Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Manual Lizbeth H F
Загружено:
api-2396743200 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
33 просмотров18 страницОригинальное название
manual lizbeth h f
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
33 просмотров18 страницManual Lizbeth H F
Загружено:
api-239674320Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 18
E
By: lizbeth Hernandez Flores
2
ndex
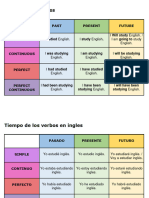
1. Past Tense ------------------------------------------------------------------ pg. 3
1.1. Past Simple ------------------------------------------------------------ pg. 4
1.2. Past Continuous ----------------------------------------------------- pag. 5
1.3. Past Perfect ------------------------------------------------------------ pag. 6
1.4. Past Perfect Continuous ------------------------------------------ pag. 7
2. Present Tense ------------------------------------------------------------- pag. 8
2.1. Present Simple ------------------------------------------------------- pag. 9
2.2. Present Continuous ------------------------------------------------ pag. 10
2.3. Present Perfect ------------------------------------------------------- pag. 11
2.4. Present Perfect Continuous ------------------------------------- pag. 12
3. Future Tense--------------------------------------------------------------- pag. 13
3.1. Future Simple -------------------------------------------------------- pag. 14
3.2. Future Continuous ------------------------------------------------- pag. 15
3.3. Future Perfect -------------------------------------------------------- pag. 16
3.4. Future Perfect Continuous -------------------------------------- pag. 17
3
4
Past Simple
Form
With regular verbs: infinite+ed
With irregular verbs: 2nd column of the irregular verbs.
Examples
Affirmative sentences:
Regular verbs: I played football.
Irregular verbs: I went to the cinema
Negative sentences (always use the auxiliary did.)
I didnt play football.
Question (use the auxiliary did)
Did you play football?
Use
1. Action finished in the past.
2. Series of complement actions in the past.
Together with the past progressive/continuous-the past interrupted an action which was
in progress in the past.
5
Past Continuous
Form
[was/were + present participle]
Form of the Past Progressive/Continuous
We use a form of to be (was or were), the infinitive of the verb and the ending ing.
to be (was, were) + infinitive + -ing
Affirmative sentences:
I/he/she/it was playing football.
We/you/they were playing football.
NOTE: Use was with I, he, she, it - and were with all other pronouns.
Negative sentences:
I/he/she/it was not playing football.
We/you/they were not playing football.
Questions:
In the Past Progressive we put the auxiliary (was or were) before the subject
(Auxiliary - Subject - Verb - Rest).
Example
Use
To indicate uncompleted action of the past (with of without time reference)
To indicate persistent abilitis of the past (with always continuosly, forever, etc.
6
Past Perfect
Form
The structure of the past perfect tense is:
subject + auxiliary verb HAVE + main verb
conjugated in simple past tense past participle
had V3
Example
Sarah had prepared dinner when her husband got home.
Had I bought a new car?
You had not cleaned the house.
Use
The past perfect tense expresses action in the past before another action in the past.
This is the past in the past.
7
Past Perfect Continuous
Form
1. Afirmativo
Sujeto + had + been + verbo en forma -ing+ ...
Examples
I had been working You had been working
2. Negativo
El negativo tiene dos formas:
Forma larga Sujeto + had + not + been + v. en forma -ing + ...
Forma corta Sujeto + hadn't + been + v. en forma -ing + ...
Example
You had not been working I hadnt been painting your house.
3. Interrogativo Afirmativo
Had + sujeto + been + verbo en forma -ing
4. Negativo
Had + sujeto + not + been + verbo en forma -ing
Hadn't + sujeto + been + verbo en forma ing
Example
Afirmativo Negativo
Had I been working? Had I not been working? Hadn't I been working?
Use
The past perfect continuous tense is like the past perfect tense, but it expresses longer
actions in the past before another action in the past.
8
9
Present Simple
Form
Sujeto Conjugacin
I, You, We, They talk, eat, learn, watch, do, go...
He, She, It talks, eats, learns, watches, does, goes...
Affirmative Sentences : Subject + verb
Negative Sentences : Subject + verb auxiliary ("to do") + auxiliary negative ("not") +
verb
Interrogative Sentences : Verb auxiliary ("to do") + subject + verb
Examples
They learn.
I do not talk. He does not eat.
Uses
Habitual actions
Acciones habituales (normalmente acompaados de adverbios de frecuencia)
Permanent states
Estados permanentes (hechos que no cambian nunca)
Feelings and emotions (like, hate, want, hope, etc.)
Sentimientos y emociones
Verb of senses (hear, taste, see, smell, sound and taste)
Verbos de sentidos
10
Present Continuous
Form
Sujeto Auxiliar (to be) Gerundio
I am talking, eating, learning, doing, going...
He, She, It is talking, eating, learning, doing, going...
You, We, They are talking, eating, learning, doing, going...
Affirmative Sentences: Subject+ verb auxiliary ("to be") + gerund ("-ing").
Negative Sentences: Subject + verb auxiliary ("to be") + auxiliary negative ("not") +
gerund ("-ing").
Interrogative Sentences: Verb auxiliary ("to be") + subject + gerundio ("-ing")?
Examples
I'm talking
They're not learning
Uses
for action happening exactly now
The action may not be happening exactly now, but it is happening just before and just
after now, and it is not permanent or habitual.
11
Present Perfect
Form
The present perfect is formed by combining the auxiliary verb has or have with the past
participle.
Subject Auxiliary Short Form Past Participle
I, You, We, They have I've, you've, we've,
they've
talked, learned,
traveled...
He, She, It has he's, she's, it's talked, learned,
traveled...
Example
I have studied. She hasn't gone to work.
Use
1. To indicate past action which is not defined by a time of occurrence.
I have eaten.
2. Used for past actions that continue into the present, or continue to affect the present.
I have been in Madrid for two weeks.
12
Present Perfect Continuous
Form
The structure of the present perfect continuous tense is:
subject + auxiliary verb + auxiliary verb + main verb
have
has been base + ing
Example
I have been I've been
You have been You've been
Uses
An action that has just stopped or recently stopped
An action continuing up to now
13
14
Future Simple
Form
he structure of the future simple tense is:
subject + auxiliary verb WILL + main verb
invariable base
will V1
Examples
I will phone her tonight.
We are going to go to the beach tomorrow.
Uses
Prediction
We often use the future simple tense to make a prediction about the future. Again, there is
no firm plan. We are saying what we think will happen.
Be
When the main verb is be, we can use the future simple tense even if we have a firm plan or
decision before speaking.
We use the future simple tense when there is no plan or decision to do something before we
speak. We make the decision spontaneously at the time of speaking.
15
Future Continuous
Form
Sujeto Auxiliares Gerundio
I will be / am going to be talking, eating, learning, doing, going...
He, She, It will be / is going to be talking, eating, learning, doing, going...
You, We, They will be / are going to be talking, eating, learning, doing, going...
Affirmative Sentences
1 Subject + "will be" + gerund... 2 Subject + verb auxiliary ("to be") + "going to be" +
gerund...
Negative Sentences
1 Subject + "will" + "not" + "be" + gerund.... 2 Subject + verb auxiliary ("to be") + "not" +
"going to be" + gerund...
Interrogative Sentences
1 Verb auxiliary "will" + subject + "be"+ gerund...? 2 Verb auxiliary ("to be") + subject +
"going to be" + gerund...?
Examples
I will be talking. / I'm going to be talking.
I will not [won't] be talking. / I'm not going to be talking.
Will you be talking? / Are you going to be talking?
Uses
The future continuous tense expresses action at a particular moment in the future. The
action will start before that moment but it will not have finished at that moment.
16
Future Perfect
Form
Is formed by combining the auxiliary verb Haber with the past participle.
In this case, Haber is conjugated in the future tenses.
Example
The party will have ended by the time you finish work.
They party won't have ended by the time you finish work.
Will the party have ended before you finish work?
Use
1. Is used to describe what will have happened in the future before a different
action takes place, or by a specific time.
17
Future Perfect Continuous
Form
Affirmative: Subject+ will + have + been + verb in form -ing + ...
Negativo: Subject + shall/will + not + have + been + verb in form -ing + ... /Subject +
shant/won't + have + been + verbo in form -ing + ...
Interrogative Affirmative: Shall/Will + subject + have + been + verb in form -ing + ...?
Interrogative Negative: Shall/Will + subject + not + have + been + verb in form -
ing + ...? / Shant/Won't + subject + have + been + verb in form -ing + ...?
Examples
I shall/will have been working/I'll have been working.
I shall/will not have been working/I shant/won't have been
working.
Afirmativo Negativo
Shall/Will I have been
working?
Shall/Will I not have been
working?
Shall/Won't I have been
working?
Uses
We use the future perfect continuous tense to talk about a long action before some
point in the future.
18
Вам также может понравиться
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideОт EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideОценок пока нет
- Tenses ExplainДокумент4 страницыTenses ExplaindedyОценок пока нет
- Simple Present: InglêsДокумент4 страницыSimple Present: Inglêsjurgute2000Оценок пока нет
- Present Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveДокумент5 страницPresent Perfect and Present Perfect ProgressiveKiara Fajardo matusОценок пока нет
- Basic Tenses PresentationДокумент14 страницBasic Tenses PresentationDuvan JadyОценок пока нет
- Simple Present: InglêsДокумент5 страницSimple Present: InglêsHodžić NisvetaОценок пока нет
- Pa2 TG 01 Efl 10egb CДокумент6 страницPa2 TG 01 Efl 10egb Csebastian delgadoОценок пока нет
- Review of English TensesДокумент8 страницReview of English TensesSyifaa' NajibОценок пока нет
- Tiempos VerbalesДокумент6 страницTiempos VerbalesTeresa MiОценок пока нет
- GrammarДокумент73 страницыGrammarFemina MadhuОценок пока нет
- Planeacion InglesДокумент16 страницPlaneacion InglesRicardo VillegasОценок пока нет
- Pre - Intermediate: Countable/ UncountableДокумент4 страницыPre - Intermediate: Countable/ UncountableAndrea Espinoza YbazetaОценок пока нет
- A Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilДокумент77 страницA Novel Idea Kamilan TakmilSofia RaheelОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент7 страницTensesSdkanisius WatuagungОценок пока нет
- Summary of The Course (Arnau P, Ainhoa M, Arnau L, Unaï H)Документ20 страницSummary of The Course (Arnau P, Ainhoa M, Arnau L, Unaï H)Jack O' Arnau FreddyОценок пока нет
- Guía de Tiempos Verbales en InglésДокумент4 страницыGuía de Tiempos Verbales en InglésMarianela LeonardelliОценок пока нет
- Trabajo de InglesДокумент3 страницыTrabajo de InglesValeria SeguraОценок пока нет
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentДокумент5 страницAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentyvbamuОценок пока нет
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentДокумент4 страницыAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentIvana PlenčaОценок пока нет
- Materi B InggrisДокумент4 страницыMateri B InggrisariОценок пока нет
- InglesДокумент20 страницInglesJesús RamsésОценок пока нет
- PastДокумент7 страницPastDIEGO ixcotОценок пока нет
- Meeting 8Документ13 страницMeeting 8Fitri DelitaОценок пока нет
- Simple SentencesДокумент14 страницSimple SentencesAdi Rahmat AnshariОценок пока нет
- English Tenses: Written By: Faris Arifiansyah Class: Xi TKJ-B School: SMKN 1 CimahiДокумент11 страницEnglish Tenses: Written By: Faris Arifiansyah Class: Xi TKJ-B School: SMKN 1 CimahiFaris ArifiansyahОценок пока нет
- Studies of English.: Simple PresenteДокумент8 страницStudies of English.: Simple PresenteluizОценок пока нет
- Lesson Nr.1: Simple Tenses Present Simple: 1. Clue WordsДокумент4 страницыLesson Nr.1: Simple Tenses Present Simple: 1. Clue WordsAdamson MikhailОценок пока нет
- 16 TensesДокумент34 страницы16 TensesMekar MeinaОценок пока нет
- Inglês - AidaДокумент10 страницInglês - Aidamuchuaneosvaldo4Оценок пока нет
- The Present TensesДокумент15 страницThe Present TenseshujjeОценок пока нет
- Inglês LeonorДокумент10 страницInglês Leonormuchuaneosvaldo4Оценок пока нет
- Problems With VerbsДокумент8 страницProblems With VerbsHafizОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect TenseДокумент30 страницPresent Perfect TenseMuthiah Nadiyah PutriОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент6 страницTensesMeklitОценок пока нет
- The Tenses - English Grammar PDFДокумент3 страницыThe Tenses - English Grammar PDFMed Amine Jomaa80% (5)
- Các thì trong Tiếng AnhДокумент15 страницCác thì trong Tiếng AnhthuhanguyenproОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishДокумент6 страницPresent Perfect Simple Tense in EnglishAntoaneta StancuОценок пока нет
- Structure of Sentence - Rules: Present Simple TenseДокумент13 страницStructure of Sentence - Rules: Present Simple TenseWaqar MughalОценок пока нет
- English Compendium 2Документ16 страницEnglish Compendium 2Erick Mendiola TorresОценок пока нет
- Past Simple: Affirmative FormДокумент5 страницPast Simple: Affirmative FormAndrea CortésОценок пока нет
- Past Continuous Tense MaterialДокумент5 страницPast Continuous Tense MaterialgibranandzackconnorОценок пока нет
- Ejemplos: The Party Will (Is Going To) Have Ended by The Time You Finish Work. I LL (I'm Going To) Have Eaten Before We MeetДокумент3 страницыEjemplos: The Party Will (Is Going To) Have Ended by The Time You Finish Work. I LL (I'm Going To) Have Eaten Before We Meetjhonas131Оценок пока нет
- Transformation of Sentences 2Документ11 страницTransformation of Sentences 2KrishnaBihariShuklaОценок пока нет
- Aprender Idiomas InglesДокумент55 страницAprender Idiomas InglesLester Acevedo CaballeroОценок пока нет
- Summary - Group 9Документ7 страницSummary - Group 9Dian Pratama AnggrainiОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect TenseДокумент11 страницPresent Perfect TenseAgusRivaiAnwarAriefrsОценок пока нет
- Modulo 7 ActividadesДокумент22 страницыModulo 7 ActividadesjosuediazОценок пока нет
- Principal Parts and Tenses of The VerbsДокумент35 страницPrincipal Parts and Tenses of The Verbs1900248Оценок пока нет
- Traditiile Romei AnticeДокумент13 страницTraditiile Romei AnticeAnonymous XsOfDozHauОценок пока нет
- Present PerfectДокумент2 страницыPresent Perfectapi-296199660Оценок пока нет
- Active VoiceДокумент13 страницActive VoiceIan Iswara MadhanОценок пока нет
- English ProjectДокумент20 страницEnglish ProjectStanciu Cosmin100% (2)
- 40 Imporant English GrammarДокумент93 страницы40 Imporant English Grammarbenbouchta sanaa100% (1)
- Key To Bachillerato 2Документ9 страницKey To Bachillerato 2rosersalou67% (3)
- Tense PresentationДокумент53 страницыTense PresentationProlificОценок пока нет
- Eight Parts of SpeechДокумент173 страницыEight Parts of SpeechJan Kenrick SagumОценок пока нет
- Simple Present TenseДокумент7 страницSimple Present TenseRini NgidihoОценок пока нет
- Present Tense: Happens Regularly in The PresentДокумент3 страницыPresent Tense: Happens Regularly in The PresentNuviettaОценок пока нет
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3От EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3Оценок пока нет
- Anallely Vela GascaДокумент1 страницаAnallely Vela Gascaapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- IngleshyДокумент2 страницыIngleshyapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- InglessДокумент1 страницаInglessapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- Ingles 1Документ2 страницыIngles 1api-239674320Оценок пока нет
- Present TenseДокумент1 страницаPresent Tenseapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- ExercisesitioДокумент1 страницаExercisesitioapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- ExercisesДокумент1 страницаExercisesapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- InventionДокумент1 страницаInventionapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- VerbssДокумент1 страницаVerbssapi-239674320Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Book For Spoken English Course - Chapter 1Документ17 страницGrammar Book For Spoken English Course - Chapter 1Amit YadavОценок пока нет
- Formula Simple Present Tense ExampleДокумент9 страницFormula Simple Present Tense ExamplesalsaaaОценок пока нет
- Presented By: Cheterina NoyaДокумент16 страницPresented By: Cheterina NoyaYudi Cristian MОценок пока нет
- Expressing FutureДокумент2 страницыExpressing FutureGRIGORE IRINA-ELENAОценок пока нет
- PAS3e L1 T U07to12B XrefДокумент1 страницаPAS3e L1 T U07to12B XrefChristina Elizabeth100% (1)
- 05 Verb-Tenses-and-Verb-Tense-Sequences-SalinasДокумент23 страницы05 Verb-Tenses-and-Verb-Tense-Sequences-SalinasAdriel Earl ToribioОценок пока нет
- Unit 1. - The Future. ExercisesДокумент12 страницUnit 1. - The Future. ExercisesAntonio Sanchez LozanoОценок пока нет
- Questions and TagsДокумент76 страницQuestions and Tagsvkm_ctr100% (1)
- Aspects of VerbsДокумент5 страницAspects of VerbsCharmange Faye BlancaОценок пока нет
- Ielts Writing Task 1Документ123 страницыIelts Writing Task 1Adalat Adel97% (72)
- How Do We Make The Future Perfect Tense?Документ3 страницыHow Do We Make The Future Perfect Tense?Roshan UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Tabla Conjugacion To HaveДокумент2 страницыTabla Conjugacion To HaveNataly BarreraОценок пока нет
- English Grammar TensesДокумент38 страницEnglish Grammar Tenseshemisphereph2981Оценок пока нет
- Perfect Tenses Worksheet #1 ANSWER KEYДокумент3 страницыPerfect Tenses Worksheet #1 ANSWER KEYKevin Denzel Tan GanОценок пока нет
- Tenses 2Документ12 страницTenses 2nurmaulia sukmaОценок пока нет
- The Student Is Expected To Recognise and Use The Following Grammatical ItemsДокумент31 страницаThe Student Is Expected To Recognise and Use The Following Grammatical ItemsAndy ZhanОценок пока нет
- English Tenses: Present TenseДокумент17 страницEnglish Tenses: Present Tensedare_numero5Оценок пока нет
- Él Estará TrabajandoДокумент2 страницыÉl Estará TrabajandoHelena Prieto GarciaОценок пока нет
- Future Perfect Simple and Future ContinuousДокумент4 страницыFuture Perfect Simple and Future ContinuousLucia Peralta LiañoОценок пока нет
- English II - UCF 1103 Group Name - Pen Pals Verb Tense: ActivityДокумент13 страницEnglish II - UCF 1103 Group Name - Pen Pals Verb Tense: ActivityHania SheikhОценок пока нет
- Escola de Línguas: RefrescamentoДокумент41 страницаEscola de Línguas: RefrescamentocristtianoОценок пока нет
- Past Tens With BanglaДокумент7 страницPast Tens With BanglaFarjana MimОценок пока нет
- All The Tenses PDFДокумент13 страницAll The Tenses PDFNabin JoshiОценок пока нет
- Engl 11 20Документ14 страницEngl 11 20Adriana IliescuОценок пока нет
- Mitchell Rachel Ielts Academic Writing Task 1 Band 8Документ73 страницыMitchell Rachel Ielts Academic Writing Task 1 Band 8mr y100% (3)
- Cartilla 2023 Paragraphs Part 3Документ30 страницCartilla 2023 Paragraphs Part 3Laury M VLОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент6 страницUntitledpetrina0903Оценок пока нет
- Tenses MCQ With AnswersДокумент27 страницTenses MCQ With AnswersAditya yadav100% (2)
- Future TenseДокумент13 страницFuture TenseZuhailieBinRohaidieОценок пока нет