Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Schematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock Syndrome
Загружено:
Ran Ma0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
231 просмотров2 страницыPathophysiology of Toxic Shock Syndrome
Оригинальное название
Schematic Diagram of the Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock Syndrome
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документPathophysiology of Toxic Shock Syndrome
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
231 просмотров2 страницыSchematic Diagram of The Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock Syndrome
Загружено:
Ran MaPathophysiology of Toxic Shock Syndrome
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
6
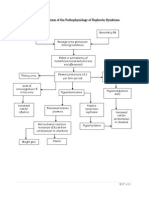
Schematic Diagram of the Pathophysiology of Toxic Shock Syndrome
Continued
Staph. Aureus Strep.
Pyogenes
Production of superantigen toxins
and absorption into the systemic
circulation
Binding of Tcell
receptor to MHC II
Excessive Tcell
proliferation and activation
Proinflammatory
mediators activation
Activation of
complement system
Cytokines
proliferation
Activation of
Coagulation system
Binding to
endothelial tissues
Vasodilatation, increased
vascular permeability
Activation of clotting
factors; decreased ATIII,
protein C and S
Endothelial
damage Hypotension
Microvascular
thrombi; DIC
Clot formation, thrombosis
of small vessels,
Decreased tissue
perfusion
Pyrogenic
effect on the
hypothalamus
Fever
Chills
7
Continuation
Clot formation, thrombosis of small
vessels,
Decreased tissue perfusion
Brain Heart Skin Gastrointestinal
Lungs
Kidneys
Liver
Altered mental
status,
confusion,
headaches,
seizures
Increased dead
space
Impaired gas
exchange
Hypoxemia
Tachycardia
Salt and water
retention
Decreased
urine output
Weakening of the
intestinal wall barrier
Bacterial/endooxin
translocation
Nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea
Damage to
hepatocytes
Increased liver enzymes,
inability to excrete toxins
Diffuse rash,
desquamation
Tachypnea
Sepsis
Increasd levels
of ammonia
Encephalopathy
Вам также может понравиться
- Pa Tho PhysiologyДокумент11 страницPa Tho PhysiologyJonathan CuaОценок пока нет
- Chronic Myeloid LeukemiaДокумент7 страницChronic Myeloid LeukemiahemendreОценок пока нет
- Day 1 BacteriaДокумент251 страницаDay 1 BacteriaLisa NetherlandОценок пока нет
- 3 Year CPC October 8, 20202Документ4 страницы3 Year CPC October 8, 20202Raian SuyuОценок пока нет
- Immunological Lab Diagnosis of TuberculosisДокумент38 страницImmunological Lab Diagnosis of TuberculosisRasha EmadОценок пока нет
- Schematic DiagramДокумент9 страницSchematic DiagramDATO-ON JOANA PAULAОценок пока нет
- Robinson Pathology Chapter 20 KidneyДокумент11 страницRobinson Pathology Chapter 20 KidneyElina Drits100% (1)
- Mechanism of HypertensionДокумент4 страницыMechanism of HypertensionAlya Putri KhairaniОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeДокумент10 страницPathophysiology of Nephrotic Syndromejoyshe111Оценок пока нет
- Chronic Inflammation Non-Specific and GranulomatousДокумент47 страницChronic Inflammation Non-Specific and GranulomatousPradeepОценок пока нет
- The Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterДокумент2 страницыThe Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterJawad Rehman100% (1)
- Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisДокумент69 страницAcute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisJirran CabatinganОценок пока нет
- Patho Unit 4.1Документ20 страницPatho Unit 4.1Lily ChouОценок пока нет
- Acute Rheumatic FeverДокумент4 страницыAcute Rheumatic FeverKelvin KurtОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Pott'S DiseaseДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of Pott'S Diseasee3runeОценок пока нет
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Документ26 страницMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovОценок пока нет
- Acute Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis APSGNДокумент16 страницAcute Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis APSGNErlin IrawatiОценок пока нет
- RabiesДокумент10 страницRabiesWinda LiraОценок пока нет
- Case Study PneumoniaДокумент14 страницCase Study PneumoniaJester GalayОценок пока нет
- Typhoid FeverДокумент23 страницыTyphoid FeverAs ShahirahОценок пока нет
- Hemolytic Anemia: MorphologyДокумент10 страницHemolytic Anemia: MorphologyAlya Putri KhairaniОценок пока нет
- Antiemetic Prophylaxis For CINV NEJM 2016Документ12 страницAntiemetic Prophylaxis For CINV NEJM 2016tcd_usaОценок пока нет
- Nasopharyngeal + Oropharyngeal Swab Inconclusive Inconclusive Inconclusive For Sars-Cov-2 Needs Clinical Correlation, Follow Up & Repeat If Required.Документ1 страницаNasopharyngeal + Oropharyngeal Swab Inconclusive Inconclusive Inconclusive For Sars-Cov-2 Needs Clinical Correlation, Follow Up & Repeat If Required.Kartik ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology Case 4 Sickle Cell AnemiaДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology Case 4 Sickle Cell AnemiaKARL MARLU LUZAОценок пока нет
- Microbiology 2Документ53 страницыMicrobiology 2pikachuОценок пока нет
- Typhoid FeverДокумент3 страницыTyphoid Feverdejay100Оценок пока нет
- Etiology of HypertensionДокумент7 страницEtiology of HypertensionAdelia Maharani DОценок пока нет
- Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis - UpToDateДокумент21 страницаPoststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis - UpToDateHandre Putra100% (1)
- UST SamplexДокумент2 страницыUST Samplexvien.rulezyahoo.comОценок пока нет
- Complement SystemДокумент6 страницComplement SystemJimit GandhiОценок пока нет
- Hypertensive Crisis - PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаHypertensive Crisis - Pathophysiologyaaron tabernaОценок пока нет
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel BakyДокумент8 страницSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel Bakyahmed gabrОценок пока нет
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Документ39 страницSystemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Nadya SabrinaОценок пока нет
- 07 Pathological ClacificationДокумент10 страниц07 Pathological Clacificationraanja2Оценок пока нет
- Bacterial MeningitisДокумент1 страницаBacterial MeningitisDavid HylandОценок пока нет
- Diabetes PathoДокумент2 страницыDiabetes Pathodrewcel100% (1)
- Hereditary SpherocytosisДокумент16 страницHereditary Spherocytosisrizi2008Оценок пока нет
- Leptospirosis: Pauline Teo Siew ChinДокумент18 страницLeptospirosis: Pauline Teo Siew Chinfarmasi_hmОценок пока нет
- Lecture 28 - Pathology of DiabetesДокумент34 страницыLecture 28 - Pathology of Diabetesapi-3703352100% (4)
- 2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersДокумент27 страниц2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersJessica StewartОценок пока нет
- Anti-Anemia and Hematopoietic Growth FactorsДокумент8 страницAnti-Anemia and Hematopoietic Growth FactorsIsabel CastilloОценок пока нет
- Materi 5Документ15 страницMateri 5navytiaraОценок пока нет
- Immune ToleranceДокумент7 страницImmune TolerancehamaadaОценок пока нет
- Pancreatic AdenocarcinomaДокумент6 страницPancreatic AdenocarcinomafikriafisОценок пока нет
- Blood Products: Product DescriptionДокумент3 страницыBlood Products: Product Descriptionkaychi zОценок пока нет
- Leptospirosis FinalДокумент5 страницLeptospirosis FinalufrieОценок пока нет
- Bates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxДокумент15 страницBates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxAdrian CaballesОценок пока нет
- Urinary SedimentsДокумент84 страницыUrinary SedimentsVench Demicais100% (3)
- Transfusion Reaction and Coombs Test: Moderator:-Dr Sanjay Agrwal Presenter: - DR Pratima Singh PG Jr-1Документ33 страницыTransfusion Reaction and Coombs Test: Moderator:-Dr Sanjay Agrwal Presenter: - DR Pratima Singh PG Jr-1UmikaguptaОценок пока нет
- Protein Energy MalnutritionДокумент16 страницProtein Energy MalnutritionAisha Abdullah ManzurОценок пока нет
- Microbiology 15 Campylobacter, Vibrio Etc 431-449Документ18 страницMicrobiology 15 Campylobacter, Vibrio Etc 431-449JenОценок пока нет
- Acute Rheumatic Fever PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаAcute Rheumatic Fever PathophysiologyMoonyeen Jann Casera BalicОценок пока нет
- Chapter 23 SummaryДокумент4 страницыChapter 23 SummaryMartin ClydeОценок пока нет
- Hyponatremia: ElectrolytesДокумент5 страницHyponatremia: ElectrolytesCyreen Jill Aliling100% (1)
- Hodgkin's DiseaseДокумент58 страницHodgkin's Diseasealibayaty1Оценок пока нет
- Tuberculosis: Lifestyle (Smoking) Environment Age GenderДокумент2 страницыTuberculosis: Lifestyle (Smoking) Environment Age GenderhannahleatanosornОценок пока нет
- 01 StudyGuide CellAdaptandNec Latham 0820-22Документ8 страниц01 StudyGuide CellAdaptandNec Latham 0820-22ivankcurryОценок пока нет
- TranscribeMe Style Guide V1.2Документ24 страницыTranscribeMe Style Guide V1.2Juan Zhao67% (6)
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeRan MaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisДокумент1 страницаPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Common Medical Abbreviations With MeaningsДокумент16 страницCommon Medical Abbreviations With MeaningsWilliam Franz SyОценок пока нет
- PathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerДокумент1 страницаPathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerRan Ma73% (11)
- Presentation of Audrey M Battu From Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI)Документ17 страницPresentation of Audrey M Battu From Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI)bobbyramakant0% (1)
- Jameson Chassin-Operative StrategyДокумент566 страницJameson Chassin-Operative StrategyMaria Alexandra100% (3)
- National Pharmaceutical Council 2003 Member Forum HighlightsДокумент7 страницNational Pharmaceutical Council 2003 Member Forum HighlightsNational Pharmaceutical CouncilОценок пока нет
- Psychological Changes of A Pregnant WomanДокумент4 страницыPsychological Changes of A Pregnant WomanEuna Patricia AguilarОценок пока нет
- The History of PsychiatryДокумент12 страницThe History of PsychiatryMarkoff Chaney100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemДокумент35 страницEndocrine SystemLinkОценок пока нет
- Approach To The Patient With Facial Erythema PDFДокумент38 страницApproach To The Patient With Facial Erythema PDFFilipa FigueiredoОценок пока нет
- Charpak: New Evidences On The Kangaroo Mother Care MethodДокумент51 страницаCharpak: New Evidences On The Kangaroo Mother Care MethodNewborn2013Оценок пока нет
- EDiR Notebook (For European Diploma in Radiology)Документ250 страницEDiR Notebook (For European Diploma in Radiology)Parthiban Bala100% (4)
- Drug InteractionДокумент151 страницаDrug Interactionapi-3724213100% (1)
- Davao Doctors CollegeДокумент8 страницDavao Doctors Collegechryzie911Оценок пока нет
- Bsped Dka Guidelines 2020Документ23 страницыBsped Dka Guidelines 2020drsaleemОценок пока нет
- Interstitial PXДокумент56 страницInterstitial PXmenkir tegegneОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Biology - Lesson Note April 8,2020Документ10 страницGrade 9 Biology - Lesson Note April 8,2020micahxОценок пока нет
- Oral Care ProtocolДокумент8 страницOral Care ProtocolQonitaNurMiladiОценок пока нет
- Endometriosis: Common and Rare Radiological Presentations Learning ObjectivesДокумент17 страницEndometriosis: Common and Rare Radiological Presentations Learning ObjectivesstefanyОценок пока нет
- DTCO-KURNOOL - Anti TB Day (3rd Friday) Reporting Format - Phc-RegardingДокумент8 страницDTCO-KURNOOL - Anti TB Day (3rd Friday) Reporting Format - Phc-Regardingkodathalapallis24Оценок пока нет
- Advance Epi & Direct Acyclic GraphДокумент14 страницAdvance Epi & Direct Acyclic GraphPurnima VermaОценок пока нет
- 6277-Article Text-44963-1-10-20221231Документ10 страниц6277-Article Text-44963-1-10-20221231Agus KarismaОценок пока нет
- Augmentin Tablet Pi Ipi13 SiДокумент11 страницAugmentin Tablet Pi Ipi13 Siاسد راجОценок пока нет
- Kode DiagnosaДокумент3 страницыKode Diagnosainterna rssaОценок пока нет
- Discharge Letter To GPДокумент18 страницDischarge Letter To GPyazzОценок пока нет
- Drug Study AzathioprineДокумент3 страницыDrug Study AzathioprineBunnie AlphaОценок пока нет
- Kshudra Roga Critical Understanding: Dr. Gaurav DesaiДокумент39 страницKshudra Roga Critical Understanding: Dr. Gaurav DesaiDrVikas100% (3)
- Bio Chapter 4Документ5 страницBio Chapter 4Aleeya MaisarahОценок пока нет
- TMJ SlidesДокумент113 страницTMJ SlidesRah Ma GhassanОценок пока нет
- Guideline Perkeni 2019 - 4Документ36 страницGuideline Perkeni 2019 - 4jktrlsОценок пока нет
- Standard Case DefinitionsДокумент10 страницStandard Case DefinitionsMohammed AbdillahiОценок пока нет
- Livedoidna VaskulopatijaДокумент5 страницLivedoidna VaskulopatijaemirkurtalicОценок пока нет