Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Single Acting Steam Engine
Загружено:
Alvin WongОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Single Acting Steam Engine
Загружено:
Alvin WongАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Single Acting
Steam Engine
Report
Aakash Sundar, William He, Jenson Ma, Boris Liang & Alvin Wong
9Engineering2 Mr. Wallace
18thMay,2014
Assembly
Appendix 3-Lathe Process
Process Descriptions Image
Facing This is when you use a
single-point tool and feeds
the end of a cylindrical
workpiece to create a flat
surface. See Figure 1
Figure 1
Parallel turning To rotate a single-point tool
parallel to the axis of
rotation. See Figure 2
Figure 2
Drilling The use of a rotating drill in
order to cut a round hole
into a workpiece. See
Figure 3
Figure 3
Cutting The use of cutting tools to
separate metal from a
workpiece in the form of
chips. See figure 4
Figure 4
Knurling To cut or tolled metal into
diamond-shaped. See
figure 5
Figure 5
Chamfering Bevel the end of a
workpiece to remove burrs.
See figure 6
Figure 6
Polishing To smoothen your
workpiece by using a file or
sandpaper. See figure 7
Figure 7
Parting To separate the finished
part from the stock
Figure 8
Boring To enlarge a hole that has
already been drilled. Boring
is used to get greater
accuracy of the diameter of
a hole. See figure 9
Figure 9
Appendix 4- Lathe Setups
Setting the Lathe Speed
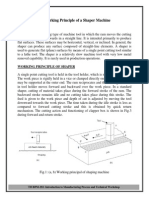
The Belt-Driven Drive Systems lathe are of the variable speed configuration. This type
of lathe either uses a mechanism to move the belt or an electronically variable speed
spindle motor. To change the lathe speed, you need to turn off the power and put a
warning sign beside the main switch. After that, you loosen the belt and move the
belt to one direction or the other. See Figure 1
Figure 10
Changing the pulley
To change the pulley, you first need to turn the power off and put a warning sign
beside the main switch. Then, open the pulley cover and remove all belts by twist the
belts out and rotate the pulley. After that, locate and remove the hexagonal bolt
from the pulley. Now, you can pull the pulley out from the shaft.
Figure 11
Typical Speeds for material groups
Material
Ballpark CS with
High-Speed Tool
Cutting Speed
High-Speed Tool
Cutting Speed
Carbide Tool
Low Carbon Steel 100 rpm 80-120 rpm 300-400 rpm
High Carbon Steel 60 rpm 60-100 rpm 200 rpm
Stainless Steel 100 rpm 100-120 rpm 240-300 rpm
Aluminum 250 rpm 400-700 rpm 800-1000 rpm
Brass & Bronze 200 rpm 110-300 rpm 600-1000 rpm
Plastics 250 rpm 200- 500 rpm 1000 rpm
Вам также может понравиться
- Case Study of Core and Pluge PreparationДокумент9 страницCase Study of Core and Pluge PreparationSpeculeОценок пока нет
- Linotype Manual: Giving Detailed Instructions of the Proper Adjustment and Care of the LinotypeОт EverandLinotype Manual: Giving Detailed Instructions of the Proper Adjustment and Care of the LinotypeОценок пока нет
- Adjustable Water Pot Faceter Head InstructionsДокумент37 страницAdjustable Water Pot Faceter Head InstructionsWarner BenavidesОценок пока нет
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsОт EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Lab Report Lathe TurningДокумент13 страницLab Report Lathe TurningSohaliaОценок пока нет
- Myford Metric ConversionДокумент5 страницMyford Metric ConversionP_I_P_HОценок пока нет
- How to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheОт EverandHow to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Roll Forging Process Shapes Metal Parts Under Compressive ForcesДокумент6 страницRoll Forging Process Shapes Metal Parts Under Compressive ForcesSaptarshi SinhaОценок пока нет
- Wood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingОт EverandWood Turning - The Lathe and Its Accessories, Tools, Turning Between Centres Face-Plate Work, Boring, PolishingОценок пока нет
- Lathe MachineДокумент12 страницLathe MachineEmy SyazlindaОценок пока нет
- 6-2 Machining Processes IДокумент44 страницы6-2 Machining Processes IOmar AhmedОценок пока нет
- Machine Tools Guide in 40 CharactersДокумент16 страницMachine Tools Guide in 40 CharactersKarОценок пока нет
- Figure 1: AISI 4140 Round BarsДокумент3 страницыFigure 1: AISI 4140 Round BarsMorena MoremoholoОценок пока нет
- Lathe ReportДокумент16 страницLathe ReportMuhammad Aisamuddin88% (8)
- Fabrication of Manual Roller Bending Machine-NEWДокумент33 страницыFabrication of Manual Roller Bending Machine-NEWDinesh Kumar100% (1)
- PAPER CUTTING MACHINE USING GENEVA MECHANISMДокумент13 страницPAPER CUTTING MACHINE USING GENEVA MECHANISMBRANDON100% (1)
- Manufacturing ProcessДокумент11 страницManufacturing ProcessRimti BhowmikОценок пока нет
- Lathe Machine OperationДокумент38 страницLathe Machine OperationInilazi JimmyОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 Workshop Teacher VersionДокумент4 страницыLab 7 Workshop Teacher Versionumar272Оценок пока нет
- Power SkivingДокумент11 страницPower SkivingahemerlyОценок пока нет
- Fabrication of Manual Roller Bending MachineДокумент10 страницFabrication of Manual Roller Bending MachineDinesh Kumar83% (6)
- 7 FrameДокумент67 страниц7 FrameAdrian MotocОценок пока нет
- Easy multi-nut car wheel removal toolДокумент61 страницаEasy multi-nut car wheel removal toolphaniОценок пока нет
- A. Shaper MachineДокумент7 страницA. Shaper Machinechandan kumarОценок пока нет
- How to Make a Slot Using a Shaper MachineДокумент4 страницыHow to Make a Slot Using a Shaper MachineMD Mahmudul Hasan MasudОценок пока нет
- Me 2356 Design and Fabrication ProjectДокумент30 страницMe 2356 Design and Fabrication ProjectvallabhОценок пока нет
- Objective:: - EquipmentДокумент3 страницыObjective:: - EquipmentUtkarsh AryaОценок пока нет
- Lathe machine safety and setup guideДокумент21 страницаLathe machine safety and setup guideWalid AdnanОценок пока нет
- What Are The Types of RollsДокумент78 страницWhat Are The Types of RollsrcmajhiОценок пока нет
- All Lab Reports of Manufacturing ProcessesДокумент28 страницAll Lab Reports of Manufacturing ProcessesZia JanОценок пока нет
- SSM College of Engineering, KOMARAPALAYAM - 638 183.: Laboratory ManualДокумент65 страницSSM College of Engineering, KOMARAPALAYAM - 638 183.: Laboratory ManualRam raoОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 06 MEMДокумент12 страницLab Report 06 MEMImdad JalaliОценок пока нет
- Mec 123 PracticalДокумент41 страницаMec 123 Practicalsanialiu2711Оценок пока нет
- Unit-II The LatheДокумент14 страницUnit-II The LatheThulasi RamОценок пока нет
- of ShaperДокумент59 страницof ShaperKishan Siddhpura56% (9)
- Nangal Fertilizer Plant HistoryДокумент24 страницыNangal Fertilizer Plant HistoryprabhjotbhangalОценок пока нет
- Design Sheet Metal CuttingДокумент27 страницDesign Sheet Metal CuttingsingamОценок пока нет
- Sheet Metal WorkingДокумент10 страницSheet Metal WorkingBhupendhar HarshawardanОценок пока нет
- LATHE - WriteupДокумент21 страницаLATHE - WriteupMERISH GURU100% (1)
- Interesting Facts About The Roller Bending Machine For SectionsДокумент5 страницInteresting Facts About The Roller Bending Machine For SectionsShaikh IbrahimОценок пока нет
- 4. RollingДокумент7 страниц4. RollingMeet BОценок пока нет
- Continuous Sheet Metal Punching MachineДокумент36 страницContinuous Sheet Metal Punching MachineHari Kesavan HОценок пока нет
- From Flat To Fab: Pattern Metals With The Economy Compact Rolling MillДокумент30 страницFrom Flat To Fab: Pattern Metals With The Economy Compact Rolling MillWiredlotus100% (7)
- SSLG-Feed Pellet Crumble MachineДокумент14 страницSSLG-Feed Pellet Crumble MachineVictor Julio Torres DazaОценок пока нет
- Man Pro Lab Exp No. 7 Working Principle of A Shaper MachineДокумент8 страницMan Pro Lab Exp No. 7 Working Principle of A Shaper Machinefotick100% (1)
- Lathe Machine OperationДокумент13 страницLathe Machine OperationRizuanul Arefin EmonОценок пока нет
- Production Technology Assignment1Документ22 страницыProduction Technology Assignment1shah shakeel rssОценок пока нет
- Shaper Planer N SlotterДокумент23 страницыShaper Planer N SlotterAtif WahidОценок пока нет
- Lab ManualДокумент43 страницыLab ManualTech OriginОценок пока нет
- Lathe Machine AttachmentДокумент15 страницLathe Machine Attachmentgajanan maharajОценок пока нет
- Lathe OperationsДокумент28 страницLathe OperationsKrunal PatilОценок пока нет
- Web QCGBДокумент19 страницWeb QCGBpramponiОценок пока нет
- Module 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesДокумент19 страницModule 4 - Classification, Applications and Operations of MachinesIsmaeli KielОценок пока нет
- Mini Lathe Operation: TurningДокумент11 страницMini Lathe Operation: TurningabyzenОценок пока нет
- For Wood Cutter MachineДокумент19 страницFor Wood Cutter MachineRahul Rajput100% (1)
- UEME3223 - Report 1Документ10 страницUEME3223 - Report 1Sinyau KhooОценок пока нет
- Slotting MachineДокумент3 страницыSlotting MachineNishit ParmarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ15 страницChapter 1surjitОценок пока нет
- Moving Castle'. Each of The Texts Has A Wide Range of Ideas On How Belonging Is FormedДокумент2 страницыMoving Castle'. Each of The Texts Has A Wide Range of Ideas On How Belonging Is FormedAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- Cash Flow Forecast Statement For Instafamous (First Quarter)Документ3 страницыCash Flow Forecast Statement For Instafamous (First Quarter)Alvin WongОценок пока нет
- Lantana: Introduced Species Alvin Wong 10GEOMДокумент10 страницLantana: Introduced Species Alvin Wong 10GEOMAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- DocДокумент2 страницыDocAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- AustralianbiotaДокумент24 страницыAustralianbiotaAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- Science NotesДокумент5 страницScience NotesAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- Balsa Wood Bridge Engineering ReportДокумент31 страницаBalsa Wood Bridge Engineering ReportAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- SpeechДокумент2 страницыSpeechAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- Alvin Wong Common Assessment Task 3 on Ethical, Social and Environmental DesignДокумент1 страницаAlvin Wong Common Assessment Task 3 on Ethical, Social and Environmental DesignAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- AMC Jun 2008Документ7 страницAMC Jun 2008Alvin WongОценок пока нет
- Hello WorldДокумент1 страницаHello WorldAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- Alvin Wong Common Assessment Task 3 on Ethical, Social and Environmental DesignДокумент1 страницаAlvin Wong Common Assessment Task 3 on Ethical, Social and Environmental DesignAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- Hello WorldДокумент1 страницаHello WorldAlvin WongОценок пока нет
- Hello WorldДокумент1 страницаHello WorldAlvin WongОценок пока нет