Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Class 7 Mouth
Загружено:
api-245312762Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Class 7 Mouth
Загружено:
api-245312762Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
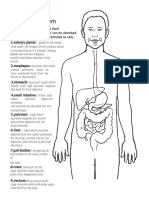
Class 7: Digestion Organs
Class: Bio 20 Unit: Human Systems Date: March 17 Teacher: Miss Olson
General Learning Outcomes:
1. Explain how the digestive and respiratory systems exchange energy and matter with the environment.
Specific Learning Outcomes: 1.1k: Identify principle structures of the digestive and respiratory systems Materials:
Time: 70 mins 9:50-11:00 Learning Objectives: Students will 1. Identify structures and function involved in the mouth in digestion 2. Investigate the role of saliva in digestion and taste
Resources:
1. Alberta Education program of studies (bio 20). 2. Science Inquiry, Bio 20 textbook 3. Student notes & pictures via Mr. Quintons & Janiskos resource files
-Notes (teacher copy) -PowerPoint Slides -Candy
Teacher Preparation:
-Review notes & make ppt,
Assessment:
-Questioning: key questions -Observation: participation in discussion, copying notes, asking questions when confused, candy tasting exercise
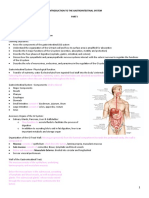
INTRODUCTION: (2 min) Recap: Last class we talked about the anatomy of the digestive system and the 4 components of digestion -What is another name for a valve or circular muscle? spincter -What is another name for a duct? tube -What are the 3 parts of the stomach? fundus, body, pyloric portion -What are the 3 salivary glands? Sublingual, Submaxillary, Parotid gland -What are the 4 components? list them on the board and briefly discuss each one 1. Ingestion: take nutrients in (bolus = food + saliva) 2. Digestion: breakdown of nutrients (chime = food + acid juices in stomach) 3. Absorption: nutrients from GI tract to blood stream (in SI) 4. Egestion: removing waste Agenda: mouth (first organ of digestion) BODY: (66 min) 1. Brainstorm & Notes & Discussion: (30 min) Structures in the mouth used for digestion and breaking apart of food: -Teeth: used to tear/shred our food we have teeth specialized for what we eat humans are omnivores so we have teeth for both plants and animals -Show real human tooth talk about roots wisdom teeth story -Tongue: contains specialized receptors called taste buds gives our food flavor also for shaping food and saliva into the bolus (preparation for swallowing) -Talk about a dry tongue = food has no flavor do candy tasting activity -Saliva: Characteristics: 1300ml is secreted per day pH = 6.8 (slightly acidic) it is 99% water
contains mucin (for lubrication) = talking and eating (swallowing) Enzymes: amylase and maltase (only digests carbs) notice ase Functions: Lubricates and moistens food in the mouth Aids in speech Dissolves food for taste Has a bacterial effect lysozyme Regulation of Saliva Secretion: Psychic stimulation thought of food Chemical stimulation type of food eaten determines secretion Mechanical stimulation physically touching glands (Dentist) Glands in the Mouth: all secrete saliva Sublingual: under the tongue Submaxillary Parotid
2. Candy Tasting: (15-20 min) -Draw and label the tongue Bitter = back of tongue Sweet = front of tongue Salty = back sides Sour = Front sides -Try placing candy on different areas of the tongue. Does the taste change? -Plug your nose and put candy on your tongue. Is the flavor the same? -Dry your tongue, place candy on the tongue. Can you taste anything? 3. Notes (10 min) -Oropharynx: junction between the mouth and the nasal cavity -Epiglottis: flap of tissue that directs food and air down the correct tube -Uvula: not a proven function -Esophagus: tube for food located below the epiglottis, food moves through this tube by gravity and peristalsis 4. Peristalsis Activity/Demo (5 min) -If a student is willing, get them to stand on their head (assistance from me and other students) and swallow water or more candy Is it still possible to swallow if youre upside down? Yes Why? Gravity is only part of it (helps), main action is peristalsis (muscles pushing food down) CLOSURE: (2 min) -Study your anatomy there will be a quiz on sometime this week (not tomorrow) -Tomorrow: Stomach
Вам также может понравиться
- Unitary MethodДокумент25 страницUnitary MethodAkhil Kumar0% (1)
- Lab 3 Diffusion and OsmosisДокумент20 страницLab 3 Diffusion and OsmosisrashadwcartwrightОценок пока нет
- Human Digestive SystemДокумент14 страницHuman Digestive Systemfatimah17Оценок пока нет
- BMEN - Digestive System 2020Документ76 страницBMEN - Digestive System 2020OliviaОценок пока нет
- Sistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)Документ28 страницSistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaОценок пока нет
- Hapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeДокумент29 страницHapter: Cell As A Unit of LifeShu85Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology,: Lecture OutlineДокумент46 страницAnatomy and Physiology,: Lecture OutlineRhona AngelaОценок пока нет
- Form 1 - 2.3Документ18 страницForm 1 - 2.3ardylea100% (1)
- Chapter 9: Nutrition and The Human Digestive SystemДокумент39 страницChapter 9: Nutrition and The Human Digestive Systemwickedbiology101Оценок пока нет
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsДокумент59 страниц2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliefeng81100% (8)
- Introduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisДокумент38 страницIntroduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisAnanta Subedi100% (1)
- Chapter2 Nutrition f2Документ42 страницыChapter2 Nutrition f2integra_7evenОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 4 Notes 2.3Документ2 страницыBiology Form 4 Notes 2.3gelgabanОценок пока нет
- Histology of Spinal Cord and Cerebellum by Dr. ROOMIДокумент21 страницаHistology of Spinal Cord and Cerebellum by Dr. ROOMIMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- 8.2 Mechanisms of BreathingДокумент44 страницы8.2 Mechanisms of Breathingwickedbiology101Оценок пока нет
- 6.2 Cell Cycle and Mitosis (The Necessity of Mitosis For Living Organisms)Документ32 страницы6.2 Cell Cycle and Mitosis (The Necessity of Mitosis For Living Organisms)wickedbiology101Оценок пока нет
- BIOL 112 Lab ReportДокумент7 страницBIOL 112 Lab Reportessexchick13Оценок пока нет
- Laboratary Lab ReportДокумент6 страницLaboratary Lab ReportMaarveen RajОценок пока нет
- Skeletal Muscle Lab ReportДокумент3 страницыSkeletal Muscle Lab Reportapi-296589762Оценок пока нет
- SCES3183 Nutrition For Human's EnzymesДокумент18 страницSCES3183 Nutrition For Human's EnzymesJacklin Ramli Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy Lecture Notes DigestiveДокумент9 страницAnatomy Lecture Notes DigestiveKenneth dela CruzОценок пока нет
- 2.4 & 2.5 Revision AnswersДокумент6 страниц2.4 & 2.5 Revision AnswersYuliya BoyalskayaОценок пока нет
- The Digestive SystemДокумент19 страницThe Digestive Systemianpoblete13Оценок пока нет
- UMSD 1213 Anatomy & Physiology Ii Bsc. (Hons) Biomedical Science 2010, Year 2 Trimester 1Документ14 страницUMSD 1213 Anatomy & Physiology Ii Bsc. (Hons) Biomedical Science 2010, Year 2 Trimester 1Tony_Tonique_Q_1649100% (1)
- Digestive and Endocrine Systems: Chapter TestДокумент5 страницDigestive and Endocrine Systems: Chapter TestJunior SencionОценок пока нет
- Transport System in PlantДокумент16 страницTransport System in PlantAbu-Omar50% (4)
- Sheep Heart Dissection LabДокумент6 страницSheep Heart Dissection Labchocoangel21Оценок пока нет
- BIO 3200 - Human Physiology LCT 1 - Ch1-5Документ9 страницBIO 3200 - Human Physiology LCT 1 - Ch1-5HoreaОценок пока нет
- Homeostasis Grade XДокумент32 страницыHomeostasis Grade XFebrian Andrei100% (1)
- Lipid - Digestion & AbsorptionДокумент33 страницыLipid - Digestion & AbsorptionsushmithagodspeedОценок пока нет
- Physics Formulae For MatriculationДокумент16 страницPhysics Formulae For MatriculationAliah Fatin Irwani75% (4)
- Digestive System PowerpointДокумент19 страницDigestive System Powerpointapi-277974939Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ7 страницChapter 2Kaness MathzОценок пока нет
- Why Do Animals Need To Move Anyway?Документ42 страницыWhy Do Animals Need To Move Anyway?genngillОценок пока нет
- Digestive System HandoutsДокумент7 страницDigestive System HandoutsClexandrea Dela Luz Corpuz100% (1)
- Digestive SystemДокумент36 страницDigestive Systembjbitscs21Оценок пока нет
- Short Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 3 Coordination and ResponseДокумент6 страницShort Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 3 Coordination and Responsesalamah_sabri75% (4)
- RPH Week 16Документ5 страницRPH Week 16mexfloziaОценок пока нет
- Biology Summary NotesДокумент5 страницBiology Summary NotesNoraОценок пока нет
- 1 Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemДокумент7 страниц1 Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemLinh Phan100% (1)
- Tubular Reabsorption & SecretionДокумент25 страницTubular Reabsorption & SecretionRishabh DangiОценок пока нет
- Bean Germination Lab QuestionsДокумент3 страницыBean Germination Lab Questionsapi-290657090100% (1)
- Endocrine System GlandsДокумент40 страницEndocrine System GlandsSolita PorteriaОценок пока нет
- Blood Cells, Immunity and Blood ClottingДокумент65 страницBlood Cells, Immunity and Blood Clottingmunaamuummee100% (1)
- Consolidation Theory of ForgettingДокумент2 страницыConsolidation Theory of ForgettingKrishna Bindu100% (2)
- Digestive SystemДокумент6 страницDigestive SystemLeylaОценок пока нет
- Phylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleДокумент5 страницPhylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleFrenzes PadabocОценок пока нет
- Intrathecal MorphineДокумент6 страницIntrathecal MorphineJoana MoreiraОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 7: Control and CoordinationДокумент30 страницChapter - 7: Control and Coordinationuma mishraОценок пока нет
- Life ProcessesДокумент53 страницыLife Processessagar100% (1)
- Lumphatic System Tortora DR - Compatibility ModeДокумент22 страницыLumphatic System Tortora DR - Compatibility Modekamalab04Оценок пока нет
- Ting. 2 KSSM Bab 4Документ18 страницTing. 2 KSSM Bab 4arasiОценок пока нет
- Digestive System Lesson Plan ELEMДокумент5 страницDigestive System Lesson Plan ELEMAngel AlibangbangОценок пока нет
- Nov 26 Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыNov 26 Lesson Planapi-237875296Оценок пока нет
- Science Digestive System Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыScience Digestive System Lesson Planapi-339651962Оценок пока нет
- Nedy Taleon-4thcotДокумент4 страницыNedy Taleon-4thcotjullienneОценок пока нет
- Grade Pre O Levels 1 - SeptemberДокумент14 страницGrade Pre O Levels 1 - SeptemberWalia AtifОценок пока нет
- Lesson Template: I.Preliminary DetailsДокумент9 страницLesson Template: I.Preliminary DetailsAnonymous pJcrvxCsGОценок пока нет
- Sense of Smell - OneДокумент4 страницыSense of Smell - Oneapi-246223353Оценок пока нет
- مذكرة شرح علوم الصف الرابع الابتدائي لغات 2015 science for primary 4 second term 2015 Prim 4secondTERM2015Документ29 страницمذكرة شرح علوم الصف الرابع الابتدائي لغات 2015 science for primary 4 second term 2015 Prim 4secondTERM2015rabei95% (55)
- Class Mission StatementДокумент1 страницаClass Mission Statementapi-245312762Оценок пока нет
- Classroom Management PlanДокумент5 страницClassroom Management Planapi-245312762Оценок пока нет
- 6math-F - Dec 3Документ2 страницы6math-F - Dec 3api-245312762Оценок пока нет
- 6sci-Ei-Nov 19Документ2 страницы6sci-Ei-Nov 19api-245312762Оценок пока нет
- Psii Growth PlanДокумент2 страницыPsii Growth Planapi-245312762Оценок пока нет
- Subway AssignmentДокумент2 страницыSubway Assignmentapi-245312762Оценок пока нет
- Lenae OlsonДокумент3 страницыLenae Olsonapi-245312762Оценок пока нет
- MT Fascia Poster 2 Final ImportanteДокумент1 страницаMT Fascia Poster 2 Final ImportanteJessé de AndradeОценок пока нет
- Biological Psychology Assignment 1Документ9 страницBiological Psychology Assignment 1Saulhe ImranОценок пока нет
- Hole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Twelfth Edition - Chapter 1 Lecture OutlineДокумент50 страницHole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Twelfth Edition - Chapter 1 Lecture OutlineCharles AvilaОценок пока нет
- A Follow-Up Study of Early Treatment of Pseudo Class III MalocclusionДокумент8 страницA Follow-Up Study of Early Treatment of Pseudo Class III MalocclusionManena RivoltaОценок пока нет
- Mri Report - Cervical Spine: Name Patient ID Accession No Age/Gender Referred by DateДокумент2 страницыMri Report - Cervical Spine: Name Patient ID Accession No Age/Gender Referred by DateKamlesh JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Orthopdic Assessment and Case Study (Plantar Fasciitis Right) Done By: Inas Dawoud Supervisor: Tamara Rizqallah 2021Документ6 страницOrthopdic Assessment and Case Study (Plantar Fasciitis Right) Done By: Inas Dawoud Supervisor: Tamara Rizqallah 2021dana shaheenОценок пока нет
- Face, Jaw: Muscles Acting On MasseterДокумент1 страницаFace, Jaw: Muscles Acting On Masseterjmccoy26Оценок пока нет
- Presentation 11Документ14 страницPresentation 11stellabrown535Оценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesДокумент13 страницCHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinОценок пока нет
- CSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemДокумент10 страницCSEC Human and Social Biology - The Skeletal SystemSamantha ThomasОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology OF HEART FAILUREДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology OF HEART FAILUREJessa AdenigОценок пока нет
- Hip Dislocation: Current Treatment Regimens: Paul Tornetta III, MD, and Hamid R. Mostafavi, MDДокумент10 страницHip Dislocation: Current Treatment Regimens: Paul Tornetta III, MD, and Hamid R. Mostafavi, MDJaime Anaya Sierra100% (1)
- Physiology of Musculoskeletal: Dr. Dr. H. Busjra M Nur MSC Dept. Physiology Fkui / FkumjДокумент51 страницаPhysiology of Musculoskeletal: Dr. Dr. H. Busjra M Nur MSC Dept. Physiology Fkui / FkumjSa'adah Munawaroh HDОценок пока нет
- 111 Peripheral NeuropathyДокумент17 страниц111 Peripheral NeuropathyjassbhanguОценок пока нет
- The History of Animals by AristotleДокумент19 страницThe History of Animals by AristotleLHIARENE ANGEL YEDRAОценок пока нет
- Deadly Knife Targets 2011 PDFДокумент1 страницаDeadly Knife Targets 2011 PDFAnonymous B5pVvSXhОценок пока нет
- 基础动力学讲义Документ188 страниц基础动力学讲义zhang yangОценок пока нет
- Thyroid Function Test 1Документ5 страницThyroid Function Test 1Jamal LiaqatОценок пока нет
- Bsoa 2 Keyboarding ModuleДокумент11 страницBsoa 2 Keyboarding Modulevenus camposanoОценок пока нет
- Neurocranium PDFДокумент7 страницNeurocranium PDFRobelle CordovaОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Excretion WsДокумент3 страницыIGCSE Excretion WsAnand Kumar Shukla100% (1)
- 5th Lesson Pediatric AssessmentДокумент7 страниц5th Lesson Pediatric AssessmentdaningdubouzetОценок пока нет
- Taping Reference Sheet-3815621Документ3 страницыTaping Reference Sheet-3815621api-383568582Оценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular SystemДокумент8 страницCardiovascular SystemHannah Grace CorveraОценок пока нет
- HomeworkbiopsychДокумент4 страницыHomeworkbiopsychJullieneОценок пока нет
- Frank Clark AutopsyДокумент8 страницFrank Clark AutopsyK Fine100% (1)
- 50 Gorgeous Medium Haircuts and Shoulder-Length Hairstyles For 2023Документ1 страница50 Gorgeous Medium Haircuts and Shoulder-Length Hairstyles For 2023Yatish BalamuruganОценок пока нет
- Effects of Yoga On Digestive SystemДокумент54 страницыEffects of Yoga On Digestive SystemManish Nahar33% (3)
- Pal Dan GumДокумент5 страницPal Dan GumJacob Post100% (1)
- Adolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisДокумент8 страницAdolescent Idiopathic ScoliosismoechielmoechieОценок пока нет
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionОт EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)От EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (12)
- Chemistry All-in-One For Dummies (+ Chapter Quizzes Online)От EverandChemistry All-in-One For Dummies (+ Chapter Quizzes Online)Оценок пока нет
- AI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceОт EverandAI and the Future of Education: Teaching in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Teaching STEM Outdoors: Activities for Young ChildrenОт EverandTeaching STEM Outdoors: Activities for Young ChildrenРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksОт EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Common Core Science 4 Today, Grade 3: Daily Skill PracticeОт EverandCommon Core Science 4 Today, Grade 3: Daily Skill PracticeРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- The School Garden Curriculum: An Integrated K-8 Guide for Discovering Science, Ecology, and Whole-Systems ThinkingОт EverandThe School Garden Curriculum: An Integrated K-8 Guide for Discovering Science, Ecology, and Whole-Systems ThinkingОценок пока нет
- What is the Scientific Method? Science Book for Kids | Children's Science BooksОт EverandWhat is the Scientific Method? Science Book for Kids | Children's Science BooksРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Chatgpt: From Zero to Hero with ChatGPT: How to Build a Profitable Amazon Self Publishing Business from ScratchОт EverandChatgpt: From Zero to Hero with ChatGPT: How to Build a Profitable Amazon Self Publishing Business from ScratchРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Stay Curious and Keep Exploring: 50 Amazing, Bubbly, and Creative Science Experiments to Do with the Whole FamilyОт EverandStay Curious and Keep Exploring: 50 Amazing, Bubbly, and Creative Science Experiments to Do with the Whole FamilyОценок пока нет
- Cool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsОт EverandCool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsОценок пока нет