Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Digital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSION
Загружено:
Ela DerarajИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Digital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSION
Загружено:
Ela DerarajАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
DIGITAL TRANSMISSION
To make an Information transmission from one point to another through a computer network, the information should be either in digital or analog signal. So, there two types of conversion that is digital-to-digital conversion & analog-to-digital conversion.
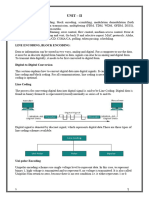
DIGITAL-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION
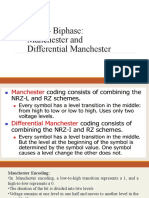
Line Coding Binary data to digital conversion. Self Synchronization The ability to maintain timing between sender and receiver. DC Components Undesirable residual direct current Extra energy and its useless Schemes Unipolar 1 = non-zero level & 0 =zero level Presence of DC Component and lack of sync because of long series of 1 or 0. Polar NRZ NRZ-Level Nonreturn to Zero 1 = negative & 0 =positive NRZ-invert Only inversion happens at bit 1. RZ [Return to Zero] 0 = negative to Zero 1 = positive to Zero 2 signal changes to encode each bit More bandwidth required Manchester 0 = positive to negative 1 = negative to positive Wastes bandwidth for long 1s or 0s
Differential Manchester Inversion in the middle of bit interval for Sync 0 = transition 1 = no transition Wastes bandwidth for long runs of 0s Bipolar 0 = zero level 1 = alternating positive and negative Less bandwidth than Manchester coding Sync loss for long 0s
Analog-to-Digital Conversion PULSE CODE MODULATION (PCM) A PCM encoder has three processes: 1.Sampling: The analog signal is sampled 2.Quantization: The sampled signal is quantized 3.Encoding: The quantized values are encoded as stream of bits.
Sampling : The process of generating pulses of zero width and of amplitude equal to the instantaneous amplitude of the analog signal. The no. of pulses per second is called sampling rate.
Quantization: The process of dividing the maximum value of the analog signal into a fixed no. of levels in order to convert the PAM into a Binary Code. The levels obtained are called quanization levels.
Вам также может понравиться
- Digital Analog 2Документ38 страницDigital Analog 2Gaurav SharmaОценок пока нет
- Data and Computer Communications: Chapter 5 - Signal Encoding TechniquesДокумент49 страницData and Computer Communications: Chapter 5 - Signal Encoding TechniquesSaurav SenОценок пока нет
- ITT400 - Chapter 4Документ58 страницITT400 - Chapter 4NOl ShAnahОценок пока нет
- 4 Digital TransmissionДокумент22 страницы4 Digital TransmissionRahul AryanОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Slide 2 EncodingДокумент19 страницWeek 2 Slide 2 EncodingvampziОценок пока нет
- EEE 367 Telecommunication Engineering: Digital TransmissionДокумент41 страницаEEE 367 Telecommunication Engineering: Digital TransmissionPhantom FireОценок пока нет
- Komdat-04-Digital Transmission-2018Документ39 страницKomdat-04-Digital Transmission-2018Atalyn TОценок пока нет
- Signal Encoding TechniquesДокумент25 страницSignal Encoding TechniquesRoy Silvester100% (1)
- Digital and Analog TransmissionДокумент47 страницDigital and Analog TransmissionRizwanAliОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Signal Encoding and Modulation TechniquesДокумент45 страницChapter 5 - Signal Encoding and Modulation TechniquesT Ritesh KumarОценок пока нет
- ConversionДокумент67 страницConversionMalar VizhiОценок пока нет
- Analog To Digital ConvertersДокумент21 страницаAnalog To Digital ConvertersMazhar AliОценок пока нет
- Computer Communication and Networks-Encoding Techniques-JasminДокумент30 страницComputer Communication and Networks-Encoding Techniques-Jasminzerihun demereОценок пока нет
- DigitalДокумент43 страницыDigitalharjind kaurОценок пока нет
- Digital ModulationДокумент48 страницDigital Modulationmekinjemal999Оценок пока нет
- CH 05 - Dcc10eДокумент55 страницCH 05 - Dcc10eMr. ShuaimiОценок пока нет
- 05.digital TransmissionДокумент65 страниц05.digital Transmissionultron zixОценок пока нет
- Handouts IIДокумент41 страницаHandouts IIAyele NugusieОценок пока нет
- Data and Computer CommunicationsДокумент53 страницыData and Computer Communicationschellam1_kalaiОценок пока нет
- Comm Chptr4Документ53 страницыComm Chptr4Muhamad Fuad100% (1)
- Lec 1Документ13 страницLec 1حسنين محمد عبدالرضا فليحОценок пока нет
- Digital TransmissionДокумент7 страницDigital TransmissionJohn HallowsОценок пока нет
- Data and Computer CommunicationsДокумент45 страницData and Computer Communicationswferry27Оценок пока нет
- CH 5 AДокумент45 страницCH 5 AArindam Banerjee100% (1)
- 6 PCM DM DPCMДокумент33 страницы6 PCM DM DPCMWidyaninurul HidayantiОценок пока нет
- GATE Online Coaching Classes: Digital CommunicationsДокумент73 страницыGATE Online Coaching Classes: Digital CommunicationsAdrian UmenganОценок пока нет
- CN Unit-IiДокумент55 страницCN Unit-Iipihadar269Оценок пока нет
- ET-353, Lecture 20 (Digitial Transmision)Документ44 страницыET-353, Lecture 20 (Digitial Transmision)Jahanzaib MushtaqОценок пока нет
- 1.4 KNR2103 - Week 9 - Day 1 - PDF PDFДокумент21 страница1.4 KNR2103 - Week 9 - Day 1 - PDF PDFسلمان اوڠОценок пока нет
- 1.4 KNR2103 - Week 9 - Day 1 - PDF PDFДокумент21 страница1.4 KNR2103 - Week 9 - Day 1 - PDF PDFسلمان اوڠОценок пока нет
- Data Communication: Lecturer: Fahim ShahzadДокумент33 страницыData Communication: Lecturer: Fahim Shahzadkaif BangashОценок пока нет
- Signal Conversions: Presented By:-Amarjit Kaur (AP)Документ21 страницаSignal Conversions: Presented By:-Amarjit Kaur (AP)parasdeep singhОценок пока нет
- Digital Transmission Transmittal of Digital Signals Between Two or More Points in A Communication SystemДокумент28 страницDigital Transmission Transmittal of Digital Signals Between Two or More Points in A Communication SystemLharie Mae BecinaОценок пока нет
- Data & Signals (Part 1) : Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringДокумент36 страницData & Signals (Part 1) : Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringJoyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ124 страницыChapter 2Taye EndeshawОценок пока нет
- Digital Communication IntroductionДокумент69 страницDigital Communication IntroductionlokeshwarrvrjcОценок пока нет
- Digital To Digital Data CommunicationДокумент10 страницDigital To Digital Data CommunicationMica GiananОценок пока нет
- Data Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 05Документ41 страницаData Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 05mr nОценок пока нет
- Lec 4Документ24 страницыLec 4بشير عماد كاظمОценок пока нет
- Digital and Analog TransmissionДокумент87 страницDigital and Analog TransmissionShounak DasguptaОценок пока нет
- Digital To Digital and Digital To Analog ConversionДокумент58 страницDigital To Digital and Digital To Analog ConversionSamavia KhanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ53 страницыChapter 2zelalemОценок пока нет
- L2 DcomДокумент38 страницL2 DcomYash ShirudeОценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing: Course Code: Credit Hours:3 Prerequisite:30107341Документ33 страницыDigital Signal Processing: Course Code: Credit Hours:3 Prerequisite:30107341محمد القدوميОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6Документ31 страницаLecture 6NANDINI AGGARWAL 211131Оценок пока нет
- Digital EncodingДокумент11 страницDigital EncodingmarxxОценок пока нет
- Lecture04 - Digital and Analog TransmissionДокумент77 страницLecture04 - Digital and Analog TransmissionifraОценок пока нет
- Wk3 - LineCoding - v2Документ50 страницWk3 - LineCoding - v2Taqris BahariОценок пока нет
- Polar Biphase Line EncodingДокумент12 страницPolar Biphase Line EncodingGerald KapinguraОценок пока нет
- Digital TransmissionДокумент6 страницDigital TransmissionHannahmhel MuanaОценок пока нет
- Signal Encoding TechniquesДокумент54 страницыSignal Encoding TechniquesAziz Ur RehmanОценок пока нет
- CSE350 Lec4 Signal Encoding V 2 2 PDFДокумент65 страницCSE350 Lec4 Signal Encoding V 2 2 PDFAftab Miraj SwachchhaОценок пока нет
- Digital TransmissionДокумент63 страницыDigital TransmissionVanessa KhalidОценок пока нет
- Chapter 01Документ20 страницChapter 01victorОценок пока нет
- Data Communication Concepts: Dr. Shuchita Upadhyaya Bhasin Professor Department of Computer Science & ApplicationsДокумент14 страницData Communication Concepts: Dr. Shuchita Upadhyaya Bhasin Professor Department of Computer Science & ApplicationsRaj VermaОценок пока нет
- Digital Communications - MatrialДокумент110 страницDigital Communications - Matrialjubair ul rehmanОценок пока нет
- Relationship Between Data Rate and Bandwidth: Duration of Each Pulse 1/2f Thus The Data Rate 2f (BPS)Документ36 страницRelationship Between Data Rate and Bandwidth: Duration of Each Pulse 1/2f Thus The Data Rate 2f (BPS)Sajjad ali KhaskheliОценок пока нет
- DC NotesДокумент212 страницDC NotesShaik Khalifa biОценок пока нет
- Pce.a.chapter1 8Документ73 страницыPce.a.chapter1 8Ela DerarajОценок пока нет
- October 2014 Intake Program Structure (CDP)Документ3 страницыOctober 2014 Intake Program Structure (CDP)Ela DerarajОценок пока нет
- Klinik Medijay: No, 12A, JLN BRP 6/11 Bukit Rahman Putra Sungai Buloh Selangor Tel/Fax: 03-61434473 /012 6253662Документ2 страницыKlinik Medijay: No, 12A, JLN BRP 6/11 Bukit Rahman Putra Sungai Buloh Selangor Tel/Fax: 03-61434473 /012 6253662Ela DerarajОценок пока нет
- Hlym 0009Документ15 страницHlym 0009Ela DerarajОценок пока нет
- DPJ 5018 Programming in Java: 1111113342muralitharan Reddy S/O GopalДокумент1 страницаDPJ 5018 Programming in Java: 1111113342muralitharan Reddy S/O GopalEla DerarajОценок пока нет
- Week/Date Topics Course Work: Methods)Документ2 страницыWeek/Date Topics Course Work: Methods)Ela DerarajОценок пока нет
- Dcs 5288 Internet & Web Publishing: Lecturer: Mrs Nurasma' ShamsuddinДокумент1 страницаDcs 5288 Internet & Web Publishing: Lecturer: Mrs Nurasma' ShamsuddinEla DerarajОценок пока нет
- Projek Pembagunan Pangkalan Data Kolej Komuniti Cawangan Klang Sesi Julai 2010Документ3 страницыProjek Pembagunan Pangkalan Data Kolej Komuniti Cawangan Klang Sesi Julai 2010Ela DerarajОценок пока нет
- Check To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsДокумент48 страницCheck To Make Sure You Have The Most Recent Set of AWS Simple Icons Creating DiagramsarunchockanОценок пока нет
- Balfour Castle EstateДокумент20 страницBalfour Castle EstatejahumphriesОценок пока нет
- SPR, RCS-9627CN, NoДокумент5 страницSPR, RCS-9627CN, NoAmaresh NayakОценок пока нет
- Harvester Main MenuДокумент3 страницыHarvester Main MenuWonderboy DickinsonОценок пока нет
- Public Economics - All Lecture Note PDFДокумент884 страницыPublic Economics - All Lecture Note PDFAllister HodgeОценок пока нет
- Graph 1: Temperature,° C of Mixture 1 (Naoh-Hcl) Against Time Taken, (Min)Документ8 страницGraph 1: Temperature,° C of Mixture 1 (Naoh-Hcl) Against Time Taken, (Min)LeeshaaLenee Paramanantha KumarОценок пока нет
- BIO CH04 FoundationsДокумент12 страницBIO CH04 FoundationsDyuana Stevenson0% (1)
- PCI20107, Overview of Boiler Commissioning and Startup PDFДокумент17 страницPCI20107, Overview of Boiler Commissioning and Startup PDFMarc AnmellaОценок пока нет
- Banking Adbl EnglishДокумент74 страницыBanking Adbl Englishdevi ghimireОценок пока нет
- Visco GraphДокумент4 страницыVisco GraphwamlinaОценок пока нет
- Module 5: Number Systems: Introduction To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Документ16 страницModule 5: Number Systems: Introduction To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Mihai MarinОценок пока нет
- Hyperinflation of Zimbabwe and The Lesson For Zimbabwe: Foreign Trade University Faculty of Banking and FinanceДокумент38 страницHyperinflation of Zimbabwe and The Lesson For Zimbabwe: Foreign Trade University Faculty of Banking and FinancePham Việt AnhОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyДокумент4 страницыFluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyMD Mahmudul Hasan Masud100% (1)
- Product Data Sheet: Type: P25-34/0DДокумент1 страницаProduct Data Sheet: Type: P25-34/0DAlejandro RustrianОценок пока нет
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterДокумент5 страницDual Nature of Radiation and Mattercopadag753Оценок пока нет
- BasicsДокумент1 страницаBasicsRishi Raj100% (1)
- Basic Customer Service SkillsДокумент90 страницBasic Customer Service SkillsGillian Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Beamer Example: Ethan AltДокумент13 страницBeamer Example: Ethan AltManh Hoang VanОценок пока нет
- Ocular Trauma - BantaДокумент211 страницOcular Trauma - BantaLuisa Fernanda Arboleda100% (1)
- Lecture # 3 Introduction To JqueryДокумент88 страницLecture # 3 Introduction To JqueryDanial AhmadОценок пока нет
- Roundtracer Flash En-Us Final 2021-06-09Документ106 страницRoundtracer Flash En-Us Final 2021-06-09Kawee BoonsuwanОценок пока нет
- Data Sheet 6GK5213-3BB00-2TB2: Transfer RateДокумент6 страницData Sheet 6GK5213-3BB00-2TB2: Transfer RateClaudiu VlasceanuОценок пока нет
- Yusof Ishak Secondary School Humanities Study Tour Ho Chi Minh City, VietnamДокумент19 страницYusof Ishak Secondary School Humanities Study Tour Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnamadamant751Оценок пока нет
- Anodizing PDFДокумент12 страницAnodizing PDFsanjay ukalkarОценок пока нет
- Revised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Документ79 страницRevised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Rodel D. LuyaoОценок пока нет
- CPM Pert Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersДокумент2 страницыCPM Pert Multiple Choice Questions and Answersptarwatkar123Оценок пока нет
- Effect of Spent Engine Oil On The Internal Structure of Corchorus OlitoriusДокумент55 страницEffect of Spent Engine Oil On The Internal Structure of Corchorus Olitoriusanon_568621284Оценок пока нет
- Angles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMДокумент18 страницAngles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMmheojhun0% (1)
- MOOT 1 (Principal Sir)Документ3 страницыMOOT 1 (Principal Sir)vaibhav jainОценок пока нет
- Install Sensor Lsi Fl061Документ14 страницInstall Sensor Lsi Fl061AlterSon Grafi KalayОценок пока нет