Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Notes On Introduction To Cells
Загружено:
api-241062194Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Notes On Introduction To Cells
Загружено:
api-241062194Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
All Materials Cmassengale
I. All Organisms are Made of Cells
A. The cell is the basic unit of structure & function B. The cell is the smallest unit that can still carry on all life processes C. Both unicellular (one celled) and multicellular (many celled) organisms are composed of cells D. Before the 17 century, no one knew cells existed
th
E. Most cells are too small to be seen with the unaided eye F. In the early 17 century microscopes were invented & cells were seen for the 1 time
th st
G. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek, a Dutchman, made the 1 hand-held microscope & viewed microscopic organisms in water & bacteria from his teeth
st
Leeuwenhoek's microscope consisted simply of:
A) a screw for adjusting the height of the object being examined B) a metal plate serving as the body C) a skewer to impale the object and rotate it D) the lens itself, which was spherical
H. In 1665, an English scientist named Robert Hooke made an improved microscope and viewed thin slices of cork viewing plant cell walls I. Hooke named what he saw "cells"
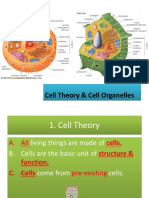
J. In the 1830s, Matthias Schleiden (botanist studying plants) & Theodore Schwann (zoologist studying animals) stated that all living things were made of cells K. In 1855, Rudolf Virchow stated that cells only arise from pre-existing cells L. Virchows idea contradicted the idea of spontaneous generation (idea that nonliving things could give rise to organisms) M. The combined work of Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow is known as the Cell Theory
Schwann
Schleiden
Virchow
II. Principles of the Cell Theory
A. All living things are made of one or more cells B. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in organisms C. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells
III. Cell Diversity
A. Not all cells are alike
B. Cells differ in size, shape, and function C. The female egg cell is the largest cell in the body & can be seen without a microscope
D. Bacterial cells are some of the smallest cells & are only visible with a microscope
E.coli Bacterial Cells E. Cells need surface area of their cell membrane large enough to adequately exchange materials with the environment (wastes, gases such as O & CO , and nutrients)
2 2
F. Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer surface area & their volume G. Small cells have more surface area for their volume of cytoplasm than large cells H. As cells grow, the amount of surface area becomes too small to allow materials to enter & leave the cell quickly enough
I. Cell size is also limited by the amount of cytoplasmic activity that the cells nucleus can control J. Cells come in a variety of shapes, & the shape helps determine the function of the cell (e.g. Nerve cells are long to transmit messages in the body, while red blood cells are disk shaped to move through blood vessels)
IV. Prokaryotes
A. Prokaryotic cells are less complex
B. Unicellular C. Do not have a nucleus & no membrane-bound organelles D. Most have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane & a single, looped chromosome (genetic material) in the cytoplasm E. Include bacteria & blue-green bacteria F. Found in the kingdom Monera
V. Eukaryotes
A. More complex cells B. Includes both unicellular & multicellular organisms C. Do have a true nucleus & membrane-bound organelles D. Organelles are internal structures in cells that perform specific functions
a. Nucleus
b. Chloroplast
c. Golgi
d. Mitochondria
E. Organelles are surrounded by a single or double membrane F. Entire eukaryotic cell surrounded by a thin cell membrane that controls what enters & leaves the cell G. Nucleus is located in the center of the cell H. The nucleus contains the genetic material (DNA) & controls the cells activities
I. Eukaryotes include plant cells, animal cells, fungi, algae, & protists J. Prokaryotes or bacteria lack a nucleus
K. Found in the kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae, & Animalia
Вам также может понравиться
- VtDA - The Ashen Cults (Vampire Dark Ages) PDFДокумент94 страницыVtDA - The Ashen Cults (Vampire Dark Ages) PDFRafãoAraujo100% (1)
- Reliability Technoology For Submarine Repeaters PDFДокумент8 страницReliability Technoology For Submarine Repeaters PDFbolermОценок пока нет
- ANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsДокумент24 страницыANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsAnghel LopezОценок пока нет
- Biology Science Class 9 Reference BookДокумент198 страницBiology Science Class 9 Reference BookJeevraj MedhiОценок пока нет
- Problem ManagementДокумент33 страницыProblem Managementdhirajsatyam98982285Оценок пока нет
- Cell To Improvement in Food Resources Chapters PDFДокумент102 страницыCell To Improvement in Food Resources Chapters PDFAbhideep JainОценок пока нет
- Summative Test Genbio 1 Q1Документ26 страницSummative Test Genbio 1 Q1Duane0% (1)
- ACE Resilience Questionnaires Derek Farrell 2Документ6 страницACE Resilience Questionnaires Derek Farrell 2CATALINA UNDURRAGA UNDURRAGAОценок пока нет
- Equine PregnancyДокумент36 страницEquine Pregnancydrdhirenvet100% (1)
- Worksheet On CellsДокумент6 страницWorksheet On CellshatchdogОценок пока нет
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsДокумент10 страницClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghОценок пока нет
- Q&A JurisdictionДокумент20 страницQ&A JurisdictionlucasОценок пока нет
- Thomas E. Skidmore-The Politics of Military Rule in Brazil, 1964-1985-Oxford University Press, USA (1988) PDFДокумент433 страницыThomas E. Skidmore-The Politics of Military Rule in Brazil, 1964-1985-Oxford University Press, USA (1988) PDFMarcelo Ramos100% (2)
- 1stQ Week5Документ3 страницы1stQ Week5Jesse QuingaОценок пока нет
- Cells Study Guide Answer KeyДокумент13 страницCells Study Guide Answer KeyLouise SagalesОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)Документ24 страницыModule 2 - Cell Structure & Function (Student Guide)greggcllam619076100% (7)
- General Biology 1 2023 ExamДокумент22 страницыGeneral Biology 1 2023 Examrolly baloОценок пока нет
- Panulaang FilipinoДокумент21 страницаPanulaang FilipinoKriza Erin B BaborОценок пока нет
- Bakhtin's Chronotope On The RoadДокумент17 страницBakhtin's Chronotope On The RoadLeandro OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of The CellДокумент17 страницStructure and Function of The CellIrene QuimsonОценок пока нет
- Elizondo Cell Theory and Cell Organelles-UpdatedДокумент14 страницElizondo Cell Theory and Cell Organelles-UpdatedRahanie Gadungan PajijiОценок пока нет
- Angelyn M. Morales Beed A-1Документ7 страницAngelyn M. Morales Beed A-1Angelyn MoralesОценок пока нет
- Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesДокумент4 страницыClass 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesneilОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science NotesДокумент8 страницChapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science Notesdeepti jainОценок пока нет
- Cell TheoryДокумент32 страницыCell TheorySumana BasuОценок пока нет
- Revision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsДокумент5 страницRevision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsArpit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Buenasher Learning Academy IncДокумент5 страницBuenasher Learning Academy IncEl CruzОценок пока нет
- Anika Baldizon Dedet - Cell Student Lecture Notes PDFДокумент3 страницыAnika Baldizon Dedet - Cell Student Lecture Notes PDFAnika Baldizon DedetОценок пока нет
- Study Material Unit - 7 Living ThingsДокумент4 страницыStudy Material Unit - 7 Living Thingsmaruchi270405Оценок пока нет
- General Biology 1 Module 1 Week 1Документ8 страницGeneral Biology 1 Module 1 Week 1Melanie OrayОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology 1.1Документ7 страницCell Biology 1.1Mirunalini GobinathОценок пока нет
- Cells Unit Powerpoint 2Документ110 страницCells Unit Powerpoint 2.....Оценок пока нет
- Bio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionДокумент24 страницыBio Lo Gym 2 Cell Structure FunctionMarmorn ArborshateОценок пока нет
- Cell AnswerДокумент2 страницыCell Answerunmuktagrahari333Оценок пока нет
- Cell Bio Chapter 1Документ22 страницыCell Bio Chapter 1GuteОценок пока нет
- (E-Module) BNA - Science - Class 9 - Part 1Документ73 страницы(E-Module) BNA - Science - Class 9 - Part 1Neetu SinhaОценок пока нет
- CellsДокумент9 страницCellsMg BhoneОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and OrganizationДокумент13 страницCell Structure and Organizationomololabalogun676Оценок пока нет
- Reviewer Science 7Документ22 страницыReviewer Science 7Arlynda LampaОценок пока нет
- 9 BiologyДокумент54 страницы9 BiologygirishtiwaskarОценок пока нет
- Biology ReviewerДокумент8 страницBiology ReviewermeliasuzzielОценок пока нет
- Lecturer 1 Cells StructureДокумент24 страницыLecturer 1 Cells StructureShivangi VermaОценок пока нет
- Cell TheoryДокумент34 страницыCell TheoryParbattie DannyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - A Tour of The CellДокумент3 страницыChapter 6 - A Tour of The CellhannahkellumОценок пока нет
- Cell TheoryДокумент13 страницCell TheoryDaryll BorjaОценок пока нет
- ch01 EdДокумент12 страницch01 EdJinette SurotОценок пока нет
- Module 1. Topic 1. IntroductionДокумент11 страницModule 1. Topic 1. IntroductionMusawwira KulidtodОценок пока нет
- ch01 Ed PDFДокумент18 страницch01 Ed PDFRachel CajilesОценок пока нет
- WEEK 1 ss2 BioДокумент4 страницыWEEK 1 ss2 BioOseni MuibaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Intro To CellДокумент6 страницChapter 1 Intro To CellrexartoozОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент4 страницыSciencesudergaming.phОценок пока нет
- Karp CH 1Документ17 страницKarp CH 1mikadeguzman100% (1)
- بايو عملي-محولДокумент8 страницبايو عملي-محولمظفر منعم ميران عباسОценок пока нет
- Lesson-Introduction To CellsДокумент11 страницLesson-Introduction To CellsAmino UsseneОценок пока нет
- c01 Instructor ManualДокумент53 страницыc01 Instructor Manualhuh ssОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and Functions: Class 8 NCERT Biology Chapter 4Документ29 страницCell Structure and Functions: Class 8 NCERT Biology Chapter 4Chitranshee RastogiОценок пока нет
- Gen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Документ68 страницGen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Ciena GaddiОценок пока нет
- SY20703 Molecular Cell Biology: (Prof. Madya Dr. Lee Ping Chin, Professor Room 69)Документ16 страницSY20703 Molecular Cell Biology: (Prof. Madya Dr. Lee Ping Chin, Professor Room 69)Charles RajОценок пока нет
- Assignment # 1: Principle of LifeДокумент10 страницAssignment # 1: Principle of LifeOmme HabibaОценок пока нет
- Chapter-8 Cell: Structure and FuctionДокумент12 страницChapter-8 Cell: Structure and FuctionTopОценок пока нет
- Earth and Life ScienceДокумент6 страницEarth and Life ScienceVeniedick Blancia ManibpelОценок пока нет
- Bio Module 2Документ9 страницBio Module 2Cecile MusaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1Документ11 страницLesson 1remshopОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelle NotesДокумент36 страницCell Organelle NotesChoebe Khaye Shoebe100% (1)
- The Basics of BiologyДокумент127 страницThe Basics of BiologyMonica SevillaОценок пока нет
- Cell Theory, Prokaryote, EukaryoteДокумент22 страницыCell Theory, Prokaryote, EukaryoteMichelle ReyesОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology & BiochemistryДокумент320 страницCell Biology & BiochemistryVai SanОценок пока нет
- The Minecraft Survival Quest ChallengeДокумент4 страницыThe Minecraft Survival Quest Challengeapi-269630780100% (1)
- Assignment Class X Arithmetic Progression: AnswersДокумент1 страницаAssignment Class X Arithmetic Progression: AnswersCRPF SchoolОценок пока нет
- ''Want To Learn To Speak Latin or Greek This (2018) Summer''Документ10 страниц''Want To Learn To Speak Latin or Greek This (2018) Summer''ThriwОценок пока нет
- Star QuizДокумент3 страницыStar Quizapi-254428474Оценок пока нет
- In Mein KampfДокумент3 страницыIn Mein KampfAnonymous t5XUqBОценок пока нет
- Yukot,+houkelin 2505 11892735 Final+Paper+Group+41Документ17 страницYukot,+houkelin 2505 11892735 Final+Paper+Group+410191720003 ELIAS ANTONIO BELLO LEON ESTUDIANTE ACTIVOОценок пока нет
- Marketing PlanДокумент41 страницаMarketing PlanMark AbainzaОценок пока нет
- Springfield College Lesson Plan Template PHED 237: The Learning and Performance of Physical ActivitiesДокумент5 страницSpringfield College Lesson Plan Template PHED 237: The Learning and Performance of Physical Activitiesapi-285421100Оценок пока нет
- MuzicaДокумент3 страницыMuzicaGiurcanas AndreiОценок пока нет
- What Is Folate WPS OfficeДокумент4 страницыWhat Is Folate WPS OfficeMerly Grael LigligenОценок пока нет
- Diode ExercisesДокумент5 страницDiode ExercisesbruhОценок пока нет
- 576 1 1179 1 10 20181220Документ15 страниц576 1 1179 1 10 20181220Sana MuzaffarОценок пока нет
- Digital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSIONДокумент2 страницыDigital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSIONEla DerarajОценок пока нет
- Chhabra, D., Healy, R., & Sills, E. (2003) - Staged Authenticity and Heritage Tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (3), 702-719 PDFДокумент18 страницChhabra, D., Healy, R., & Sills, E. (2003) - Staged Authenticity and Heritage Tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (3), 702-719 PDF余鸿潇Оценок пока нет
- Karly Hanson RèsumèДокумент1 страницаKarly Hanson RèsumèhansonkarlyОценок пока нет
- Types of Numbers: SeriesДокумент13 страницTypes of Numbers: SeriesAnonymous NhQAPh5toОценок пока нет
- Reported Speech StatementsДокумент1 страницаReported Speech StatementsEmilijus Bartasevic100% (1)
- #6 Decision Control InstructionДокумент9 страниц#6 Decision Control InstructionTimothy King LincolnОценок пока нет
- Finding Nemo 2Документ103 страницыFinding Nemo 2julianaОценок пока нет
- Final PS-37 Election Duties 06-02-24 1125pm)Документ183 страницыFinal PS-37 Election Duties 06-02-24 1125pm)Muhammad InamОценок пока нет