Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Toler-Problem-Based Learning
Загружено:
api-238290989Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Toler-Problem-Based Learning
Загружено:
api-238290989Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
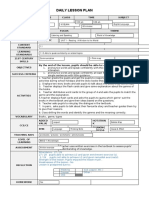
Hierarchic: 4 Main Ideas
s
TM
Makes Sense Sense Strategies Strategies Makes
Box frame
2008 Edwin Ellis, All Rights Reserved Published by Makes Sense Strategies, LLC, !rth"!rt, AL www#MakesSenseStrategies#$!%
Name:
Whitney Toler
Is about
Date:
10/29/2013
Problem-Based Learning
Main idea Main idea
A set of teaching models that uses problems as the focus for developing problem-solving skills, content, and self-regulation.
Main idea Main idea
Planning
Implementing
Assessment
Motivation
Identifying a Topic: topic should be complex and abstract than teaching a concept. Planning is also less concrete Specific Learning Objectives: 2 types 2 types of objectives: develop problem solving skills and become self-directed learners Identifying Problems: Make problems clear, concrete and personalized so the problems are more effective Make sure students have prior knowledge of the topic Access Materials: Pairs or groups of three are more effective Give the students all the necessary materials to carry out the performed task Small groups will acquire more equipment Groups should be mixed
Phase I: Review and Present Problems: Attract the students attention and hook them into the lesson. Informally asses the students previous knowledge Provide a concrete focus for the lesson Presents the student with a specific, concrete problem to solve Phase II: Devise a strategy: Ensure to the extent possible that students are using fruitful approach to solving the problem Devise a strategy for solving the problem Teacher feedback about the strategy Phase III: Implement the Strategy: Provide students with experience in solving problems Teacher monitors behavior Teacher provides feedback as students work Phase IV: Discuss and Evaluate Results: Provide students with feedback about their efforts Guide a Discussion of the results
Alternative Assessment: direct examination of students performance on significant task that are relevant to life outside of school Emphasizes high-ordered thinking Gives teachers opportunities to assess students knowledge and correct students misconceptions. Performance Assessment: task in which students demonstrate their level of competence or knowledge or skill carrying out an activity or creating a product Allows teachers to assess their students work while engaging in problem-solving situations Systematic Observation: requires teachers to specify criteria for the process they are assessing and take notes on based on the criteria. Checklist: written description of dimensions that must be present in an acceptable performance Rating scales: written descriptions of the dimensions of an acceptable performance with scales of values on which each dimension is rated Groups vs. Individuals: Assess students indivually based on the fact that they might cheat or not contribute to the group
Capitalize on the motivating effect of curiosity, challenge, authentic tasks, involvement, and autonomy Arouse curiosity and present a challenge that intrinsically motivate students Authentic task: learning activities that require understand that can be used in the world outside the classroom Authentic task motivate because students see abstract concepts and how these process relate to the real world Students autonomy increases when students have a choice in deciding what to do and how they should carry out the task
So what? What is important to understand about this?
Students learn how to become self-directed leaders. Students learn how to apply problem-solving skills towards problems. Students also learn how to work in groups to use problem-solving skills. Arouse curiosity in students so they are intrinsically motivated to figure out the problem.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Techniques of The ObserverДокумент175 страницTechniques of The Observershanben100% (6)
- Science in Early Childhood Classrooms Content and ProcessДокумент11 страницScience in Early Childhood Classrooms Content and Processapi-378051746Оценок пока нет
- Manifestors, It's Not Personal - Leela Swann-HerbertДокумент2 страницыManifestors, It's Not Personal - Leela Swann-HerbertZenZol67% (3)
- Di lp1Документ1 страницаDi lp1api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- 5e LP GroupДокумент3 страницы5e LP Groupapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Whit ResumeДокумент2 страницыWhit Resumeapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- LBLF TolerДокумент7 страницLBLF Tolerapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- March 16-20,2015Документ7 страницMarch 16-20,2015api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- 5E Lesson Plan: ENGAGEMENT (18 Points) : Day 1Документ2 страницы5E Lesson Plan: ENGAGEMENT (18 Points) : Day 1api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Intgerative lp2Документ1 страницаIntgerative lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- LD lp2Документ1 страницаLD lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- PB lp2Документ1 страницаPB lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Di lp2Документ1 страницаDi lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- LD lp1Документ1 страницаLD lp1api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Jigsaw IIДокумент1 страницаJigsaw IIapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Stad lp2Документ1 страницаStad lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- PB lp1Документ1 страницаPB lp1api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Toler InquiryДокумент1 страницаToler Inquiryapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- C A lp1Документ1 страницаC A lp1api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- C A lp2Документ1 страницаC A lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Jigsaw lp1Документ1 страницаJigsaw lp1api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Jigsaw lp2Документ1 страницаJigsaw lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- GD lp1Документ1 страницаGD lp1api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Whit C-A ModelДокумент1 страницаWhit C-A Modelapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- StadДокумент1 страницаStadapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- DiscussionДокумент1 страницаDiscussionapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- GD lp2Документ1 страницаGD lp2api-238290989Оценок пока нет
- IntegrativeДокумент1 страницаIntegrativeapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Guided Discovery: Box FrameДокумент1 страницаGuided Discovery: Box Frameapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- LD ModelДокумент1 страницаLD Modelapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Wat 0001 SpreadsheetДокумент3 страницыWat 0001 Spreadsheetapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Di ModelДокумент1 страницаDi Modelapi-238290989Оценок пока нет
- Machine Learning Unit Wise Important QuestionsДокумент2 страницыMachine Learning Unit Wise Important Questionsprashanth kumarОценок пока нет
- HOUSEKEEPING - WEEK 1 UpdatedДокумент5 страницHOUSEKEEPING - WEEK 1 UpdatedMaria Rizza IlaganОценок пока нет
- Dokument 12Документ1 страницаDokument 12Nina KoisОценок пока нет
- Artefact Design Behavior Change Strategy CardsДокумент14 страницArtefact Design Behavior Change Strategy CardsAnonymous MP1sRvОценок пока нет
- Journalism and Mass CommunicationsДокумент9 страницJournalism and Mass CommunicationsShiv TharuzОценок пока нет
- WHLP Eapp Mod 10Документ2 страницыWHLP Eapp Mod 10Jezza LapigueraОценок пока нет
- Unit 1. An Introduction To Statistical Data Analysis Report: Getting StartedДокумент54 страницыUnit 1. An Introduction To Statistical Data Analysis Report: Getting StartedTrang DươngОценок пока нет
- "The Effect of Time Management in Reducing Stress AmongДокумент7 страниц"The Effect of Time Management in Reducing Stress AmongLyvaОценок пока нет
- Case Study Questions HPДокумент9 страницCase Study Questions HPWaqar HassanОценок пока нет
- How To Make Best Use of This Book: What Is A Large Multilevel Class?Документ15 страницHow To Make Best Use of This Book: What Is A Large Multilevel Class?IrguensОценок пока нет
- 50 ITEMS - Facilitating Learning ExamДокумент102 страницы50 ITEMS - Facilitating Learning ExamJonathan EstoquiaОценок пока нет
- Basic Prepositions of Place WorksheetДокумент4 страницыBasic Prepositions of Place WorksheetYadily Santos HidalgoОценок пока нет
- Quality of Work Life As A Predictor of Work Engagement Among The Teaching Faculty at King Abdulaziz UniversityДокумент21 страницаQuality of Work Life As A Predictor of Work Engagement Among The Teaching Faculty at King Abdulaziz UniversitythevamayanОценок пока нет
- How To Write A Reflective EssayДокумент2 страницыHow To Write A Reflective EssayMeha Raj100% (1)
- Fundamentals of NursingДокумент485 страницFundamentals of Nursingshenric16100% (1)
- Daily Lesson PlanДокумент6 страницDaily Lesson PlanVanaja ThiagarajanОценок пока нет
- Population Vs SampleДокумент5 страницPopulation Vs Sampleronald bantuganОценок пока нет
- PSPv2022 01 19Документ31 страницаPSPv2022 01 19Bernard Jayve PalmeraОценок пока нет
- 10 Grade "B" Daily Routine Ii Bimester Unit 3: Languages: Brain Power Boosters Evaluation Criteria: Needs To Improve 1 Fair 2 Good 3 Excellent 4Документ8 страниц10 Grade "B" Daily Routine Ii Bimester Unit 3: Languages: Brain Power Boosters Evaluation Criteria: Needs To Improve 1 Fair 2 Good 3 Excellent 4Juan T.Оценок пока нет
- Heilman Gender Stereotypes and Workplace Bias, 2012 ROBДокумент23 страницыHeilman Gender Stereotypes and Workplace Bias, 2012 ROBCarolina Gomes de AraújoОценок пока нет
- Airbus BBA Candidate Report 11032843Документ6 страницAirbus BBA Candidate Report 11032843Bahareh MaghaniОценок пока нет
- Your Ipersonic TypeДокумент4 страницыYour Ipersonic TypeJade Clarke-MackintoshОценок пока нет
- Morph Practice NewДокумент4 страницыMorph Practice NewBùi Quang TrânОценок пока нет
- Great Books DraculaДокумент5 страницGreat Books Draculaprof_Christian100% (1)
- Overview On The Arabic CasesДокумент5 страницOverview On The Arabic CasesFrancesco TivoliОценок пока нет
- Speed of Trust Lsot 1 Day OutlineДокумент1 страницаSpeed of Trust Lsot 1 Day OutlineValaki MimiОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningДокумент7 страницCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMERCEDITA S. TOJINOОценок пока нет