Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
1 Pendahuluan
Загружено:
Dimas Rangga WisnuadiОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1 Pendahuluan
Загружено:
Dimas Rangga WisnuadiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
Sistem Komunikasi I
Dr. Arfianto Fahmi
2
Outline
Kontrak Belajar
Silabus Perkuliahan
Dasar Komunikasi
SISTEM KOMUNIKASI I (TTG3A3)
Kelas : TT-37-G1
Jadwal Kuliah
Selasa 10.30 R.B105
Kamis 10.30 R.207
Dosen : Tim
Prasyarat :
Rangkaian Listrik
Sinyal dan Sistem
Kalkulus
Probabilitas dan Statistika
3
Komponen Penilaian
UTS : 35 %
UAS : 40 %
QUIZ : 12.5 %
TUGAS : 12.5 %
Syarat minimal kehadiran : 75 %
4
Rencana Materi Kuliah
1. Review Transformasi Foerier
2. Sistem Amplitude Modulation (AM)
3. Sistem Frequency Modulation (FM)
4. Noise pada Sistem Komunikasi
5. Sistem Pradeteksi dan Kinerjanya
6. Kinerja/performansi sistem AM dan FM
7. ADC dan Multiplexing
8. Pengantar Komunikasi Digital
5
6
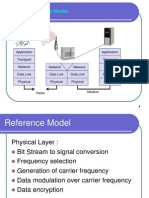
Overview
7
Communication System
Transmitter
Receiver
Transmission
Channel
Message
source
Destination
Noise
8
Frequency For Wireless Communication
1 Mm
300 Hz
10 km
30 kHz
100 m
3 MHz
1 m
300 MHz
10 mm
30 GHz
100 m
3 THz
1 m
300 THz
visible
light
VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF SHF EHF infrared UV
optical transmission
coax cable twisted
pair
Designation Abbreviation Frequencies Free-space Wavelengths
Very Low Frequency VLF 9 kHz - 30 kHz 33 km - 10 km
Low Frequency LF 30 kHz - 300 kHz 10 km - 1 km
Medium Frequency MF 300 kHz - 3 MHz 1 km - 100 m
High Frequency HF 3 MHz - 30 MHz 100 m - 10 m
Very High Frequency VHF 30 MHz - 300 MHz 10 m - 1 m
Ultra High Frequency UHF 300 MHz - 3 GHz 1 m - 100 mm
Super High Frequency SHF 3 GHz - 30 GHz 100 mm - 10 mm
Extremely High Frequency EHF 30 GHz - 300 GHz 10 mm - 1 mm
9
Digital Communication State of the art of
Communication
Advantages of digital communications:
Regenerator receiver
Different kinds of digital signal are treated
identically.
Data
Voice
Media
Propagation distance
Original
pulse
Regenerated
pulse
A bit is a bit!
10
Transmission Terminology
11
Type Of Media Transmission
Guided Media
Conductive metal
twisted pair, coaxial cable
Glass or plastic
fiber optics
Microwave
terestrial, satellite
MUX
Satellite
Fiber-optics cable
Radio link
Coaxial cable
MUX
12
Guided Media (Wireline)
Twisted Pair Cable
Coaxial Cables
13
Microwave System
Transmission between two ground stations
Distance 50 km (depend on the height of antennas)
Microwave links are widely used to provide communication links when it is impractical
or too expensive to install physical transmission media.
Long Haul Radios: ~ 30 - 80 km
2 GHz, 7 GHz
Medium Haul Radios: ~ 25 - 45 km
10 GHz, 13 GHz, 15 GHz
Short Haul Radios: ~ 5 - 30 km
18 GHz, 23 GHz, 26 GHz, 38 GHz,
14
Satellite / VSAT System
Receive and retransmit using transponder
Separate frequencies are assigned for
upward transmission (uplink)
downward transmission
(downlink)
The optimum frequency range for satellite
transmission is in the range 1 to 10 GHz.
Below 1 GHz, there is significant noise from
natural sources, atmospheric noise, and noise
from electronic devices. Above 10 GHz, the
signal is attenuated by atmospheric absorption.
15
Optical Fiber
Drive
Circuit
Sumber
Cahaya
Optical
RX
Optical
Tx
Electronic
Detektor
cahaya
prosesor
Sinyal
input
elektrik
Transmitter
Receiver
Regenerator
Ke perangkat lain
Amplifier
Sinyal
Output
elektrik
coupler
splice
connector
Serat
optik
Optical Amplifier
Gambar 1.6. Elemen utama sistem komunikasi serat optik
16
Celluler Network
BTS
Cellular
Backbone
BTS
BTS
BTS
BTS
BTS
BTS
STM-1 Ring
STM-0 / PDH Approach
BTS
17
Noise, Interferensi, Multipath
Noise
Sinyal pengganggu yang
dihasilkan oleh alam
maupun manusia
Sifat : wideband, daya
rendah, aditif
Interferensi, Jamming
Sinyal pengganggu dari
sistem lain yang
mempunyai frekuensi yang
sama
Sifat : narrow band, daya
tinggi
Multipath
Sinyal dengan perambatan
yang berbeda
t
f
V, P
V, P
interferer
f
18
Redaman dan Distorsi Sinyal
Di dalam media transmisi, sinyal
akan mengalami dua hal:
Redaman, penurunan
intensitas sinyal
membatasi jarak
Distorsi, perubahan
bentuk sinyal akibat
perubahan fasa,
frekuensi, dan polarisasi
19
End
Вам также может понравиться
- Introduction to Communication SystemsДокумент52 страницыIntroduction to Communication SystemsSatish KumarОценок пока нет
- 1.introduc Tion To Microwave EngineeringДокумент33 страницы1.introduc Tion To Microwave EngineeringTrung Nguyen DacОценок пока нет
- Week 1 Lecture 1Документ40 страницWeek 1 Lecture 1athomeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ64 страницыChapter 1Nur Fakhrul Razee Bin Mohd AzmiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsДокумент59 страницChapter 1 Introduction To Communication Systemswleum100% (1)
- Basic Mechanism and Need of ModulationДокумент25 страницBasic Mechanism and Need of ModulationAnonymous WMhwZnYZОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Intro To Communication System-1Документ51 страницаChapter 1 - Intro To Communication System-1Shreesh ParteОценок пока нет
- Intro To Electronic Communication SystemДокумент17 страницIntro To Electronic Communication SystemRyan Anthony AndalОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 1 - Chapter 1Документ5 страницLecture Notes 1 - Chapter 1sohailahmed714319Оценок пока нет
- A Historical Perspective: Overview of Optical Fiber CommunicationsДокумент5 страницA Historical Perspective: Overview of Optical Fiber CommunicationsRakesh RtОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationДокумент58 страницCHAPTER 1 Introduction To CommunicationadibОценок пока нет
- Lecture23 1233854096875992 3Документ41 страницаLecture23 1233854096875992 3Mohammed RizwanОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 & 2Документ69 страницUnit 1 & 2Saiyma Fatima RazaОценок пока нет
- L1. Transmission Line Theory: ObjectivesДокумент13 страницL1. Transmission Line Theory: ObjectivesBrisc BiancaОценок пока нет
- Bio MimeticДокумент20 страницBio MimeticRajat PratapОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Communication SystemДокумент35 страницIntroduction To Communication Systemmohd_anip9774Оценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Electronics Communications SystemsДокумент32 страницыFundamentals of Electronics Communications SystemsRonilloyd SantosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION: 1.1 Basics of Embedded SystemsДокумент44 страницыChapter 1: INTRODUCTION: 1.1 Basics of Embedded SystemsFaiz AhmedОценок пока нет
- Notes - ch1 CommunicationДокумент4 страницыNotes - ch1 CommunicationCwezy ZhoorОценок пока нет
- Kyrl Pogi Science ReportДокумент25 страницKyrl Pogi Science ReportMyrna ChattoОценок пока нет
- Wireless Networks: Introduction To Wireless CommunicationДокумент27 страницWireless Networks: Introduction To Wireless CommunicationAnam ManzoorОценок пока нет
- Lec1 WN Introduction (13!11!2018) (Dr. Rabia Riaz)Документ49 страницLec1 WN Introduction (13!11!2018) (Dr. Rabia Riaz)majid jalilОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Analog CommunicationsДокумент45 страницIntroduction To Analog CommunicationsAnonymous G5D0xzq2Оценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 1 BlakeДокумент13 страницCHAPTER 1 BlakeGennelyn IsraelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2-1Документ80 страницChapter 2-1MehariОценок пока нет
- EERF 6330 - RF Integrated Circuit Design: Prof. Bhaskar Banerjee University of Texas at DallasДокумент29 страницEERF 6330 - RF Integrated Circuit Design: Prof. Bhaskar Banerjee University of Texas at Dallasjatayu2011Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Communication SystemsДокумент19 страницIntroduction To Communication SystemsSolomon Tadesse AthlawОценок пока нет
- 3.transmission Media - SlideДокумент79 страниц3.transmission Media - Slideanika tabassumОценок пока нет
- Telecommunications and NetworksДокумент35 страницTelecommunications and NetworksFarel KawilarangОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Communication SystemДокумент60 страницIntroduction To Communication Systemsadik03leftОценок пока нет
- Free Space Experiments With Mimo Umts High Speed Downlink Packet AccessДокумент6 страницFree Space Experiments With Mimo Umts High Speed Downlink Packet Accesstaquanglam181Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Electronic CommunicationДокумент11 страницIntroduction To Electronic CommunicationDenzel Ivan PalatinoОценок пока нет
- RADAR SYSTEM ASSIGNMENT RADIO FREQUENCY SPECTRUMДокумент7 страницRADAR SYSTEM ASSIGNMENT RADIO FREQUENCY SPECTRUMHAJRA khalidОценок пока нет
- Notes-Lec 7 Radio PropagationДокумент35 страницNotes-Lec 7 Radio PropagationDuy LeОценок пока нет
- Telecommunications and NetworksДокумент35 страницTelecommunications and NetworksManish ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 (Based On Topics 1 & 2) : Transmission LinesДокумент3 страницыHomework 1 (Based On Topics 1 & 2) : Transmission LinesÃmër Ãl-MøhïãОценок пока нет
- JP 1Документ90 страницJP 1yashОценок пока нет
- Unit 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Historical Notes-Communication SystemsДокумент55 страницUnit 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Historical Notes-Communication Systemsbad is good tatyaОценок пока нет
- Cse Notes PDFДокумент77 страницCse Notes PDFAshutosh AcharyaОценок пока нет
- Data and Computer CommunicationsДокумент45 страницData and Computer CommunicationsSam ZahzouhiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Electronic CommunicationДокумент62 страницыChapter 1 Introduction To Electronic Communicationmcruz_1919360% (1)
- Data and Computer CommunicationsДокумент33 страницыData and Computer CommunicationsPutri Sakina Nur AwaliyahОценок пока нет
- OFC Lec 1 2003 FormatДокумент15 страницOFC Lec 1 2003 FormatTarek MahmudОценок пока нет
- FM Transmitter by YewlsewДокумент50 страницFM Transmitter by Yewlsewyewlsewmekonen75% (8)
- Komdat Pertemuan-02 Media Komunikasi DataДокумент10 страницKomdat Pertemuan-02 Media Komunikasi DataZulfa RangkutiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsДокумент16 страницChapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsMelz WiggieОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Microwave Circuits & SystemsДокумент15 страницIntroduction To Microwave Circuits & Systemsgetahun fentawОценок пока нет
- Data and Computer Communications: - Transmission MediaДокумент39 страницData and Computer Communications: - Transmission MediaSukumarGaorobChakmaОценок пока нет
- Transmission Media Characteristics and FactorsДокумент39 страницTransmission Media Characteristics and Factorskongnyuy sidonne vernyuyОценок пока нет
- Princom IntroДокумент44 страницыPrincom IntroRichster LofrancoОценок пока нет
- RF Communication Circuit DesignДокумент32 страницыRF Communication Circuit DesignAkhilesh MohanОценок пока нет
- Microwave Engineering NotesДокумент17 страницMicrowave Engineering NotesVamsi Krishna Dokku100% (1)
- Communication System Lecture OverviewДокумент66 страницCommunication System Lecture OverviewUmer farooqОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ53 страницыChapter 1Renz Benhar Ocon BobadillaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Spectrum NotesДокумент8 страницUnit 1 - Spectrum Notesdeepas dineshОценок пока нет
- Lec 1 Dcs - Fall 2012 (M.SC)Документ60 страницLec 1 Dcs - Fall 2012 (M.SC)Basir UsmanОценок пока нет
- Transmission MediaДокумент33 страницыTransmission MediaWayan MardikaОценок пока нет
- Transmission Media Types and CharacteristicsДокумент79 страницTransmission Media Types and CharacteristicsGanesh KumarОценок пока нет
- 16 Ofdm PDFДокумент4 страницы16 Ofdm PDFmusОценок пока нет
- WWW - Dartmouth.edud Sullivan ColorsmithДокумент1 страницаWWW - Dartmouth.edud Sullivan ColorsmithDimas Rangga WisnuadiОценок пока нет
- LTE A FAQs PDFДокумент5 страницLTE A FAQs PDFDimas Rangga WisnuadiОценок пока нет
- HARQДокумент6 страницHARQDimas Rangga WisnuadiОценок пока нет
- Cellular Planning of 802.16e WiMAX NetworksДокумент4 страницыCellular Planning of 802.16e WiMAX NetworksTarek Al AshhabОценок пока нет
- Heterogeneous NetworksДокумент6 страницHeterogeneous NetworkslinccdanielОценок пока нет
- Internetworking 3GPP (AAA Proxy)Документ10 страницInternetworking 3GPP (AAA Proxy)Dimas Rangga WisnuadiОценок пока нет
- PR 1Документ1 страницаPR 1Dimas Rangga WisnuadiОценок пока нет
- Nilai UTS RL Sem 2013-2014Документ1 страницаNilai UTS RL Sem 2013-2014Dimas Rangga WisnuadiОценок пока нет
- What Is High Speed PCB DesignДокумент13 страницWhat Is High Speed PCB DesignjackОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Instruments: Learning ObjectivesДокумент88 страницAircraft Instruments: Learning ObjectivesjhОценок пока нет
- Activasi Modem TC301 - Inspection Guidance (For Distributor)Документ5 страницActivasi Modem TC301 - Inspection Guidance (For Distributor)Gold d Roger twoОценок пока нет
- 2. Flight Inspection with Drone (2022) - 최승원Документ34 страницы2. Flight Inspection with Drone (2022) - 최승원Undral BatbayarОценок пока нет
- JVC KD r540 Manual de InstruccionesДокумент16 страницJVC KD r540 Manual de InstruccionesJesus FloresОценок пока нет
- A DUAL CAPACITIVELY FED Broadband Patch - Motl - 2000Документ3 страницыA DUAL CAPACITIVELY FED Broadband Patch - Motl - 2000Saikat Ch BakshiОценок пока нет
- Pioneer vsx-416 vsx-516 SM PDFДокумент143 страницыPioneer vsx-416 vsx-516 SM PDFCARLOS HOLGUINОценок пока нет
- Training Course - 5G RAN2.1 Beam ManagementДокумент36 страницTraining Course - 5G RAN2.1 Beam Managementh sОценок пока нет
- Mid 2Документ19 страницMid 2rangavalliОценок пока нет
- Recommended 5G Frequency Bands EvaluationДокумент4 страницыRecommended 5G Frequency Bands Evaluationvasilis_theoОценок пока нет
- World Tanker Ship Management: Vessel Name: M.T. Agros Index of Digitization of Vessel DocumentsДокумент41 страницаWorld Tanker Ship Management: Vessel Name: M.T. Agros Index of Digitization of Vessel DocumentsसचिनरावतОценок пока нет
- MTB 53 09 DF 11Документ3 страницыMTB 53 09 DF 11GiotbuonkhongtenToiОценок пока нет
- Service Manual: Av Receiver Model ModelДокумент204 страницыService Manual: Av Receiver Model ModelJJ ChávezОценок пока нет
- Week 6 - Pengolahan Sinyal ECG PDFДокумент39 страницWeek 6 - Pengolahan Sinyal ECG PDFHafiyyan Abdul AzizОценок пока нет
- HFSS by Devashish GuptaДокумент1 страницаHFSS by Devashish GuptaDevashishGuptaОценок пока нет
- IV Year B.Tech. ECE - II Semester Cellular and Mobile CommunicationsДокумент20 страницIV Year B.Tech. ECE - II Semester Cellular and Mobile Communicationsdini9491Оценок пока нет
- SeparationДокумент34 страницыSeparationJamesОценок пока нет
- EMI Troubleshooting App Note 48W 67730 0Документ22 страницыEMI Troubleshooting App Note 48W 67730 0john BronsonОценок пока нет
- GSM 350 PG2 InstallationManualДокумент1 страницаGSM 350 PG2 InstallationManualcbochrisОценок пока нет
- Kartu MinatДокумент43 страницыKartu MinatDian OctavianiОценок пока нет
- SPS-1000V-5 SPS-1000V-5: Radar Warning System Radar Warning SystemДокумент2 страницыSPS-1000V-5 SPS-1000V-5: Radar Warning System Radar Warning SystemadrianioantomaОценок пока нет
- Gps in Surveying PDFДокумент3 страницыGps in Surveying PDFJaiОценок пока нет
- Pioneer VSX-321-K-PДокумент0 страницPioneer VSX-321-K-PJuan Carlos100% (1)
- A Wideband Voltage Mode Doherty Power Amplifier: RMO4D-4Документ4 страницыA Wideband Voltage Mode Doherty Power Amplifier: RMO4D-4MerkOnerОценок пока нет
- 4164 5995 1 PBДокумент7 страниц4164 5995 1 PBmohamed rizwanОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Spectrum Sharing: Driving 5G To Scale: by Sean KinneyДокумент16 страницDynamic Spectrum Sharing: Driving 5G To Scale: by Sean Kinneymonel_24671100% (1)
- MPX Avc BДокумент3 страницыMPX Avc BAbdoulaye Andillo MahamadouОценок пока нет
- LEC 01 Class D Audio Amplifiers 1Документ7 страницLEC 01 Class D Audio Amplifiers 1Angel ZumbaОценок пока нет
- Differential Pressure Transmitters: Abb Measurement & Analytics - Data SheetДокумент32 страницыDifferential Pressure Transmitters: Abb Measurement & Analytics - Data SheetRonaldo JuniorОценок пока нет
- MTSLR300N User ManualДокумент8 страницMTSLR300N User ManualRodríguezОценок пока нет