Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chemistry Chapter 4 Test Review Be Able To Define The
Загружено:
anon-5794470 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров2 страницыBe able to list, in order, seven forms of electromagnetic radiation. Describe the contributions of max planck, bohr, henri debroglie, Erwin Schrodinger. Know that light and matter both have dual wave / particle nature.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Chemistry Chapter 4 Test Review Be Able to Define The
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документBe able to list, in order, seven forms of electromagnetic radiation. Describe the contributions of max planck, bohr, henri debroglie, Erwin Schrodinger. Know that light and matter both have dual wave / particle nature.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров2 страницыChemistry Chapter 4 Test Review Be Able To Define The
Загружено:
anon-579447Be able to list, in order, seven forms of electromagnetic radiation. Describe the contributions of max planck, bohr, henri debroglie, Erwin Schrodinger. Know that light and matter both have dual wave / particle nature.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
CHEMISTRY
CHAPTER 4
TEST REVIEW
Be able to define the following terms:
electromagnetic diffraction
radiation interference
electromagnetic quantum theory
spectrum orbital
frequency quantum number
wavelength principal quantum
trough number
crest angular momentum
inversely proportional quantum number
directly proportional (orbital quantum
photoelectric effect number)
quantum magnetic quantum
photon number
bright line spectrum spin quantum number
energy level electron configuration
ground state Aufbau Principle
excited state Pauli exclusion principle
energy level transition Hund’s Rule
Lyman series orbital notation
Balmer series Noble gas notation
Paschen series Electron configuration
Bohr model notation.
1)Be able to list, in order, seven forms of electromagnetic radiation. (the
members of the electromagnetic spectrum)
2)Be able to draw and label a “typical” wave form. Be able to solve
problems for the equation that relates wave speed, wavelength, and wave
frequency.
3)Be able to describe the contributions of Max Planck, Albert Einstein,
Niels Bohr, Henri DeBroglie, Erwin Schrodinger, and Werner Heisenberg.
4)Be able to tell what a bright line spectrum tells us about matter (atoms
and elements)
5)Be able to solve problems for the equation that relates energy to the
speed of light, Planck’s constant, wavelength, and frequency of light.
6)Explain how electromagnetic radiation and photons are related to
energy level transitions.
7)Be able to name the three bright line spectra of hydrogen. Tell what
form of electromagnetic radiation each shows and what energy level
transition each represents.
8)Be able to compare and constrast the following: Dalton’s atomic
model, Thomson’s model, Rutherford’s model, Bohr’s model, and the
electron cloud (quantum) model of the atom.
9)Know that light and matter both have dual wave/particle nature.
10)Be able to name and describe four quantum numbers.
11)Be able to use quantum number to describe the “locations” of
electrons in the electron cloud of atoms.
12)Be able to use Aufbau Principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s
Rule to describe electron configuration notation, orbital notation, and
Noble-Gas notation for any element.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Nanocoatings - Principles and Practice - From Research To ProductionДокумент344 страницыNanocoatings - Principles and Practice - From Research To ProductionTihomir Uzelac100% (1)
- Assistive Technology Assessment Plan (ATAP) : DemographicsДокумент5 страницAssistive Technology Assessment Plan (ATAP) : Demographicsanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- The Civil WarДокумент2 страницыThe Civil Waranon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 5SE 3trategies: %xampleДокумент3 страницы5SE 3trategies: %xampleanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 5SE AND:, Esson #OpyrightДокумент5 страниц5SE AND:, Esson #Opyrightanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 3olve: 'RaphДокумент4 страницы3olve: 'Raphanon-579447Оценок пока нет
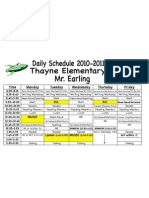
- Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: P.E. P.EДокумент1 страницаTime Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: P.E. P.Eanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- $raw "Est: %stimateДокумент3 страницы$raw "Est: %stimateanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 'Oal 6/#!"5,!29 3lope 9our: %xampleДокумент3 страницы'Oal 6/#!"5,!29 3lope 9our: %xampleanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 'Raph 4WO: #HeckingДокумент3 страницы'Raph 4WO: #Heckinganon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 'Raph: 'Oal Standard 6/#!"5,!29 0arent 9ourДокумент4 страницы'Raph: 'Oal Standard 6/#!"5,!29 0arent 9ouranon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Physical Education /aerobicsДокумент1 страницаPhysical Education /aerobicsanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Lacrosse Study Guide: About The GameДокумент2 страницыLacrosse Study Guide: About The Gameanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Worksheet Section 1 & 2 Section 1Документ2 страницыChapter 6 Worksheet Section 1 & 2 Section 1anon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Curriculum For Aerobics Units To Be CoveredДокумент1 страницаCurriculum For Aerobics Units To Be Coveredanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 14-20 Year Old DriversДокумент11 страниц14-20 Year Old Driversanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Soccer Rules - IntroductionДокумент6 страницSoccer Rules - Introductionanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент2 страницыUntitledanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Questions?: Graduated Driver LicensingДокумент2 страницыQuestions?: Graduated Driver Licensinganon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Wyoming Motorcycle Laws RoadДокумент2 страницыWyoming Motorcycle Laws Roadanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Beginning Keyboarding Numbers LessonДокумент1 страницаBeginning Keyboarding Numbers Lessonanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Driving Log: Drivers Education Practice ChecklistДокумент1 страницаDriving Log: Drivers Education Practice Checklistanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Rubric For Sport Skills: PointsДокумент1 страницаRubric For Sport Skills: Pointsanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Internet Use Is Required For PracticeДокумент2 страницыInternet Use Is Required For Practiceanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Weight Training Final ProjectДокумент1 страницаWeight Training Final Projectanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Internet Usage Is RequiredДокумент3 страницыInternet Usage Is Requiredanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Informal GeometryДокумент3 страницыInformal Geometryanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Supply List: 1 Box of 8 Regular Crayons (Red, Yellow, Blue, Green, Purple, Orange, Black, and Brown)Документ1 страницаSupply List: 1 Box of 8 Regular Crayons (Red, Yellow, Blue, Green, Purple, Orange, Black, and Brown)anon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Team Frisbee Games: UltimateДокумент3 страницыTeam Frisbee Games: Ultimateanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- Svhs Course SyllabusДокумент4 страницыSvhs Course Syllabusanon-579447Оценок пока нет
- 5SY42047 Datasheet enДокумент6 страниц5SY42047 Datasheet enRiver Trash andОценок пока нет
- Sinyal Dan Sistem Latihan Soal Dan SolusiДокумент12 страницSinyal Dan Sistem Latihan Soal Dan SolusiMuh Indjra DijeОценок пока нет
- KN/M Cohesion Kpa 120 Internal Friction Angle º 26 24: Type Parameter Satuan GT 01 GT 02 GT 03 Material Unit WeightДокумент3 страницыKN/M Cohesion Kpa 120 Internal Friction Angle º 26 24: Type Parameter Satuan GT 01 GT 02 GT 03 Material Unit WeightsaffitriОценок пока нет
- Creep, Shrinkage & ElasticityДокумент33 страницыCreep, Shrinkage & ElasticityMia HussainОценок пока нет
- jmm7 7 007 - MicrogeneratorДокумент9 страницjmm7 7 007 - MicrogeneratorsajanОценок пока нет
- CH 7Документ19 страницCH 7Iratechaos100% (4)
- Soil Plant Water Relationships by Mark Behan 1992Документ157 страницSoil Plant Water Relationships by Mark Behan 1992Thiago NettoОценок пока нет
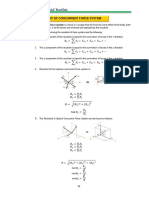
- Statics of Rigid Bodies:: Resultant of Concurrent Force SystemДокумент9 страницStatics of Rigid Bodies:: Resultant of Concurrent Force SystemLance CastilloОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table: Periodicity: Prepared By: Ling Pick YiengДокумент15 страницPeriodic Table: Periodicity: Prepared By: Ling Pick YiengJun Hong TeeОценок пока нет
- Thermal Design of Heat ExchangerДокумент9 страницThermal Design of Heat ExchangerNaqqash SajidОценок пока нет
- Civflum Quiz 1Документ4 страницыCivflum Quiz 1Jhun CastroОценок пока нет
- Assignment IVДокумент2 страницыAssignment IVDechenPemaОценок пока нет
- Term Project-I Mechanics of CompositesДокумент2 страницыTerm Project-I Mechanics of CompositesParveen Sahni ErОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Sum, Difference, Product Identities & EquationsДокумент2 страницыTrigonometric Sum, Difference, Product Identities & EquationsAnderson AlfredОценок пока нет
- Physics Chapter 15 OscillationsДокумент37 страницPhysics Chapter 15 Oscillationshidrovo3589100% (1)
- EE6711-Power System Simulation LaboratoryДокумент157 страницEE6711-Power System Simulation LaboratoryTushar ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- ESAS Part-4Документ15 страницESAS Part-4Marche Sebastian100% (1)
- Taller #1 Tfi ConversionesДокумент2 страницыTaller #1 Tfi ConversionesDavid GuerreroОценок пока нет
- 6 - Breakdown in Solid and Liquid DielectricДокумент53 страницы6 - Breakdown in Solid and Liquid Dielectricatik jawadОценок пока нет
- Describing Water Waves Worksheets-Páginas-1-3Документ3 страницыDescribing Water Waves Worksheets-Páginas-1-3Dylan Mora FrancoОценок пока нет
- Modul Pintas Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 Skema Jawapan Matematik Kertas 2 1449/2Документ9 страницModul Pintas Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 Skema Jawapan Matematik Kertas 2 1449/2dahlia24Оценок пока нет
- 11.1 and 11.2 Practice QuestionsДокумент17 страниц11.1 and 11.2 Practice QuestionsVineetKumarОценок пока нет
- Agitator Power Requirement and Mixing Intensity CalculationДокумент28 страницAgitator Power Requirement and Mixing Intensity Calculationcandra100% (3)
- Babita Kumari: Education SkillsДокумент2 страницыBabita Kumari: Education SkillsN NandiniОценок пока нет
- The Mole and StoichiometryДокумент14 страницThe Mole and StoichiometryJulie Amor ZantuaОценок пока нет
- Crgo1 PDFДокумент8 страницCrgo1 PDFimadhuryya5023Оценок пока нет
- The Effects of Unbalanced Networks On Synchronous and Asynchronous Machine Transient StabilityДокумент9 страницThe Effects of Unbalanced Networks On Synchronous and Asynchronous Machine Transient StabilitykfaliОценок пока нет
- 1 Drag of A Cylinder Using Pendulum MethodДокумент9 страниц1 Drag of A Cylinder Using Pendulum MethodHarsh MehtaОценок пока нет
- Chap 17 No 2Документ2 страницыChap 17 No 2blackwellbertОценок пока нет