Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Na (G) + CL (G) Nacl (S) : Lattice Enthalpy
Загружено:
Jorose10Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Na (G) + CL (G) Nacl (S) : Lattice Enthalpy
Загружено:
Jorose10Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
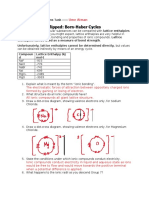
Lattice Enthalpy
The standard lattice enthalpy is the enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions from its constituent elements under standard conditions. It is a measure of ionic bond strength.
Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s)
Enthalpy of formation = the sum of all other enthalpy changes Sum of clockwise = sum of anticlockwise Lattice enthalpy = Enthalpy of formation (sum of everything else) Hess Law states that if a reaction can take place by more than one route and the initial and final conditions are the same the total enthalpy change for each route is the same Lattice enthalpy = -411 ((+107) + (+496) + (+122) + (-349)) = -787 KJ Mol-1
Figure 1 from chemguide
Enthalpy change of hydration: The enthalpy change when one mole of isolated gaseous ions is dissolved in water to form one mole of aqueous ions under standard conditions Na+ (g) + aq Na+ (aq) Enthalpy change of solution: The enthalpy change when one mole of compound is completely dissolved in water under standard conditions NaCl(s) + aq NaCl (aq) It can be positive or negative!
Calculating Lattice Enthalpy from Enthalpy Changes of Solution and Hydration
Lattice Enthalpy
Route One: Lattice enthalpy and enthalpy change of solution K+ (g) + Cl- (g) KCl(s) KCl(s) + aq K+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) +26 KJ Mol-1 Route Two: Hydration of K+ (g) and Cl- (g) ions K+(g) + aq K+ (aq) -322 KJ Mol-1 Cl-(g) + aq Cl- (aq) -363 KJ Mol-1 Put them together: -322 + (-363) = Lattice enthalpy + 26 Lattice enthalpy = -322 363 - 26 = -711 KJ Mol-1
Factors Affecting Lattice Enthalpies and Enthalpy of Hydration Lattice Enthalpy: Ionic Size Smaller ions pack more closely together so attract each other more strongly in a lattice, whereas larger ions are further apart in the lattice and are attracted less strongly. As ionic radius increases: Attraction between ions decreases Lattice enthalpy is less exothermic
Ionic Charge: The stronger the charge, the more exothermic the lattice enthalpy. So small, highly charged ions in a lattice have the MOST exothermic lattice enthalpies. Enthalpy Change of Hydration Ionic Size As the ionic radius becomes smaller, enthalpy change of hydration is more exothermic as the ion can more strongly attract water molecules to release energy. Ionic Charge The more strongly charged an ion, the greater attraction it has for water molecules- so hydration enthalpy is more negatively
Вам также может понравиться
- Topic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesДокумент10 страницTopic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesHenry SupriОценок пока нет
- Ionic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsДокумент9 страницIonic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsAnastasia ErshОценок пока нет
- 3 Electrochemistry 33Документ33 страницы3 Electrochemistry 33Aryan POONIAОценок пока нет
- Lattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration EnthalpyДокумент8 страницLattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration Enthalpyzubair0% (1)
- Chemical EnergeticsДокумент7 страницChemical EnergeticsRaiyan RahmanОценок пока нет
- H - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice EnergyДокумент31 страницаH - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice Energysepti handayaniОценок пока нет
- 15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyДокумент14 страниц15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyZara BrookesОценок пока нет
- Chem1 Module8Документ23 страницыChem1 Module8carlgavinsletartigasОценок пока нет
- 15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsДокумент16 страниц15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsGiselle PeachОценок пока нет
- Mod 5 Revision Guide 1 ThermodynamicsДокумент9 страницMod 5 Revision Guide 1 ThermodynamicsnomoszengОценок пока нет
- Born Haber CycleДокумент16 страницBorn Haber CyclePartha SenguptaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Atomic StrutureДокумент36 страницChemistry Atomic StrutureAshish NagaichОценок пока нет
- 1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaДокумент8 страниц1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaRabia RafiqueОценок пока нет
- 1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaДокумент8 страниц1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics Aqamzy8zhq9sfОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry PPT NotesДокумент23 страницыElectrochemistry PPT NotesHemanshi KocharОценок пока нет
- Electro Chemistry (Final) - 01-TheoryДокумент35 страницElectro Chemistry (Final) - 01-TheoryRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- 15.1 Energy CyclesДокумент28 страниц15.1 Energy CyclesNico Theodorus SimamoraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Electrochemistry: ElectrolysisДокумент106 страницChapter 7 Electrochemistry: ElectrolysisNeesha RamnarineОценок пока нет
- Lattice EnergyДокумент30 страницLattice EnergyNitya DewiОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 2023 ElectrochemistryДокумент46 страницCHAPTER 2 2023 Electrochemistrym.yassinmansor19Оценок пока нет
- F325 Lattice EnthalpyДокумент12 страницF325 Lattice EnthalpyDoc_Croc100% (1)
- 13 Energetics II PDFДокумент11 страниц13 Energetics II PDFSamson AmosОценок пока нет
- Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistyДокумент24 страницыRedox Reactions & ElectrochemistyDeep Chavan100% (1)
- CIE Chemistry Revision Guide For A2 LevelДокумент19 страницCIE Chemistry Revision Guide For A2 LevelBakhita MaryamОценок пока нет
- CIE Chemistry Revision Guide For A2 LevelДокумент15 страницCIE Chemistry Revision Guide For A2 LevelBakhita MaryamОценок пока нет
- 04-Electrochemical Kinetics of CorrosionДокумент40 страниц04-Electrochemical Kinetics of Corrosionmubsan100% (1)
- Electrochemistry 2Документ42 страницыElectrochemistry 2Sara FatimaОценок пока нет
- NEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryДокумент24 страницыNEET UG Chemistry Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryAmanОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry, PPT 3Документ33 страницыElectrochemistry, PPT 3Ernest Nana Yaw AggreyОценок пока нет
- 0BwSxA9Cnz5kvaVNNZzZpSENmdzg PDFДокумент54 страницы0BwSxA9Cnz5kvaVNNZzZpSENmdzg PDFThakur Aryan Singh100% (2)
- Electrochemistry - NotesДокумент4 страницыElectrochemistry - Notesn611704Оценок пока нет
- Bornhaber & Kapustinskii EqnДокумент8 страницBornhaber & Kapustinskii EqnEbsiba Beaula JОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry: (Tuesday, 8 May 2017)Документ18 страницElectrochemistry: (Tuesday, 8 May 2017)mipa amarОценок пока нет
- Electromotiveforcefinal 200727 135128Документ15 страницElectromotiveforcefinal 200727 135128Mohit AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Physical & Chemical Properties (Cont'D.)Документ36 страницPhysical & Chemical Properties (Cont'D.)Nagwa MansyОценок пока нет
- MSB Class 11 Chemistry-Ch5Документ26 страницMSB Class 11 Chemistry-Ch5zaiddparkar1Оценок пока нет
- Lattice Energy A Level A2 Chemistry CIEДокумент5 страницLattice Energy A Level A2 Chemistry CIErayaОценок пока нет
- Thermo ChemistryДокумент13 страницThermo ChemistryGalib FidaОценок пока нет
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYДокумент176 страницELECTROCHEMISTRYgsvssumaОценок пока нет
- The Structure of Ionic SolidsДокумент7 страницThe Structure of Ionic SolidsJaba PriyaОценок пока нет
- Iconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistДокумент12 страницIconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistKingson_786Оценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент63 страницыElectrochemistryomer faruqeОценок пока нет
- B CyclesДокумент21 страницаB CyclesTeejay MakazhuОценок пока нет
- Tpss 435: Chapter 6: Cation Exchange ReactionsДокумент11 страницTpss 435: Chapter 6: Cation Exchange ReactionsRonny NguyenОценок пока нет
- Flipped: Born-Haber Cycles: Chemsheets Definitions TaskДокумент3 страницыFlipped: Born-Haber Cycles: Chemsheets Definitions TaskShahnaz AhmedОценок пока нет
- 94 Enthalpies of SolutionДокумент4 страницы94 Enthalpies of SolutionJude PeelОценок пока нет
- Unit 4.1Документ5 страницUnit 4.1Tilak K CОценок пока нет
- Handout ElectroChemistry BY S.KДокумент16 страницHandout ElectroChemistry BY S.Katsats815Оценок пока нет
- Minimum Learning Material XiiДокумент27 страницMinimum Learning Material XiiSmv KumОценок пока нет
- Chemical Energetics NotesДокумент7 страницChemical Energetics NotesSalwa Ag Akbar100% (1)
- Chem-11 Short Note On Unit ThreeДокумент11 страницChem-11 Short Note On Unit ThreeFida FekaduОценок пока нет
- Class XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicДокумент60 страницClass XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicBaljit Singh100% (1)
- Born Haber Cycles: + - Latt - 1 + - Latt - 1Документ5 страницBorn Haber Cycles: + - Latt - 1 + - Latt - 1Pedro Moreno de SouzaОценок пока нет
- Unit-I Electrochemistry & CorrosionДокумент38 страницUnit-I Electrochemistry & CorrosionNitish ReddyОценок пока нет
- Ck&e 1Документ33 страницыCk&e 1Zekarias LibenaОценок пока нет
- Revision Notes ChemДокумент48 страницRevision Notes ChemUmer Sayeed SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОценок пока нет