Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Clinicaldvts
Загружено:
api-251977061Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Clinicaldvts
Загружено:
api-251977061Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
DEEP VEIN
THROMBOSIS
(DVT)
By Katie Coon and Stephanie Ford
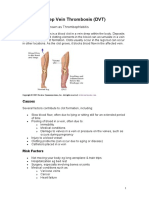
WHAT IS A DVT?
A blood clot in a deep leg
vein caused by abnormal
circulation or clotting of
the blood.
Contributing Factors:
- Being overweight
- Oral contraceptives
- Smoking
- Injury to vein
- Family history - Older age
- Recent surgery - Pregnancy
- Prolonged periods without movement
Complications:
- Shortness of breath or dyspnea
- Chest pain
- Repeated cough/ bloody sputum
- Fever > 100.4 Celsius
- Increased swelling or pain in leg
- Spreading redness
- Unexpected bleeding
HOW SERIOUS IS A DVT?
According to the CDC
approximately 1-2 per 1,000 persons are affected by DVTs each year.
for people over age 80, the incidence increases to 1 per 100 persons.
60,000 100,000 persons dies each year from DVT/PE.
On 4N patients are susceptible to DVTs because
they have had trauma causing vein injury
they have injuries that cause immobility
they are post-operative
IMPLICATIONS OF A DVT
For the patient
Death
Pulmonary embolism
Long term anticoagulants
Increased length in hospital stay
For the institution
Implementation of anticoagulants
Implementation of DVT protocol
Estimated cost is $10,000 per DVT and $20,000 per PE
For healthcare resources
Increase in costs
The need for overall resources increases
PATIENT CARE
Stay off of affected leg as much as possible
When sitting of lying down, keep leg elevated
Use compression stockings to improve blood flow
Move ankles, toes, and knees to stimulate blood flow
Take anticoagulants exactly as directed
PREVENTING A DVT
Improve blood flow back to the heart
Develop a regular exercise program
Lose weight and lower blood pressure
Quit smoking
Elevate legs that feel swollen or heavy
When sitting, wiggle toes and tighten calves
Wear elastic stockings
Monitor vitamin K intake if on anticoagulants
THE NURSING ROLE
Assess
Swelling and pain in one or both legs( pain may only occur when ambulating or
standing)
Warmth of the skin of the affected leg
Red or discolored skin
Fatigue of the leg
Veins are visible at the surface
Positive Homans sign
Plan
Use medications, along with compression devices to diminish the clot
Monitor labs to determine the need for further use of anticoagulants
Diet education (vitamin K)
NURSING ROLE CONT.
Intervene
Elevation of legs
Begin administration of anticoagulants/thrombolytic and analgesics
Monitor labs (PTT, CBC, PT, INR)
Compression devices
Warm compress to affected area
Bed rest
Evaluate
Labs
Pain
Decrease in swelling/edema
D-dimer/ ultrasound
Diet (Vitamin K)
SPECTRUMS INITIATIVES
PREVENTION WITH.
Ambulation
PCDs/SCDs
Anticoagulants
Lovenox
Heparin
Nomogram
EDUCATION MATERIALS
/Library/Encyclopedia/85,P08252
http://www.nursingcenter.com/lnc/journalarticle?Article_ID=11974
98
http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dvt/index.html
http://www.clotconnect.org/healthcare-professionals/patient-
handouts
Вам также может понравиться
- Peripheral Arterial DiseaseДокумент40 страницPeripheral Arterial Diseaseuseofforcelaw100% (1)
- Deep Vein Thrombosis-2Документ12 страницDeep Vein Thrombosis-2mariaОценок пока нет
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)Документ15 страницDeep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)arcci balinasОценок пока нет
- DVTДокумент7 страницDVTAnggun SafariantiniОценок пока нет
- Prevention of DVT/PE: Noornadia BT Yahaya 050100841Документ32 страницыPrevention of DVT/PE: Noornadia BT Yahaya 050100841Nadia YahayaОценок пока нет
- DVT assessment and managementДокумент15 страницDVT assessment and managementAcohCChaoОценок пока нет
- Arterial and Venous 2010Документ120 страницArterial and Venous 2010Amy100% (2)
- Kuliah Thrombosis 2015 NNДокумент39 страницKuliah Thrombosis 2015 NNBeladiena Citra SiregarОценок пока нет
- CHD Updated March 20Документ69 страницCHD Updated March 20Jibran Jones GarciaОценок пока нет
- DVT Prevention EducationДокумент5 страницDVT Prevention Educationapi-549337910Оценок пока нет
- Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes Treatment Complications PreventionДокумент5 страницDeep Vein Thrombosis: Causes Treatment Complications PreventionRaghav Suri100% (2)
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionДокумент5 страницRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- Deep Vein ThrombosisДокумент42 страницыDeep Vein ThrombosisNsklm100% (7)
- Cardiovascular-Disorders Group4 3NFДокумент10 страницCardiovascular-Disorders Group4 3NFDarren RobertoОценок пока нет
- Travel DVT Risk & PreventionДокумент3 страницыTravel DVT Risk & PreventionandreaОценок пока нет
- Deep Vein Thrombosis: Case PresentationДокумент19 страницDeep Vein Thrombosis: Case PresentationFebriadi RОценок пока нет
- Oet Reading - DVTДокумент11 страницOet Reading - DVTOlive GroupОценок пока нет
- Cardio, Respi, GastroДокумент11 страницCardio, Respi, Gastrojeshema100% (1)
- Postpartal ThrombophlebitisДокумент8 страницPostpartal ThrombophlebitisnursereviewОценок пока нет
- Prevention of DVTДокумент49 страницPrevention of DVTMariya DantisОценок пока нет
- Lower Extremity Edema – Causes, Treatment, and PreventionДокумент10 страницLower Extremity Edema – Causes, Treatment, and PreventionRafan AddisОценок пока нет
- Swelling in LegДокумент3 страницыSwelling in LegNeeraj SethiОценок пока нет
- Fuentes, AlvinoДокумент6 страницFuentes, AlvinoJaphet RacaОценок пока нет
- Risks of DVT and Prevention StrategiesДокумент12 страницRisks of DVT and Prevention StrategiesShilpaОценок пока нет
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 2Документ87 страницUpper Respiratory Tract Infections 2wellYONGОценок пока нет
- DVT & Varicose VeinsДокумент30 страницDVT & Varicose VeinsMargaret Xaira Rubio MercadoОценок пока нет
- DVT MatisseДокумент31 страницаDVT MatisseMaretha Dyah AnggrainiОценок пока нет
- What is thrombophlebitis? Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentДокумент3 страницыWhat is thrombophlebitis? Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentJanelle Lois EscolanoОценок пока нет
- Postpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestДокумент8 страницPostpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestLei OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыNursing Care PlanMa Rafaela Rosales PalomponОценок пока нет
- What Is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) ?: Blood VesselsДокумент6 страницWhat Is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) ?: Blood VesselsmainehoonaОценок пока нет
- Thromboembolic disorderДокумент26 страницThromboembolic disorderRahul BaruahОценок пока нет
- Patient Education Power Point DVTДокумент14 страницPatient Education Power Point DVTMihaela PopescuОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Case Presentation: Managing ComplicationsДокумент7 страницDiabetes Case Presentation: Managing Complicationskhalid.zainabОценок пока нет
- 217 RF Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionДокумент8 страниц217 RF Peripheral Neurovascular Dysfunctionapi-271775750Оценок пока нет
- 100 Item Quiz 401Документ21 страница100 Item Quiz 401Sheryl Anne GonzagaОценок пока нет
- Deep Venous Thrombosis: Prepared By: Brian John T. Ampong BSN IiДокумент15 страницDeep Venous Thrombosis: Prepared By: Brian John T. Ampong BSN Iijoyrena ochondraОценок пока нет
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers Prevention & ManagementДокумент59 страницDiabetic Foot Ulcers Prevention & Managementcharity kalinowsky100% (2)
- Diabetic Foot Dr. Sobia FinДокумент139 страницDiabetic Foot Dr. Sobia FinvizzieОценок пока нет
- Peripheral Vascular Disorders Venous ThrombosisДокумент32 страницыPeripheral Vascular Disorders Venous ThrombosisMarlene MathewОценок пока нет
- 780 Adult Cardio Resp Assess DSTДокумент10 страниц780 Adult Cardio Resp Assess DSTgyansa123Оценок пока нет
- Respiratory Problems and Cystic FibrosisДокумент16 страницRespiratory Problems and Cystic FibrosisNica Nix100% (5)
- Alegrias Pat-FundsДокумент14 страницAlegrias Pat-Fundsapi-324006383Оценок пока нет
- Ms Flash CardsДокумент15 страницMs Flash CardsMia MalazoОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Cardio-Respiratory AssessmentДокумент9 страницPediatric Cardio-Respiratory AssessmentRicky SpideyОценок пока нет
- Midwifery IIДокумент5 страницMidwifery IIPal SedОценок пока нет
- Puerperal Venous ThrombosisДокумент25 страницPuerperal Venous ThrombosisAnitha ThankappanОценок пока нет
- Venous Disorder: Venous Thrombosis, Chronic Venous Insufficiency, Varicose VeinsДокумент53 страницыVenous Disorder: Venous Thrombosis, Chronic Venous Insufficiency, Varicose Veinshitesh315Оценок пока нет
- DVTДокумент4 страницыDVTMàŗwā TāhāОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of Adults With Vascular ProblemsДокумент54 страницыNursing Care of Adults With Vascular ProblemsTraci Ann NewberryОценок пока нет
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) : Education For NursesДокумент26 страницDeep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) : Education For NursesVashОценок пока нет
- Dvt. BPTДокумент25 страницDvt. BPTAanchal GuptaОценок пока нет
- Osteoporosis: Risk FactorsДокумент7 страницOsteoporosis: Risk FactorsJmarie Brillantes PopiocoОценок пока нет
- Deep Vein ThrombosisДокумент3 страницыDeep Vein Thrombosisglenn johnston100% (1)
- Oversaturated: A Guide to Conversations About Fats With Your PatientsОт EverandOversaturated: A Guide to Conversations About Fats With Your PatientsОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Hypertension, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesОт EverandPulmonary Hypertension, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesОценок пока нет
- A Simple Guide to Blood Clot in Lungs, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОт EverandA Simple Guide to Blood Clot in Lungs, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Critical Thinking Summary 2Документ5 страницCritical Thinking Summary 2api-251977061Оценок пока нет
- Critical Thinking SummaryДокумент5 страницCritical Thinking Summaryapi-251977061Оценок пока нет
- Pico Research ProposalДокумент1 страницаPico Research Proposalapi-251977061Оценок пока нет
- Coonk CapstoneseminarДокумент23 страницыCoonk Capstoneseminarapi-251977061Оценок пока нет
- Service Learning PosterДокумент1 страницаService Learning Posterapi-251977061Оценок пока нет
- Coonk Nurs441 CompartmentsyndromeДокумент13 страницCoonk Nurs441 Compartmentsyndromeapi-251977061Оценок пока нет
- Obstetrics and GynacologyДокумент14 страницObstetrics and GynacologykalkidanОценок пока нет
- 020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Документ12 страниц020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Sargonan RaviОценок пока нет
- Resume - Viroja Sweta For PortfolioДокумент1 страницаResume - Viroja Sweta For Portfolioapi-608195339Оценок пока нет
- Minimum Inhibitory ConcentrationДокумент7 страницMinimum Inhibitory ConcentrationToshio HamazakiОценок пока нет
- Autism Facts vs Myths: Debunking Common MisconceptionsДокумент14 страницAutism Facts vs Myths: Debunking Common Misconceptionsawardeco01Оценок пока нет
- Recent Trends in Insulin Drug Delivery SystemДокумент39 страницRecent Trends in Insulin Drug Delivery Systemandry natanel tonyОценок пока нет
- Milobar Alexus Resume MayoДокумент2 страницыMilobar Alexus Resume Mayoapi-338646789Оценок пока нет
- OSCE Chart Cough (KK)Документ4 страницыOSCE Chart Cough (KK)api-26938624Оценок пока нет
- Fetal risks of macrosomia in diabetic pregnanciesДокумент27 страницFetal risks of macrosomia in diabetic pregnanciesIful SaifullahОценок пока нет
- Transverse Dimension Diagnosis and Relevance to Functional OcclusionДокумент6 страницTransverse Dimension Diagnosis and Relevance to Functional OcclusionDino MainoОценок пока нет
- The Use of Superficial Heat For Treatment of TempoДокумент6 страницThe Use of Superficial Heat For Treatment of TempoJulianaОценок пока нет
- Important Classifications PDFДокумент42 страницыImportant Classifications PDF330 Himank MehtaОценок пока нет
- Autism and Dietary Therapy: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureДокумент6 страницAutism and Dietary Therapy: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureAntiopi PanteliОценок пока нет
- Case Study PneumothoraxДокумент9 страницCase Study PneumothoraxLee_Cabral_693967% (3)
- Remote Area Nursing Emergency GuidelinesДокумент325 страницRemote Area Nursing Emergency Guidelineslavinia_dobrescu_1Оценок пока нет
- Shaw 2004Документ7 страницShaw 2004Mouloudi NajouaОценок пока нет
- Kali Bichromicum 30C For COPD 2005Документ8 страницKali Bichromicum 30C For COPD 2005Dr. Nancy MalikОценок пока нет
- Nursing Management - Colon CancerДокумент7 страницNursing Management - Colon CancerReese Alessandra GandulfoОценок пока нет
- 2017 Ayurvedic Concept of ShatkriyakalaДокумент8 страниц2017 Ayurvedic Concept of ShatkriyakalaTúlio Laraia CoutinhoОценок пока нет
- MSUDДокумент23 страницыMSUDDivya AjithОценок пока нет
- Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia in Infants and Children: Pathophysiology and TreatmentДокумент11 страницHypokalemia and Hyperkalemia in Infants and Children: Pathophysiology and TreatmentAnantaBenvenutoОценок пока нет
- Prolonged LaborДокумент13 страницProlonged Laborsujinaranamagar18Оценок пока нет
- Hypertension in PregnancyДокумент18 страницHypertension in Pregnancyshubham kumarОценок пока нет
- Source Control in Emergency General SurgeryДокумент21 страницаSource Control in Emergency General SurgerylaviniaОценок пока нет
- English Intervention DialogueДокумент3 страницыEnglish Intervention DialogueJihan Irbah TrianiОценок пока нет
- 13 - Adverse Drug Reactions CausesДокумент4 страницы13 - Adverse Drug Reactions CausesRojas Evert AlonsoОценок пока нет
- QuestionsДокумент6 страницQuestionsLorvic Andrew Juanson UmaliОценок пока нет
- Amavatha & VathasonithaДокумент125 страницAmavatha & VathasonithaCicil AbrahamОценок пока нет
- CH 14 Part 1 Principles of Disease & Epidemiology (FA20)Документ15 страницCH 14 Part 1 Principles of Disease & Epidemiology (FA20)sammy alanОценок пока нет
- 2.3. Mental Health Nursing: Course DescriptionДокумент5 страниц2.3. Mental Health Nursing: Course Descriptioncharanjit kaurОценок пока нет