Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Normal Distribution Formula When Score Mean and Standard Deviation Is Given
Загружено:
api-260339450Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Normal Distribution Formula When Score Mean and Standard Deviation Is Given
Загружено:
api-260339450Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
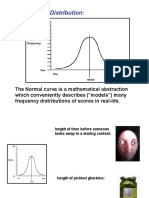
NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
I. Distributions
a. Normal Curve
1) The normal curve is a theoretically perfect frequency polygon in which the mean, median, and mode all coincide in the
center that takes the form of a symmetrical bell-shaped curve. Curve developed by De Moivre (French Mathematician), with
the notion that many human traits, such as intelligence, attitudes, and personality, are distributed among the population in a
fairly "normal way. For example, most of the IQ scores will fall around the mean (100), and there will be relatively few
extreme scores, such as below 55 and over 145.
2) In hypothesis testing, we consider the probability that a given difference or relationship could occur by chance alone.
Understanding the normal curve helps understand concepts underlying hypothesis testing.
3) Baseline of the normal curve is measured in standard deviation units shown by the small letter z. A score that is one
standard deviation above the mean symbolized by +1z, and -1z shows a score that is one standard deviation below the mean.
4) In a normal distribution, approximately 34% of the scores fall between the mean and one standard deviation above the
mean.
68% of the scores fall between -1z and +1z.
34% of scores fall between the mean and +1z
14% of scores fall between +1z and +2z
2% of scores fall between +2z and +3z
34% of scores fall between the mean and -1z
14% of scores fall between -1z and -2z
2% of scores fall between -2z and -3z
Example: GRE Examination is scaled to have:
a mean of 500
and a standard deviation of 100.
If 68% of the scores fall between +1z, 68% of the scores fall between 400 and 600
( -1z = 500 - 100 = 400 and + 1z = 500 + 100 = 600).
Ninety six percent of the scores fall between 300 and 700 (-2z = 500 - (2)(100) = 300 and +2z = 500 + (2)(100) = 700).
FORMULA: +1z() + = scores that fall within 68% range on the top
-1z() + = scores that fall within 68% range on the bottom
Population - parameter Sample - statistic
mean mu
x x bar
standard deviation sigma s
z score = (x - mean)/sd Z z
Approximately 68% of the observations
fall within 1 standard deviation of the
mean
Approximately 95% of the observations
fall within 2 standard deviations of the
mean
Approximately 99.7% of the
observations fall within 3 standard
deviations of the mean
Вам также может понравиться
- ISYE 2028 Chapter 8 SolutionsДокумент41 страницаISYE 2028 Chapter 8 SolutionsWillie Seo100% (2)
- Standard Score and Normal distMEdДокумент12 страницStandard Score and Normal distMEdRizalyn GepilanoОценок пока нет
- Regular How The Garcia Girls Lost Their Accents Agenda Chart - StudentsДокумент7 страницRegular How The Garcia Girls Lost Their Accents Agenda Chart - Studentsapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- ToothThe ToothGrowth Data Analysis in R GrowthДокумент3 страницыToothThe ToothGrowth Data Analysis in R GrowthdsasasОценок пока нет
- 6385.scribe Confidence IntervalsДокумент4 страницы6385.scribe Confidence IntervalselgorilagrandeОценок пока нет
- Week#7 SIM (Normal Distribution)Документ27 страницWeek#7 SIM (Normal Distribution)Mr.JoJIОценок пока нет
- Normal DistributionДокумент25 страницNormal DistributionPauline Anne LopezОценок пока нет
- Week11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)Документ59 страницWeek11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)düşünennurОценок пока нет
- NormalDistribution2012 PDFДокумент29 страницNormalDistribution2012 PDFElisa Dela Reyna BaladadОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Session 2Документ23 страницыModule 2 Session 2MihirОценок пока нет
- Assignment 9 Nomor 1Документ2 страницыAssignment 9 Nomor 1Alexander Steven ThemasОценок пока нет
- Normal DistributionДокумент8 страницNormal DistributionMai MomayОценок пока нет
- Saint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesДокумент11 страницSaint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesJimkenneth RanesОценок пока нет
- Module 5Документ3 страницыModule 5PhoebePhebz RicarteОценок пока нет
- Module 5Документ3 страницыModule 5Bagacay Elementary School (R V - Albay)Оценок пока нет
- 14 Normal DistributionДокумент37 страниц14 Normal DistributionJomar Porteros100% (2)
- Normal DistributionДокумент25 страницNormal DistributionMina BhattaОценок пока нет
- Normal Curve PowerpointДокумент18 страницNormal Curve PowerpointKatherine PanganibanОценок пока нет
- Handout-B-Standard-Score-And-Normal-Dist Advance StatisticsДокумент13 страницHandout-B-Standard-Score-And-Normal-Dist Advance StatisticsRichard HisanzaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ4 страницыChapter 7Riezel PepitoОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution 2012Документ29 страницNormal Distribution 2012Gabriel LloydОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ4 страницыChapter 7Riezel PepitoОценок пока нет
- Normal CurveДокумент37 страницNormal CurveNeerajОценок пока нет
- StatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFДокумент9 страницStatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFMark Cidric Roquero IIОценок пока нет
- Niepid: Research Methods Normal DistributionДокумент6 страницNiepid: Research Methods Normal Distributionsucess psychologyОценок пока нет
- Statistics 17 18Документ21 страницаStatistics 17 18hc4kmx75bkОценок пока нет
- Normal 30Документ2 страницыNormal 30Kerdid SimbolonОценок пока нет
- Stat 3Документ12 страницStat 3Von Edrian PaguioОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 The Normal DistributionДокумент12 страницChapter 4 The Normal Distributionleonessa jorban cortesОценок пока нет
- QTM Cycle 7 Session 4Документ79 страницQTM Cycle 7 Session 4OttilieОценок пока нет
- PPT+59+ +Ex+11B+Standardisation,+68!95!99.7+RuleДокумент23 страницыPPT+59+ +Ex+11B+Standardisation,+68!95!99.7+RuleRalph Rezin MooreОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution and Standard Normal DistributionДокумент46 страницNormal Distribution and Standard Normal DistributionazmanrafaieОценок пока нет
- 1 Normal DistributionДокумент34 страницы1 Normal DistributionDANELYN PINGKIANОценок пока нет
- Normal Curve Standard Normal CurveДокумент33 страницыNormal Curve Standard Normal CurveJahanvi AundhiyaОценок пока нет
- The Normal CurveДокумент29 страницThe Normal CurveKent gonzagaОценок пока нет
- Normal Curve - March 2 2023Документ25 страницNormal Curve - March 2 2023Jerus Leojen TanОценок пока нет
- The Standard Normal Probability Distribution: ObjectivesДокумент15 страницThe Standard Normal Probability Distribution: ObjectivesJason BigataОценок пока нет
- Normal DistributionДокумент23 страницыNormal DistributionPriya bhattiОценок пока нет
- Statistics in PsychologyДокумент15 страницStatistics in PsychologyNehaОценок пока нет
- Chapter6 StatsДокумент4 страницыChapter6 StatsPoonam NaiduОценок пока нет
- ND MaterialsДокумент23 страницыND MaterialsCharlene FiguracionОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution Nov 2021 - FinalДокумент36 страницNormal Distribution Nov 2021 - FinalmussaОценок пока нет
- RMP470S Lecture 7 - One-DimensionalstatisticsДокумент27 страницRMP470S Lecture 7 - One-Dimensionalstatisticsgundokaygee17Оценок пока нет
- Day 02-Random Variable and Probability - Part (I)Документ34 страницыDay 02-Random Variable and Probability - Part (I)Sparsh VijayvargiaОценок пока нет
- Day 8 - Introduction To ProbabilityДокумент5 страницDay 8 - Introduction To ProbabilityLianne SedurifaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5 Z ScoreДокумент32 страницыLesson 5 Z ScoreLala CkeeОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4.2 Normal DistributionДокумент60 страницLesson 4.2 Normal DistributionMA. PATRICIA MAYJANNA HAROОценок пока нет
- Instructor's Presentation - Normal DistributionДокумент22 страницыInstructor's Presentation - Normal DistributionMar LagmayОценок пока нет
- CheatsheetДокумент9 страницCheatsheetI FОценок пока нет
- Z-Score Problems With The Normal Model: ObjectiveДокумент24 страницыZ-Score Problems With The Normal Model: ObjectiveCleverton da VeigaОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution Undergrad 2022Документ41 страницаNormal Distribution Undergrad 2022gerwadakasumuni2121Оценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution1Документ8 страницNormal Distribution1ely san100% (1)
- Standard DeviationДокумент3 страницыStandard DeviationJaliya KumarasingheОценок пока нет
- Presentation 7 Chap6Документ17 страницPresentation 7 Chap6Kevin NyakundiОценок пока нет
- The Normal DistributionДокумент14 страницThe Normal DistributionWajahat NaeemОценок пока нет
- Coefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurveДокумент5 страницCoefficient of Variation and Areas Under Normal CurvemochiОценок пока нет
- 5 Z&NormalДокумент33 страницы5 Z&NormalRosemarie GasparОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 - BДокумент49 страницLesson 4 - Bmajellalpha.ongyacoОценок пока нет
- The Uplift Project: Enhancing and Propagating Intelligence and LongevityОт EverandThe Uplift Project: Enhancing and Propagating Intelligence and LongevityОценок пока нет
- Global Theory of a Second Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equation with a Polynomial CoefficientОт EverandGlobal Theory of a Second Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equation with a Polynomial CoefficientОценок пока нет
- AP English Literature & Composition Course Syllabus: Ms. K. Mitchell - Class WebsiteДокумент9 страницAP English Literature & Composition Course Syllabus: Ms. K. Mitchell - Class Websiteapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Ms Mitchells Virtual LockerДокумент5 страницMs Mitchells Virtual Lockerapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Ap Psychology Syllabus Google DocsДокумент10 страницAp Psychology Syllabus Google Docsapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Composition SyllabusДокумент4 страницыAdvanced Composition Syllabusapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Regular Expository Composition SyllabusДокумент5 страницRegular Expository Composition Syllabusapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Ms Mitchells Virtual LockerДокумент5 страницMs Mitchells Virtual Lockerapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- 2020-21 Mitchell Avid 12 SyllabusДокумент4 страницы2020-21 Mitchell Avid 12 Syllabusapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Current Honors Contemporary Composition and American Lit Course Syllabus With Modified 2020 Grading ScaleДокумент7 страницCurrent Honors Contemporary Composition and American Lit Course Syllabus With Modified 2020 Grading Scaleapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Ap Psych Summer Assignment 2020Документ13 страницAp Psych Summer Assignment 2020api-260339450Оценок пока нет
- 2020 Biblical Classical Allusions Overview Ap Lit Summer AssignementДокумент9 страниц2020 Biblical Classical Allusions Overview Ap Lit Summer Assignementapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- 12 Thhonorssummerreading 2020Документ2 страницы12 Thhonorssummerreading 2020api-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Regular Modern Literature Syllabus With Modified 2020 Grading ScaleДокумент5 страницRegular Modern Literature Syllabus With Modified 2020 Grading Scaleapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- 2020 Biblical Classical Allusions Overview Ap Lit Summer AssignementДокумент9 страниц2020 Biblical Classical Allusions Overview Ap Lit Summer Assignementapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Online Chapter Summary How The Garcia Girls Lost Their AccentsДокумент1 страницаOnline Chapter Summary How The Garcia Girls Lost Their Accentsapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- 2020 - Literary AnalysisДокумент56 страниц2020 - Literary Analysisapi-2603394500% (1)
- Great Gatsby Independent Study Agenda Chart - StudentsДокумент4 страницыGreat Gatsby Independent Study Agenda Chart - Studentsapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- List of Free Response Questions For Advanced Placement English Literature Exams 1990-2019Документ4 страницыList of Free Response Questions For Advanced Placement English Literature Exams 1990-2019api-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Honors How The Garcia Girls Lost Their Accents Agenda Chart - StudentsДокумент6 страницHonors How The Garcia Girls Lost Their Accents Agenda Chart - Studentsapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- 2020 Tfa Independent Study AssingnmentДокумент36 страниц2020 Tfa Independent Study Assingnmentapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Unit 11 Social Psychology Independent Study Packet Due DatesДокумент2 страницыUnit 11 Social Psychology Independent Study Packet Due Datesapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Unit 11 Chapter 14 Independent Study PacketДокумент52 страницыUnit 11 Chapter 14 Independent Study Packetapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Really Reading Strategy For Emotional NeglectДокумент2 страницыReally Reading Strategy For Emotional Neglectapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- 2020 - Literary AnalysisДокумент56 страниц2020 - Literary Analysisapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Characterization Chart For Pauline BreedloveДокумент2 страницыCharacterization Chart For Pauline Breedloveapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Which One of Us Is Truly Crazy Reading QuestionsДокумент1 страницаWhich One of Us Is Truly Crazy Reading Questionsapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Long Term ConsequencesДокумент9 страницLong Term ConsequencesAndrás KardosОценок пока нет
- NeglectДокумент4 страницыNeglectapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Emotional NeglectДокумент3 страницыEmotional Neglectapi-260339450Оценок пока нет
- Bisotat For MlsДокумент57 страницBisotat For MlsABAYОценок пока нет
- PR2 First QuarterДокумент73 страницыPR2 First QuarterWitny LantanoОценок пока нет
- Data Driven Decision Making Syllabus ImppppДокумент4 страницыData Driven Decision Making Syllabus ImppppHemang LathОценок пока нет
- Artificial Intelligence: Semester ProjectДокумент7 страницArtificial Intelligence: Semester ProjectAbdullah AmmarОценок пока нет
- Dlsau Stat Presentation Sept 10Документ42 страницыDlsau Stat Presentation Sept 10Labarinto Eron JohnОценок пока нет
- Auditing SPC InspectionДокумент11 страницAuditing SPC InspectionManu ElaОценок пока нет
- CHM 421 - ToPIC 3 - StatisticsДокумент58 страницCHM 421 - ToPIC 3 - StatisticsthemfyОценок пока нет
- Tool CommunicationДокумент6 страницTool CommunicationAllanSalardaAdemОценок пока нет
- Indian Railways MacroeconomicsДокумент28 страницIndian Railways MacroeconomicsVarun AnandОценок пока нет
- Risk AMPДокумент4 страницыRisk AMPEl Ehsan Abinya FatihОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент36 страницPDFvishwasdeepjoshiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14Документ16 страницChapter 14tamiОценок пока нет
- Teaching SosiologyДокумент16 страницTeaching SosiologyNurSyuhada BujangОценок пока нет
- Scientific MethodДокумент11 страницScientific MethodPatricia100% (2)
- Explainable Machine Learning For Land Cover Classification An Introductory Guide - FinalДокумент54 страницыExplainable Machine Learning For Land Cover Classification An Introductory Guide - Finalherlambang rachmanОценок пока нет
- (GROUP 1) Perceived Level of Readiness of BSA Students in Taking The Integration Examination of Far Easter University - Alabang A.Y. 2023-2024Документ41 страница(GROUP 1) Perceived Level of Readiness of BSA Students in Taking The Integration Examination of Far Easter University - Alabang A.Y. 2023-2024Ramona DadorОценок пока нет
- Micromax PresentationДокумент13 страницMicromax Presentationkashish khetrapalОценок пока нет
- Confidence Intervals For The Mean When Σ Is KnownДокумент4 страницы Confidence Intervals For The Mean When Σ Is KnownBernadette FigarumОценок пока нет
- 150114863016cre Textnayeemshowkatnonprobabilityandprobabilitysampling PDFДокумент10 страниц150114863016cre Textnayeemshowkatnonprobabilityandprobabilitysampling PDFFajriОценок пока нет
- DATA SCIENCE SYLLABUS 2nd YearДокумент58 страницDATA SCIENCE SYLLABUS 2nd YearNEVER SETTLEОценок пока нет
- Kinney 8e - IM - CH 03Документ17 страницKinney 8e - IM - CH 03Ted Bryan D. CabaguaОценок пока нет
- Solution CVEN2002 Solutions 1 7Документ22 страницыSolution CVEN2002 Solutions 1 7Kai LiuОценок пока нет
- Removable and Fixed Implant Supported Prostheses in Edentulous Jaws Post Loading Implant LossДокумент25 страницRemovable and Fixed Implant Supported Prostheses in Edentulous Jaws Post Loading Implant LossLuis Fernando RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Final Exam (Bus. Statistics)Документ1 страницаFinal Exam (Bus. Statistics)RodelJoaquinoОценок пока нет
- QUESTIONS TRIAL KMJ AM025 - Part2Документ2 страницыQUESTIONS TRIAL KMJ AM025 - Part2Adibah NajihahОценок пока нет
- An Overview and Framework For PD Backtesting and BenchmarkingДокумент16 страницAn Overview and Framework For PD Backtesting and BenchmarkingCISSE SerigneОценок пока нет
- The Relationship Between Pain, Analgesics and Survival in Patients With Advanced CancerДокумент10 страницThe Relationship Between Pain, Analgesics and Survival in Patients With Advanced CancerKayoОценок пока нет
- A Convenient Approach For Penalty Parameter Selection in Robust Lasso RegressionДокумент12 страницA Convenient Approach For Penalty Parameter Selection in Robust Lasso Regressionasfar as-salafiyОценок пока нет