Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lec13 (1) Integrals Triples
Загружено:
David Atilio Dominguez PozoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lec13 (1) Integrals Triples
Загружено:
David Atilio Dominguez PozoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
MATH 209Calculus, III
Volker Runde
University of Alberta
Edmonton, Fall 2011
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Triple integrals over rectangular boxes, I
As in two variables. . .
Let
B := {(x, y, z) : a x b, c y d, r z s}
be a rectangular box. Divide:
[a, b] into n subintervals [x
j 1
, x
j
] of length x =
ba
n
;
[c, d] into m subintervals [y
k1
, y
k
] of length x =
dc
m
;
[r , s] into subintervals [z
1
, z
] of length z =
sr
.
Set
B
j ,k,
:= [x
j 1
, x
j
] [y
k1
, y
k
] [z
1
, z
].
Fix a support point (x
j
, y
k
, z
) in B
j ,k,
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Triple integrals over rectangular boxes, II
Denition
The triple integral of f over B is dened as
___
B
f (x, y, z) dV
= lim
n,m,
n
j =1
m
k=1
=1
f (x
j
, y
k
, z
) xyz
. .
=:V
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Triple integrals over rectangular boxes, III
Theorem (Fubinis theorem for triple integrals)
Let B = [a, b] [c, d] [r , s] be a rectangular box, and let
f : B R be continuous. Then
___
B
f (x, y, z) dV =
_
s
r
_
d
c
_
b
a
f (x, y, z) dx dy dz.
(The order of integration is arbitrary.)
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, I
Example
Let B := [0, 1] [1, 2] [0, 3], and f (x, y, z) := xyz
2
. Then:
___
B
f (x, y, z) dV =
_
1
0
_
3
0
_
2
1
xyz
2
dy dz dx
=
_
1
0
_
3
0
xy
2
z
2
2
y=2
y=1
dz dx =
_
1
0
_
3
0
2xz
2
xz
2
2
dz dx
=
3
2
_
1
0
_
3
0
xz
2
dz dx =
3
2
_
1
0
xz
3
3
z=3
z=0
dx
=
1
2
_
1
0
27x dx =
27
4
x
2
x=1
x=0
=
27
4
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Solid regions of type I, I
Denition
A solid region E R
3
is said to be of type I if there are
D R
2
and continuous functions u
1
, u
2
: D R with u
1
u
2
such that
E = {(x, y, z) : (x, y) D, u
1
(x, y) z u
2
(x, y)}.
(D is called the projection of E onto the xy-plane.)
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Solid regions of type I, II
Example
The solid region
E = {(x, y, z) : x
2
+ y
2
+ z
2
R
2
}
is of type I with
D = {(x, y) : x
2
+ y
2
R
2
},
u
1
(x, y) =
_
R
2
x
2
y
2
,
u
2
(x, y) =
_
R
2
x
2
y
2
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Solid regions of type I, III
Integration over solid regions of type I
___
E
f (x, y, z) dV =
__
D
_
_
u
2
(x,y)
u
1
(x,y)
f (x, y, z) dz
_
dA.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, II
Example
Let E be the ball centered at (0, 0, 0) of radius R. Then the
volume of E is
V =
___
E
1 dV
=
__
D
_
_
R
2
x
2
y
2
R
2
x
2
y
2
1 dz
_
dA = 2
__
D
_
R
2
x
2
y
2
dA
= 2
_
2
0
_
R
0
_
R
2
r
2
cos
2
r
2
sin
2
r dr d
= 2
_
2
0
_
R
0
_
R
2
r
2
r dr d = 4
_
R
0
_
R
2
r
2
r dr =
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, III
Example (continued)
= 4
_
R
0
_
R
2
r
2
r dr
= 2
_
0
R
2
u du = 2
_
R
2
0
u du
= 2
_
2
3
u
3
2
u=R
2
u=0
_
=
4
3
R
3
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Solid regions of type I, IV
Case 1
D is of type I, i.e.,
D = {(x, y) : x [a, b], g
1
(x) y g
2
(x)}.
Then
E = {(x, y, z) : a x b,
g
1
(x) y g
2
(x), u
1
(x, y) z u
2
(x, y)}
and
___
E
f (x, y, z) dV =
_
b
a
_
g
2
(x)
g
1
(x)
_
u
2
(x,y)
u
1
(x,y)
f (x, y, z) dz dy dx.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Solid regions of type I, V
Case 2
D is of type II, i.e.,
D = {(x, y) : y [c, d], h
1
(y) x h
2
(y)}.
Then
E = {(x, y, z) : c y d,
h
1
(y) x h
2
(y), u
1
(x, y) z u
2
(x, y)}
and
___
E
f (x, y, z) dV =
_
d
c
_
h
2
(y)
h
1
(y)
_
u
2
(x,y)
u
1
(x,y)
f (x, y, z) dz dx dy.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, IV
Example
Let E be the solid tetrahedron bounded by the planes x = 0,
y = 0, z = 0, and x + y + z = 1. Evaluate
___
E
z dV.
E is of type I:
E = {(x, y, z) : (x, y) D, 0 z 1 x y}
with
D = {(x, y) : x [0, 1], 0 y 1 x},
so that
E = {(x, y, z) : 0 x 1, 0 y 1 x, 0 z 1 x y}.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, V
Example (continued)
Hence:
___
E
z dV =
__
D
__
1xy
0
z dz
_
dA
=
__
D
(1 x y)
2
2
dA =
1
2
_
1
0
_
1x
0
(1 x y)
2
dy dx
=
1
2
_
1
0
(1 x y)
3
3
y=1x
y=0
dx =
1
6
_
1
0
(1 x)
3
dx
=
1
6
_
(1 x)
4
4
x=1
x=0
_
=
1
24
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Solid regions of type II
Denition
A solid region E R
3
is said to be of type II if there are
D R
2
and continuous functions u
1
, u
2
: D R with u
1
u
2
such that
E = {(x, y, z) : (y, z) D, u
1
(y, z) x u
2
(y, z)}.
Integration over solid regions of type II
___
E
f (x, y, z) dV =
__
D
_
_
u
2
(y,z)
u
1
(y,z)
f (x, y, z) dx
_
dA.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Solid regions of type III
Denition
A solid region E R
3
is said to be of type III if there are
D R
2
and continuous functions u
1
, u
2
: D R with u
1
u
2
such that
E = {(x, y, z) : (x, z) D, u
1
(x, z) y u
2
(x, z)}.
Integration over solid regions of type III
___
E
f (x, y, z) dV =
__
D
_
_
u
2
(x,z)
u
1
(x,z)
f (x, y, z) dy
_
dA.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, VI
Example
Let E be the solid region bounded by the paraboloid
y = x
2
+ z
2
and the plane y = 4. Evaluate
___
E
x
2
+ z
2
dV.
E is of type I:
E =
_
(x, y, z) : (x, y) D,
_
y x
2
z
_
y x
2
_
with
D = {(x, y) : x [2, 2], x
2
y 4},
so that
E =
_
(x, y, z) : x [2, 2], x
2
y 4,
_
y x
2
z
_
y x
2
_
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, VII
Example (continued)
Then:
___
E
_
x
2
+ z
2
dV =
__
D
_
_
yx
2
yx
2
_
x
2
+ z
2
dz
_
dA
=
_
2
2
_
4
x
2
_
yx
2
yx
2
_
x
2
+ z
2
dz dy dx
= ???
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, VIII
Example (continued)
E is also of type III:
E = {(x, y, z) : (x, y) D, x
2
+ z
2
y 4}
with
D = {(x, z) : x
2
+ z
2
4},
so that
E = {(x, y, z) : x
2
+ z
2
4, x
2
+ z
2
y 4}.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, IX
Example (continued)
Thus:
___
E
_
x
2
+ z
2
dV =
__
D
__
4
x
2
+z
2
_
x
2
+ z
2
dy
_
dA
=
__
D
(4 x
2
z
2
)
_
x
2
+ z
2
dA
=
_
2
0
_
2
0
(4 r
2
)rr dr d = 2
_
2
0
4r
2
r
4
dr
= 2
_
4r
3
3
r
5
5
r =2
r =0
_
= 2
_
32
3
32
5
_
=
128
15
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, X
Example
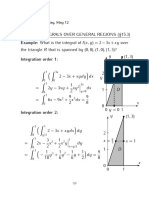
Find the volume of the tetrahedron T bounded by the planes
x + 2y + z = 2, x = 2y, x = 0, and z = 0.
Projecting T onto the xy-plane, we obtain
D =
_
(x, y) : 0 x 1,
x
2
y 1
x
2
_
,
so that
T =
_
(x, y, z) : 0 x 1,
x
2
y 1
x
2
, 0 z 2 x 2y
_
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, XI
Example (continued)
V =
___
T
1 dV =
_
1
0
_
1
x
2
x
2
_
2x2y
0
1dz dy dx
=
_
1
0
_
1
x
2
x
2
2 x 2y dy dx =
_
1
0
(2 x)y y
2
y=1
x
2
y=
x
2
dx
=
_
1
0
(2 x)
_
1
x
2
_
_
1
x
2
_
2
(2 x)
x
2
+
_
x
2
_
2
dx
=
_
1
0
x
2
2x +1 dx =
_
1
0
(x 1)
2
dx =
(x 1)
3
3
x=1
x=0
=
1
3
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Mass and moments of solid objects, I
The mass of a solid object
Let E R
3
be a solid object.
Let (x, y, z) be the density of E at (x, y, z). Then the total
mass of E is
m =
___
E
(x, y, z) dV.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Mass and moments of solid objects, II
Moments and center of mass
The moments of E about the three coordinate planes are:
M
yz
=
___
E
x(x, y, z) dV,
M
xz
=
___
E
y(x, y, z) dV,
M
xy
=
___
E
z(x, y, z) dV.
The center of mass of E is located at ( x, y, z) where
x =
M
yz
m
, y =
M
xz
m
, z =
M
xy
m
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, XII
Example
Find the center of mass of the solid body E with constant
density , bounded by the parabolic cylinder x = y
2
and the
planes x = z, z = 0, and x = 1.
Describe E as a type I solid region:
E = {(x, y, z) : (x, y) D, 0 z x}
with
D = {(x, y) : 1 y 1, y
2
x 1},
so that
E = {(x, y, z) : 1 y 1, y
2
x 1, 0 z x}.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, XIII
Example (continued)
Therefore:
m =
___
E
dV =
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
_
x
0
dz dx dy
=
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
x dx dy =
_
1
1
x
2
2
x=1
x=y
2
dy =
2
_
1
1
1 y
4
dy
=
_
1
0
1 y
4
dy =
_
y
y
5
5
y=1
y=0
_
=
4
5
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, XIV
Example (continued)
Furthermore:
M
yz
=
___
E
x dV =
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
_
x
0
x dz dx dy
=
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
x
2
dx dy =
_
1
1
x
3
3
x=1
x=y
2
dy =
_
1
1
1
3
y
6
3
dy
=
2
3
_
1
0
1 y
6
dy =
2
3
_
y
y
7
7
y=1
y=0
_
=
4
7
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, XV
Example (continued)
Moreover:
M
xz
=
___
E
y dV =
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
_
x
0
y dz dx dy
=
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
xy dx dy =
_
1
1
x
2
y
2
x=1
x=y
2
dy
=
_
1
1
y
3
y
5
3
dy = 0.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, XVI
Example (continued)
Finally:
M
xy
=
___
E
z dV =
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
_
x
0
z dz dx dy
=
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
z
2
2
z=x
z=0
dx dy =
2
_
1
1
_
1
y
2
x
2
dx dy
=
2
_
1
1
x
3
3
x=1
x=y
2
dy =
2
_
1
1
1
3
y
6
3
dy
=
3
_
1
0
1y
6
dy =
3
_
y
y
7
7
y=1
y=0
_
=
3
_
1
1
7
_
=
2
7
.
MATH 209
Calculus,
III
Volker Runde
Triple
integrals
Applications
of triple
integrals
Examples, XVII
Example (continued)
Hence, the center of mass of E is at
( x, y, z) =
_
M
yz
m
,
M
xz
m
,
M
xy
m
_
=
_
5
7
, 0,
5
14
_
.
Вам также может понравиться
- Lec14 (1) Integral Triples Cilindrica y EsfericaДокумент27 страницLec14 (1) Integral Triples Cilindrica y EsfericaDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- MATH 209-Calculus, III: Volker RundeДокумент15 страницMATH 209-Calculus, III: Volker RundeDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Math 55 Exercises First ExamДокумент2 страницыMath 55 Exercises First ExamAngelica CanoОценок пока нет
- MATH 20E - Final Exam: Solutions To Practice Problems: Alina BucurДокумент9 страницMATH 20E - Final Exam: Solutions To Practice Problems: Alina BucurJames Hyun Wook ParkОценок пока нет
- Term Test (2005) Sample2Документ3 страницыTerm Test (2005) Sample2Peng XuОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam: Mt1005 - Calculus 2 - Semester 203Документ1 страницаMidterm Exam: Mt1005 - Calculus 2 - Semester 203Phuong Nghi TruongОценок пока нет
- Problems Metric SpacesДокумент15 страницProblems Metric Spacesmarina_bobesiОценок пока нет
- Midterm 100 SolДокумент6 страницMidterm 100 Solsfluk2Оценок пока нет
- Integrales DoblesДокумент7 страницIntegrales DoblescarinasubiraОценок пока нет
- Math 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsДокумент3 страницыMath 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsexamkillerОценок пока нет
- Remark. Happy Holiday, Don't Forget Our Mid-Term Test 1 After HolidayДокумент2 страницыRemark. Happy Holiday, Don't Forget Our Mid-Term Test 1 After HolidayeouahiauОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Fall 10 So LsДокумент9 страницFinal Exam Fall 10 So LsMark LevitzОценок пока нет
- Department of Mathematics, IIT Kharagpur MA10002: Mathematics-II Assignment-2 On Integral CalculusДокумент1 страницаDepartment of Mathematics, IIT Kharagpur MA10002: Mathematics-II Assignment-2 On Integral CalculusSidMadharchodОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - IntegrationДокумент11 страницChapter 3 - IntegrationMuhamad NazrinОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Calculus of Multi Variables 2011Документ22 страницыLecture 2 Calculus of Multi Variables 2011Yiauw ShenqОценок пока нет
- W2Документ2 страницыW2Berven ZhakataОценок пока нет
- Problems AnswersДокумент15 страницProblems Answersanand singhОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Session 1 - Multiple IntegralsДокумент2 страницыTutorial Session 1 - Multiple IntegralsdjamalaberraneОценок пока нет
- Final Practice SolДокумент11 страницFinal Practice SolChris MoodyОценок пока нет
- Complex Numbers Additional Notes 1Документ11 страницComplex Numbers Additional Notes 1Jade GurtizaОценок пока нет
- Multivariable Calculus TestДокумент10 страницMultivariable Calculus TestPriyanka VinayОценок пока нет
- 15.1 - Vector Calculus - Div & CurlДокумент29 страниц15.1 - Vector Calculus - Div & Curlkhanshaheer477Оценок пока нет
- Fe Tutorials Sem2Документ8 страницFe Tutorials Sem2narendasreОценок пока нет
- Analele S Tiint Ifice Ale Universit AT Ii "Al.I.Cuza" Ias I Tomul XLVI, S.I A, Matematic A, 2000, f.1Документ22 страницыAnalele S Tiint Ifice Ale Universit AT Ii "Al.I.Cuza" Ias I Tomul XLVI, S.I A, Matematic A, 2000, f.1Safoora ElienОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Double IntegralsДокумент8 страниц2.1 Double Integralsmukesh3021Оценок пока нет
- Divergence and Curl: Intermediate MathematicsДокумент29 страницDivergence and Curl: Intermediate MathematicsguideОценок пока нет
- Divergence and Curl: Intermediate MathematicsДокумент29 страницDivergence and Curl: Intermediate MathematicsSunil NairОценок пока нет
- Linear AlgebraДокумент6 страницLinear AlgebraPeterОценок пока нет
- Second Midterm Exam Math 212 Fall 2010Документ7 страницSecond Midterm Exam Math 212 Fall 2010Mark LevitzОценок пока нет
- Solution To Practice Problems For Test 2Документ6 страницSolution To Practice Problems For Test 2Kuldeep KushwahaОценок пока нет
- Differential GeometryДокумент125 страницDifferential Geometrynimbigli7943100% (1)
- First Midterm Exam: Solutions Math 212 Fall 2010Документ5 страницFirst Midterm Exam: Solutions Math 212 Fall 2010Mark LevitzОценок пока нет
- III SEM - EC31 - Unit - IVДокумент49 страницIII SEM - EC31 - Unit - IVJoash Clavin John ClaytonОценок пока нет
- Samplem 1Документ3 страницыSamplem 1ishtiaqawan6354Оценок пока нет
- Solution. For Any Point P (X, Y, Z) Lying in The Intersection, Then The Real NumbersДокумент1 страницаSolution. For Any Point P (X, Y, Z) Lying in The Intersection, Then The Real NumberseouahiauОценок пока нет
- Vector CalculusДокумент11 страницVector CalculusApetsi AmpiahОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 6 5Документ24 страницыLecture Notes 6 5yordanosgetahun887Оценок пока нет
- Solutions To Practice Session 7 (Week 7) : 2013 The University of SydneyДокумент5 страницSolutions To Practice Session 7 (Week 7) : 2013 The University of SydneydivaaaaaaaaaОценок пока нет
- Error FunДокумент10 страницError FunIkram Ben SalemОценок пока нет
- Maths 2Документ4 страницыMaths 2Pradeep MkОценок пока нет
- Anti-Differentiation (Integration) : y X + y X + yДокумент4 страницыAnti-Differentiation (Integration) : y X + y X + ygilalulaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2 Partial Derivatives Engineering Applications of Partial DerivativesДокумент2 страницыTutorial 2 Partial Derivatives Engineering Applications of Partial Derivatives23065609Оценок пока нет
- Cal2 FE Sem2 1516Документ3 страницыCal2 FE Sem2 1516Thảo Nguyễn Thị ThanhОценок пока нет
- Examen FinalДокумент4 страницыExamen Finaloliver lopezОценок пока нет
- Self-Exercises 1Документ1 страницаSelf-Exercises 1visahОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1Документ15 страницTutorial 1Faris HishamОценок пока нет
- PART4 Tensor CalculusДокумент43 страницыPART4 Tensor CalculusAjoy SharmaОценок пока нет
- 2.first Order and First DegreeДокумент13 страниц2.first Order and First Degreeshaz333Оценок пока нет
- Differential Calculus Unit-Ii: DX y D y DX Dy yДокумент1 страницаDifferential Calculus Unit-Ii: DX y D y DX Dy yssuthaaОценок пока нет
- Midterm 2 Practice Problem Solutions V 2Документ14 страницMidterm 2 Practice Problem Solutions V 2VivekDixitОценок пока нет
- SSCE1993 Tutorial 1Документ14 страницSSCE1993 Tutorial 1jinОценок пока нет
- Math 203Документ2 страницыMath 203Rick AndrewsОценок пока нет
- MATH2019 Course Problems 2012s1Документ15 страницMATH2019 Course Problems 2012s1Seanam DMОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Letter 103/3/2012: Calculus in Higher Dimensions MAT2615Документ19 страницTutorial Letter 103/3/2012: Calculus in Higher Dimensions MAT2615gizzarОценок пока нет
- Calculus of Variations ExamplesДокумент7 страницCalculus of Variations ExamplesBrianWeathersОценок пока нет
- H2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimДокумент27 страницH2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimGale HawthorneОценок пока нет
- X+y Xy 2 2 2 2 2 2Документ4 страницыX+y Xy 2 2 2 2 2 2NGET SenghuochОценок пока нет
- Solution. For Any Point P (X, Y, Z) Lying in The Intersection, Then The Real NumbersДокумент1 страницаSolution. For Any Point P (X, Y, Z) Lying in The Intersection, Then The Real NumberseouahiauОценок пока нет
- Lec16 (1) Integrales LineaДокумент35 страницLec16 (1) Integrales LineaDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Lec15 (1) Campo VectorialДокумент5 страницLec15 (1) Campo VectorialDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Lec7 (1) Valores Maximos y MinimosДокумент22 страницыLec7 (1) Valores Maximos y MinimosDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Lec4 (1) PlanoTangente y AproxLinealДокумент13 страницLec4 (1) PlanoTangente y AproxLinealDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Lec6 (1) DerivadaDireccional y GradienteДокумент20 страницLec6 (1) DerivadaDireccional y GradienteDavid Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Looking Ahed 1Документ42 страницыLooking Ahed 1David Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Lec 20Документ20 страницLec 20David Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Looking Ahed 1Документ42 страницыLooking Ahed 1David Atilio Dominguez PozoОценок пока нет
- Calicut University Engineering Syllabus 2014 SchemeДокумент186 страницCalicut University Engineering Syllabus 2014 SchemebbjahbsОценок пока нет
- Phase Plan 2022-23Документ1 страницаPhase Plan 2022-23Aarav SinghОценок пока нет
- Untitled PDFДокумент173 страницыUntitled PDFNguvuluОценок пока нет
- Numerical Differentiation & Integration: 8.2.1 Derivatives Using Newton's Forward Interpolation FormulaДокумент22 страницыNumerical Differentiation & Integration: 8.2.1 Derivatives Using Newton's Forward Interpolation FormulairinОценок пока нет
- International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)Документ7 страницInternational Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)inventionjournalsОценок пока нет
- Mata Gujri College: Fatehgarh SahibДокумент21 страницаMata Gujri College: Fatehgarh SahibSuman KumarОценок пока нет
- S11 - Transform Calculus and Its ApplicationsДокумент5 страницS11 - Transform Calculus and Its ApplicationsVISION GAMINGОценок пока нет
- Matemáticas Avanzadas para Ingeniería Peter O'Neil 7ma Edición Sol PDFДокумент684 страницыMatemáticas Avanzadas para Ingeniería Peter O'Neil 7ma Edición Sol PDFOttoHinder50% (2)
- CalculusVolume1 OPДокумент829 страницCalculusVolume1 OPMOHAMMED IRFANUDDIN100% (1)
- Integration Substitution PDFДокумент8 страницIntegration Substitution PDFEnrique Gonzalez0% (1)
- RTT Examples and Continuity Eq 09-30-2016Документ21 страницаRTT Examples and Continuity Eq 09-30-2016الطيب كمالОценок пока нет
- Triangular ElementДокумент24 страницыTriangular ElementkatakgorengОценок пока нет
- Time-Harmonic Current Distribution On Conductor Grid in Horizontally Stratified Multilayer MediumДокумент21 страницаTime-Harmonic Current Distribution On Conductor Grid in Horizontally Stratified Multilayer MediumMirko ZvirkoОценок пока нет
- Course Outline - Engineering Mathematics - IIIДокумент6 страницCourse Outline - Engineering Mathematics - IIIShivam KumarОценок пока нет
- B SC MathematicsДокумент35 страницB SC Mathematicsbharathi rajОценок пока нет
- University of Asia Pacific (UAP) : Department of Basic Sciences and Humanities Course OutlineДокумент8 страницUniversity of Asia Pacific (UAP) : Department of Basic Sciences and Humanities Course OutlineMd. Tanimul HasanОценок пока нет
- Pressure Drop in The Flow of Compressible FluidsДокумент3 страницыPressure Drop in The Flow of Compressible FluidsJie ChinaОценок пока нет
- Goldmakher, L. Differentiation Under The Integral SignДокумент4 страницыGoldmakher, L. Differentiation Under The Integral SignuashdiuahsduiОценок пока нет
- 1686893598Документ30 страниц1686893598DeepakОценок пока нет
- Line Integral ExampleДокумент7 страницLine Integral ExampleRomesor ApolОценок пока нет
- BE (Chem) MBA SyllabusДокумент93 страницыBE (Chem) MBA SyllabusRitam GhoshОценок пока нет
- Matlab Tutorial NelsonДокумент70 страницMatlab Tutorial NelsonAaqibali LudhianviОценок пока нет
- List of ASI CoursesДокумент15 страницList of ASI CoursesWilson An100% (1)
- Agricultural Engineering 2010Документ112 страницAgricultural Engineering 2010Adil Hussain100% (1)
- V. I. Agoshkov, P. B. Dubovski, V. P. Shutyaev - Methods For Solving Mathematical Physics Problems-Cambridge International Science Publishi (2006)Документ335 страницV. I. Agoshkov, P. B. Dubovski, V. P. Shutyaev - Methods For Solving Mathematical Physics Problems-Cambridge International Science Publishi (2006)Ijaz TalibОценок пока нет
- Syllabus, Math 2550 (Introduction To Multivariable Calculus) Prof. Wing Suet Li, Spring 2020Документ7 страницSyllabus, Math 2550 (Introduction To Multivariable Calculus) Prof. Wing Suet Li, Spring 2020ChrisОценок пока нет
- K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology BE EEE II (Secong Year) SyllabusДокумент68 страницK.S.Rangasamy College of Technology BE EEE II (Secong Year) SyllabusSuganthan HarmlessОценок пока нет
- B.SC II YearДокумент10 страницB.SC II Yearnavi09Оценок пока нет
- Circumference of An EllipseДокумент4 страницыCircumference of An Ellipsemanuel_alejandro88100% (1)
- Fem Python PDFДокумент70 страницFem Python PDFNikola AndjelicОценок пока нет