Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Textchart
Загружено:
api-211294917Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Textchart
Загружено:
api-211294917Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
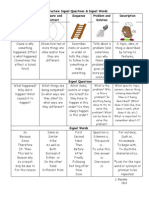
Structure
Definition
The author explains a topic, idea, person, place, or thing by listing characteristics, features, and examples. Focus is on one thing and its components.
Signal Words
For example Characteristics are Such as Looks like Consists of For instance Most important *Look for topic word (or synonym) to be repeated throughout the text.
Graphic Organizers
Concept Map
Summary Questions
What specific person, place, thing, event, or concept is being described? How is the topic described? (How does it work? What does it do? What does it look like? Etc.) What are the most important attributes or characteristics? How can the topic be classified? (For example, a robin can be classified as a type of bird.)
Paragraph Frames
A ________ is a type of _________. It is made up of ____________ and looks like ___________. Some ________ have _________ such as _________. For example, _____________.
Description
______ has several characteristics. One characteristic is _______. Another is ___, which is important because ___________.
Sequence
The author lists items or events in numerical or chronological order. Describes the order of events or how to do or make something.
First, second, third Next Then, after Before, prior to Not long after While, meanwhile Simultaneously At the same time Following Finally At last In the end On (date) At (time) Directions
Timeline 1 2
4 5
What sequence of events is being described? What are the major events or incidents that occur?
Step 3
Here is how a _________ is made. First, _________. Next, ____________. Then, ______________. Finally, ____________.
Steps/Directions
Step 1 Step 2
What are the steps, directions, or procedures to follow? (What must be done first, second, etc.?) What is the beginning event? What other events or steps are included? What is the final outcome, event, or step?
On (date) _________ happened. Prior to that _________ was ________. Then __________. After that _____________. In the end, ____________________.
Cycle/Circle
Compare and Contrast
The author explains how two or more things are alike and/or how they are different.
Differs from Similar to In contrast Alike Same as As well as On the other hand Both Either , or Not only, but also Yet, although, but, However On the other hand * Also look for est words: best, fewest, tallest, etc.
Venn Diagram
What items are being compared? What is it about them that is being compared? What characteristics of items form the basis of the comparison?
_____________ and ___________ are alike in several ways. Both ________ and __________ have similar ___________. Both also ________ as well as _________. On the other hand, one way they differ is _________. Another difference is ___________. Although they share _____, only ____ is the _____-est.
T-Chart What characteristics do they have in common; how are these items alike? In what way are these items different? Alike Different
*All five text structures are tested on Kansas Reading Assessment
C.Simoneau, K.Orcutt, T.Konrade ESSDACK
Side
Structure
Description
The author lists one or more causes or events and the resulting consequences or effects. Effect = What happened? Cause = What made it happen? Purpose is to explain why or how something happened, exists, or works. *Often there will be an if/then pattern
Signal Words
Reasons why Reasons for Ifthen As a result of Therefore Because of So Since In order to Leads or leads to Effects of Caused by Result Outcome Impact Influenced by Brought about by
Graphic Organizers
Effect #1
Summary Questions
What happened? Why did it happen? What was the reason for?
Paragraph Frames
The reason why ________ happened was because of __________. If ________ hadnt happened, then _________. Due to _________ occurring, ______. This explains why _______. The cause of ___________is not easy to define. Some people think the cause is ____________. Others believe the main cause is ___________. Understanding the cause of _____________ is important because _____________________. The effects of ________ are significant because
Cause and Effect
Cause
Effect #2 What was the effect(s) of the event? What happened as a result of.? Effect #3 What were the results or outcomes caused by the event? In what ways did prior event(s) cause or influence the main event? Will this result always happen from these causes?
Cause #1 Cause #2 Cause #3 Effect
_______. One effect of ______ is __________. Another result is ________________________. Because of these outcomes, it important that ________________________________.
Problem and Solution
The author states a problem and lists one or more possible solutions to the problem. May also include the pros and cons for the solutions.
Problem is Dilemma is Puzzle is Solved Question Answer Because Since This led to The main difficulty One possible solution is One challenge Therefore, This led to, so that Ifthen, thus
Fishbone Problem
What is the problem(s)? Who had the problem? What is causing the problem? Solutions Why is this a problem?
____________ had/is a problem because ________________. One possible solution is ____________. This answer is good because ____________. Therefore, _______________. As a result, ____________. The problem of __________ really boils down to the issue of ______________. In the past, the common solution was to_________________. However, this was only effective in terms of __________________. There are now other solutions that might work. One option would be to ______________________.
Problem #2 Problem #2 Problem #2 Solution
What is wrong and how can it be taken care of? What solutions are recommended or attempted? What can be improved, changed, fixed, or remedied? What are the pros and cons of the solutions offered?
*All five text structures are tested on Kansas Reading Assessment
C.Simoneau, K.Orcutt, T.Konrade ESSDACK
Side
Вам также может понравиться
- 2-3 and 2-4 Text StructuresДокумент2 страницы2-3 and 2-4 Text Structuresapi-265305338Оценок пока нет
- Summary Frames Are Powerful Tools For Teaching Independent Reading, Thinking and WritingДокумент1 страницаSummary Frames Are Powerful Tools For Teaching Independent Reading, Thinking and WritingEsmeralda CartagenaОценок пока нет
- Retelling Teacher PowerpointДокумент42 страницыRetelling Teacher PowerpointAmado Ramon UslaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide Text StructuresДокумент4 страницыStudy Guide Text StructuresTessa JОценок пока нет
- Writing Reflection For Paper 1Документ2 страницыWriting Reflection For Paper 1api-317135260Оценок пока нет
- Graphic Organizer TemplatesДокумент38 страницGraphic Organizer Templatesanna39100% (2)
- Learning Packet in English 3: WEEK 28 (April 26 - 30, 2021)Документ4 страницыLearning Packet in English 3: WEEK 28 (April 26 - 30, 2021)Aizel Nova Fermilan ArañezОценок пока нет
- Ielts Writing Task 2Документ35 страницIelts Writing Task 2vijaya100% (1)
- Eapp - Week 2 Las 1-3Документ5 страницEapp - Week 2 Las 1-3Genventures TVОценок пока нет
- Literacy Question PromptsДокумент6 страницLiteracy Question Promptsapi-292055333Оценок пока нет
- M3D2 HandoutДокумент26 страницM3D2 HandoutSakTeen [สักตีน]Оценок пока нет
- Cause & Effect EssayДокумент4 страницыCause & Effect EssaypretywomnОценок пока нет
- U4 - Before ClassДокумент8 страницU4 - Before ClassBảo ChâuОценок пока нет
- Ac Differentiation StrategiesДокумент54 страницыAc Differentiation Strategiesapi-283087248Оценок пока нет
- Writing Task 2: ST ND RD TH THДокумент13 страницWriting Task 2: ST ND RD TH THsukhdeeprandhawaОценок пока нет
- Text Structures With Summary Questions and Paragraph FramesДокумент2 страницыText Structures With Summary Questions and Paragraph Framesapi-322660744Оценок пока нет
- Introduction - Writing PacketДокумент7 страницIntroduction - Writing PacketDavid Velez GonzalezОценок пока нет
- GROUP2Документ20 страницGROUP2calyxdelfinОценок пока нет
- Help and Advice For Keeping A Journal in Ib Theatre Part 11Документ19 страницHelp and Advice For Keeping A Journal in Ib Theatre Part 11api-291947860100% (1)
- Teaching Experiment Lesson Plan TemplateДокумент5 страницTeaching Experiment Lesson Plan Templateapi-283311423Оценок пока нет
- CH 1problem Solving NotesДокумент16 страницCH 1problem Solving NotesMuhammad IbrarОценок пока нет
- What Is An Expository EssayДокумент4 страницыWhat Is An Expository EssayKristell PungtilanОценок пока нет
- Problem Solution EssaysДокумент9 страницProblem Solution EssaysĐinh Khắc Nhật TrườngОценок пока нет
- TextstructuresignalwordsДокумент2 страницыTextstructuresignalwordsapi-246965227Оценок пока нет
- SPEAKING FRAME FOR CANDIDATES (PART 3-Part 1)Документ2 страницыSPEAKING FRAME FOR CANDIDATES (PART 3-Part 1)TRACY VIANNEY ANO MoeОценок пока нет
- Text Structure FramesДокумент1 страницаText Structure FramesmrboyerОценок пока нет
- Problem and Solution EssayДокумент13 страницProblem and Solution EssaysachithraОценок пока нет
- LHO2 Intro. To Note Taking SSДокумент8 страницLHO2 Intro. To Note Taking SSSalih Can ŞenОценок пока нет
- Homeroom Guidance 8 2 2Документ14 страницHomeroom Guidance 8 2 2Romeo jr RamirezОценок пока нет
- ELA TAKS Warm-Ups (Grades 6-11)Документ5 страницELA TAKS Warm-Ups (Grades 6-11)eva.bensonОценок пока нет
- The Composing Process - StudentsДокумент7 страницThe Composing Process - StudentsKan KanОценок пока нет
- Presentation OutlineДокумент5 страницPresentation Outlinecontroloperation1Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 SummarizingДокумент27 страницLesson 3 SummarizingLuisa CarpioОценок пока нет
- 6 Types of Ielts Tasks 1 and 2Документ9 страниц6 Types of Ielts Tasks 1 and 2MA W.Оценок пока нет
- (Brief Discussion of The Lesson, If Possible Cite Examples) : SUBJECT (Uppercase and Bold)Документ33 страницы(Brief Discussion of The Lesson, If Possible Cite Examples) : SUBJECT (Uppercase and Bold)KD DelayunОценок пока нет
- 5-21-15 Ac Differentiation StrategiesДокумент49 страниц5-21-15 Ac Differentiation Strategiesapi-335454276Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 10Документ3 страницыLesson 10Vea Patricia AngeloОценок пока нет
- TemplateДокумент3 страницыTemplateChauhan SumitОценок пока нет
- FS2 Ep3 10Документ28 страницFS2 Ep3 10DianneОценок пока нет
- Creative Problem Solving Juntune PDFДокумент15 страницCreative Problem Solving Juntune PDFAhmed AbenОценок пока нет
- Summary Opinion and SupportДокумент2 страницыSummary Opinion and Supportapi-237077794Оценок пока нет
- Abstract FormatДокумент1 страницаAbstract FormatHéctorОценок пока нет
- Raw Q3 Las 1Документ15 страницRaw Q3 Las 1Abegail CastilloОценок пока нет
- Student Feedback FormДокумент4 страницыStudent Feedback FormAyyaz QamarОценок пока нет
- 雅思寫作 SIMON 最終確定版Документ201 страница雅思寫作 SIMON 最終確定版Olive FangОценок пока нет
- Our Lady of The Pillar Academy-Bago (Olpa-B.I.), Inc. Mabini Street., Brgy. Ma-Ao, Bago CityДокумент13 страницOur Lady of The Pillar Academy-Bago (Olpa-B.I.), Inc. Mabini Street., Brgy. Ma-Ao, Bago Citylarahpalencia13Оценок пока нет
- Finding The Pattern OrganizationДокумент12 страницFinding The Pattern OrganizationAnggun Novita RiniОценок пока нет
- Engl 10 Module 5Документ9 страницEngl 10 Module 5Jess Anthony Efondo100% (2)
- (Brief Discussion of The Lesson, If Possible Cite Examples) : SUBJECT (Uppercase and Bold)Документ20 страниц(Brief Discussion of The Lesson, If Possible Cite Examples) : SUBJECT (Uppercase and Bold)Dhan GregorioОценок пока нет
- Module 2 EappДокумент5 страницModule 2 EappShiela DimayugaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Statement of Goals and ChoicesДокумент1 страницаUnit 1 Statement of Goals and Choicesapi-355348604Оценок пока нет
- Text Structure Features&OrganisationДокумент48 страницText Structure Features&OrganisationMax AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Cause and Effect EssayДокумент2 страницыCause and Effect EssayPete Wang100% (1)
- Week 2 Readings-Introduction To Paragraphs WritingДокумент14 страницWeek 2 Readings-Introduction To Paragraphs WritingRandy RebmanОценок пока нет
- Organization and Text Mapping: Reading For General InterestДокумент22 страницыOrganization and Text Mapping: Reading For General InterestrizkiОценок пока нет
- Templates For All IELTS Essays TypesДокумент9 страницTemplates For All IELTS Essays TypesSimpleng Buhay80% (10)
- Practice Makes Perfect: Advanced English Grammar for ESL Learners, Second EditionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect: Advanced English Grammar for ESL Learners, Second EditionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- IELTS Academic Writing: How To Write 8+ Answers For The IELTS Exam!От EverandIELTS Academic Writing: How To Write 8+ Answers For The IELTS Exam!Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- AgendaДокумент2 страницыAgendaapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Courtneeng 495 ThesispaperДокумент29 страницCourtneeng 495 Thesispaperapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Tkhsstaffmeeting9 18 13Документ2 страницыTkhsstaffmeeting9 18 13api-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Ed 310 ClassroommanagementplanДокумент18 страницEd 310 Classroommanagementplanapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- English 9 ListofproblemsДокумент1 страницаEnglish 9 Listofproblemsapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Folio 1029transitionsitipДокумент3 страницыFolio 1029transitionsitipapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Folio Copyof111conclusionsandtextstructuresitipДокумент3 страницыFolio Copyof111conclusionsandtextstructuresitipapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Folio Copyof114textstructureitipДокумент3 страницыFolio Copyof114textstructureitipapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- English 9 CauseandeffectstressДокумент1 страницаEnglish 9 Causeandeffectstressapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Printable Writingessays Conclusion HsДокумент2 страницыPrintable Writingessays Conclusion Hsapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Folio ConclusionsitipДокумент3 страницыFolio Conclusionsitipapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Ed 399 InstructionalplanДокумент7 страницEd 399 Instructionalplanapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Folio Copyof1031favoritewordsitipДокумент3 страницыFolio Copyof1031favoritewordsitipapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- CCSS ELA Literacy RL 11 12 1Документ3 страницыCCSS ELA Literacy RL 11 12 1api-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Folio Copyof116symbolismlessonplanitipДокумент4 страницыFolio Copyof116symbolismlessonplanitipapi-211294917Оценок пока нет
- Reciprocal Teaching Approach With Self-Regulated Learning (RT-SRL) : Effects On Students' Reading Comprehension, Achievement and Self-Regulation in ChemistryДокумент29 страницReciprocal Teaching Approach With Self-Regulated Learning (RT-SRL) : Effects On Students' Reading Comprehension, Achievement and Self-Regulation in ChemistryAmadeus Fernando M. PagenteОценок пока нет
- WAT English Language Ability Form 2020 PDFДокумент1 страницаWAT English Language Ability Form 2020 PDFEmre KaraОценок пока нет
- The ROLE OF PARENTS IN THE EDUCATION OFДокумент18 страницThe ROLE OF PARENTS IN THE EDUCATION OFLenyBarroga100% (1)
- Living DangerouslyДокумент4 страницыLiving Dangerouslyv4freedom100% (1)
- EOM Lecture Notes-1 PDFДокумент16 страницEOM Lecture Notes-1 PDFChris MarvinОценок пока нет
- Five Year MA Integrated Regulations & Syllabus-030714Документ100 страницFive Year MA Integrated Regulations & Syllabus-030714anoopОценок пока нет
- Pesantren Dan Bahasa ArabДокумент15 страницPesantren Dan Bahasa ArabFEBRYОценок пока нет
- Thesis For Geriatric CareДокумент6 страницThesis For Geriatric CareTweenie Dalumpines100% (1)
- Lacan Kojeve and Hippolite On The SubjectДокумент14 страницLacan Kojeve and Hippolite On The Subjectmadspeter100% (2)
- Legal Ethics CasesДокумент126 страницLegal Ethics CasesKaye TolentinoОценок пока нет
- Identity-Protective Cognition ThesisДокумент37 страницIdentity-Protective Cognition ThesisJohn BurkeОценок пока нет
- MEC420 - Kinematics of ParticlesДокумент55 страницMEC420 - Kinematics of ParticlesWaIe AzfarОценок пока нет
- MSC Social Development Practice at The Bartlett Development Planning Unit. University College LondonДокумент2 страницыMSC Social Development Practice at The Bartlett Development Planning Unit. University College LondonThe Bartlett Development Planning Unit - UCLОценок пока нет
- Leaderboards in Esl SzimmerДокумент10 страницLeaderboards in Esl Szimmerapi-415572187Оценок пока нет
- Philosophical Approaches To Ethics-4Документ18 страницPhilosophical Approaches To Ethics-4Harsh Thaker100% (1)
- Samiah International Builders LTD - Harshit VermaДокумент27 страницSamiah International Builders LTD - Harshit VermaStarОценок пока нет
- Selena Savic Event Movement ArchitectureДокумент18 страницSelena Savic Event Movement ArchitectureThomasHubertОценок пока нет
- Speech Act Communicative StrategyДокумент3 страницыSpeech Act Communicative StrategyKathleen BurlasОценок пока нет
- Light After DarknessДокумент47 страницLight After DarknessAvinashmachadoОценок пока нет
- Saki Project 890Документ90 страницSaki Project 890Ramesh DonОценок пока нет
- Jose Prager - Name & SignДокумент7 страницJose Prager - Name & SignFreddie666100% (4)
- Employee CounsellingДокумент7 страницEmployee CounsellingShikha SrivastwaОценок пока нет
- Post StructuralismДокумент26 страницPost StructuralismnatitvzandtОценок пока нет
- Resume Bab 4 Mankiw EnglishДокумент5 страницResume Bab 4 Mankiw EnglishSeno Bayu R WОценок пока нет
- Introduction Medieval and Post MedievalДокумент5 страницIntroduction Medieval and Post MedievalSándor KissОценок пока нет
- You, Me and Us Respectful Relationships Education Program: Training ManualДокумент257 страницYou, Me and Us Respectful Relationships Education Program: Training ManualWomen's Health West100% (1)
- IFEM AppP PDFДокумент7 страницIFEM AppP PDFPippo MiriОценок пока нет
- Cost of Smell EditedДокумент5 страницCost of Smell EditedRonalyn Panganiban Verona100% (3)
- Ob 15Документ40 страницOb 15fastus15Оценок пока нет
- Salazar Otero A Tale of A Tool: The Impact of Sims's Vector Autoregressions On Macroeconometrics Hope 2019 0510557Документ22 страницыSalazar Otero A Tale of A Tool: The Impact of Sims's Vector Autoregressions On Macroeconometrics Hope 2019 0510557boris salazar trujilloОценок пока нет