Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Upset Forging Die Design
Загружено:
Chinmay DasИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Upset Forging Die Design
Загружено:
Chinmay DasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Module-II of PDPT
2.3 UPSET FORGING DIE DESIGN
In upset forgings, as a rule, no reduction in cross section occurs and, therefore, the stock to be chosen is of
the smallest area of cross section of the component. Also, very small or negligible flash is provided in upset
forgings. Depending on the shape of the upsetting to be done, the number of passes or blows in the die are
to be designed. The amount of upsetting to be done in a single stage is limited. To arrive at the safe amount
of upsetting in a given pass, the following three rules are to be satisfied to achieve defect free upset
forgings.
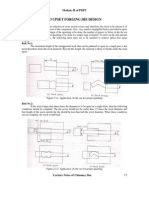
Rule No.1:
The maximum length of the unsupported stock that can be gathered or upset in a single pass is not
more than three times the stock diameter. Beyond this length, the material is likely to buckle under the axial
upset.
Figure 2.3.1: Application of rule one for proper upsetting
Rule No.2:
If the stock longer than three times the diameter is to be upset in a single blow, then the following
conditions should be complied. The die cavity should not be wider than 1.5 times the stock diameter and
free length of the stock outside the die should be less than half the stock diameter. When these conditions
are not complied, the stock would bend.
Figure 2.3.2: Application of rule two for proper upsetting
Lecture Notes of Chinmay Das 13
Module-II of PDPT
Rule No.3:
For upsetting the stock which is longer than three times the diameter and free length of stock
outside the die is up to 2.5 times the diameter, the following conditions should be satisfied. The metal is to
be confined into a conical cavity made in the punch with the mouth diameter not exceeding 1.5 times the
stock diameter and the bottom size being 1.25 times the stock diameter. Also, it is necessary that the
heading tool recess be not less than two thirds the length of the working stock or not less than working
stock minus 2.5 times the stock diameter.
Figure 2.3.3: Application of rule three for proper upsetting
The above are the absolute limits for proper upsetting. But in practice it may be possible to cross these
absolute limits.
Location of Cavities
The upset cavities may entirely be kept in the gripper dies or in the heading tool or part in the
gripper and part in the heading tool. The choice of
location mainly depends on the severity of the
upsetting and the convenient location of flash for
trimming. Simple forgings requiring smaller upsetting
may contain the complete die cavity in the heading
tool. Also complex shapes requiring severe upsetting
are obtained with the die cavity completely in the
gripper die.
For very simple shapes, one pass may be enough to
obtain the final shape, but majority of forgings require
three or more passes. If trimming of flash is included,
then an additional pass is required. All these passes are
arranged on the die block in an order and the stock is
moved from one pass to the other sequentially. While
designing the heading tool or the punch to slide into the
gripper die, it is necessary to provide clearance
between the two such that no seizure takes place due to
uneven expansion or due to scales of the punch and die.
Figure 2.3.4: Location of cavities
This clearance should be of the order of 0.125 to 0.200 mm. The length of gripping portion of the gripper
die should be maintained between 3 and 4 times the stock diameter.
Lecture Notes of Chinmay Das 14
Module-II of PDPT
Figure 2.3.5: Gripper die section
Stock size, mm R, mm A, mm C, mm
10 5 0.05 0.40
16 8 0.06 0.40
20 10 0.08 0.40
22 11 0.09 0.40
25 12.5 0.10 0.40
32 16 0.13 0.80
40 20 0.15 0.80
45 22.5 0.17 0.80
50 25 0.18 0.80
65 32.5 0.19 1.20
75 37.5 0.20 1.20
Table –I: Gripper die dimension
Figure 2.3.6: Upset forging products
Lecture Notes of Chinmay Das 15
Module-II of PDPT
Reference:
1. Manufacturing Technology by P.N.Rao, TMH , page 272 -275
2. Dies, Moulds and Jigs by V. Vladimirov, MIR Publishers, page 301-304
3. Manufacturing Engineering and Technology by Kalpakjian and Schmid, Pearson Education, page
353-355
Review Questions
1. Why lower taper angles are provided in upset forging dies?
2. In which case cavities are made in header tool of upsetting die?
3. The steel bolt is manufactured by which process and how?
4. Why negligible or no flash is provided in upset forging die?
5. Write various materials used for manufacture of forging die.
6. How is stock requirements determined in the case of upset forging?
7. What is the basis for the design of upset forging dies? State various rules.
8. What methods are available to a die designer when the stock length is too long compared to its
diameter while upsetting?
9. What are the advantages and limitations of upset forging?
10. Why cold shuts are not observable in upset forging process?
Lecture Notes of Chinmay Das 16
Вам также может понравиться
- Drop Forging Die DesignДокумент6 страницDrop Forging Die DesignChinmay Das88% (8)
- Engineering Equipment for Foundries: Proceedings of the Seminar on Engineering Equipment for Foundries and Advanced Methods of Producing Such Equipment, Organized by the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeОт EverandEngineering Equipment for Foundries: Proceedings of the Seminar on Engineering Equipment for Foundries and Advanced Methods of Producing Such Equipment, Organized by the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeОценок пока нет
- Mould & Core Material for the Steel Foundry: The Commonwealth and International Library: Foundry Technology DivisionОт EverandMould & Core Material for the Steel Foundry: The Commonwealth and International Library: Foundry Technology DivisionОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Working of Metals: Theory and PracticeОт EverandMechanical Working of Metals: Theory and PracticeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Die Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsОт EverandDie Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Applied Science in the Casting of MetalsОт EverandApplied Science in the Casting of MetalsK. StraussОценок пока нет
- Die Casting Design and Spec Guide PDFДокумент16 страницDie Casting Design and Spec Guide PDFKhổng MạnhОценок пока нет
- Gating SystemДокумент27 страницGating SystemAnup Tigga75% (4)
- Gating System Design For Casting Thin Aluminium Alloy (Al-Si) PlatesДокумент10 страницGating System Design For Casting Thin Aluminium Alloy (Al-Si) PlatesKhin Aung ShweОценок пока нет
- Cold FormingДокумент25 страницCold Formingpatel ketan100% (3)
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelОт EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelОценок пока нет
- Bulk Deformation Processes-ForgingДокумент14 страницBulk Deformation Processes-ForgingIziОценок пока нет
- Roll Forging Process Shapes Metal Parts Under Compressive ForcesДокумент6 страницRoll Forging Process Shapes Metal Parts Under Compressive ForcesSaptarshi SinhaОценок пока нет
- Information Symposium Measurement and Control Techniques in Rolling: Luxembourg, 2 and 3 September 1981От EverandInformation Symposium Measurement and Control Techniques in Rolling: Luxembourg, 2 and 3 September 1981Оценок пока нет
- Current Advances in Mechanical Design & Production IV: Proceedings of the Fourth Cairo University MDP Conference, Cairo, 27-29 December 1988От EverandCurrent Advances in Mechanical Design & Production IV: Proceedings of the Fourth Cairo University MDP Conference, Cairo, 27-29 December 1988Y. H. KabilОценок пока нет
- Powder Metallurgy of Superalloys: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsОт EverandPowder Metallurgy of Superalloys: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsОценок пока нет
- The Foseco Foundryman's Handbook: Facts, Figures and FormulaeОт EverandThe Foseco Foundryman's Handbook: Facts, Figures and FormulaeT.A. BurnsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Die CastingДокумент48 страницDie CastingramuthukumarОценок пока нет
- Diamond Chemical Vapor Deposition: Nucleation and Early Growth StagesОт EverandDiamond Chemical Vapor Deposition: Nucleation and Early Growth StagesОценок пока нет
- Five Steps To Improving Die PerformanceДокумент5 страницFive Steps To Improving Die Performanceromanhawranek100% (1)
- Die Casting GuidelinesДокумент12 страницDie Casting GuidelinesMichael Arvin GabineteОценок пока нет
- Cold Forming Glossary of Terms PDFДокумент17 страницCold Forming Glossary of Terms PDFLuis LujanoОценок пока нет
- NADCA Product Specification Standards For Die CastingДокумент272 страницыNADCA Product Specification Standards For Die CastingWilian Nagano100% (1)
- Squeeze CastingДокумент38 страницSqueeze Castingjishnus100% (1)
- Die Casting DesignДокумент20 страницDie Casting Designtiep_design100% (1)
- Aluminium Die Casting Lubrication Technology and Trends en v1Документ6 страницAluminium Die Casting Lubrication Technology and Trends en v1g_nazario100% (1)
- Precision Forging Processes GuideДокумент35 страницPrecision Forging Processes GuideRiski RamadhanОценок пока нет
- Casting Processes: DR Ajay BatishДокумент46 страницCasting Processes: DR Ajay BatishAlisha GuptaОценок пока нет
- AluMINIUM PQ2 DIAGRAM BE GLUPДокумент76 страницAluMINIUM PQ2 DIAGRAM BE GLUPSimon RisteskiОценок пока нет
- An Investment Casting Atlas of Defects GuideДокумент61 страницаAn Investment Casting Atlas of Defects Guidewilsonmeneses2014100% (4)
- HPDC Runner and Gating System DesignДокумент18 страницHPDC Runner and Gating System DesignMNОценок пока нет
- 3D Systems Guide To Processing QuickCast PatternsДокумент48 страниц3D Systems Guide To Processing QuickCast Patternscgonzo100% (2)
- Guide to Eyelet Drawing ProcessДокумент49 страницGuide to Eyelet Drawing ProcessPra Vee33% (3)
- Diecasting DefectsДокумент14 страницDiecasting DefectsEdwardОценок пока нет
- A RUNNER-GATE DESIGN SYSTEM FOR DIE CASTING DIESДокумент9 страницA RUNNER-GATE DESIGN SYSTEM FOR DIE CASTING DIESKetan ChhedaОценок пока нет
- Cold FormingДокумент7 страницCold FormingglaxionОценок пока нет
- Product Design For Sand CastingДокумент10 страницProduct Design For Sand CastingChinmay Das100% (7)
- Primary Aluminium Casting Alloys 2010 - Rheinfelden Alloys - ENДокумент117 страницPrimary Aluminium Casting Alloys 2010 - Rheinfelden Alloys - ENtahera aqeelОценок пока нет
- Operator TrainingДокумент38 страницOperator TrainingluisA1923Оценок пока нет
- Temperature ControlДокумент60 страницTemperature ControlKmilo Giraldo100% (4)
- Report On Material Used For Making Dies For Pressure Die Casting of Alluminium Alloys.2Документ21 страницаReport On Material Used For Making Dies For Pressure Die Casting of Alluminium Alloys.2Maroof Alam100% (2)
- Forging Die DesignДокумент6 страницForging Die Designرضوان العادلى100% (1)
- Solidification of CastingsДокумент7 страницSolidification of CastingsChinmay Das86% (7)
- Blanking and Piercing Die DesignДокумент12 страницBlanking and Piercing Die DesignChinmay Das100% (12)
- Sheet Metal OperationДокумент17 страницSheet Metal Operationsekar_scribd60% (5)
- Welding FundamentalsДокумент6 страницWelding FundamentalsChinmay Das100% (1)
- Upset Forging Die DesignДокумент4 страницыUpset Forging Die DesignChinmay Das50% (2)
- Forging Design ConsiderationsДокумент6 страницForging Design ConsiderationsChinmay Das100% (2)
- Casting DefectsДокумент5 страницCasting DefectsChinmay Das89% (9)
- 1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IДокумент8 страниц1.6.1 Die Casting (Pressure Die Casting) : Module-I of Manufacturing Science-IChinmay Das100% (2)
- Moulding Sand PropertiesДокумент6 страницMoulding Sand PropertiesChinmay Das100% (1)
- Melting PracticeДокумент5 страницMelting PracticeChinmay Das67% (3)
- Gating System DesignДокумент11 страницGating System DesignChinmay Das95% (19)
- Metal CastingДокумент12 страницMetal CastingChinmay Das100% (4)
- Moulding ProcessesДокумент10 страницMoulding ProcessesChinmay Das67% (3)
- Product Design For Sand CastingДокумент10 страницProduct Design For Sand CastingChinmay Das100% (7)
- Sand Moulding MaterialsДокумент3 страницыSand Moulding MaterialsChinmay Das100% (3)
- Design of Single Point Cutting ToolДокумент13 страницDesign of Single Point Cutting ToolChinmay Das82% (11)
- Eudragit ReviewДокумент16 страницEudragit ReviewlichenresearchОценок пока нет
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)Документ3 страницыUT Dallas Syllabus For Ee3311.002.07f Taught by Gil Lee (Gslee)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupОценок пока нет
- Week 6Документ7 страницWeek 6Nguyễn HoàngОценок пока нет
- Chapter 08Документ18 страницChapter 08soobraОценок пока нет
- Types of LogoДокумент3 страницыTypes of Logomark anthony ordonioОценок пока нет
- Class 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesДокумент8 страницClass 9th Chemistry Unit#4 Structure of MoleculesIrfanullahОценок пока нет
- The Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeДокумент44 страницыThe Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeYiğit KılıçОценок пока нет
- AJK Newslet-1Документ28 страницAJK Newslet-1Syed Raza Ali RazaОценок пока нет
- Rubric - Argumentative EssayДокумент2 страницыRubric - Argumentative EssayBobОценок пока нет
- IEC-60721-3-3-2019 (Enviromental Conditions)Документ12 страницIEC-60721-3-3-2019 (Enviromental Conditions)Electrical DistributionОценок пока нет
- BMXNRPДокумент60 страницBMXNRPSivaprasad KcОценок пока нет
- Riedijk - Architecture As A CraftДокумент223 страницыRiedijk - Architecture As A CraftHannah WesselsОценок пока нет
- Operation Guide For The Mercedes-Benz GLA/CLAДокумент5 страницOperation Guide For The Mercedes-Benz GLA/CLASantosh TalankarОценок пока нет
- STEM Spring 2023 SyllabusДокумент5 страницSTEM Spring 2023 SyllabusRollins MAKUWAОценок пока нет
- The Emperor Jones: What's Inside in ContextДокумент27 страницThe Emperor Jones: What's Inside in ContextHarshvardhan RaiОценок пока нет
- Drypro832 PreInstallGude 0921YH220B 070627 FixДокумент23 страницыDrypro832 PreInstallGude 0921YH220B 070627 FixRicardoОценок пока нет
- Brooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницBrooks Cole Empowerment Series Becoming An Effective Policy Advocate 7Th Edition Jansson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlois.guzman538100% (12)
- Masonry Brickwork 230 MMДокумент1 страницаMasonry Brickwork 230 MMrohanОценок пока нет
- Ipo Exam Revised SyllabusДокумент1 страницаIpo Exam Revised Syllabusজ্যোতিৰ্ময় বসুমতাৰীОценок пока нет
- Malaysia Year 2011 Calendar: Translate This PageДокумент3 страницыMalaysia Year 2011 Calendar: Translate This PageStorgas FendiОценок пока нет
- EMECH 2 MarksДокумент18 страницEMECH 2 MarkspavanraneОценок пока нет
- Compare and Contrast High School and College EssayДокумент6 страницCompare and Contrast High School and College Essayafibkyielxfbab100% (1)
- BỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO ĐỀ THI HỌC PHẦN KINH TẾ VĨ MÔДокумент5 страницBỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO ĐỀ THI HỌC PHẦN KINH TẾ VĨ MÔPhạm Thu NgaОценок пока нет
- Korba - BAH Online Temp MonitoringДокумент7 страницKorba - BAH Online Temp Monitoringrama jenaОценок пока нет
- Electrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент18 страницElectrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediapayments8543Оценок пока нет
- C11 RacloprideДокумент5 страницC11 RacloprideAvina 123Оценок пока нет
- A Woman's Talent Is To Listen, Says The Vatican - Advanced PDFДокумент6 страницA Woman's Talent Is To Listen, Says The Vatican - Advanced PDFhahahapsuОценок пока нет
- Published Filer List 06072019 Sorted by CodeДокумент198 страницPublished Filer List 06072019 Sorted by Codeherveduprince1Оценок пока нет
- Mark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'Документ5 страницMark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'bhaskkarОценок пока нет
- Aircraft ChecksДокумент10 страницAircraft ChecksAshirbad RathaОценок пока нет