Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Covalent Bonding
Загружено:
masoman60 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров1 страница1
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ1
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров1 страницаCovalent Bonding
Загружено:
masoman61
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
Covalent bonding
-Always between non-metals
-No electrons transfer but shared
-stronger bonds
-each shared pair of electrons orbits both nuclei
Elements in need
The lord has built into element atoms the need to complete their outer shells. This is the driving
force behind the formation of chemical compounds. Chemical reactions are all about the
rearrangement of electrons between atoms to meet the needs of as many atoms as possible. The
rearrangement of electrons produces bonds or attractions between atomic particles.
The covalent bonding
Covalent bonds have the highest bonds energies, meaning they are the strongest bonds. They are
formed when atoms share a common pool of electrons.
Covalent bonds are found within all molecules, whether the molecules are compounds such as h2o
or elements such as 02
Covalent bonds are found within all radicals. Radicals such as SO4 2- often survive chemical changes
without alteration because of the strength of the covalent bonds.
Covalernt bonds hold together the atoms in all network solids (macromolecular crystals) Network
solids include elements such as carbon or compounds such as quartz SiO2. Little wonder that such
cyristals are hard and have high melting points. These solids consist of giant molecules. The crystals
are a collection of giant chain, sheet or 3d macromolecules.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Building Over or Near Council Sewer and Water Mains GuidelinesДокумент41 страницаBuilding Over or Near Council Sewer and Water Mains Guidelinesmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Commerce RevisionДокумент3 страницыCommerce RevisionFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Seven Components of The Maya ReligionДокумент4 страницыThe Seven Components of The Maya Religionmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Science NotesДокумент9 страницScience NotesFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
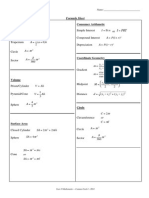
- 2014-10T4 Formula SheetДокумент1 страница2014-10T4 Formula Sheetmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- Ktas 8821798Документ1 страницаKtas 8821798masoman6Оценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Bibliography For Untitled at 08-20-14, 06-11AMДокумент2 страницыBibliography For Untitled at 08-20-14, 06-11AMmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Political InvolvementДокумент1 страницаPolitical InvolvementFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- Information Report: Bipolar Disorder: DesireДокумент3 страницыInformation Report: Bipolar Disorder: DesireFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Bibliography For Untitled at 08-20-14, 06-11AMДокумент2 страницыBibliography For Untitled at 08-20-14, 06-11AMmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- A Person Who Has Good Mental Health Has Good Emotional and Social Wellbeing As Well As The Capacity To Cope With ChallengesДокумент2 страницыA Person Who Has Good Mental Health Has Good Emotional and Social Wellbeing As Well As The Capacity To Cope With ChallengesFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Commerce RevisionДокумент3 страницыCommerce RevisionFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- Task 2 - Practical TaskДокумент2 страницыTask 2 - Practical Taskmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Answer To QuestionsДокумент1 страницаAnswer To Questionsmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- Commerce RevisionДокумент3 страницыCommerce RevisionFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- A Person Who Has Good Mental Health Has Good Emotional and Social Wellbeing As Well As The Capacity To Cope With ChallengesДокумент2 страницыA Person Who Has Good Mental Health Has Good Emotional and Social Wellbeing As Well As The Capacity To Cope With ChallengesFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- Analyse Identify The Components and The Relationships Between Them Draw OutДокумент1 страницаAnalyse Identify The Components and The Relationships Between Them Draw Outmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Science Assignment BibliographyДокумент2 страницыScience Assignment Bibliographymasoman6Оценок пока нет
- Analyse Identify The Components and The Relationships Between Them Draw OutДокумент1 страницаAnalyse Identify The Components and The Relationships Between Them Draw Outmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- SikДокумент1 страницаSikmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- MacbethДокумент4 страницыMacbethmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- A Person Who Has Good Mental Health Has Good Emotional and Social Wellbeing As Well As The Capacity To Cope With ChallengesДокумент2 страницыA Person Who Has Good Mental Health Has Good Emotional and Social Wellbeing As Well As The Capacity To Cope With ChallengesFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- About 2000 Years Ago God Sent An Angel To IsraelДокумент2 страницыAbout 2000 Years Ago God Sent An Angel To Israelmasoman6Оценок пока нет
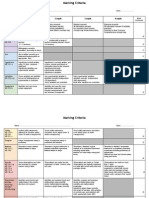
- Outcomes 1 Mark 2 Mark 3 Mark 4 Mark: Mark Achieved Background Information & Concept MapДокумент3 страницыOutcomes 1 Mark 2 Mark 3 Mark 4 Mark: Mark Achieved Background Information & Concept Mapmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- Commerce RevisionДокумент3 страницыCommerce RevisionFilip GorgijovskiОценок пока нет
- MacbethДокумент4 страницыMacbethmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- The Seven Components of The Maya ReligionДокумент4 страницыThe Seven Components of The Maya Religionmasoman6Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Science Assignment BibliographyДокумент2 страницыScience Assignment Bibliographymasoman6Оценок пока нет
- SikДокумент1 страницаSikmasoman6Оценок пока нет