Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Vector Calculs and Applications
Загружено:
Selvam Irse0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров3 страницыThis document contains formulas and theorems relating to vector calculus, including vector formulae, the divergence theorem and corollaries, Stokes' theorem and a corollary, common vector differential quantities in polar and spherical coordinates, and the Navier-Stokes equations in cylindrical polar coordinates. It defines vector operations like divergence, curl, and del, and provides their representations in different coordinate systems. It also presents integral theorems relating operations like divergence and curl to surface and volume integrals.
Исходное описание:
vector calculus
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document contains formulas and theorems relating to vector calculus, including vector formulae, the divergence theorem and corollaries, Stokes' theorem and a corollary, common vector differential quantities in polar and spherical coordinates, and the Navier-Stokes equations in cylindrical polar coordinates. It defines vector operations like divergence, curl, and del, and provides their representations in different coordinate systems. It also presents integral theorems relating operations like divergence and curl to surface and volume integrals.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров3 страницыVector Calculs and Applications
Загружено:
Selvam IrseThis document contains formulas and theorems relating to vector calculus, including vector formulae, the divergence theorem and corollaries, Stokes' theorem and a corollary, common vector differential quantities in polar and spherical coordinates, and the Navier-Stokes equations in cylindrical polar coordinates. It defines vector operations like divergence, curl, and del, and provides their representations in different coordinate systems. It also presents integral theorems relating operations like divergence and curl to surface and volume integrals.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
4H FLUID DYNAMICS Vector Formulae and Theorems of Vector Calculus
Vector Formulae
a (b c) = (a c)b (a b)c (F) = 0 f = 0
(F) = (F) 2 F
(f F) = f F + f F
(f F) = F f + f F
(F G) = F(G) G(F) + (G )F (F )G If x = rer is the position vector with respect to some origin, then 2 x = 3 , x = 0 , er = , er = 0 r
(F G) = G (F) F (G)
(F G) = (F )G + (G )F + F (G) + G (F)
The Divergence Theorem and Corollaries
In the following V is a volume bounded by a closed surface S ,
V
F dV = f dV =
F dS f dS
(Divergence theorem)
F dV =
dS F f g dS (f g gf ) dS (Greens rst identity) (Greens theorem)
f 2 g + f g dV =
V
f 2 g g 2 f dV =
Stokes Theorem and a Corollary
In the following S is an open surface bounded by the contour C ,
S
(F) dS =
S
F dx f dx
(Stokes theorem)
dS f = 1
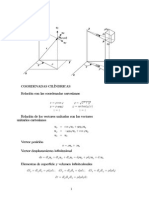
Common Vector Dierential Quantities in Polar Coordinates
Cylindrical Polars (s, , z )
f = F = F = f 1 f f es + e + ez s s z 1 F Fz 1 (sFs ) + + s s s z 1 Fz Fs F Fz es + e s z z s 1 1 Fs + (sF ) ez s s s f 1 2f 1 2f s + 2 2+ 2 s s s s z 2 F Fs es 2 Fs 2 2 s s 2 Fs F + 2 F + 2 2 e + 2 Fz ez s s
2 f = 2 F =
Spherical Polars (r, , )
f = F = F = f 1 f 1 f er + e + e r r r sin 1 1 F 1 2 ( r F ) + (sin F ) + r r2 r r sin r sin 1 F (sin F ) er r sin 1 Fr 1 1 1 Fr + (rF ) e + (rF ) e r sin r r r r r 1 1 f 1 2f 2 f r + sin + r2 r r r2 sin r2 sin2 2 2Fr 2 2 F 2 Fr 2 2 (sin F ) 2 er r r sin r sin 2 Fr F 2 cos F + 2 F + 2 2 2 2 2 e r r sin r sin 2 cos F F 2 Fr + 2 2 2 2 e + 2 F + 2 r sin r sin r sin 2
2 f = 2 F =
The Navier-Stokes Equations in Cylindrical Polar Coordinates
The Navier-Stokes equations in cylindrical polars (s, , z ) are: u2 us 1 p us 2 u + (u)us = + 2 us 2 2 t s s s s 2 us u us u 1 p u + (u)u + = + 2 u 2 + 2 t s s s s uz 1 p + (u)uz = + 2 uz , t z 1 1 u uz (sus ) + + = 0. s s s z where u f = us f u f f + + uz . s s z ,
Вам также может понравиться
- Vector Calculus Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаVector Calculus Cheat SheetdeskfanОценок пока нет
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)От EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Calculus FormulasДокумент13 страницAdvanced Calculus Formulasvignes011Оценок пока нет
- Stokes TheoremДокумент25 страницStokes Theoremqiangho100% (1)
- PH-801: Important Formula: Cartesian Coordinate SystemДокумент2 страницыPH-801: Important Formula: Cartesian Coordinate SystemHimadri ChakrabortiОценок пока нет
- Vector CalculusДокумент27 страницVector CalculusHarpreetSinghОценок пока нет
- Chuong IIДокумент154 страницыChuong IINguyenHoangKhaОценок пока нет
- Vector Analysis Formulas (Electromagnetic Fields)Документ2 страницыVector Analysis Formulas (Electromagnetic Fields)Quý HoàngОценок пока нет
- AM5570 Vectors TensorsДокумент5 страницAM5570 Vectors TensorsrickyspaceguyОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Identities: Formula Sheet Ee2Fh3Документ4 страницыTrigonometric Identities: Formula Sheet Ee2Fh3takazogluОценок пока нет
- Polar GradientДокумент1 страницаPolar GradientRamon ConpeОценок пока нет
- Derivation of LapceДокумент6 страницDerivation of LapcecasprossОценок пока нет
- Multivariable Calculus Worked Solutions Chapter 1, Part 1: Derivatives and DifferentialsДокумент9 страницMultivariable Calculus Worked Solutions Chapter 1, Part 1: Derivatives and DifferentialsmohammedОценок пока нет
- Vector Operator Identities: D DF F D DP PДокумент8 страницVector Operator Identities: D DF F D DP PAshvin GraceОценок пока нет
- Preg. 4 .15Документ9 страницPreg. 4 .15Ditmar Sayritupac VenturaОценок пока нет
- Curvilinear CoordinatesДокумент18 страницCurvilinear Coordinatesali_naghedifar100% (1)
- Solid Angle Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаSolid Angle Cheat SheetRaj BhaktaОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheet CME 342Документ4 страницыFormula Sheet CME 342Ahmad ElhajОценок пока нет
- Gu Ia de Problemas de La Secci On 2.5 Del Libro Mathematical Methods For Physicists, Sixth Edition, de George ArfkenДокумент8 страницGu Ia de Problemas de La Secci On 2.5 Del Libro Mathematical Methods For Physicists, Sixth Edition, de George ArfkenSergio AguilarОценок пока нет
- Problem Sheet 3 MaДокумент4 страницыProblem Sheet 3 Makanini7438Оценок пока нет
- Starea de Solicitare Planã in Coordonate Polare Conditii de ConturДокумент2 страницыStarea de Solicitare Planã in Coordonate Polare Conditii de ConturMese CipresОценок пока нет
- 1112 Ma 1 C Prac HW2 SolnДокумент3 страницы1112 Ma 1 C Prac HW2 SolnRamon ConpeОценок пока нет
- Curvilinear Coordinates: OutlineДокумент18 страницCurvilinear Coordinates: Outlinealagarg137691Оценок пока нет
- Formula in ElectromagnetДокумент5 страницFormula in ElectromagnetSamir YadavОценок пока нет
- 3 Dimensional BoxДокумент4 страницы3 Dimensional BoxhuuutschОценок пока нет
- x = Ω cos ' Ω = p x + y y = Ω ' ' = arctan (y/x) z = z z = zДокумент4 страницыx = Ω cos ' Ω = p x + y y = Ω ' ' = arctan (y/x) z = z z = zSeoane34Оценок пока нет
- Gradiant PDFДокумент4 страницыGradiant PDFMartinI.IseckОценок пока нет
- Equation SheetДокумент2 страницыEquation SheetKevin ChauОценок пока нет
- Homework 5BДокумент5 страницHomework 5BRylee LymanОценок пока нет
- 16 AAA Navier-Stokes PDFДокумент5 страниц16 AAA Navier-Stokes PDFFejs Za ScribdОценок пока нет
- Geometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid AngleДокумент1 страницаGeometry of Radiation: Plane Angle Solid Angle Differential Solid Angleapi-248972228Оценок пока нет
- 216 38 Solutions Numerical Problems Chapter 1 Coordinate Systems TransformationДокумент28 страниц216 38 Solutions Numerical Problems Chapter 1 Coordinate Systems TransformationSuraj GargОценок пока нет
- ps3 FinalДокумент59 страницps3 FinalEwanko100% (1)
- The Wave Equation in Cylindrical CoordinatesДокумент6 страницThe Wave Equation in Cylindrical CoordinatesAntonio LiraОценок пока нет
- Phy 102 Formulae KleppnerДокумент1 страницаPhy 102 Formulae Kleppnergayatri rainaОценок пока нет
- Formulario: L Ogica Matem AticaДокумент10 страницFormulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDaniel ChuquipomaОценок пока нет
- Chapt 09 2Документ47 страницChapt 09 2최진수Оценок пока нет
- Complex Analysis 1990Документ38 страницComplex Analysis 1990Suresh KannanОценок пока нет
- Curl and DivДокумент3 страницыCurl and DivgjdapromiseОценок пока нет
- Prob2 16Документ7 страницProb2 16EddieОценок пока нет
- A Short Note Expanding Functions As Outer Infinite CompositionsДокумент6 страницA Short Note Expanding Functions As Outer Infinite CompositionsJohn GillОценок пока нет
- Ma1c Practical 2011-2012Документ5 страницMa1c Practical 2011-2012Ramon ConpeОценок пока нет
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Документ5 страницMultivariable Calculus, 2007-03-15. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4Оценок пока нет
- Fórmulas de Análisis Vectorial PDFДокумент1 страницаFórmulas de Análisis Vectorial PDFNatalia GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Exam Formulas For CALCULUSДокумент3 страницыExam Formulas For CALCULUSWendy HuynhОценок пока нет
- Solutions For Math 311 Assignment #3Документ5 страницSolutions For Math 311 Assignment #3Anthony Bare Huané SalcedoОценок пока нет
- Boltzmann Eqn Notes1Документ7 страницBoltzmann Eqn Notes1np_nikhilОценок пока нет
- Math 248 Homework 1: Edward BurkardДокумент11 страницMath 248 Homework 1: Edward BurkardAnonymous NIL0zLRSjIОценок пока нет
- The Laplacian: Basic MathematicsДокумент33 страницыThe Laplacian: Basic Mathematicsgeo_biОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3 Solutions: February 2015Документ7 страницAssignment 3 Solutions: February 2015Rohan NaiduОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mathematics FormulaДокумент4 страницыEngineering Mathematics FormulaMaw IubuybОценок пока нет
- Directional DerivativesДокумент15 страницDirectional DerivativesNicole WilsonОценок пока нет
- File 1Документ2 страницыFile 1Byron LauraОценок пока нет
- Exam - 2011 10 28Документ5 страницExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4Оценок пока нет
- F R FN: CurlДокумент5 страницF R FN: CurlShe DilОценок пока нет
- FormulariumДокумент7 страницFormulariumKamilОценок пока нет
- Useful Vector Formulae: Appendix AДокумент3 страницыUseful Vector Formulae: Appendix AYuvarajaОценок пока нет
- Solution For Chapter 24Документ8 страницSolution For Chapter 24Sveti JeronimОценок пока нет
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОт EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОценок пока нет