Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Physics II Crib
Загружено:
NareshJagathkarАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics II Crib
Загружено:
NareshJagathkarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
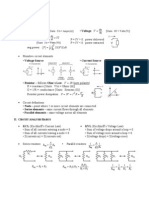
PHYSICS II Electricity and Magnetism, Thermodynamics
Coulombs Law Dipoles Electric Flux
(on axis)
(Gausss Law)
when to
surface
when to
surface
( plane) Potential Energy
Charge Densities
)
Electric Field
r from Point
r from Line
Electric Potential (Voltage)
(Uniform E Field)
(V is constant along
equipotential lines)
Capacitors Plane
(independent of r)
(Charge stored in parallel
capacitors)
Hoop with radius a,
distance x along axis
Disk with radius R ,
distance x along axis
)
Spherical Conductor
Spherical Insulator
Inside
Outside a (Filled)
Cylinder
Constants
)
Kinematics
E inside conductor is 0.
-
-
-
-
+
+
+
+
V
low
V
high
z
a b
L
PHYSICS II Electricity and Magnetism, Thermodynamics
B Fields Due to Wire B Field from Moving Charge Faradays Law
(Direction from right hand rule)
Ohms Law
Magnetic Force Right Hand Rules
B Field From Loop of Wire
(at center)
(along axis)
Biot-Savart Law
||
Resistors
Capacitors
Amperes Law
EM Waves
(Total Current Enclosed by Loop)
Solenoid
(Poynting Vector-
Energy Transfer in
Direction of Travel)
, turns per length
Cyclotron
RC Circuits
Kirchoffs Laws
()
Power
Constants
I
n
d
u
c
e
d
E
M
F
Polarization
(Natural Light when Polarized)
PHYSICS II Electricity and Magnetism, Thermodynamics
Specific Heat Ideal Gas Law Unit Conversions
C
v
= Molar Specific Heat at constant
volume
C
p
= C
v
+ R = Molar Specific Heat at
constant pressure
T
K
= T
C
+ 273.15
T
F
= T
C
1.8 + 32
1 L = 0.001 m
3
= 1000 cm
3
1 atm = 101.325 kPa
()
R
BASIC GAS PROCESSES
Process: Definition: Stays Constant: Work: Heat:
Isochoric V and p/T
Isobaric p and V/T
Isothermal T and pV (
Adiabatic
All gas processes First law
Ideal-gas law
Heat Engine Refrigerator
(
Specific Heats of Common Gases
Gas C
p
C
V
He 20.8 12.5 1.67
Ne 20.8 12.5 1.67
Ar 20.8 12.5 1.67
H
2
28.7 20.4 1.4
N
2
29.1 20.8 1.4
O
2
29.2 20.9 1.4
Вам также может понравиться
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Оценок пока нет
- Iintroduction & Overview of Electrode Processes (Ch. 1)Документ48 страницIintroduction & Overview of Electrode Processes (Ch. 1)GIRMA SELALE GELETAОценок пока нет
- 4-Electrochemical Kinetics of CorrosionДокумент84 страницы4-Electrochemical Kinetics of Corrosion이선엽Оценок пока нет
- Current Electricity Part 01Документ120 страницCurrent Electricity Part 01Vishal MehtaОценок пока нет
- Modeling and Simulation of Multiphase Arc Plasma For Material ProcessingДокумент49 страницModeling and Simulation of Multiphase Arc Plasma For Material ProcessingbaruaeeeОценок пока нет
- AI 12 ElectrochemistryДокумент23 страницыAI 12 ElectrochemistryLintangNurAnggraeniОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Lecture 25Документ14 страницLecture 25iggyОценок пока нет
- AtomicHandWrittenNotes BulutayДокумент222 страницыAtomicHandWrittenNotes BulutaySwashy Yadav50% (2)
- Resistive Plate Chambers For Experiments at India Based Neutrino ObservatoryДокумент42 страницыResistive Plate Chambers For Experiments at India Based Neutrino Observatoryvarunk8275Оценок пока нет
- Advances in Magnetohydrodynamics: Proceedings of a Colloquium Organized by the Department of Fuel Technology and Chemical Engineering at Sheffield University, October 1961От EverandAdvances in Magnetohydrodynamics: Proceedings of a Colloquium Organized by the Department of Fuel Technology and Chemical Engineering at Sheffield University, October 1961I. A. McGrathОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringДокумент46 страницFundamentals of Electrical EngineeringRaza SikandarОценок пока нет
- Circuit AnalysisДокумент15 страницCircuit AnalysisoffnruninОценок пока нет
- ECEN460 2017 Lect1Документ39 страницECEN460 2017 Lect1hurОценок пока нет
- Lec01 1Документ63 страницыLec01 1awabnasirahmednasirОценок пока нет
- Sensors and Transducers: The Thermal Energy DomainДокумент25 страницSensors and Transducers: The Thermal Energy Domainpajarillo0Оценок пока нет
- Mj2411 Renewable Energy Technology - 1Документ27 страницMj2411 Renewable Energy Technology - 1Kazim RazaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide Midterm Exam Phy-113-01 Spring 2024Документ9 страницStudy Guide Midterm Exam Phy-113-01 Spring 2024fhhdghgjfggОценок пока нет
- PDO Course 2Документ67 страницPDO Course 21MM1R HL'Оценок пока нет
- Hydronamic MethodДокумент20 страницHydronamic MethodSeho SunОценок пока нет
- Ee 213Документ22 страницыEe 213ALLADO, ALBERT JR. G.Оценок пока нет
- Time Dependent Currents in RC CircuitsДокумент20 страницTime Dependent Currents in RC Circuitsmurali_j17Оценок пока нет
- An-Najah University: Electrical Circuits LabДокумент7 страницAn-Najah University: Electrical Circuits LabAdel AtawiОценок пока нет
- HighVoltageEngineering PDFДокумент46 страницHighVoltageEngineering PDFBruno LopesОценок пока нет
- CHEG320 Electrochemistry LecturesДокумент114 страницCHEG320 Electrochemistry LecturesqalanisОценок пока нет
- Plasma Discharge FundamentalsДокумент74 страницыPlasma Discharge Fundamentalsgamarino48Оценок пока нет
- Disorder and Magnetic Field Tuned Insulating State in A-Ino Superconducting FilmsДокумент54 страницыDisorder and Magnetic Field Tuned Insulating State in A-Ino Superconducting FilmsMaoz OvadiaОценок пока нет
- SKF3013 Physical Chemistry I: Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarДокумент24 страницыSKF3013 Physical Chemistry I: Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarAisha NajihaОценок пока нет
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsОт EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckОценок пока нет
- CAPE U2 LAB#2 Azariah BarrettДокумент6 страницCAPE U2 LAB#2 Azariah BarrettazaribarrОценок пока нет
- HT1 Solution Home Mid ExamДокумент4 страницыHT1 Solution Home Mid ExambodeОценок пока нет
- ET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture2 PDFДокумент36 страницET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture2 PDFAnonymous AMjDOJ0lОценок пока нет
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Документ20 страницThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazОценок пока нет
- Personal Formula Sheets Phy JeeДокумент2 страницыPersonal Formula Sheets Phy JeeA human BeingОценок пока нет
- 6 Vacuum GaugesДокумент89 страниц6 Vacuum Gaugesapi-3856548100% (1)
- w14d2 Class 35Документ72 страницыw14d2 Class 35eviroyerОценок пока нет
- Assignment TheoryДокумент11 страницAssignment TheoryChomfwix VlogsОценок пока нет
- Physics 1220/1320: Electromagnetism - Part One: ElectrostaticsДокумент70 страницPhysics 1220/1320: Electromagnetism - Part One: ElectrostaticsbeckerinskiОценок пока нет
- Phys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3Документ3 страницыPhys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3zxc100311Оценок пока нет
- Summary of The Rad CourseДокумент132 страницыSummary of The Rad CourseYonatan6248Оценок пока нет
- Cheg320 Electrochemistry LecturesДокумент114 страницCheg320 Electrochemistry Lecturesapi-259261742100% (1)
- PN Junction Diode Characteristics - FinalДокумент6 страницPN Junction Diode Characteristics - FinalHARSH AGNIHOTRIОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Theory-ECE305 - Chapter5 Current and ConductorsДокумент17 страницElectromagnetic Theory-ECE305 - Chapter5 Current and ConductorsabdullahОценок пока нет
- Summary w05d1Документ2 страницыSummary w05d1hamrobeknurullayev21Оценок пока нет
- EIS BoukampДокумент97 страницEIS BoukampMiraldaОценок пока нет
- Lecture #1 Introduc - On To Electrochemistry: Kaori SugiharaДокумент47 страницLecture #1 Introduc - On To Electrochemistry: Kaori SugiharaLoga NathanОценок пока нет
- FE Exam Review2011Документ53 страницыFE Exam Review2011Juan Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Leccion - 07 - Revision - Conceptos - Transmisión de Calor123Документ46 страницLeccion - 07 - Revision - Conceptos - Transmisión de Calor123miriОценок пока нет
- Lecture 13 KДокумент19 страницLecture 13 KKalyani ChandpurkarОценок пока нет
- Ch.1 DC CircuitsДокумент40 страницCh.1 DC Circuitsaattish100% (1)
- Chapter 4Документ41 страницаChapter 4Anil ParmarОценок пока нет
- Hot-Wire Anemometry - With Mathematical ExpresionДокумент63 страницыHot-Wire Anemometry - With Mathematical ExpresionKannan RamarajОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Electronics and Breadboard CircuitsДокумент83 страницыIntroduction To Electronics and Breadboard CircuitsMadhavDhruvОценок пока нет
- Diodes, Triodes, Thermistors, Opto-Isolators, & PhototransistorsДокумент46 страницDiodes, Triodes, Thermistors, Opto-Isolators, & PhototransistorsZorila AlexandruОценок пока нет
- 3 - Electric CircuitsДокумент35 страниц3 - Electric CircuitsKARTHIK S SОценок пока нет
- Physics U1&2 Sep 2023 VF TsepДокумент57 страницPhysics U1&2 Sep 2023 VF TsepkitsuniesОценок пока нет
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonОт EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IОт EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IОценок пока нет
- Your Name: Company, Location - Job TitleДокумент1 страницаYour Name: Company, Location - Job TitleGOVIND KUMARОценок пока нет
- QpaperДокумент3 страницыQpaperNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- QpaperДокумент2 страницыQpaperNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- 117FZ112017Документ3 страницы117FZ112017ANKESHОценок пока нет
- The Kashmir Crisi1Документ5 страницThe Kashmir Crisi1NareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Artificial Intelligence TemplateДокумент2 страницыArtificial Intelligence TemplateNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Systems Technology Assignment 10 (Multiple Choice Questions)Документ2 страницыManufacturing Systems Technology Assignment 10 (Multiple Choice Questions)NareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- 115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkДокумент2 страницы115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Engineering Heat TransferДокумент74 страницыIntroduction To Engineering Heat Transferpkpnitian_152297088Оценок пока нет
- Finite Element MethodsДокумент3 страницыFinite Element MethodsNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- MEFA All UnitsДокумент138 страницMEFA All Unitsshiva santoshОценок пока нет
- The Kashmir Crisi1Документ5 страницThe Kashmir Crisi1NareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Matlab Tutorial PDFДокумент48 страницMatlab Tutorial PDFPrasad KavthakarОценок пока нет
- 07a50305-Design of Machine ElementsДокумент8 страниц07a50305-Design of Machine ElementsNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Question Paper JntuhДокумент1 страницаQuestion Paper JntuhNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Design of Machine Members IIДокумент2 страницыDesign of Machine Members IINareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Bearings 13 PDFДокумент48 страницBearings 13 PDFNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- 115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkДокумент2 страницы115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Student Slides M6Документ14 страницStudent Slides M6niyo7Оценок пока нет
- 2019 Metal Cutting Metal Forming Metrology PDFДокумент203 страницы2019 Metal Cutting Metal Forming Metrology PDFZia Ur Rehman100% (1)
- Drilling PDFДокумент32 страницыDrilling PDFاحمد عمر حديدОценок пока нет
- FM Question Model 2Документ8 страницFM Question Model 2aadhanОценок пока нет
- 115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkДокумент8 страниц115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- CP-104 Accounting For ManagersДокумент662 страницыCP-104 Accounting For ManagersRenjith Ranganadhan100% (1)
- 7 Shpaper PlanerДокумент29 страниц7 Shpaper PlanerfamilyumaОценок пока нет
- Metallurgy and Material ScienceДокумент2 страницыMetallurgy and Material ScienceNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- 3.3 Compressed Air SystemДокумент9 страниц3.3 Compressed Air SystemstephenОценок пока нет
- Drilling PDFДокумент32 страницыDrilling PDFاحمد عمر حديدОценок пока нет
- 115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkДокумент8 страниц115dx Disaster Management - TextmarkNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет
- Jntuh Question PaperДокумент27 страницJntuh Question PaperNareshJagathkarОценок пока нет