Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
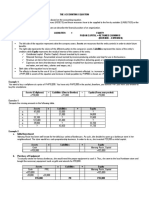
Chapter 4: General Principles of Accounting
Загружено:
libraolrackОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 4: General Principles of Accounting
Загружено:
libraolrackАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHAPTER 4: GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING
An important part of accounting is identifying or specifying the entity for which the
financial statements are being prepared. The accounting entity maybe different than the
legal entity. The entity being studied may be a subsidiary of a larger corporation.
Financial Accounting: provides general-purpose financial statements or reports to aid
decision makers, both internal and external to the organiation, such as the following
!. balance sheet
". statement of revenues and expenses
#. statement of cash flows
$. statement of changes in fund balances
%anagerial Accounting: primarily concerned with preparing financial information for a
specific purpose, usually internal users
&iabilities: represent the claim of one entity on another's assets
(evenues: correspond to the increases in fund balance from the sale of goods or
delivery of services )when the accrual principle of accounting is used, this is recorded
when the revenue is earned which is not necessarily the same as when it is collected*
+xpenses: costs incurred by a business to provide goods or services that reduce fund
balance )under the accrual principle of accounting, this is recorded when the assets are
used to provide the good or service, not necessarily when they are paid for*
,et income: the difference between revenue and expense
The value of assets must always e-ual the combined value of liabilities and net assets
)or fund balance*. Assets / &iabilities 0 ,et Assets.
1henever a financial transaction occurs, such as borrowing money or purchasing
supplies, it is important to keep the accounting e-uation in balance.
The values on the balance sheet represent the ac-uisition cost of the asset and may not
represent the assets current value if it were sold or replaced. 1hy use the ac-uisition or
historical cost rather than current market value or replacement value2 The current
market value may be hard to determine for used e-uipment if it were sold and appraisals
may or may not be accurate. The replacement value may be hard to determine if there
is new technology on the market or if the technology is obsolete. 3ow do you define the
correct replacement2 +specially in health care markets, older technologies are replaced
by new ones rather than similar ones.
4nvestments made by business firms must earn a rate of return higher than their cost of
financing the investment. The rate of return earned on a investment will depend on
whether the cost at the time of investment, the market value of the asset, or the
replacement cost is used in determining the rate of return. 1hen analying the return on
the investment, the cost at the time of the investment will not be useful for future
decision making. This will tell you how well the investment has done but will not tell you
how it will do in the future. 4f the replacement value is used, this will tell whether a
similar investment would do well in the future.
CHAPTER 5: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Balance Sheet
5perating 6ycle: length of time between ac-uisition of materials and services and
collection of revenue generated by them
6urrent Assets: assets that are expected to be exchanged for cash or consumed during
the operating cycle of the entity )or one year, whichever is longer*
!. cash and cash e-uivalents )cash: currency, coins, negotiable instruments
such as money orders or personal checks. cash e-uivalents: savings
accounts, certificates of deposit, must be capable of being transformed into
cash easily*. used to meet normal daily demands for cash
". accounts receivable )represent legally enforceable claims on customers for
prior services or goods*, represents the amount of money expected to be
collected in the next year for services provided. usually different from the
actual patient charges since most charges have some allowance that reduces
the amount that will actually be paid )such as a charity allowance, courtesy
allowance, or contractual allowance*
#. inventories7supplies: items that are to be used in the delivery of health care
services such as normal office supplies to laboratory supplies
$. prepaid expenses: expenditures made for future service )such as prepayment
of insurance premiums*
8roperty and +-uipment: fixed assets or plant property and e-uipment )capital assets*,
shown at the historical cost or ac-uisition cost ad9usted for depreciation
!. land and improvements: represent the historical cost of land owned and any
improvements made to it, land may not be depreciated but improvements
may be
". buildings and e-uipment: represent all buildings and e-uipment owned by the
entity and used during the normal course of its operations. stated at historical
cost. may be classified into three categories)fixed e-uipment, ma9or movable
e-uipment, minor e-uipment*
#. construction in progress: money expended on pro9ects not yet complete at
the time the statement is prepared
$. allowance for depreciation: represents the accumulated depreciation taken on
the asset to the date of the financial statement
Assets That 3ave &imited :se: certain funds may be restricted by the board, some may
be restricted by a third party
5ther Assets: not current and do not involve property and e-uipment, usually either
investments or intangible assets
6urrent &iabilities: obligations that are expected to re-uire payment in cash during the
coming year or operating cycle )whichever is longer*
!. accounts payable: represent the entity's promise to pay money for goods or
services it receives
". accrued liabilities: obligations that result from prior operations )a legal
obligation to make future payment, such as interest*
#. current portion of long-term debt: represents the amount of principal that will
be repaid on the indebtedness within the coming year )not the total payment
for the year since that would include both the interest and principal payment*
,on-6urrent &iabilities: include obligations that will not re-uire payment in cash for at
least one year or more, such as accrued retirement costs or long-term debt
Accrued 4nsurance 6osts: represents the present value of expected or estimated claims
that the organiation will be responsible for paying
&ong-Term ;ebt: represents the amount of long-term indebtedness that is not due in the
next year
:nrestricted ,et Assets: represent the difference between assets and the claim to those
assets by third parties or liabilities
Statement of Reen!e" an# E$%en"e"
(evenue: in healthcare it usually comes from three sources
!. patient services revenue: represents the amount of revenue that results from
the provision of health care services to patients, the amount expected to be
collected from the patient services provided, actual charges are usually
higher and then reduced for contractual allowances and charity care. some of
this is estimated at the end of the year for payments that have not actually
been received but payment from third-party payers is expected under
contractual arrangements
)a* contractual allowances: difference between hospital charges and the
amounts that certain payers have agreed to pay
)b* charity care: represents services provided for which payment was
never expected )different from bad debt*
)c* bad debt: incurred on patients for whom services were provided and
payment was expected, but no payment was made, they are not
deducted from revenue but reported as an expense
". other revenue: generated from normal day-to-day operations not directly
related to patient care, such as
)a* research and grants
)b* rentals of space and e-uipment
)c* sales of medical and pharmacy items to non-patients
)d* cafeteria or gift shop sales
)e* investment income from malpractice trust funds
#. non-operating gains )losses*: gains and losses result from peripheral or
incidental transactions, the following are often categoried as non-operating
gains or losses
)a* contributes or donations that are unrestricted income from endowments
)b* income from the investment of unrestricted funds
)c* gains or losses on sale of property
)d* net rental of facilities not used in the operation of the facility
5perating +xpenses: there are two ways that expenses may be categoried )!* by cost
or responsibility center or )"* by ob9ect or type of expenditure. usually reported by cost
ob9ect. the following categories may be included
!. salaries and wages
". fringe benefits
#. professional fees
$. supplies
<. interest
=. bad debt expense
>. depreciation )an allocation for the cost of the decline in value or productivity*
and amortiation )the allocation of the cost of an intangible asset over its
lifetime*
?. restructuring cost
+xpenditures and expenses may not be e-ual in any given year
Вам также может понравиться
- General Principles of Accounting ExplainedДокумент4 страницыGeneral Principles of Accounting ExplainednikowawaОценок пока нет
- 4) Net Working Capital:: Finance JargonsДокумент4 страницы4) Net Working Capital:: Finance JargonsnavyaekkiralaОценок пока нет
- Elements of Financial Statements & The Recognition Criteria For Assets & LiabilitiesДокумент13 страницElements of Financial Statements & The Recognition Criteria For Assets & LiabilitiesdeepshrmОценок пока нет
- Financial Accounting - Chapter 4Документ3 страницыFinancial Accounting - Chapter 4gjemiljesyla1Оценок пока нет
- Anglais s1Документ9 страницAnglais s1JassОценок пока нет
- Acctg 311N - First Trinal 1Документ11 страницAcctg 311N - First Trinal 1Raenessa FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Unit 7 Business Accounting and Finance Key TermsДокумент36 страницUnit 7 Business Accounting and Finance Key TermsAndrei AndreeaОценок пока нет
- Corporate FininanceДокумент10 страницCorporate FininanceMohan KottuОценок пока нет
- Homework PDFДокумент8 страницHomework PDFTracey NguyenОценок пока нет
- Balance Sheet and Financial StatementДокумент3 страницыBalance Sheet and Financial StatementRochelle AntoinetteОценок пока нет
- The Five Major Accounts & The Chart of AccountsДокумент29 страницThe Five Major Accounts & The Chart of AccountsPrecious Leigh VillamayorОценок пока нет
- English Accounting TermsДокумент8 страницEnglish Accounting TermsRobiMuhammadIlhamОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting 6th Canadian Edition by LibbyДокумент29 страницSolution Manual For Financial Accounting 6th Canadian Edition by Libbya84964899475% (4)
- IAS 7: Statement of Cash Flow: Single CompanyДокумент27 страницIAS 7: Statement of Cash Flow: Single CompanyAfsanaОценок пока нет
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideОт EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideОценок пока нет
- TA CN Tai Chinh Ngan Hang 21.7 (2) - 40 - Unit 4 - Financial StatementsДокумент17 страницTA CN Tai Chinh Ngan Hang 21.7 (2) - 40 - Unit 4 - Financial StatementsPhương NhiОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of AccountingДокумент73 страницыFundamentals of AccountingCarmina Dongcayan100% (2)
- Solution manual for financial accounting 11th edition robert libby patricia libby frank hodgeДокумент52 страницыSolution manual for financial accounting 11th edition robert libby patricia libby frank hodgemarcuskenyatta275Оценок пока нет
- ACCA NoteДокумент21 страницаACCA NoteTanbir Ahsan RubelОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Balance Sheet: Assets Liabilities Owner's (Stockholders') EquityДокумент7 страницIntroduction To Balance Sheet: Assets Liabilities Owner's (Stockholders') EquityChanti KumarОценок пока нет
- 02 ChapДокумент41 страница02 ChapTanner Womble100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting 11th Edition Robert Libby, Patricia Libby, Frank Hodge Verified Chapter's 1 - 13 CompleteДокумент70 страницSolution Manual For Financial Accounting 11th Edition Robert Libby, Patricia Libby, Frank Hodge Verified Chapter's 1 - 13 Completemarcuskenyatta275Оценок пока нет
- Acct Module 2Документ13 страницAcct Module 2Trisha Mae BrazaОценок пока нет
- Accounting Cheat SheetsДокумент4 страницыAccounting Cheat SheetsGreg BealОценок пока нет
- The Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingДокумент32 страницыThe Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDINIE RUZAINI BINTI MOH ZAINUDINОценок пока нет
- BACNTHIДокумент3 страницыBACNTHIFaith CalingoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 0 Financial StatementsДокумент8 страницChapter 0 Financial StatementsmafezОценок пока нет
- Financial Statement Analysis: Assignment OnДокумент6 страницFinancial Statement Analysis: Assignment OnMd Ohidur RahmanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Accounting, Journal, Ledger, Trial BalanceДокумент74 страницыIntroduction To Accounting, Journal, Ledger, Trial Balanceagustinn agustinОценок пока нет
- Summary Intermediate Financial AccountingДокумент10 страницSummary Intermediate Financial AccountingRenz EdilloОценок пока нет
- Financial ManagementДокумент32 страницыFinancial ManagementAirah Gale A. DalugduganОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting, 8th Canadian Edition 2024, by Libby, Hodge, Verified Chapters 1 - 13, Complete Newest VersioДокумент51 страницаSolution Manual For Financial Accounting, 8th Canadian Edition 2024, by Libby, Hodge, Verified Chapters 1 - 13, Complete Newest Versiomarcuskenyatta275Оценок пока нет
- Accounting ElementsДокумент5 страницAccounting ElementsMavic Escuadro LaraОценок пока нет
- Download the original attachment - The complete basics of accountingДокумент32 страницыDownload the original attachment - The complete basics of accountingvijayОценок пока нет
- Financialfeasibility 200129141325Документ20 страницFinancialfeasibility 200129141325Princess BaybayОценок пока нет
- Governmental and Nonprofit Accounting 10Th Edition Smith Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент52 страницыGovernmental and Nonprofit Accounting 10Th Edition Smith Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJoanSmithrgqb100% (9)
- IAS 7-Statements of Cash FlowsДокумент41 страницаIAS 7-Statements of Cash Flowstmandikutse04Оценок пока нет
- Objectives of Financial Management: Securities Markets and Financial InstitutionДокумент15 страницObjectives of Financial Management: Securities Markets and Financial InstitutionMujadid ArhamОценок пока нет
- ACTBAS1 - Lesson 2 (Statement of Financial Position)Документ47 страницACTBAS1 - Lesson 2 (Statement of Financial Position)AyniNuydaОценок пока нет
- The Accounting EquationДокумент5 страницThe Accounting EquationHuskyОценок пока нет
- Continuity Assumption: Prepaid Receivable Receivable, PrepaidДокумент4 страницыContinuity Assumption: Prepaid Receivable Receivable, PrepaidcannickgОценок пока нет
- Dejillas - 107Документ16 страницDejillas - 107Bea Marie DejillasОценок пока нет
- Present Value, Net Present Value, and other Financial Terms ExplainedДокумент6 страницPresent Value, Net Present Value, and other Financial Terms ExplainedArs KhanОценок пока нет
- Libby Financial Accounting Chapter14Документ7 страницLibby Financial Accounting Chapter14Jie Bo TiОценок пока нет
- Cima F1 Chapter 4Документ20 страницCima F1 Chapter 4MichelaRosignoli100% (1)
- Bunwin Residence: Is The Company Profitable??Документ6 страницBunwin Residence: Is The Company Profitable??Pum MineaОценок пока нет
- Cash Flow Analysis GuideДокумент15 страницCash Flow Analysis Guidekyungsoo100% (1)
- Stock ResearchДокумент50 страницStock Researchvikas yadavОценок пока нет
- Accounting NotesДокумент3 страницыAccounting NotesMir TowfiqОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 SummaryДокумент3 страницыChapter 3 SummaryDarlianne Klyne BayerОценок пока нет
- The Accounting EquationДокумент4 страницыThe Accounting EquationjcwimzОценок пока нет
- Chap 2 - SFARДокумент6 страницChap 2 - SFARApril Joy ObedozaОценок пока нет
- Final ProjectДокумент39 страницFinal ProjectJerry SharmaОценок пока нет
- Managerial ACGT: Key for business decisionsДокумент4 страницыManagerial ACGT: Key for business decisionsmperenОценок пока нет
- Basic Accounting.Документ3 страницыBasic Accounting.Sanjay MeenaОценок пока нет
- Balance SheetДокумент8 страницBalance SheetadjeponehОценок пока нет
- Fa Module 2: Accounting Equation: LECTURE 1:the Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities + Owner's EquityДокумент6 страницFa Module 2: Accounting Equation: LECTURE 1:the Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities + Owner's EquitycheskaОценок пока нет
- Mid Term TopicsДокумент10 страницMid Term TopicsТемирлан АльпиевОценок пока нет
- Process For Cash Flow StatementsДокумент33 страницыProcess For Cash Flow StatementsP3 PowersОценок пока нет
- R2Total Quality ManagementДокумент4 страницыR2Total Quality ManagementlibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Manage farm business info with MISДокумент17 страницManage farm business info with MISKisilu MbathaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1-Intro To MGT ActngДокумент7 страницLecture 1-Intro To MGT ActnglibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Written Report On GG and CSRДокумент6 страницWritten Report On GG and CSRlibraolrackОценок пока нет
- What Is Accounting?Документ1 страницаWhat Is Accounting?Ali Bukhari ShahОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1-Intro To MGT ActngДокумент7 страницLecture 1-Intro To MGT ActnglibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1-Intro To MGT ActngДокумент7 страницLecture 1-Intro To MGT ActnglibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Relevant Costing CPARДокумент13 страницRelevant Costing CPARxxxxxxxxx100% (2)
- Hoyle 11e Chapter 10Документ57 страницHoyle 11e Chapter 10bliska100% (2)
- Cash equivalents and bad debt expenseДокумент29 страницCash equivalents and bad debt expenselibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Management Information SystemsДокумент14 страницChapter 1: Introduction To Management Information SystemsvinuoviyanОценок пока нет
- Calculating unrealized intercompany inventory profit adjustmentДокумент22 страницыCalculating unrealized intercompany inventory profit adjustmentxxxxxxxxx100% (3)
- International Financial Accounting and ReportingДокумент2 страницыInternational Financial Accounting and ReportinglibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15: Short-Term Liabilities QuestionsДокумент191 страницаChapter 15: Short-Term Liabilities QuestionslibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Market Participation by Rural Households in A Low-Income CountryДокумент55 страницMarket Participation by Rural Households in A Low-Income CountrylibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Corporate Governance GuidelinesДокумент7 страницCorporate Governance GuidelineslibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15: Short-Term Liabilities QuestionsДокумент191 страницаChapter 15: Short-Term Liabilities QuestionslibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement GuideДокумент45 страницBalance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement Guidelibraolrack100% (1)
- Chapter 9Документ6 страницChapter 9libraolrackОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Advanced Accounting: (Check Figures For Multiple Choice Questions Not Provided.)Документ1 страницаFundamentals of Advanced Accounting: (Check Figures For Multiple Choice Questions Not Provided.)libraolrackОценок пока нет
- 02 Advanced AccountingДокумент9 страниц02 Advanced AccountinglibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Joint VentureДокумент28 страницJoint VentureJovani TomaleОценок пока нет
- Philippine Tax FactsДокумент9 страницPhilippine Tax FactsAizel MaronillaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ5 страницChapter 5chocolatebears67% (3)
- Practical Accounting 1 With AnswersДокумент10 страницPractical Accounting 1 With Answerslibraolrack50% (8)
- OECD Principles of Corporate GovernanceДокумент9 страницOECD Principles of Corporate GovernancelibraolrackОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Cost Accounting ProblemsДокумент8 страницChapter 3 Cost Accounting Problemsxxxxxxxxx100% (1)
- Business Article - The Business Value of Good Corporate GovernanceДокумент8 страницBusiness Article - The Business Value of Good Corporate Governancemanpreetkr26Оценок пока нет
- Chapter04 (1) Advanced Accounting Larson Reference AnswersДокумент31 страницаChapter04 (1) Advanced Accounting Larson Reference AnswersRamez AhmedОценок пока нет
- Simple Balance Sheet For Sole Proprietorship or PartnershipДокумент2 страницыSimple Balance Sheet For Sole Proprietorship or PartnershipMary86% (7)
- CA - Zam Dec-2017Документ102 страницыCA - Zam Dec-2017Dixie CheeloОценок пока нет
- Investment ValueДокумент11 страницInvestment ValueNURASIKIN ABDUL RAHIMОценок пока нет
- Audit program for PPE valuation and depreciationДокумент5 страницAudit program for PPE valuation and depreciationxstljvllОценок пока нет
- Sol05 4eДокумент74 страницыSol05 4eFathurОценок пока нет
- W1-Unit 5 Assignment Brief V1.2 1 2Документ11 страницW1-Unit 5 Assignment Brief V1.2 1 2himanshusharma9435Оценок пока нет
- SAR-MAR-210422-1227PM - RR - 034-COPY 1.editedДокумент12 страницSAR-MAR-210422-1227PM - RR - 034-COPY 1.editedJishnu ChaudhuriОценок пока нет
- Ratio Analysis: Interpretation of Financial Statements: 1) Profitability RatiosДокумент4 страницыRatio Analysis: Interpretation of Financial Statements: 1) Profitability RatiosCollen MahamboОценок пока нет
- A Study On Working Capital Management With Special Reference To Tube Products of India Limited, ChennaiДокумент41 страницаA Study On Working Capital Management With Special Reference To Tube Products of India Limited, ChennaiBasant NagarОценок пока нет
- Original PDF Financial Management Core Concepts 4th Edition by Raymond Brooks PDFДокумент42 страницыOriginal PDF Financial Management Core Concepts 4th Edition by Raymond Brooks PDFmathew.robertson818100% (33)
- Comparable Company Analysis - 1Документ8 страницComparable Company Analysis - 1mohd shariqОценок пока нет
- Cost Accounting ConceptsДокумент18 страницCost Accounting Concepts18arshiОценок пока нет
- Accounting EquationДокумент5 страницAccounting EquationLucky Mark Abitong75% (12)
- CostingДокумент294 страницыCostingNeel HatiОценок пока нет
- IAS 40 Investment Property GuideДокумент29 страницIAS 40 Investment Property GuideNollecy Takudzwa BereОценок пока нет
- financial accounting definitionsДокумент6 страницfinancial accounting definitionskingkhan009Оценок пока нет
- HARD ROCK COMPANY Statement of Financial PositionДокумент3 страницыHARD ROCK COMPANY Statement of Financial PositionJade Lykarose Ochavillo GalendoОценок пока нет
- Discontinued OperationsДокумент22 страницыDiscontinued OperationsJeff KinutsОценок пока нет
- Sun Pharma Audit ReportДокумент42 страницыSun Pharma Audit ReportAnjelika ViescaОценок пока нет
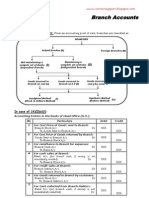
- Branch Accounts: Classification of BranchesДокумент8 страницBranch Accounts: Classification of BranchesgargaldoОценок пока нет
- 1.0 Ratio AnalysisДокумент6 страниц1.0 Ratio Analysissam1702Оценок пока нет
- FAR210 - Feb 2023 - SSДокумент11 страницFAR210 - Feb 2023 - SSfarisha aliahОценок пока нет
- IAS 28 Sol. Man.Документ27 страницIAS 28 Sol. Man.asher phoenixОценок пока нет
- Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold (Practice Quiz)Документ4 страницыInventory and Cost of Goods Sold (Practice Quiz)Monique100% (1)
- The Little Book of Valuation Book SummaryДокумент12 страницThe Little Book of Valuation Book SummaryKapil AroraОценок пока нет
- Ibf ReportДокумент22 страницыIbf ReportAbeer ArifОценок пока нет
- Module 3 - Overview of NPOДокумент19 страницModule 3 - Overview of NPOJebong CaguitlaОценок пока нет
- Final FSQ12022 - PT Blue Bird - TBK - 31 Mar 2022Документ105 страницFinal FSQ12022 - PT Blue Bird - TBK - 31 Mar 202239. ALIF FAJAR ADHAR MAPAREPPAОценок пока нет
- Partnership Dissolution: Prepared By: Cristopherson A. Perez, CPAДокумент59 страницPartnership Dissolution: Prepared By: Cristopherson A. Perez, CPAKyla de SilvaОценок пока нет
- MidtermsДокумент9 страницMidtermsRae SlaughterОценок пока нет