОценок пока нет
- Lug SupportДокумент2 страницыLug SupportSachin5586Оценок пока нет
- Saddle Road Transportation Analysis 1Документ2 страницыSaddle Road Transportation Analysis 1vpjagannaathОценок пока нет
- Lifting Lug Analysis DesignДокумент5 страницLifting Lug Analysis DesignAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Tema ChecklistДокумент2 страницыTema ChecklistAdrian Stoicescu100% (1)
- Base Ring Fillet Size CalculationДокумент4 страницыBase Ring Fillet Size Calculationmiteshpatel191Оценок пока нет
- Rectangular Tanks:: Rectangle Tank DesignДокумент23 страницыRectangular Tanks:: Rectangle Tank Designshna jabarОценок пока нет
- Skirt Support Analysis Per en 13445Документ13 страницSkirt Support Analysis Per en 13445karthik1amarОценок пока нет
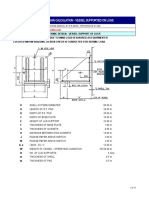
- Sample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On LugsДокумент11 страницSample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On LugsSiva baalan100% (2)
- Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Lifting Trunnion Common Practices PDFДокумент4 страницыBoiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Lifting Trunnion Common Practices PDFAlexandru AsmarandeiОценок пока нет
- Platform Cleat CalculationДокумент1 страницаPlatform Cleat Calculationmiteshpatel191Оценок пока нет
- Solid Mechanics (Bending of A T Beam Lab Report)Документ12 страницSolid Mechanics (Bending of A T Beam Lab Report)rajesh yadavОценок пока нет
- Ldo Storage Tank Calculation 170Документ6 страницLdo Storage Tank Calculation 170م.ذكى فضل ذكى100% (1)
- Tank DesignДокумент89 страницTank Designpatrickandreas77Оценок пока нет
- Pressure Vessel Lifting Lug CalculationДокумент2 страницыPressure Vessel Lifting Lug Calculationtekstep767% (3)
- Etank Full ReportДокумент108 страницEtank Full ReportFaizal SattuОценок пока нет
- 2400 Tema DCДокумент7 страниц2400 Tema DCMasoodMiyanОценок пока нет
- Cs & Las Impact Req - Asme Sec Viii Div 2Документ16 страницCs & Las Impact Req - Asme Sec Viii Div 2AmitNarayanNitnawareОценок пока нет
- Standard Size Trap - Taylor ForgeДокумент1 страницаStandard Size Trap - Taylor ForgeAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engineering Design 8thДокумент12 страницMechanical Engineering Design 8thStipendijeVlaОценок пока нет
- Saddle CalculationДокумент10 страницSaddle Calculationpharis_chrisОценок пока нет
- Design of Reinforced Concrete RING BEAM FOUNDATIONДокумент2 страницыDesign of Reinforced Concrete RING BEAM FOUNDATIONnirmal suthar100% (1)
- EJMA 8th Edition - 2003Документ212 страницEJMA 8th Edition - 2003Alessio Barbone100% (4)
- Internal Pipe Distributor Design ProcedureДокумент5 страницInternal Pipe Distributor Design Proceduresenthil kumarОценок пока нет
- Nozzle Load AnalysisДокумент2 страницыNozzle Load Analysisvm153748763Оценок пока нет
- WF, Unp, Angle, Pipe Steel Profile CalculationДокумент24 страницыWF, Unp, Angle, Pipe Steel Profile CalculationFian ArdiyanaОценок пока нет
- Prying Action A General TreatmentДокумент9 страницPrying Action A General TreatmentFWICIP100% (1)
- SP-2069 Specification For Pressure VesselsДокумент68 страницSP-2069 Specification For Pressure Vesselsarjunprasannan7Оценок пока нет
- Anchor Bolt CalculationДокумент8 страницAnchor Bolt CalculationRajput Pratiksingh100% (1)
- Analysis of a rectangular pressure vesselДокумент7 страницAnalysis of a rectangular pressure vesselPressure VesselОценок пока нет
- 28 Roark Flat PlatesДокумент14 страниц28 Roark Flat Platesgutmont0% (1)
- Cdo CalcДокумент3 страницыCdo CalcJeric FarinОценок пока нет
- Tailing Lug Design FormulaДокумент2 страницыTailing Lug Design FormulaRajeshОценок пока нет
- Jn1399 - 71t Lifting LugДокумент5 страницJn1399 - 71t Lifting LugRiyan EsapermanaОценок пока нет
- Bab Iii: Re-Design Dan Hasil Perhitungan Horizontal Pressure VesselДокумент36 страницBab Iii: Re-Design Dan Hasil Perhitungan Horizontal Pressure VesselTri AgungОценок пока нет
- IIT Hyderabad Faculty Housing Design CalculationsДокумент33 страницыIIT Hyderabad Faculty Housing Design CalculationssmijusОценок пока нет
- Ccsviiid1 2260Документ2 страницыCcsviiid1 2260DieguitoOmarMoralesОценок пока нет
- 7-12-0024 Rev 7Документ1 страница7-12-0024 Rev 7cynideОценок пока нет
- Concrete Anchor Foundation Bolt Design Calculations With Example As Per ACI 318 Appendix D-Part7-Pryout Strength in ShearДокумент4 страницыConcrete Anchor Foundation Bolt Design Calculations With Example As Per ACI 318 Appendix D-Part7-Pryout Strength in ShearVenu GopalОценок пока нет
- Trunnion 6 TonДокумент3 страницыTrunnion 6 TonEngr Khurram Jaan RamayОценок пока нет
- Skirt Design - For Small VesselsДокумент7 страницSkirt Design - For Small VesselsSakthi VelОценок пока нет
- Blind ThicknessДокумент1 страницаBlind ThicknessRizwan Waheed KhanОценок пока нет
- Tailing LugДокумент3 страницыTailing LugSajad AbdulОценок пока нет
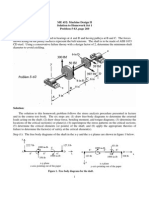
- Solution Tutorial - 1Документ2 страницыSolution Tutorial - 1Akash FuryОценок пока нет
- Stress Concentrations - Lab ReportДокумент6 страницStress Concentrations - Lab ReportArunodha HettiarachchiОценок пока нет
- PHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2Документ12 страницPHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2harshitaОценок пока нет
- Home Work 5 - Chapter 5: SolutionsДокумент6 страницHome Work 5 - Chapter 5: SolutionssarahhОценок пока нет
- Hw1 Sol Fall 2015Документ8 страницHw1 Sol Fall 2015Ong Kok Meng100% (1)
- Circular Shaft em 327: Mechanics of Materials Laboratory: ObjectivesДокумент4 страницыCircular Shaft em 327: Mechanics of Materials Laboratory: ObjectivesSumit SharmaОценок пока нет
- RC Beam Torsion DesignДокумент33 страницыRC Beam Torsion Design2011kumarОценок пока нет
- Exercises On Stress StateДокумент4 страницыExercises On Stress StatecusanhОценок пока нет
- Double Bottom Petroleum Storage Tanks ExplainedДокумент10 страницDouble Bottom Petroleum Storage Tanks ExplainedAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Typical SupportДокумент9 страницTypical SupportAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Uniform Building Code Volume 21997Документ545 страницUniform Building Code Volume 21997raymond100% (1)
- PEG Property Document Copy RestrictionsДокумент1 страницаPEG Property Document Copy RestrictionsAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- AutoPIPE Vessel FundamentalsДокумент172 страницыAutoPIPE Vessel FundamentalsAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Fouling and Plate Heat ExchangerДокумент3 страницыFouling and Plate Heat ExchangerAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Soil InvestigationДокумент23 страницыSoil InvestigationAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Pagine Da De-Mystifying AutoCAD Plant 3D IsometricsДокумент10 страницPagine Da De-Mystifying AutoCAD Plant 3D IsometricsAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Terminations For Steel Wire Ropes Safety: ÖnormДокумент5 страницTerminations For Steel Wire Ropes Safety: ÖnormAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Aws Welding SymbolsДокумент2 страницыAws Welding SymbolsAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Terminations For Steel Wire Ropes Safety: ÖnormДокумент5 страницTerminations For Steel Wire Ropes Safety: ÖnormAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Terminations For Steel Wire Ropes Safety: ÖnormДокумент5 страницTerminations For Steel Wire Ropes Safety: ÖnormAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- Pagine Da NAYYAR M. L. - Piping HandbookДокумент5 страницPagine Da NAYYAR M. L. - Piping HandbookAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет
- AppuntiДокумент2 страницыAppuntiAlessio BarboneОценок пока нет