Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Micro Turbine
Загружено:
ravikiranzz12345Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Micro Turbine
Загружено:
ravikiranzz12345Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
MICROTURBINE
TECHNICAL
SEMINAR
PRESENTED BY
K.NARESH (13881D5404)
Under the Guidance of:
Prof.D.Shobha Rani (Phd)
Professor&HOD
INTRODUCTION
Micro turbine is new type of combustion turbine used for
stationary energy generation.
It is also called as TURBO ALTERNATOR.
Approximately the size of a refrigerator with outputs of 25
to 500 kW.
They provide not only electricity , but the thermal energy
to provide for all heating and cooling needs.
WHAT IS A MICROTURBINE
They evolved from automotive and truck turbochargers,
auxiliary power units for airplanes
It comprised of a compressor, combustor, turbine,
alternator, recuperator and generator.
Waste heat recovery can be used with these system to
achieve greater efficiency upto 80%.
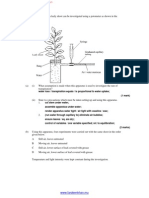
COMPONENETS OF A MICROTURBINE
Turbo Compressor
Combustor
Generator
Recuperator
Turbine
Power Electronics
WORKING PRINCIPLE
Microturbine engine has only one moving part, basically a
shaft.
At one end of the shaft is a turbine wheel, at the opposite
end of the shaft is permanent magnet electric generator,
and at the mid point of that shaft is an air impeller wheel(
air compressor).
Compressor drawing air in it an compressing it, and then
pumping it into combustor.
TYPES OF MICROTURBINE
There are two types of Microturbines
Unrecuperated (simple cycle ) Microturbine
Recuperated Miroturbine.
UNRECUPERTED MICROTURBINE
In simple cycle or recuperated turbine, compressed air is
mixed with fuel and burned under constant pressure
conditions.
Simple cycle Microturbines have lower efficiencies around
15%.
It has lower capital costs, higher reliability.
RECUPERTED TYPE
Recuperated units use a sheet metal heat exchanger that
recovers temperature of the air stream supplied to the
combustor.
Further exhaust heat recovery can be used in cogeneration
configuration.
It has higher efficiencies around 30-40%.
RECUPERATED MICROTURBINE
CHARACTERITICS OF MICROTURBINES
Distributed generation
Quality power and reliability
Stand by power
Boost power
Low cost energy
Combined heat and power (cogeneration)
DISTRIBUTED ENERGY GENERATION
Energy produced in thermal and hydro electric power
plants is distributed to the users through network of line
called the power grid.
On site power generation means power is generated right
where it is needed.
ADVANTAGES OF DISTRIBUTED GENERATION
The losses during power transmission are greatly reduced.
The combined heat and power (CHP) technology can be
applied to microturbine to get 80% efficiency.
This lowers emission and operating cost and increase
efficiency.
ADVANTAGES
Small number of moving parts
Compact size
Lightweight
Good efficiencies in cogeneration
Low emission
Can utilize waste fuels
Long maintenance interval
No vibration
Less noise than reciprocating engines
APPLICATIONS OF MICROTURBINES
Combined heat and power (co-generation)
Distributed power generation
Hospitals
Backup generators
Vehicle applications
Hybrid vehicle(microturbine to high speed alternator)
Hybrid vehicle (microturbine and fuel cell together)
MICROTURBINE MANUFACTURERS
Bowman power systems
Capstone Turbine Cooperation
Elliott energy systems
Turbec AB
Ingersoll-Rand Company
ECONOMICS
Capital cost ranges from $700-$1100 /KW and targeting a
future cost below $650/KW.
Maintanance cost $0.005-0.016\kw
Maintenance Interval: 5,000-8,000hrs
CONCLUSION
Nowadays Microturbines are becoming wide spread for
distributed power and combined heat and power
applications.
There is very definitely a trend toward installing
microturbine system onsite not only for generating electric
power , But also for meeting site heating and cooling
needs.
Typical micro turbine efficiencies are 25 to 35%. When we
combined heat and power cogeneration system, efficiencies
of greater than 80 percent are commonly achieved.
THANK YOU
Any Queries?
Вам также может понравиться
- REC College Principles of Chemical Engineering - Comparison of Centrifugal vs Positive Displacement PumpsДокумент7 страницREC College Principles of Chemical Engineering - Comparison of Centrifugal vs Positive Displacement PumpsYunardi YusufОценок пока нет
- Electrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977От EverandElectrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977Оценок пока нет
- PETROFED workshop discusses Oxy Enrich process for increasing sulfur recovery capacityДокумент22 страницыPETROFED workshop discusses Oxy Enrich process for increasing sulfur recovery capacitysara25dec689288Оценок пока нет
- A Text Book on Power Distribution and Distributed GenerationОт EverandA Text Book on Power Distribution and Distributed GenerationОценок пока нет
- Novel Approach For Enhanced H2S Recovery From Sour Water StrippersДокумент12 страницNovel Approach For Enhanced H2S Recovery From Sour Water Strippersmksscribd100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Assignment QuestionsДокумент2 страницыHeat Transfer Assignment QuestionsMurali KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Purge Gas Purification and Recovery in Ammonia Plants: Process DescriptionДокумент5 страницPurge Gas Purification and Recovery in Ammonia Plants: Process DescriptionFerdian AziziОценок пока нет
- Complete PFDДокумент5 страницComplete PFDAriff FikriОценок пока нет
- TR Analysis in SimulationДокумент16 страницTR Analysis in SimulationnookalaraviОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент15 страницPDFJohansen HasugianОценок пока нет
- Piping Design 5 PDFДокумент9 страницPiping Design 5 PDFSandra MArrugo100% (1)
- Compressor SurgeДокумент3 страницыCompressor SurgeajaysapruОценок пока нет
- 30K - Shell DMR (Dual MR) Liquefaction ProcessesДокумент10 страниц30K - Shell DMR (Dual MR) Liquefaction ProcessesPutu Indra MahatrisnaОценок пока нет
- Tabla de TokensДокумент1 страницаTabla de TokensAnonymous uCYIu1Оценок пока нет
- Failure of Ammonia-1 Natural Gas Compressor Train Catastrophic FailureДокумент9 страницFailure of Ammonia-1 Natural Gas Compressor Train Catastrophic Failurevaratharajan g rОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis of Exposed Pipeline Under Natural ConvectionДокумент6 страницThermal Analysis of Exposed Pipeline Under Natural ConvectionSyahrizalYusoffОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Depressuring PDFДокумент16 страницDynamic Depressuring PDFAsimОценок пока нет
- Process Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisДокумент6 страницProcess Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisHanan Ahmed Ibrahim100% (1)
- 11 - ENGINEERING - DESIGN - GUIDELINE - Separator Vessel - REV01Документ28 страниц11 - ENGINEERING - DESIGN - GUIDELINE - Separator Vessel - REV01Nadine MohamedОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower 434Документ15 страницCooling Tower 434arslan MaqboolОценок пока нет
- 17-ApGreid - Pump Sizing Rev.2Документ14 страниц17-ApGreid - Pump Sizing Rev.2Dhanny MiharjaОценок пока нет
- Flarenet Model Setup: Fan, YiДокумент11 страницFlarenet Model Setup: Fan, YiShamsMohdОценок пока нет
- TEP03 Part4 AbsorptionДокумент28 страницTEP03 Part4 AbsorptionEK63Оценок пока нет
- Mercury Removal ProcessesДокумент10 страницMercury Removal ProcessessalemОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedДокумент3 страницыTutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedTara PillayОценок пока нет
- Oil Characterization: Process Simulation Using HYSYS V8Документ18 страницOil Characterization: Process Simulation Using HYSYS V8Jagan BoseОценок пока нет
- Predict Storage-Tank Heat Transfer: PreciselyДокумент6 страницPredict Storage-Tank Heat Transfer: PreciselyRuben LealОценок пока нет
- Super Critical BoilerДокумент32 страницыSuper Critical BoilerNardo LlanosОценок пока нет
- Vaccon Pump Selection GuideДокумент3 страницыVaccon Pump Selection Guideviveksingh061Оценок пока нет
- SMR Hydrogen Generators-Technologies and Producers 2009Документ28 страницSMR Hydrogen Generators-Technologies and Producers 2009Zoran JuricОценок пока нет
- Kettle Reboilers Chemical Engineering Design Ray SinnoyДокумент6 страницKettle Reboilers Chemical Engineering Design Ray SinnoyFederico BogettiОценок пока нет
- Vacuum Breaker ValveДокумент2 страницыVacuum Breaker ValveRaghunath YeturiОценок пока нет
- Recommended Steam Piping Velocities 2Документ1 страницаRecommended Steam Piping Velocities 2Hassan AbdulAzim FadilОценок пока нет
- Flare Sweep GasДокумент5 страницFlare Sweep GasChem.EnggОценок пока нет
- Cooling System of Haenam-Jeju HVDC SystemДокумент6 страницCooling System of Haenam-Jeju HVDC SystemMohit Kumar ChowdaryОценок пока нет
- Power 101: Flue Gas Heat Recovery in Power PlantsДокумент6 страницPower 101: Flue Gas Heat Recovery in Power PlantsknsaravanaОценок пока нет
- BM15-17 UdaanДокумент105 страницBM15-17 UdaanAnonymous HzljLSMcОценок пока нет
- AQ10T-BFM, 363PL 2335kWДокумент2 страницыAQ10T-BFM, 363PL 2335kWLiviu ConstantinОценок пока нет
- Appendix Flash DrumДокумент2 страницыAppendix Flash DrumRodney Craft100% (1)
- Definition & Types of Reboilers - A. Thermosiphon - : Reboiler CircuitsДокумент2 страницыDefinition & Types of Reboilers - A. Thermosiphon - : Reboiler CircuitsWade ColemanОценок пока нет
- Natural Gas ProcessingДокумент6 страницNatural Gas ProcessingsgrsthОценок пока нет
- Fast Evaluation of Thermodynamic Properties of Superheated Steam A Cubic Equation of StateДокумент9 страницFast Evaluation of Thermodynamic Properties of Superheated Steam A Cubic Equation of StateShalehAhmadОценок пока нет
- Liquefaction of Natural Gas Using Single Stage Mixed Refrigerant PRICO ProcessДокумент8 страницLiquefaction of Natural Gas Using Single Stage Mixed Refrigerant PRICO ProcessHaru MasaОценок пока нет
- KG32903 Process Control and InstrumentationДокумент40 страницKG32903 Process Control and InstrumentationhellothereОценок пока нет
- HVAC Systems and Equipment 2012 REF: CHAPTER 13. HYDRONIC HEATING AND COOLINGДокумент7 страницHVAC Systems and Equipment 2012 REF: CHAPTER 13. HYDRONIC HEATING AND COOLINGhenhuangОценок пока нет
- The Layout of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery LabДокумент4 страницыThe Layout of Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery LabAhmad RazaОценок пока нет
- Rotary heat exchangers recover up to 90% heatДокумент11 страницRotary heat exchangers recover up to 90% heatAhmed HadadОценок пока нет
- Class Example Pump Sizing-Module 5 - Sep28Документ6 страницClass Example Pump Sizing-Module 5 - Sep28Stefan De BeerОценок пока нет
- 14 Hot Oil Systems v3Документ14 страниц14 Hot Oil Systems v3sssss100% (1)
- Vapour Absorption Machine Basics PresentationДокумент16 страницVapour Absorption Machine Basics PresentationAyub GNОценок пока нет
- 1.2.2 Thermodynamics and HYSYS - 5 PDFДокумент26 страниц1.2.2 Thermodynamics and HYSYS - 5 PDFWelisson SilvaОценок пока нет
- Modeling Mineral Size Reduction in The Closed-Circuit Ball Mill at The Pine Point Mines Concentrator (1981)Документ18 страницModeling Mineral Size Reduction in The Closed-Circuit Ball Mill at The Pine Point Mines Concentrator (1981)Ryan Cunningham100% (1)
- Process DescriptionДокумент6 страницProcess Descriptionافكر اشتري كورياОценок пока нет
- Acid Gas Sweetening Simulation SetupДокумент16 страницAcid Gas Sweetening Simulation Setupome solОценок пока нет
- Hysys Class 5Документ5 страницHysys Class 5Salim ChohanОценок пока нет
- Compare Vapor Pressures of Hydrogen, Methane, Ethylene and Ethane in Aspen PlusДокумент10 страницCompare Vapor Pressures of Hydrogen, Methane, Ethylene and Ethane in Aspen Plusmukeshg108Оценок пока нет
- Micro TurbineДокумент24 страницыMicro Turbinesabale_007Оценок пока нет
- Micro Turbine Generating SystemДокумент12 страницMicro Turbine Generating SystemRajesh CharyОценок пока нет
- Microturbines: Within This PageДокумент12 страницMicroturbines: Within This PagekarpakkiОценок пока нет
- Belden CatalogДокумент24 страницыBelden CatalogMani MaranОценок пока нет
- Digital B&W Copiers (D154/D155-NA) Parts CatalogДокумент118 страницDigital B&W Copiers (D154/D155-NA) Parts Catalogkhoi vuОценок пока нет
- Cricothyroidotomy and Needle CricothyrotomyДокумент10 страницCricothyroidotomy and Needle CricothyrotomykityamuwesiОценок пока нет
- LOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorДокумент1 страницаLOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorHorizon 99Оценок пока нет
- Appendix C: Time Value of MoneyДокумент15 страницAppendix C: Time Value of MoneyrockerОценок пока нет
- Edexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)Документ16 страницEdexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)FardeenKhanОценок пока нет
- Biology BIOL 1003 CH 1-3 QuizДокумент14 страницBiology BIOL 1003 CH 1-3 QuizYummyWords100% (1)
- 1 John 2:15-27 - Bible Commentary For PreachingДокумент6 страниц1 John 2:15-27 - Bible Commentary For PreachingJacob D. GerberОценок пока нет
- Textile Pretreatment and Finishing 2023Документ205 страницTextile Pretreatment and Finishing 2023Aweru gebremariamОценок пока нет
- Design of PID controllersДокумент4 страницыDesign of PID controllersFseha GetahunОценок пока нет
- Exercise Stress TestingДокумент54 страницыExercise Stress TestingSaranya R S100% (2)
- Overlord - Volume 01 - The Undead KingДокумент223 страницыOverlord - Volume 01 - The Undead KingPaulo FordheinzОценок пока нет
- AOAC 2012.11 Vitamin DДокумент3 страницыAOAC 2012.11 Vitamin DPankaj BudhlakotiОценок пока нет
- Porta by AmbarrukmoДокумент4 страницыPorta by AmbarrukmoRika AyuОценок пока нет
- Downstream Processing and Bioseparation - Recovery and Purification of Biological Products PDFДокумент313 страницDownstream Processing and Bioseparation - Recovery and Purification of Biological Products PDFgonbio67% (3)
- SSX Diaphragm: Truextent® Replacement Diaphragms For JBL and RADIANДокумент2 страницыSSX Diaphragm: Truextent® Replacement Diaphragms For JBL and RADIANIvica IndjinОценок пока нет
- Bajaj Auto Company NewДокумент94 страницыBajaj Auto Company Newbhas_786Оценок пока нет
- Patient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NДокумент43 страницыPatient Positioning: Complete Guide For Nurses: Marjo S. Malabanan, R.N.,M.NMercy Anne EcatОценок пока нет
- H. Bateman, A. Erdélyi Et Al. - Higher Transcendental Functions 3 (1955, McGraw-Hill)Документ310 страницH. Bateman, A. Erdélyi Et Al. - Higher Transcendental Functions 3 (1955, McGraw-Hill)ITALO HERRERA MOYAОценок пока нет
- Kuffner Final PresentationДокумент16 страницKuffner Final PresentationSamaa GamalОценок пока нет
- II Unit - End EffectorsДокумент49 страницII Unit - End EffectorsGnanasekarОценок пока нет
- Pentecostal Ecclesiology: Simon K.H. Chan - 978-90-04-39714-9 Via Free AccessДокумент156 страницPentecostal Ecclesiology: Simon K.H. Chan - 978-90-04-39714-9 Via Free AccessStanley JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Mahle KFWA MAIN Data SheetДокумент4 страницыMahle KFWA MAIN Data SheetRudnikОценок пока нет
- Ethics Module 2 - NotesДокумент1 страницаEthics Module 2 - Notesanon_137579236Оценок пока нет
- PC Assembly PlantДокумент19 страницPC Assembly Plantmuyenzo100% (1)
- Basler Electric 87T - Great InfoДокумент3 страницыBasler Electric 87T - Great InfoMrОценок пока нет
- 2 Profile OMORIS - Presentation 2020-2Документ20 страниц2 Profile OMORIS - Presentation 2020-2lemuel bacsaОценок пока нет
- Sensor Controlled Animatronic Hand: Graduation Project PresentationДокумент24 страницыSensor Controlled Animatronic Hand: Graduation Project PresentationAnonymous D2FmKSxuuОценок пока нет
- Stavanger Tourist SpotДокумент96 страницStavanger Tourist Spotregupathi6413Оценок пока нет
- r05320202 Microprocessors and Micro ControllersДокумент7 страницr05320202 Microprocessors and Micro ControllersSri LalithaОценок пока нет