Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Evolution Test Review
Загружено:
api-237316144Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Evolution Test Review
Загружено:
api-237316144Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name: _______________________________Date: __________________ Period: _____________
Evolution Test Review
Circle the answer that best completes the statement. DARWINS THEORY: 1. A well supported, testable explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world is called a ________________ A. hypothesis B. theory C. law D. prediction 2. Darwins voyage on the H.M.S.__________________ led him to propose a revolutionary hypothesis about life. A. Collie B. Cheetah C. Beagle D. Lion 3. Darwins hypothesis about how life changes over time in now called the Theory of __________. A. Evolution B. Variation C. Derived characters D. Use and disuse 4. Of all the places he visited, the ___________________ Islands influenced Darwins ideas about evolution the most. A. Hawaiian B. Aleutian C. Beagle D. Galapagos 5. In addition to observing living organisms, Darwin studied the preserved remains of ancient organisms called _________________ A. fossils B. homologous structures C. adaptations D. vestigial organs 6. On the Galapagos Islands, Darwin observed that the characteristics of many animals and plants A. all looked alike B. varied from island to island C. were acquired through use
EVOLUTION 7. Structures that have different mature forms, but develop from the same embryonic structure are called _______________ structures. A. Darwinian B. Lamarckian C. homologous D. fossils 8. Because of its similarities to artificial selection, Darwin referred to the survival of the fittest as __________________________, A. use it or lose it B. natural selection C. homologous structures D. struggle for existence 9. The idea that each living species has descended with changes from other species over time is called ________________. A. descent with modification B. struggle for existence C. artificial selection D. acquired traits 10. The natural differences between individuals of a species are referred to as_________________ A. fitness B. natural selection C. adaptations D. natural variation 11. When farmers select the largest hogs, the fastest horses, or the cows that produce the most milk for breeding it is called ________________. A. natural selection B. artificial selection C. survival of the fittest D. homologous variation 12. An inherited characteristic that increases an organisms ability to survive and reproduce in its specific environment is called a(n) __________________. A. homologous structure B. vestigial organ C. adaptation D. speciation 13. A human appendix, whale hipbones, and a skinks legs are examples of _________________ A. homologous structures B. embryonic mates C. vestigial organs
14. The bones in the diagram at the left are examples of ____________ A. homologous structures B. embryonic mates C. vestigial organs 15. Competition for food, space, and other resources among members of a species is called ____ A. common descent B. artificial selection C. survival of the fittest D. struggle for existence 16. The ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in a specific environment is called ______ A. fitness B. common descent C. survival of the fittest D. struggle for existence 17. All of the following play a role in Darwins Theory of Evolution EXCEPT ___________ A. natural variation B. survival of the fittest C. struggle for existence D. inheritance of acquired traits PATTERNS OF EVOLTUON AND SELECTION 18. Darwin believed in the idea that evolution happened slowly over a long period of time called A. punctuated equilibrium B. gradualism C. symbiosis D. mass extinction 19. Which of the following must be TRUE for Hardy-Weinberg to apply to a population? A. The population must be small. B. There must be NO movement in or out. C. Mutations cant happen. D. Natural selection can occur. E. Mating must be random.
20. A situation in which the allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of individuals is know as the ___________________ A. genetic equilibrium B. founder effect C. Hardy-Weinberg principle D. polygenic evolution 21. Any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population is called ________________. A. punctuated equilibrium B. mutation C. evolution D. genetic equilibrium
22. Which of the following is most likely to have caused the change in the population shown in the graphs at the left? A. a new predator prefers dark-tan crabs B. a new predator prefers light-tan crabs C. a new beach color makes medium-tan crabs the least visible D. a new beach color makes medium-tan crabs the most visible Answer the following questions in complete sentences 1. As a naturalist, Darwin observed what islands? ______________________________ what observations did he make on those islands? 2. What is survival of the fittest? Give an example
3. What is artificial selection? Name a group of people practice artificial selection?
4. Which organisms in a population survive to reproduce?
5. What was Darwins theory? Give the 3 main points that Darwin based his theory on
6. Give the definition of evolution by natural selection.
7. What is a vestigial structure?
8. What is a homologous structure?
9. What evidence did Darwin use to support his theory of evolution? 10. Natural selection is also known as: 11. If a mutation introduces a new gene into a population, what factor(s) would determine if that new gene will increase in the population?
12. When is a mutation considered helpful?
13. What is adaptation?
14. What is a gene pool?
15. What is a mutation? Consider the following scenarios and answer them in complete sentences 16. What will happen to a species (organism) that lacks variation that allows it to adapt to its environment?
17. In Arizona, a rabbit had a litter of babies. Some of its offspring were white and some were brown. An owl started to prey and eat the white rabbits. This is an example of:
18. A student hypothesizes that thick leg muscles is an inherited trait in cats. The student collects data on several cats and the data shows that cats that live outdoors have thicker leg muscles than cats that live indoors. What conclusion can be drawn from this data?
19. Water fowls such as ducks and swans have webbed feet whereas birds on land have clawed feet. What would explain this difference?
20. What are the two sources of genetic variation?
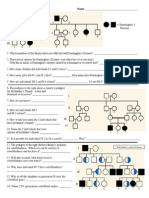
Analyzing Diagrams and Pictures 21. According to this family tree how many animals have jaws?
What is the above diagram called:________________________________ 22. According to this family tree which member probably changed the least over time? Charlie Brown Charlie Red Charlie BlueGreen Charlie BlueYellow
Charlie Brown Charlie Brown
Charlie Blue
Charlie Brown 23. The below diagram is showing you what kind of sturctures?_____________________________
24. Examine the graphs below:
________________________
_______________________
________________________
Match the graph with the population description: _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals at one end of the normal distribution curve higher than that of individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals in the middle higher than that of individuals at the extreme ends _____ In which of these is the fitness of individuals at the extreme ends higher than that of individuals in the middle Read the following scenarios and match the letter of the graphs above o the scenario below. You may use the graphs more than once. _____ Human babies born smaller than average are likely to be less healthy and less likely to survive. Larger than average babies are likely to have difficulty being born. The fitness of these larger or smaller weight babies is lower than average-sized babies so human babies tend to born of average size. _____ Birds with bigger, thicker beaks can feed more easily on larger, harder seeds. A food shortage causes the supply of small and medium seeds to run low, leaving only larger seeds. Birds with bigger beaks show greater fitness than birds with medium or small beaks. Over time more birds with bigger beaks survive and reproduce. _______ The orange and black pattern of a Monarch butterfly serves as a warning to sharp-eyed birds that the Monarch is poisonous to eat and tastes bad. Individuals with the brightest color pattern were more likely to warn off birds and survive to reproduce than those with a dull or medium color pattern. Over time and many generations, the Monarch population became more brightly-colored.
_______ In birds, feather color among males is more likely to attract a mate, but also more likely to attract a predator. Over time and many generations, the highest frequency color is for males with medium colors, while males with very dull colors and males with very bright colors became increasingly rare. _______ A population of birds lives in an area where plants with medium sized seeds are wiped out by a fungal infection. Birds with unusually large or small beaks would have higher fitness than those with medium sized beaks. Over time the population splits into two subgroups; one that eats small seeds and one that eats large seeds.
Вам также может понравиться
- Test TL 7 Answer KeyДокумент3 страницыTest TL 7 Answer Keyapi-23638709044% (9)
- Biology BIOL 1003 CH 1-3 QuizДокумент14 страницBiology BIOL 1003 CH 1-3 QuizYummyWords100% (1)
- Cell Test PracticeДокумент7 страницCell Test Practiceapi-240396878Оценок пока нет
- Biology Chapter 11 TestДокумент11 страницBiology Chapter 11 Testmohamad aliОценок пока нет
- Mitosis Meiosis Music Video ProjectДокумент3 страницыMitosis Meiosis Music Video Projectapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Rubric Myp Genetic Counseling Project Rev 10-13Документ1 страницаRubric Myp Genetic Counseling Project Rev 10-13api-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Test 1 - AnswersДокумент0 страницTest 1 - AnswersOnlyMyWayОценок пока нет
- Taller EvolucionДокумент5 страницTaller EvolucionCarlosPalmethPetrovaОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 10 - 3rd QUARTER EXAMДокумент5 страницSCIENCE 10 - 3rd QUARTER EXAMalmira villarealОценок пока нет
- Evolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersДокумент10 страницEvolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersSuhani SinhaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 10.3 Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент7 страницLesson 10.3 Multiple Choice Questionstsrif0% (1)
- Finals - Biology 2Документ12 страницFinals - Biology 2Leonel Mendoza100% (1)
- Third Quarterly Test in Science 10Документ9 страницThird Quarterly Test in Science 10Tristan PereyОценок пока нет
- Evolution Test 2012Документ10 страницEvolution Test 2012369220Оценок пока нет
- Module 28 - EditedДокумент11 страницModule 28 - Editedrichard reyesОценок пока нет
- Biology Chapter 16 18 Evolution and Classification NotesДокумент11 страницBiology Chapter 16 18 Evolution and Classification NotesTiffany GallinaОценок пока нет
- WEEK 2 - SummativeДокумент1 страницаWEEK 2 - SummativeCristelle EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Darwin Natural Selection Test QuestionsДокумент13 страницDarwin Natural Selection Test QuestionsDavid GiraldoОценок пока нет
- 12.4.3: Evolution Fill in The Blank WithДокумент3 страницы12.4.3: Evolution Fill in The Blank Withapi-25965241Оценок пока нет
- Evolution Test: Multiple ChoiceДокумент5 страницEvolution Test: Multiple ChoiceJoshua WhiteОценок пока нет
- Assessment ScoreДокумент3 страницыAssessment ScoreAnthony RamosОценок пока нет
- Summative Test in General Biology 2Документ2 страницыSummative Test in General Biology 2rolly baloОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 Biology TestДокумент8 страницChapter 11 Biology Testmohamad aliОценок пока нет
- Biology2 Q3 Module 3 Evolution and - Origin of BiodiversityДокумент15 страницBiology2 Q3 Module 3 Evolution and - Origin of BiodiversityDrew MalubagОценок пока нет
- Section 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case: Publication of On The Origin of SpeciesДокумент5 страницSection 15-3 Darwin Presents His Case: Publication of On The Origin of Speciesali floresОценок пока нет
- Evolution TestДокумент8 страницEvolution TestShriya VenkataramanОценок пока нет
- ch9 11Документ21 страницаch9 1113jabbasОценок пока нет
- Exam.danhsДокумент4 страницыExam.danhsJhamel A. GragantaОценок пока нет
- Biology Quiz Chapter 7 & 8 ReviewДокумент4 страницыBiology Quiz Chapter 7 & 8 ReviewConnor BrooksОценок пока нет
- Evolution Test 2Документ7 страницEvolution Test 2PT - 09SL 728582 John Fraser SSОценок пока нет
- 2022 PT 2 Earthlifesci11Документ3 страницы2022 PT 2 Earthlifesci11JANET LAPITANОценок пока нет
- Biology Revision SheetДокумент35 страницBiology Revision SheetJana AljundiОценок пока нет
- FINAL EXAM COVERS EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEДокумент6 страницFINAL EXAM COVERS EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEMarina AbanОценок пока нет
- Dependent or IndependentДокумент31 страницаDependent or IndependentChonama FetalcoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 and 7 Pre-Test: Multiple ChoiceДокумент7 страницChapter 6 and 7 Pre-Test: Multiple ChoiceKrishna KolluriОценок пока нет
- Animal Behavior ChaptestДокумент4 страницыAnimal Behavior ChaptestRommel Bauza100% (4)
- Grade 8 Bio4Документ4 страницыGrade 8 Bio4J DОценок пока нет
- Evolution Test Review KeyДокумент5 страницEvolution Test Review Keyapi-242868690Оценок пока нет
- Biology Reviews Test 4 and 5 With AnswersДокумент18 страницBiology Reviews Test 4 and 5 With AnswersLauren DixonОценок пока нет
- Text Test Bank 11Документ11 страницText Test Bank 11n1n2n3nОценок пока нет
- 6th Grade Science Review 11/28/2004Документ11 страниц6th Grade Science Review 11/28/2004Jason PantojaОценок пока нет
- Pre Test in Enhanced Science Biology 9 2023 2024Документ3 страницыPre Test in Enhanced Science Biology 9 2023 2024Aldyn MangatОценок пока нет
- Grade-12 General-Biology2 Q3 Module 3 Evolution and - Origin of Biodiversity.-For-PrintingДокумент14 страницGrade-12 General-Biology2 Q3 Module 3 Evolution and - Origin of Biodiversity.-For-Printingairamaymalicdem052Оценок пока нет
- Long Test 3 Ready To PrintДокумент3 страницыLong Test 3 Ready To Printjayrald cruzadaОценок пока нет
- Chapt 18Документ12 страницChapt 18AmaniОценок пока нет
- Anselmo A. Sandoval Memorial National High School Biology ExamДокумент4 страницыAnselmo A. Sandoval Memorial National High School Biology ExamRodel Matulin CatajayОценок пока нет
- Species Interactions and Biological CommunitiesДокумент14 страницSpecies Interactions and Biological CommunitiesRebecca EsОценок пока нет
- Bio Evolution Exam 1 ReviewДокумент4 страницыBio Evolution Exam 1 Reviewmuskaanbhar0304Оценок пока нет
- Midterm1.4.test Bio1m03Документ9 страницMidterm1.4.test Bio1m03violet.pandas37Оценок пока нет
- Genetic variation and natural selectionДокумент4 страницыGenetic variation and natural selectionMansour AbdallaОценок пока нет
- BILD 3 Practice Final FA08Документ10 страницBILD 3 Practice Final FA08George Chen100% (1)
- Cbleano Activity 6,7 Ngec1223 Big HistoryДокумент7 страницCbleano Activity 6,7 Ngec1223 Big HistoryJemuel Devlin GuintoОценок пока нет
- Letran de Davao, Inc.: Before The NumberДокумент3 страницыLetran de Davao, Inc.: Before The NumberappleОценок пока нет
- DiagnosticДокумент1 страницаDiagnosticAlvin RuizОценок пока нет
- Evolution: Species, However, The First Editions of His Book Never Actually Used Evolution But Rather He Used TheДокумент7 страницEvolution: Species, However, The First Editions of His Book Never Actually Used Evolution But Rather He Used Thejanice alquizarОценок пока нет
- Long QuizДокумент3 страницыLong Quizfernandezkhryztal30Оценок пока нет
- Study Guide AnswersДокумент4 страницыStudy Guide AnswersKymberОценок пока нет
- Biology Chapter 10 Test Answer KeyДокумент9 страницBiology Chapter 10 Test Answer Keymohamad aliОценок пока нет
- Chapt 11Документ12 страницChapt 11Rebecca EsОценок пока нет
- Biology: (Effective Alternative Secondary Education)Документ25 страницBiology: (Effective Alternative Secondary Education)Jonathan TabbunОценок пока нет
- Lesson 6 Final EllenДокумент4 страницыLesson 6 Final EllenChow GalanidaОценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Exam in Earth ScienceДокумент8 страниц2nd Quarter Exam in Earth SciencePearl Eloise BautistaОценок пока нет
- Evolution Test ReviewДокумент8 страницEvolution Test Reviewapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- MicroscopeДокумент1 страницаMicroscopeapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Eoc ReviewДокумент33 страницыEoc Reviewapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Research AssignmentДокумент2 страницыResearch Assignmentapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Test ReviewДокумент8 страницUnit 1 Test Reviewapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Skin ProjectДокумент2 страницыSkin Projectapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Biology-Mid-Term-Study-Guide Sleem 14-15Документ12 страницBiology-Mid-Term-Study-Guide Sleem 14-15api-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy Bone Brochure ProjectДокумент2 страницыAnatomy Bone Brochure Projectapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Midterm Review 14 15Документ10 страницMidterm Review 14 15api-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Biology Test Review SleemДокумент2 страницыBiology Test Review Sleemapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- 2014 Spring Final Exam ReviewДокумент6 страниц2014 Spring Final Exam Reviewapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Human Body PowerpointДокумент25 страницMuscles of The Human Body Powerpointapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Integumentary System Study GuideДокумент4 страницыIntegumentary System Study Guideapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Cell Poster Self-Guided Blank DefДокумент3 страницыCell Poster Self-Guided Blank Defapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Test Review RevДокумент5 страницTest Review Revapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Garden DesignsДокумент2 страницыGarden Designsapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Project - FinalДокумент5 страницProject - Finalapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Brain ProjectДокумент4 страницыBrain Projectapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Up The YangtzeДокумент1 страницаUp The Yangtzeapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Cell ProjectДокумент4 страницыCell Projectapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Eoc ReviewДокумент33 страницыEoc Reviewapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Genetics Study GuideДокумент6 страницGenetics Study Guideapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Pedigree Homework Worksheet RevДокумент2 страницыPedigree Homework Worksheet Revapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Human Body PowerpointДокумент25 страницMuscles of The Human Body Powerpointapi-237316144100% (1)
- Mock Un Global Warming DebateДокумент1 страницаMock Un Global Warming Debateapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- c3 Chromosome Mutation Stations StudentsДокумент23 страницыc3 Chromosome Mutation Stations Studentsapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Biography Book Report Assignment SheetДокумент1 страницаBiography Book Report Assignment Sheetapi-237316144Оценок пока нет
- Applications of BiosystematicsДокумент13 страницApplications of BiosystematicsKrizia Corrine St. PeterОценок пока нет
- Lamarck V DarwinДокумент2 страницыLamarck V Darwinapi-209631924Оценок пока нет
- Nardia Harley - Monohybrid Practice ProblemsДокумент3 страницыNardia Harley - Monohybrid Practice ProblemsNardia HarleyОценок пока нет
- How The Present System of Classification of Organisms Is Based On Evolutionary RelationshipsДокумент16 страницHow The Present System of Classification of Organisms Is Based On Evolutionary RelationshipsCRYSTAL CLAIRE PORRASОценок пока нет
- Exercise 4Документ2 страницыExercise 4Nishiyama AkemiОценок пока нет
- 3 Population GeneticsДокумент95 страниц3 Population GeneticsYuhua SunОценок пока нет
- Fruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Документ3 страницыFruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Kieu MuОценок пока нет
- Evolution Book HistoryДокумент7 страницEvolution Book HistoryTASNIA SIRAJ OISHBYОценок пока нет
- Punnett-Square-worksheet STD 10 Answer KeyДокумент2 страницыPunnett-Square-worksheet STD 10 Answer Keyroblox dude ibbuzummer100% (1)
- Natural Selection Lab-Phet Simulation Astrid 10DДокумент8 страницNatural Selection Lab-Phet Simulation Astrid 10DMary Fatima LlanesОценок пока нет
- Coalescent TheoryДокумент9 страницCoalescent TheoryNorberto Francisco BaldiОценок пока нет
- 4b BIOL 1001 W2023 How Does Natural Selection Affect VariationДокумент5 страниц4b BIOL 1001 W2023 How Does Natural Selection Affect Variations3ippnpОценок пока нет
- Major Transitions RevisitedДокумент330 страницMajor Transitions RevisitedDavid PérezОценок пока нет
- A Molecular Anthropological Study of Altaian Histories UtilizingДокумент400 страницA Molecular Anthropological Study of Altaian Histories Utilizingsergio_hofmann9837Оценок пока нет
- Virus BingoДокумент17 страницVirus BingoLaura Melissa CastilloОценок пока нет
- Evolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo-Devo) : Past, Present, and FutureДокумент10 страницEvolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo-Devo) : Past, Present, and Futureteju patneediОценок пока нет
- Higher Categories and Higher TaxaДокумент19 страницHigher Categories and Higher TaxaXainab SaeedОценок пока нет
- 05 02 Evolutionary RelationshipsДокумент4 страницы05 02 Evolutionary RelationshipsIsra ImrozОценок пока нет
- Mendel's LawДокумент4 страницыMendel's LawAngela Dez Therese AdefuinОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Charles DarwinДокумент3 страницыAnalysis of Charles DarwinAki SeijiОценок пока нет
- Template - EarthandLifeSci12 - Q2 - Mod13 - Process - of - Evolution - Ver3Документ44 страницыTemplate - EarthandLifeSci12 - Q2 - Mod13 - Process - of - Evolution - Ver3BG Hommer GuimaryОценок пока нет
- GRADE 12 Bio Unit 4&5Документ53 страницыGRADE 12 Bio Unit 4&5beabzkОценок пока нет
- Cladograms and Phylogenic TreesДокумент5 страницCladograms and Phylogenic TreesRachel WОценок пока нет
- AP Biology:: Evolution of PopulationsДокумент18 страницAP Biology:: Evolution of PopulationsAbhinav BasvojuОценок пока нет
- Homoplasy: Homoplastic. It Is Derived From The Two Ancient Greek WordsДокумент5 страницHomoplasy: Homoplastic. It Is Derived From The Two Ancient Greek WordsNTA UGC-NETОценок пока нет
- 5905 Et 21-Biosystematics-EtДокумент10 страниц5905 Et 21-Biosystematics-EtAnjali Singh100% (1)
- Getting To Know Charles Darwin - Text Analysis and ComprehensionДокумент4 страницыGetting To Know Charles Darwin - Text Analysis and ComprehensionrainbowОценок пока нет
- Worksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 3: Theories of Evolution and The Development of Evolutionary ThoughtДокумент10 страницWorksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 3: Theories of Evolution and The Development of Evolutionary ThoughtShastine ClaorОценок пока нет
- Population GeneticsДокумент51 страницаPopulation Geneticsdjahara88Оценок пока нет
- Making of TheoryДокумент3 страницыMaking of TheoryMSHYDERABAD4334Оценок пока нет