Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transportation Services
Загружено:
Charming Dabandan100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
1K просмотров16 страницA review of the history of transportation and travel shows that the evolution took seven eras. Pre-industrial travel system era was the period before the widespread industrialization in Europe and North America. The automobile was predominant over other travel modes from 1920 to 1945.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документA review of the history of transportation and travel shows that the evolution took seven eras. Pre-industrial travel system era was the period before the widespread industrialization in Europe and North America. The automobile was predominant over other travel modes from 1920 to 1945.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
1K просмотров16 страницTransportation Services
Загружено:
Charming DabandanA review of the history of transportation and travel shows that the evolution took seven eras. Pre-industrial travel system era was the period before the widespread industrialization in Europe and North America. The automobile was predominant over other travel modes from 1920 to 1945.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 16
Transportation Services
Transposition and Travel
Evolution
Transportation and Travel have undergone many
changes. A review of the history of transportation
and travel shows that the evolution took seven
eras:
1. Pre-industrial travel system era
2. Early industrial travel system era
3. Mature-railway system era
4. Express travel system era
5. Automobile-based travel system era
6. Modern-tourism travel system era
7. Post-mobility adjustment era
Pre-Industrial Travel System Era
This was the period before the widespread
industrialization in Europe and North America.
It was before the development of railways in the
two continents.
There were few common carriers.
There were almost no regularly scheduled
transportation services.
There was a little travel.
Travelers made their own arrangements with
several suppliers.
It was the era of stagecoach and wayside inn.
Only few people had money and reason to travel.
Early-Industrial travel System Era
During the era, the road improvement such as
railways, canals, and steamship services were
brought about due to rapid industrialization and
advances in transportation technology.
Common carriers came into existence and began
to offer regularly scheduled transportation services.
Travel increased because more people had money
to travel.
Mature-Railway System Era
This era was characterized by railway which expanded their operations
by running hotels and providing other related services. Travel agencies and
tour companies were formed. More people traveled in this era than the later
ones.
Thomas Cook innovator; began his company activity in the UK in 1840.
Express-Travel System Era
During this era, express services
increased. Trains and other forms of
transportation did not stop at every station
or terminal but only at the major ones.
This increased the speed of travel and
encouraged more travel than before.
Automobile-Based Travel System
Era This influence of the privately-owned
automobile was enhanced in North America and
Europe from 1920 onwards. Motorways, interstate
highways, and other trunk highways were
developed in the latter half of this era which was
from 1920-1974. The automobile was predominant
over other travel modes from 1920 to 1945.
Automobile-Based Travel System Era
Modern Tourism Travel System Era
The period from 1945-1974 is known as he modern tourism travel
system era. Car ownership continued to grow at a fast rate, mainly at the
expense of long-distance rail travel. Mass air travel was another post World
War II occurrence. The introduction of wide-bodied jets in 1970 greatly
increased air travel. The mass tourism philosophy and marketing approaches
were prevalent during 1950s and 1960s.
Post-Mobility Adjustment Era
This era began in 1973-1974 as a result of the oil embargo generated by
OPEC and the resulting of increase in fuel prices. The events of the energy crisis
basically changed the travel patterns throughout the world. The present era is
one in which travelers continue to look to alternative group oriented modes of
transportations.
Selection of Transportation Modes
Reasons why people select one transportation mode for their travels:
1. Cost
2. Traveling time
3. Safety
4. Convenience
5. Comfort
6. Availability
7. Frequency of trips
8. Ground services
9. Terminal facilities and locations
10. Status and prestige
11. Departure and Arrival times
Jagdish Sheth developed a theory identifying transportation variables and the
value of travelers. Factors are: functional, aesthetics/emotional,
social/organizational, situational and curiosity.
Travel by Train
Trains stimulated travel within United States, Canada, and Europe in 19
th
and
early 20
th
centuries.
The first transcontinental route in United States was completed in 1869.
In 1863, long distance rail travel boosted when George M. Pullman built the
Pullman coach, a luxury first-class sleeping and dining facility.
in 1929, US railroads carried 77 percent of the nations passenger traffic.
1950, the growth of private automobile ownership and usage declined to
46%.
Rail Passenger Service Act became a law in Octeber 1970 to save the
railroad industry.
The negative factors of rail travel are:
Slowness in reaching the destination
Inflexible departure times
Lack of quality in food services
Travel by Ship
Travel by sheep preceded travel by train not until the middle of 19
th
century
that travel by ocean liners became prominent.
Oceans liners used to provide an important link to passengers between
continents.
1840, steamship era began when Sir Samuel Cunard pioneered the first
transatlantic-scheduled liner trips.
1960s, travel by ships expired, cruises took over the place of regularly
scheduled passenger ships.
Cruise Ship
A Cruise ship is both a floating hotel and resort
Three Types:
1. Short Cruises one or less week accommodation
2. Intermediate-long Cruises one to four weeks accommodation
3. Long Cruises one to three months accommodation
Ferry/Ferrying
This is a type of cruise travel which only last for one day or less and is
usually used for short duration sightseeing.
Travel by Automobile
Carl Benz, real inventor of automobile. He was from Mannheim, Germany.
Henry Ford produced his Model T car with mass production in 1908.
The advent of the automobile spread the benefits of tourism more widely and
enabled people to travel individually or in private small groups.
Two Aspects of Automobile Travel
1. Recreation Vehicles
2. Car Rentals
Travel by Bus/Motor coach
>Bus travel is the most flexible and economical form of transportation.
Early 1900s busses were first used to carry passengers intercity.
1928, Greyhound Company, the largest privately-owned bus company in the
world was established.
Charter and tour services is the fastest growing segment of the bus or motor
coach industry.
Travel by Air
Travel by airplane had a revolutionary impact on tourism from World War II
onwards.
1927, the air industry developed regularly-scheduled passenger trips
between Boston and New York.
1920s government helped the development of air travel by subsidizing air
companies.
Varney(now United Airlines) was one of the mail carrying airlines which
began in April 1926.
April 19, 1926 Western Airlines began its passenger service when it carried a
woman passenger along with the mail.
1927, American Airways had its first flight when it carried mail from Key West,
Florida to Havana, Cuba.
World War II influenced the development of the airline Industry. It helped to
further improve airplanes by accelerating technological research to improve
their size and speed.
late1950s and early1960s , commercial jet aircrafts were introduced
increasing the speed of travel, creating smoother flights and greater seating
capacity for passengers.
1970, the commercial airline industry improved with the introduction of wide-
bodied aircrafts.
Travel by Air
Bermuda Agreement and the 8 freedoms of the air:
1. First freedom: The right of the airline to overfly one country to get to another.
2. Second freedom: The right of an airplane to land in another country for
technical stopover but does not pick up or drop off traffic.
3. Third freedom: The right of an airline, registered in country X, to drop off
traffic from country X to country Y.
4. Fourth freedom: The right of an airline, registered in country X to
carry back traffic to country X from country Y.
5. Fifth freedom: The right of an airline, registered in country X, to collect
traffic in country Y and fly on to country Z, so long, as the flight either
originates or terminates in country X.
6. Sixth freedom: The right of an airline, registered in country X, to carry traffic
to a gateway(a point in country X) and then abroad. The traffic has neither
its origin nor ultimate destination in country X.
7. Seventh freedom: The right of an airline, registered in country X, to operate
entirely outside of country X in carrying traffic between two other countries.
8. Eight freedom: The right of an airline, registered in country X, to carry traffic
between any points in some foreign country; also known as cabotage.
Travel by Air
Airline Deregulation:
1978, U.S. congress passed Airline Deregulation Act of 1978 which
provided for the gradual phasing-out of the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB)
and removed many of the regulations governing air carrier routes and fares.
Before 1978, the CAB set airline fares according to route distances and the
industry average. By the end of 1982, all official controls and domestic U.S.
air fares were abandoned. Today, no airline has exclusive right to any market
in the United States.
Deregulation is a critical factor affecting airline operations.
Deregulation is spreading throughout the world. In Europe, it is called
liberation.
End
Вам также может понравиться
- Laws Regulating Transportation EstablishmentsДокумент43 страницыLaws Regulating Transportation EstablishmentsOyhoc Ella Mae Evon100% (3)
- Chapter 12 Tourism Distribution ChannelДокумент16 страницChapter 12 Tourism Distribution ChannelSharlyne PimentelОценок пока нет
- THM07 Module 2 The Tourist Market and SegmentationДокумент14 страницTHM07 Module 2 The Tourist Market and Segmentationjennifer mirandaОценок пока нет
- THM07 Module 11 Destination Branding and MarketingДокумент14 страницTHM07 Module 11 Destination Branding and Marketingjennifer miranda100% (2)
- Enhanced Enterprise Risk ManagementДокумент21 страницаEnhanced Enterprise Risk ManagementCharlene Kronstedt100% (1)
- Report On Shangri-La (3500)Документ21 страницаReport On Shangri-La (3500)Niyati SinghОценок пока нет
- Transportation Evolution: A Historical Overview of Developments in the Transportation SectorДокумент23 страницыTransportation Evolution: A Historical Overview of Developments in the Transportation SectorJulieSanchezErsandoОценок пока нет
- NEUST Safety TourДокумент5 страницNEUST Safety TourArjay SolisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ43 страницыChapter 4Agee Kaina Giron100% (1)
- GDS TOU312 3 Tour Packaging and CostingДокумент49 страницGDS TOU312 3 Tour Packaging and CostingMonik100% (2)
- Food and Beverages SectorДокумент39 страницFood and Beverages SectorKRISP ABEARОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 The History of Tourism and HospitalityДокумент5 страницUnit 2 The History of Tourism and HospitalityErizza JavierОценок пока нет
- 4.principles Tour GuidingДокумент23 страницы4.principles Tour GuidingGabriel Martinas100% (2)
- QSM Prelim Tourism and Hospitality Service StrategyДокумент24 страницыQSM Prelim Tourism and Hospitality Service StrategyMICKEY CALADIAOОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Travelers Motivations and ProfileДокумент4 страницыChapter 2 Travelers Motivations and ProfileMary Grace Mende75% (4)
- Micro Perspective of Tourism & Hospitaity ManagementДокумент9 страницMicro Perspective of Tourism & Hospitaity ManagementRikki Vergara FloresОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Transportation in Hospitality Ad Tourism Industry PDFДокумент31 страницаChapter 8 - Transportation in Hospitality Ad Tourism Industry PDFPn Firdaus100% (1)
- THM07 Module 4 Tourism Marketing and The Communication ProcessДокумент13 страницTHM07 Module 4 Tourism Marketing and The Communication Processjennifer miranda100% (1)
- Module 3 TOURISM AND CULTUREДокумент7 страницModule 3 TOURISM AND CULTURECarl Anthony P. Pilapil100% (1)
- Micro Perspective of Tourism and Hospitality PDFДокумент33 страницыMicro Perspective of Tourism and Hospitality PDFsad nu100% (1)
- Fundamentals in Lodging Operation Chapter 1Документ18 страницFundamentals in Lodging Operation Chapter 1Kimberly WenceslaoОценок пока нет
- WK 1 Applied Business Tools Technologies and EconomicsДокумент6 страницWK 1 Applied Business Tools Technologies and EconomicsSarah Marianne KingОценок пока нет
- Tour and Travel ManagementДокумент8 страницTour and Travel ManagementNicole SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 1Документ29 страницChapter - 1Faith GgОценок пока нет
- Module 1. Intro To Tourism and Hospitality (Quality Service in T & H) - THCC 216Документ6 страницModule 1. Intro To Tourism and Hospitality (Quality Service in T & H) - THCC 216Maritoni MedallaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 Tourism PromotionДокумент15 страницChapter 11 Tourism PromotionSharlyne PimentelОценок пока нет
- Chapter2 The Tourism Public SectorДокумент61 страницаChapter2 The Tourism Public SectorRenz Jerome BregabrielОценок пока нет
- THM07 Module 1 Tourism MarketingДокумент14 страницTHM07 Module 1 Tourism Marketingjennifer miranda100% (1)
- Cultural Tourism Factors That Appeal To TravelersДокумент51 страницаCultural Tourism Factors That Appeal To TravelersCha Garcia100% (2)
- Accommodation Operation and ManagementДокумент7 страницAccommodation Operation and ManagementQueen Bee100% (1)
- THM07 Module 7 Tourism Promotion IДокумент18 страницTHM07 Module 7 Tourism Promotion Ijennifer miranda100% (1)
- Sustainable Tourism: TMPC 0313Документ49 страницSustainable Tourism: TMPC 0313Jomer Sidon BalgosОценок пока нет
- Philippine Tourism, Geography, and CultureДокумент4 страницыPhilippine Tourism, Geography, and CultureTristan Troy CuetoОценок пока нет
- Managing Events from Start to FinishДокумент42 страницыManaging Events from Start to FinishCorine Joy TapoОценок пока нет
- Intro To Domestic TourismДокумент22 страницыIntro To Domestic TourismMichael Jr Zeuqirne100% (4)
- THM07 Module 12 The Marketing PlanДокумент12 страницTHM07 Module 12 The Marketing Planjennifer miranda100% (1)
- Air Transport Definition Advantages DisadvantagesДокумент8 страницAir Transport Definition Advantages DisadvantagesMaritoni MedallaОценок пока нет
- Prelim Module. TOURISM AND HOSPITALITY MARKETINGДокумент42 страницыPrelim Module. TOURISM AND HOSPITALITY MARKETINGRofil Albao100% (1)
- Topic 6 Diversities - Simple and ComplexДокумент23 страницыTopic 6 Diversities - Simple and ComplexXIAOОценок пока нет
- THC 107 - Tourism-Marketing-Syllabus-UpdatedДокумент12 страницTHC 107 - Tourism-Marketing-Syllabus-UpdatedEdel MikelОценок пока нет
- Transportation Management (BSTM 1)Документ12 страницTransportation Management (BSTM 1)Maritoni Medalla100% (1)
- Trends and Issues in The Tourism and Hospitality IndustryДокумент15 страницTrends and Issues in The Tourism and Hospitality IndustryGoogly Eyes0% (1)
- Evolution of Transportation and its Role in Tourism DevelopmentДокумент17 страницEvolution of Transportation and its Role in Tourism DevelopmentCarl Anthony P. PilapilОценок пока нет
- The History of TourismДокумент18 страницThe History of TourismSim BelsondraОценок пока нет
- Philippine College of Science and Technology: Module 1: Introduction To Tourism Product and DevelopmentДокумент4 страницыPhilippine College of Science and Technology: Module 1: Introduction To Tourism Product and DevelopmentCher Edz HarrisonОценок пока нет
- The Nature of MiceДокумент31 страницаThe Nature of MiceMariah Eloisa De Guzman0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Macro BTM PDFДокумент20 страницChapter 1 Macro BTM PDFGela Oh100% (1)
- Sustainable Management of Tourism and HospitalityДокумент6 страницSustainable Management of Tourism and HospitalityDal.giОценок пока нет
- Program, Production and Staging for MICE EventsДокумент21 страницаProgram, Production and Staging for MICE EventsGlenn BragaОценок пока нет
- THC100 Course Syllabus OverviewДокумент8 страницTHC100 Course Syllabus OverviewKristine Lyn CamposОценок пока нет
- THM07 Module 3 Tourism and Consumer BehaviourДокумент15 страницTHM07 Module 3 Tourism and Consumer Behaviourjennifer mirandaОценок пока нет
- Information Technology Infrastructure in The Hospitality IndustryДокумент17 страницInformation Technology Infrastructure in The Hospitality IndustryCristel Jean Sadueste100% (1)
- THCC 214 Module 1 overview of tourism originsДокумент7 страницTHCC 214 Module 1 overview of tourism originsMaritoni Medalla100% (1)
- Hospitality LawДокумент5 страницHospitality LawAl-juffrey Luis AmilhamjaОценок пока нет
- History of Philippine Tourism: From Ancient Times to PresentДокумент21 страницаHistory of Philippine Tourism: From Ancient Times to PresentAyen Malabarbas100% (1)
- Javillo - Lesson 1.1 Learning TaskДокумент2 страницыJavillo - Lesson 1.1 Learning TaskJEANE WILMAE JAVILLO100% (1)
- Module 002: The Meaning and Classification of Tour GuideДокумент4 страницыModule 002: The Meaning and Classification of Tour GuideEve Fajardo-Sanchez100% (1)
- Identify The Meaning and Describe The Mandate, Functions, and Compositions of The Following Tourism OrganizationsДокумент8 страницIdentify The Meaning and Describe The Mandate, Functions, and Compositions of The Following Tourism OrganizationsAngelica IlaganОценок пока нет
- Empowering social consciousness through responsible tourism integrationДокумент3 страницыEmpowering social consciousness through responsible tourism integrationManuОценок пока нет
- Ch. 4 - Micro Perspective of The Tourism and HospitalityДокумент20 страницCh. 4 - Micro Perspective of The Tourism and HospitalityFrancine BalansagОценок пока нет
- Midterm THC 219Документ11 страницMidterm THC 219Tachibana AsakiОценок пока нет
- Module IV - TRANSPORTATION SECTORДокумент17 страницModule IV - TRANSPORTATION SECTORSHERWIN GONZALESОценок пока нет
- Vinayak Resume 2022Документ5 страницVinayak Resume 2022Maitry VasaОценок пока нет
- Understanding the Cradle-to-Grave Carbon Footprint of Structural Precast ConcreteДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding the Cradle-to-Grave Carbon Footprint of Structural Precast ConcretetdrnkОценок пока нет
- Global Iconic Brand - NikeДокумент36 страницGlobal Iconic Brand - NikePankajОценок пока нет
- Maximization of Social Welfare.: Unit 5Документ16 страницMaximization of Social Welfare.: Unit 5samОценок пока нет
- FC ProjectДокумент25 страницFC ProjectRaut BalaОценок пока нет
- BacДокумент2 страницыBacmaslia zulkipliОценок пока нет
- Arsh CV 1402Документ3 страницыArsh CV 1402Osman RahmaniОценок пока нет
- Contact details and account statement for HDFC Mutual Fund investmentДокумент3 страницыContact details and account statement for HDFC Mutual Fund investmentrekha nairОценок пока нет
- Finals: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentДокумент2 страницыFinals: University of Santo Tomas Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentSecret SecretОценок пока нет
- 12 Accountancy Notes CH03 Change in Profit Sharing Ratio of Existing Partness 01Документ7 страниц12 Accountancy Notes CH03 Change in Profit Sharing Ratio of Existing Partness 01sakshamkohli970% (1)
- Cost Build Up Template for Road RepairsДокумент14 страницCost Build Up Template for Road RepairsJohn Ray CuevasОценок пока нет
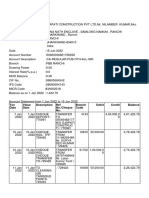
- TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Branch Code Debit Credit BalanceДокумент14 страницTXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Branch Code Debit Credit BalanceRishav AnandОценок пока нет
- NRT/KS/19/5542: CLS-17300 1 (Contd.)Документ2 страницыNRT/KS/19/5542: CLS-17300 1 (Contd.)prajwal khotОценок пока нет
- Directorate of Panchayats Thiruvananthapuram: Name Shri./Smt. P V BeenaДокумент1 страницаDirectorate of Panchayats Thiruvananthapuram: Name Shri./Smt. P V BeenaIsacjohnkurishinkalОценок пока нет
- Batch 5 Breakout 1Документ5 страницBatch 5 Breakout 1RISHI DAILY VOLGSОценок пока нет
- Raju Omlet Case StudyДокумент10 страницRaju Omlet Case StudyGauri DurejaОценок пока нет
- When A Representative Payee Manages Your MoneyДокумент8 страницWhen A Representative Payee Manages Your MoneyAnna MОценок пока нет
- DREAMAPPLY How To Pay The Application FeeДокумент4 страницыDREAMAPPLY How To Pay The Application FeeQader KarimiОценок пока нет
- What Is A Cryptocurrency ?Документ13 страницWhat Is A Cryptocurrency ?Э. Цэнд-АюушОценок пока нет
- 603 TimetableДокумент8 страниц603 Timetablegiudittaa_Оценок пока нет
- Nestle Group Antitrust Law Policy September 2016Документ8 страницNestle Group Antitrust Law Policy September 2016yuszriОценок пока нет
- Partnership FormationДокумент5 страницPartnership FormationMary Elisha PinedaОценок пока нет
- Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), DhanbadДокумент2 страницыIndian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), DhanbadBharat KumarОценок пока нет
- Ihsan Ullah Mechanical EngineerДокумент2 страницыIhsan Ullah Mechanical Engineerihsan ullahОценок пока нет
- Computerization in Retail ShopsДокумент78 страницComputerization in Retail ShopsMrinal DeyОценок пока нет
- Kartik - Double EnteryДокумент17 страницKartik - Double EnterySathya SeelanОценок пока нет
- An Improvement of Three Leg Signalized Intersections in Duhok City, Kurdistan-Iraq (Baran 2018)Документ6 страницAn Improvement of Three Leg Signalized Intersections in Duhok City, Kurdistan-Iraq (Baran 2018)Baran BaranyОценок пока нет
- Engineer's Resume for Medical Equipment SalesДокумент3 страницыEngineer's Resume for Medical Equipment SalesShibleОценок пока нет