Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
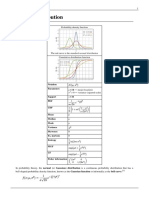
Special Continuous Probability Distributions
Загружено:
nofacejackИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Special Continuous Probability Distributions
Загружено:
nofacejackАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Special Continuous
Probability
Distributions
1
Uniform Distribution
A random variable X is said to follow
a uniform distribution (over the
interval [a,b]) if its density is given
by:
1
, ,
( ; , )
0 , elsewhere
a x b b a
f x a b
b a
s s >
Uniform Distribution
1/(b-a)
a c d b
( ) (1/( ))*( ) P c X d b a d c < < =
Uniform Distribution
If X is uniformly distributed over [a,b]
then [Notation: X~uniform(a,b):
X~U(a,b)]
2
2
( )
2
( )
( )
12
X
X
a b
E X
b a
Var X
o
+
= =
= =
Normal Probability
Distribution
The normal probability distribution
(simply normal distribution) is one of
many possible types of probability
distribution of a continuous random
variable.
It is regarded as one of the most
important in the sense that of its
usefulness in many applications.
5
Characteristics
It is bell-shaped and
symmetric.
It is characterized by two
parameters: mean and
standard deviation.
Different combinations of
mean and standard
deviation gives rise to
different normal
distributions.
6
Characteristics
Total area under the curve is 1.
Asymptotic about the x-axis
NOTATION: If the r.v. X follows a
normal distribution with a given mean
and variance
Different values of mean and
variance define different normal
distributions (many of them!)
7
) , ( ~
2
o N X
Examples
Two different normal distributions with
different means but same variances
Examples
Two different normal distributions with
same means but different variances
variances
Examples
Two different normal distributions with
different means and variances
Standard Normal
Distribution
A special type of normal distribution (standard
normal distribution or z-distribution) having a
mean 0 and variance 1. That is
It is special because areas under such
distribution is tabulated.
Such table can also be used to find areas
(probabilities) of any normal distribution by the
following transformation
) 1 , 0 ( ~ N Z
11
) , ( ~ ), 1 , 0 ( ~
2
o
o
N X N
X
Z
=
Вам также может понравиться
- Yehuda Berg Satan PDFДокумент77 страницYehuda Berg Satan PDFOswaldo Archundia100% (7)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент941 страницаNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentPriya VenugopalОценок пока нет
- The Big Book of Mind-Bending PuzzlesДокумент338 страницThe Big Book of Mind-Bending PuzzlesAustin Albert93% (14)
- Course For Loco Inspector Initial (Diesel)Документ239 страницCourse For Loco Inspector Initial (Diesel)Hanuma Reddy93% (14)
- Tsang Mui Millennium School 2019-2020 English Worksheet: Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Form of The VerbsДокумент46 страницTsang Mui Millennium School 2019-2020 English Worksheet: Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Form of The VerbscocoyipОценок пока нет
- Distribución GaussianaДокумент26 страницDistribución GaussianaSara DiSuОценок пока нет
- Continuous Probability DistributionДокумент47 страницContinuous Probability DistributionBrigitta AngelinaОценок пока нет
- FBA1202 Statistics W10Документ104 страницыFBA1202 Statistics W10ilayda demirОценок пока нет
- Random Variables and Probability Distribution: Purnomo Jurusan Teknik Mesin UGMДокумент48 страницRandom Variables and Probability Distribution: Purnomo Jurusan Teknik Mesin UGMYusnanda Agus NОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент22 страницыNormal Distribution - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLieu Dinh PhungОценок пока нет
- Lecture11 (Week 12) UpdatedДокумент34 страницыLecture11 (Week 12) UpdatedBrian LiОценок пока нет
- Istanbul Aydin University: Chapter 4: Probability DistributionsДокумент12 страницIstanbul Aydin University: Chapter 4: Probability Distributionsxxnameless 97Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: Continuous Probability DistributionsДокумент4 страницыChapter 2: Continuous Probability DistributionsRUHDRAОценок пока нет
- Chap4 ElsyДокумент60 страницChap4 ElsyKamil IbraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ16 страницChapter 6Khay OngОценок пока нет
- Continuous DistributionsДокумент10 страницContinuous Distributionsogonnaakuneme830Оценок пока нет
- Kto12 Probability and StatisticsДокумент40 страницKto12 Probability and Statisticsjun del rosarioОценок пока нет
- Quiz 2 Covered Materials In: - Chapter 5 - Chapter 6 - Chapter 7Документ27 страницQuiz 2 Covered Materials In: - Chapter 5 - Chapter 6 - Chapter 7Aaron Hayyat0% (1)
- Business Stat & Emetrics101Документ38 страницBusiness Stat & Emetrics101kasimОценок пока нет
- Unit 1: Random Variables and Probability DistributionsДокумент41 страницаUnit 1: Random Variables and Probability DistributionsMariam LortkipanidzeОценок пока нет
- ch08 ContinuousProbabilityDistributionsДокумент10 страницch08 ContinuousProbabilityDistributionsdavidОценок пока нет
- Ratio DistributionДокумент5 страницRatio DistributionVlk WldОценок пока нет
- Normal DistДокумент2 страницыNormal DistnooluoitОценок пока нет
- PROSTAT Lecture9 HandoutsДокумент6 страницPROSTAT Lecture9 HandoutsJubillee MagsinoОценок пока нет
- CH 05Документ76 страницCH 05Michael FernoОценок пока нет
- Distribution: Dr. H. Gladius Jennifer Associate Professor SPH, SrmistДокумент23 страницыDistribution: Dr. H. Gladius Jennifer Associate Professor SPH, SrmistCharan KОценок пока нет
- Normal DistributionДокумент30 страницNormal Distributionbraulio.dantas-1Оценок пока нет
- LectureДокумент6 страницLectureJubillee MagsinoОценок пока нет
- Lecture No.9Документ12 страницLecture No.9Awais RaoОценок пока нет
- Some Continuous and Discrete Distributions: X y B AДокумент8 страницSome Continuous and Discrete Distributions: X y B ASandipa MalakarОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент11 страницAssignmentshan khanОценок пока нет
- 8b Basic Probability DistributionsДокумент13 страниц8b Basic Probability DistributionsChan AnsonОценок пока нет
- Most Important Theoratical Questions of QTДокумент26 страницMost Important Theoratical Questions of QTIsmith PokhrelОценок пока нет
- Geometry in SpaceДокумент9 страницGeometry in SpacejennajennjenjejОценок пока нет
- Chapters 7,8,9Документ4 страницыChapters 7,8,9sarkarigamingytОценок пока нет
- Probability Distribution II - Normal Distribution & Small Sampling Distribution (Students Notes) MAR 23Документ27 страницProbability Distribution II - Normal Distribution & Small Sampling Distribution (Students Notes) MAR 23halilmohamed830Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Probability Distributions: 4.1 Random VariablesДокумент53 страницыChapter 4: Probability Distributions: 4.1 Random VariablesGanesh Nagal100% (1)
- Normal DistributionДокумент59 страницNormal DistributionAkash Katariya100% (1)
- Topic05.Normal DistrДокумент27 страницTopic05.Normal DistrDavid LeОценок пока нет
- Continuous Random VariablesДокумент156 страницContinuous Random Variablesmaliktayyab15112003Оценок пока нет
- MASTAT - Ch5 Continuous Distributions - 022518Документ7 страницMASTAT - Ch5 Continuous Distributions - 022518ventus5thОценок пока нет
- Probability and Statistics Mat 271EДокумент50 страницProbability and Statistics Mat 271Egio100% (1)
- The Uniform DistributnДокумент7 страницThe Uniform DistributnsajeerОценок пока нет
- M3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFДокумент23 страницыM3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFÖzZíé Ming RenОценок пока нет
- M3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFДокумент23 страницыM3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFÖzZíé Ming RenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 NorDIsДокумент73 страницыChapter 3 NorDIsreg.anything29Оценок пока нет
- Continuous Probability DistributionsДокумент3 страницыContinuous Probability DistributionsLuke CruzОценок пока нет
- Probabilidad y EstadisticaДокумент9 страницProbabilidad y EstadisticaCynthia MaciasОценок пока нет
- Continuous Random VariableДокумент44 страницыContinuous Random Variableranjitbiswal547Оценок пока нет
- Continuous Distributions: Section 2Документ27 страницContinuous Distributions: Section 2eng ineera100% (1)
- CH 8 - Special Continuous Probability DistributionДокумент12 страницCH 8 - Special Continuous Probability DistributionhehehaswalОценок пока нет
- Uniform Distribution: Function Is Given byДокумент2 страницыUniform Distribution: Function Is Given byFabricio GZ100% (1)
- Normal DistributionДокумент22 страницыNormal Distributionaamirali31Оценок пока нет
- FRM Part 1: DistributionsДокумент25 страницFRM Part 1: DistributionsRa'fat JalladОценок пока нет
- Probability DistributionДокумент21 страницаProbability Distributiontaysirbest0% (1)
- Normal Probaility DistributionДокумент13 страницNormal Probaility DistributionAbdul TukurОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1: MSC StatisticsДокумент5 страницAssignment 1: MSC StatisticsAlvera MeharОценок пока нет
- Extreme Behavior of Bivariate Elliptical Distributions: Alexandru V. Asimit, Bruce L. JonesДокумент9 страницExtreme Behavior of Bivariate Elliptical Distributions: Alexandru V. Asimit, Bruce L. JonesMahfudhotinОценок пока нет
- Continuous Probability DistributionДокумент60 страницContinuous Probability DistributionJethro MiñanoОценок пока нет
- Variance and Mean of A Distribution Powerpoint PresentationДокумент34 страницыVariance and Mean of A Distribution Powerpoint PresentationNikka VeronОценок пока нет
- Probability Densities 1Документ38 страницProbability Densities 1Armand DaputraОценок пока нет
- 04 NormalDistributionДокумент43 страницы04 NormalDistributionShane Olen GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Continuous Random Variables: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinДокумент38 страницContinuous Random Variables: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinadamОценок пока нет
- Reactions of AlkanesДокумент1 страницаReactions of AlkanesnofacejackОценок пока нет
- 1-Chemical Analysis - Quantitation - SДокумент39 страниц1-Chemical Analysis - Quantitation - SnofacejackОценок пока нет
- Pericyclic Reactions PDFДокумент41 страницаPericyclic Reactions PDFnofacejack67% (3)
- 5-AAS SДокумент39 страниц5-AAS SnofacejackОценок пока нет
- Lesson 9: Rectangular Coordinate PlaneДокумент1 страницаLesson 9: Rectangular Coordinate PlanenofacejackОценок пока нет
- Introduction To AlgebraДокумент1 страницаIntroduction To AlgebranofacejackОценок пока нет
- Molecular Logic of Life Student NotesДокумент4 страницыMolecular Logic of Life Student Notesnofacejack67% (3)
- PROTEINS Updated Feb2010Документ10 страницPROTEINS Updated Feb2010nofacejackОценок пока нет
- Rev Bio 4th 10-11 (Part 2)Документ4 страницыRev Bio 4th 10-11 (Part 2)nofacejackОценок пока нет
- Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass SpectrometryДокумент44 страницыInfrared Spectroscopy and Mass SpectrometrynofacejackОценок пока нет
- Glycosaminoglycan Monsaccharide Components Function: LinkageДокумент1 страницаGlycosaminoglycan Monsaccharide Components Function: LinkagenofacejackОценок пока нет
- Monosaccharides (Aldoses) : Biochem Structure Sheet 1. CarbohydratesДокумент1 страницаMonosaccharides (Aldoses) : Biochem Structure Sheet 1. CarbohydratesnofacejackОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids: C COO H N H CHДокумент2 страницыAmino Acids: C COO H N H CHnofacejackОценок пока нет
- Phase-Locked Loop Independent Second-Order Generalized Integrator For Single-Phase Grid SynchronizationДокумент9 страницPhase-Locked Loop Independent Second-Order Generalized Integrator For Single-Phase Grid SynchronizationGracella AudreyОценок пока нет
- The 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All TimeДокумент4 страницыThe 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All Timeungku1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodДокумент6 страницChapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodMbali MagagulaОценок пока нет
- Bryophytes MorphologyДокумент9 страницBryophytes Morphologyrachna singh0% (1)
- Electron Withdrawing and Electron Donating GroupsДокумент2 страницыElectron Withdrawing and Electron Donating GroupsOmar Abd ElsalamОценок пока нет
- Leica Rugby 320 410 420 BRO En-1Документ6 страницLeica Rugby 320 410 420 BRO En-1luigiabeОценок пока нет
- JCB R135 & R155-HD Skid Steer-New BrochureДокумент8 страницJCB R135 & R155-HD Skid Steer-New BrochureAshraf KadabaОценок пока нет
- BÀI TẬP TA 9 THEO CHUYÊN ĐỀ NGỮ PHÁPДокумент213 страницBÀI TẬP TA 9 THEO CHUYÊN ĐỀ NGỮ PHÁPhoangmaiОценок пока нет
- Research Report 2011 Asses Water ChambalДокумент41 страницаResearch Report 2011 Asses Water Chambalsamyak sambhareОценок пока нет
- Design and Management of Mettur Dam by Predicting Seepage Losses Using Remote SensingДокумент10 страницDesign and Management of Mettur Dam by Predicting Seepage Losses Using Remote SensingInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementОценок пока нет
- Lexus JTJBT20X740057503 AllSystemDTC 20230702045631Документ2 страницыLexus JTJBT20X740057503 AllSystemDTC 20230702045631Venerable DezzyОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Anther Culture: Submitted To Submitted byДокумент22 страницыPresentation On Anther Culture: Submitted To Submitted byvishnu0751Оценок пока нет
- SCM 025-108 M2Документ8 страницSCM 025-108 M2kazdanoОценок пока нет
- Power SupplyДокумент79 страницPower SupplySharad KumbharanaОценок пока нет
- Long Quiz 1 Eim Tools, MaterialsДокумент1 страницаLong Quiz 1 Eim Tools, MaterialsLea Ann PalaciosОценок пока нет
- LESSON 2 Facilities Location StrategiesДокумент2 страницыLESSON 2 Facilities Location StrategiesElle LeeОценок пока нет
- Fermat Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionДокумент4 страницыFermat Contest: Canadian Mathematics Competitionสฮาบูดีน สาและОценок пока нет
- Case Study Mental HealthДокумент12 страницCase Study Mental Healthapi-603895785Оценок пока нет
- SW Chapter 21 KeyДокумент9 страницSW Chapter 21 KeykylevОценок пока нет
- Modern Residential Housing in UAEДокумент15 страницModern Residential Housing in UAEBee Dan BudhachettriОценок пока нет
- WPP Jak Campus - Defect All Level - 18042023Документ15 страницWPP Jak Campus - Defect All Level - 18042023bbm FebriОценок пока нет
- Medgroup Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge: - Design and Prototype The New Medgroup TopologyДокумент4 страницыMedgroup Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge: - Design and Prototype The New Medgroup TopologyvilanchОценок пока нет
- Flap Designs For Flap Advancement During Implant Therapy A Systematic Review 2016 PDFДокумент8 страницFlap Designs For Flap Advancement During Implant Therapy A Systematic Review 2016 PDFRohit ShahОценок пока нет
- HandbikeДокумент10 страницHandbikeLely JuniariОценок пока нет
- Catalyst Worksheet - SHHSДокумент3 страницыCatalyst Worksheet - SHHSNerd 101Оценок пока нет
- Iare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0Документ20 страницIare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0projects allОценок пока нет
- Sip Dissertation - Final - Final For CollegeДокумент17 страницSip Dissertation - Final - Final For Collegevikashirulkar922Оценок пока нет