Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Physics Prac 2 For Upload
Загружено:
DirkMyburghОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics Prac 2 For Upload
Загружено:
DirkMyburghАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aim:
The aim of this experiment is to determine the acceleration due to gravity using a simple pendulum.
Theory:
When determining the acceleration due to gravity using a simple pendulum, we use the following
equation:
Where L is the length of the pendulum, the acceleration due to gravity is g, and the period of the
pendulum T (the time it takes for one complete swing)
From this equation we get:
, where
is the gradient of the graph of
versus L.
Method:
1. The simple pendulum was set up using a retort stand, a piece of string (1m), 2
similar coins and a bob (heavy weight).
2. The length of the string pendulum was accurately recorded.
3. The bob was given a small displacement, and allowed to swing freely.
4. By using a stopwatch, the time for 10 complete swings (back and forth), was
recorded accurately, and was repeated 3 times.
5. Steps 2 4 were repeated for the different lengths: 0.8m, 0.6m, 0.4m, 0.3m, and
0.2m.
6. All of the results were recorded in a table.
7. All measurements were recorded accurately.
8. From the results and measurements the value of was calculated using the gradient
of the graph as well as the following formula:
.
Results:
Table 1: The results following experiment 2.
Length of
pendulum
(L)(m)
Time for 10 complete swings (s)
Mean time
for 10
swings (s)
Period, T
Time for 1
swing (s)
Reading 1 Reading 2 Reading 3
0.8 17.66 17.71 17.82 17.73 1.773 3.14
0.6 15.50 15.31 15.44 14.42 1.442 2.08
0.4 12.50 12.59 12.66 12.58 1.258 1.58
0.3 10.87 10.78 10.85 10.83 1.083 1.17
0.2 8.85 8.75 8.72 8.77 0.877 0.77
Calculations:
From the graph we can calculate m, which is the gradient:
Let be equal to
so that
Conclusion:
The value of is a constant, it is the acceleration due to gravity and is 9.8 m/s
2
.
From the calculations it is found that has a value of 9.86 m/s
2
. This value is fairly close to the
accepted value of , which is 9.8 m/s
2
.
Вам также может понравиться
- Distillation Example 4 and 5Документ2 страницыDistillation Example 4 and 5DirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- Control Schemes of Unit OpsДокумент3 страницыControl Schemes of Unit OpsDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- Bhopal Incident ReportДокумент4 страницыBhopal Incident ReportDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- Analytical Solution For A Double Pipe Heat Exchanger With Non Adiabatic Condition at The Outer Surface 1987 International Communications in Heat and MДокумент8 страницAnalytical Solution For A Double Pipe Heat Exchanger With Non Adiabatic Condition at The Outer Surface 1987 International Communications in Heat and MDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
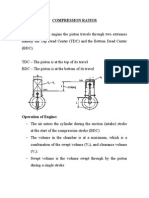
- Compression RatiosДокумент14 страницCompression RatiosDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- The World's Water Vol 8Документ483 страницыThe World's Water Vol 8DirkMyburgh100% (2)
- Extended SurfacesДокумент13 страницExtended SurfacesDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- Physics Prac 1 ExperimentДокумент1 страницаPhysics Prac 1 ExperimentDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- Jean Lèonard Marie Poiseuille PPT FINALДокумент12 страницJean Lèonard Marie Poiseuille PPT FINALDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- HOUSS PresentationДокумент4 страницыHOUSS PresentationDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- Physics Prac 9Документ5 страницPhysics Prac 9DirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- Temperature Measurement Devices, An AssignmentДокумент6 страницTemperature Measurement Devices, An AssignmentDirkMyburghОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)