Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 1 Section 2
Загружено:
api-243271979Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 1 Section 2
Загружено:
api-243271979Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
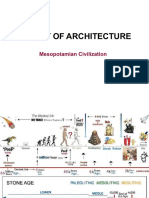
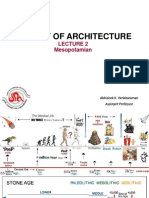
Chapter 1 Section 2 Mesopotamian Civilization Mesopotamians Civilization The cradle of civilization Began in the valleys of the Tigris and
Euphrates Rivers Had the following: Cities Government Art Religion Class divisions Writing systems Why were river valleys important Good farming conditions Provided fish Provided water Easy to travel Allowed trade Cities took shape and needed organization Formed government Took charge of food supplies Building project Made laws Assembled armies Developed religion Started art Invented writing Created a calendar Had a class structure The rise of Sumer Now southern Iraq Bounded by the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers Later the Greeks called this area Mesopotamia The land between the rivers
In the fertile Crescent, a curving strip of land from the Mediterranean sea to the Persian Gulf Hot, dry climate Unpredictable flooding that left rich soil Learned to build dams and channels to control the floods Built walls, waterways, and ditches to bring water to the fields (irrigation) City-states Isolated from each other by geography (mudflats & Deserts) Had own government Went to war against each other Surrounded itself with a wall Used river mud with crushed reeds to form bricks that were dried in the sun Gods and rulers Believed in many gods Each god had power over natural force or human activity Built a temple, a ziggurat, to the chief god mountain of god hills of heaven Top was a shrine where only a priest or priestess could go Contained places, royal storehouses, and citys treasury Later kings ran the government Position became hereditary Life in Sumer Kings lived in large places Ordinary people lived in small mud-brick houses Most people farmed Some were artisans, merchants, or traders Social classes Upper class-kings, priests, and government officials Middle class-artisan, merchants, farmers, and fishers (the largest group) Lower class-enslaved people who worked on farms or in the temples
Men Headed the household Only men could go to school Edubba-tablet house Women Could buy and sell property Could run businesses Why was writing important Sumers greatest invention Kept records Passed ideas to others Cuneiform Wedge-shaped marks cut into clay tablets with a sharp reed Scribes were wealthy boys Sumerian literature Epic of Gilgamesh Worlds oldest story About a king who traveled the world looking for a way to live forever Advances in science & math Irrigation Wagon wheel Plow Sailboat Geometry Number system based on 60 12-month calendar
Вам также может понравиться
- Ancient Sumer: Discovering Our Past Ancient CivilizationsДокумент23 страницыAncient Sumer: Discovering Our Past Ancient CivilizationsGiudi RosatoОценок пока нет
- City-States of Ancient SumerДокумент16 страницCity-States of Ancient Sumerkjkirk60% (5)
- Ancient MesopotamiaДокумент6 страницAncient MesopotamiaJacob Kahle HortonОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamian ArchitectureДокумент79 страницMesopotamian ArchitectureAbhishek Venkitaraman Iyer100% (2)
- Ancient MesopotamiaДокумент37 страницAncient MesopotamiaRod de CastroОценок пока нет
- CHP 4 L 1Документ4 страницыCHP 4 L 1Marwa AEbrahimОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia - Land Between Two Rivers: LocationДокумент8 страницMesopotamia - Land Between Two Rivers: LocationEl JayОценок пока нет
- H-4 Mesopotamian CivilizationДокумент79 страницH-4 Mesopotamian CivilizationVinayak RuhelaОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Human SettlementДокумент79 страницEvolution of Human Settlementshabareesh kailainathanОценок пока нет
- History of Human CivilizationДокумент79 страницHistory of Human CivilizationChem VathoОценок пока нет
- Ancient Sumer and EgyptДокумент84 страницыAncient Sumer and EgyptSrood TalibОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Section 1 The Mesopotamian CivilizationДокумент20 страницChapter 2 Section 1 The Mesopotamian CivilizationIslam BourbalaОценок пока нет
- MessageДокумент2 страницыMessageCapОценок пока нет
- World History 1 Chapter 1Документ9 страницWorld History 1 Chapter 1Missy MangibunongОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamian CivilizationДокумент19 страницMesopotamian CivilizationAziz Khan100% (2)
- Mesopotamian CivilizationДокумент11 страницMesopotamian CivilizationAsif Iqbal ShuvroОценок пока нет
- Sumerian CivilizationДокумент9 страницSumerian CivilizationLuluОценок пока нет
- Ancient Middle East and EgyptДокумент50 страницAncient Middle East and EgyptDokter AnestesiОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia: Cradle of CivilizationДокумент27 страницMesopotamia: Cradle of CivilizationAdorskie Aquino GermonoОценок пока нет
- Notes 06. Early CivilizationsДокумент12 страницNotes 06. Early Civilizationselmitxel100% (1)
- MesopotamiaДокумент6 страницMesopotamiaRamita UdayashankarОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia PPT - Mrityunjay MauryaДокумент27 страницMesopotamia PPT - Mrityunjay MauryaMritunjay MauryaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Section 2 The Fertile CrescentДокумент25 страницChapter 2 Section 2 The Fertile CrescentMatt Hasquin100% (1)
- MesopotamiaДокумент23 страницыMesopotamiamoisesbarcayola0% (2)
- CivilizationДокумент116 страницCivilizationRyazan AlesterОценок пока нет
- Hancy OangetДокумент23 страницыHancy OangetJoashОценок пока нет
- Ancient CivilizationДокумент20 страницAncient CivilizationZam Pamate100% (2)
- Mesopotamia: Cradle of CivilizationДокумент20 страницMesopotamia: Cradle of CivilizationHimani GuptaОценок пока нет
- World History Mesopotamia: Chapter 4 Notes Grade 8Документ44 страницыWorld History Mesopotamia: Chapter 4 Notes Grade 8api-326175299Оценок пока нет
- 2.1 City-States Mesopotamia 9no AДокумент10 страниц2.1 City-States Mesopotamia 9no ACamila SantosОценок пока нет
- History-Notes 2nd FormДокумент3 страницыHistory-Notes 2nd FormNaima hutchinsonОценок пока нет
- The Rise of Sumerian and Akkadian: Reynan M. Macarang Bsed Ii-Social ScienceДокумент59 страницThe Rise of Sumerian and Akkadian: Reynan M. Macarang Bsed Ii-Social ScienceAngelica Landoy100% (1)
- World History: Modern - Unit 0 (Foundations)Документ88 страницWorld History: Modern - Unit 0 (Foundations)Sahil KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Module C-STSДокумент7 страницModule C-STSAndrina CabreraОценок пока нет
- Roi Hy 5 Early Societies of The Tigris and Euphrates Valley Ver 1Документ19 страницRoi Hy 5 Early Societies of The Tigris and Euphrates Valley Ver 1Emily TrávezОценок пока нет
- Ancient Civilizations Topic: Sumerian Civilization MesopotamiaДокумент47 страницAncient Civilizations Topic: Sumerian Civilization MesopotamiaSheila AguadoОценок пока нет
- Meaning of MesopotamiaДокумент57 страницMeaning of MesopotamiaJoela CastilОценок пока нет
- History of MesopotamiaДокумент15 страницHistory of MesopotamiaElmoОценок пока нет
- Ed - Chapter 2Документ34 страницыEd - Chapter 2api-239995826Оценок пока нет
- Southwest AsiaДокумент36 страницSouthwest AsiaRhe YaОценок пока нет
- Anc Civ Final Study GuideДокумент14 страницAnc Civ Final Study GuideDeven PatelОценок пока нет
- MESOPOTAMIAДокумент22 страницыMESOPOTAMIAar.hammadhameedОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia:: "The Cradle of Civilization"Документ41 страницаMesopotamia:: "The Cradle of Civilization"Andrea Huecas TriaОценок пока нет
- Ancient CivilizationsДокумент90 страницAncient CivilizationsRolean Grace Cabayao Sangarios100% (1)
- Southwest Asia's CivilizationДокумент37 страницSouthwest Asia's CivilizationRoseMarie Masongsong IIОценок пока нет
- Chapter Assessment and VocabularyДокумент3 страницыChapter Assessment and Vocabularysamed brionesОценок пока нет
- Akkadian Empire A History From Beginning To End (Mesopotamia History) PDFДокумент38 страницAkkadian Empire A History From Beginning To End (Mesopotamia History) PDFEvrem Ekol100% (1)
- Unidad 2 RevisadaДокумент5 страницUnidad 2 Revisadanoodle. melioОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia: Jana HaythamДокумент6 страницMesopotamia: Jana HaythamjanaОценок пока нет
- Ancient Egypt:: "The Gift of The Nile"Документ59 страницAncient Egypt:: "The Gift of The Nile"Mizanur Rahman PeashОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia IntroДокумент25 страницMesopotamia IntroAemarie JacintoОценок пока нет
- Final Presentation On MesopotamiaДокумент31 страницаFinal Presentation On MesopotamiamonalallОценок пока нет
- CivilizationДокумент132 страницыCivilizationRyazan Alester0% (1)
- The Word Mesopotamia Is Greek For 'Land Between Rivers'.: Political Condition of MesopotamiaДокумент3 страницыThe Word Mesopotamia Is Greek For 'Land Between Rivers'.: Political Condition of MesopotamiachikОценок пока нет
- Egypt CivilizationДокумент31 страницаEgypt Civilizationmaria sabirОценок пока нет
- ChapterДокумент8 страницChapterHsu Sandi AungОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia, Rise and Fall: Ancient Worlds and Civilizations, #1От EverandMesopotamia, Rise and Fall: Ancient Worlds and Civilizations, #1Оценок пока нет
- Writing and City Life: Meospotamia and Its GeographyДокумент5 страницWriting and City Life: Meospotamia and Its GeographyLabhanshi BhargavaОценок пока нет
- McKenzie2007 Article ConnectivityAndScaleInCultural PDFДокумент2 страницыMcKenzie2007 Article ConnectivityAndScaleInCultural PDFLolita UmarОценок пока нет
- Work DoneДокумент2 страницыWork DonealexОценок пока нет
- Sun'S Path: - Geometry of Solar Movement - Sun Path Diagram/ Solar Chart - Altitude and Azimuth Angles - Shading DevicesДокумент35 страницSun'S Path: - Geometry of Solar Movement - Sun Path Diagram/ Solar Chart - Altitude and Azimuth Angles - Shading DevicesVineetha RatishОценок пока нет
- Holderness Case StudyДокумент2 страницыHolderness Case Studymrstone77Оценок пока нет
- GPS Error and Its Effects On Movement AnalysisДокумент17 страницGPS Error and Its Effects On Movement AnalysisPaul DupontОценок пока нет
- Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources Regulation No.7 of 2012Документ28 страницMinistry of Energy and Mineral Resources Regulation No.7 of 2012Didik Hari PambudiОценок пока нет
- 13 Moons in MotionДокумент41 страница13 Moons in MotionChromaticghost2100% (4)
- Telluric CurrentДокумент4 страницыTelluric CurrentWassim HelouОценок пока нет
- Cognitive Development and Conservation Tasks by Jean PiagetДокумент3 страницыCognitive Development and Conservation Tasks by Jean Piagetteachersmanual100% (5)
- Kamasutra Simplified and DetailedДокумент830 страницKamasutra Simplified and DetailedSpiritualHelp88% (8)
- 11 Physics Chapter 8 Assignment 1Документ1 страница11 Physics Chapter 8 Assignment 1nellai kumarОценок пока нет
- Httpsca1 Tls - Edcdn.comdocumentsworksheet 1 For Teachers PDFДокумент8 страницHttpsca1 Tls - Edcdn.comdocumentsworksheet 1 For Teachers PDFAthena Monica Carmela AltamuraОценок пока нет
- 3.3bjhbbbb BattttttДокумент14 страниц3.3bjhbbbb BattttttSipu GiriОценок пока нет
- 2016 - Hassen Et Al - Journal of HydrologyДокумент14 страниц2016 - Hassen Et Al - Journal of HydrologyAnonymous KxvIaYEEОценок пока нет
- Lab Report - My Own 123Документ3 страницыLab Report - My Own 123api-237765556Оценок пока нет
- Why The Moon's Orbit Is ConvexДокумент2 страницыWhy The Moon's Orbit Is ConvexAnonymous e8BzOGqlawОценок пока нет
- Crypto Charted Newsletter June 2021Документ6 страницCrypto Charted Newsletter June 2021Preeti YadavОценок пока нет
- HURST 2016 - Their World, A Diversity of MISS Environments LB 5384 PDFДокумент391 страницаHURST 2016 - Their World, A Diversity of MISS Environments LB 5384 PDFEduardo100% (1)
- Science of ScienceДокумент10 страницScience of Scienceabhisek guptaОценок пока нет
- Desain Bendungan Pada Zona PatahanДокумент12 страницDesain Bendungan Pada Zona PatahandeadromeoОценок пока нет
- The Living World: Mind MapДокумент12 страницThe Living World: Mind MapPrince100% (1)
- Kundali Match Based On Ashta KutaДокумент2 страницыKundali Match Based On Ashta KutaKALSHUBH100% (1)
- Rock Anchor MethodologyДокумент9 страницRock Anchor Methodologykaleswara_tellakulaОценок пока нет
- ParajitДокумент15 страницParajitAbhishek ChandraОценок пока нет
- Room-And-pillar Method of Open Stope MiningДокумент6 страницRoom-And-pillar Method of Open Stope MiningIsmaelОценок пока нет
- Biology 1010 Signature Assignment FinalДокумент8 страницBiology 1010 Signature Assignment Finalapi-460003323Оценок пока нет
- Seismic Risk in JordanДокумент18 страницSeismic Risk in JordanJihad TámímíОценок пока нет
- Oro Industries Email Brochure Ver 3.4 PDFДокумент14 страницOro Industries Email Brochure Ver 3.4 PDFFranco Boulle100% (1)
- Approach To Political ScienceДокумент17 страницApproach To Political ScienceRandy Raj OrtonОценок пока нет
- Earth Not A Globe Review The Vol III No 6 Sept Dec 1896Документ7 страницEarth Not A Globe Review The Vol III No 6 Sept Dec 1896Anonymous Ory6nQjiyОценок пока нет