Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Physics Reference Table
Загружено:
api-266144722Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics Reference Table
Загружено:
api-266144722Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY 12234
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ PHYSICS
2006 Edition
List of Physical Constants
Name Symbol Value
Universal gravitational constant G 6.67 10
11
Nm
2
/kg
2
Acceleration due to gravity g 9.81 m/s
2
Speed of light in a vacuum c 3.00 10
8
m/s
Speed of sound in air at STP 3.31 10
2
m/s
Mass of Earth 5.98 10
24
kg
Mass of the Moon 7.35 10
22
kg
Mean radius of Earth 6.37 10
6
m
Mean radius of the Moon 1.74 10
6
m
Mean distanceEarth to the Moon 3.84 10
8
m
Mean distanceEarth to the Sun 1.50 10
11
m
Electrostatic constant k 8.99 10
9
Nm
2
/C
2
1 elementary charge e 1.60 10
19
C
1 coulomb (C) 6.25 10
18
elementary charges
1 electronvolt (eV) 1.60 10
19
J
Plancks constant h 6.63 10
34
Js
1 universal mass unit (u) 9.31 10
2
MeV
Rest mass of the electron m
e
9.11 10
31
kg
Rest mass of the proton
m
p
1.67 10
27
kg
Rest mass of the neutron m
n
1.67 10
27
kg
Prefixes for Powers of 10
Prefix Symbol Notation
tera T 10
12
giga G 10
9
mega M 10
6
kilo k 10
3
deci d 10
1
centi c 10
2
milli m 10
3
micro 10
6
nano n 10
9
pico p 10
12
Approximate Coefficients of Friction
Kinetic Static
Rubber on concrete (dry) 0.68 0.90
Rubber on concrete (wet) 0.58
Rubber on asphalt (dry) 0.67 0.85
Rubber on asphalt (wet) 0.53
Rubber on ice 0.15
Waxed ski on snow 0.05 0.14
Wood on wood 0.30 0.42
Steel on steel 0.57 0.74
Copper on steel 0.36 0.53
Teflon on Teflon 0.04
P
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 Edition Page 2
10
21
10
20
10
19
10
18
10
17
10
16
10
15
10
14
10
13
10
12
10
11
10
10
10
9
10
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
Gamma Rays
X rays
Ultraviolet Infrared
Microwaves
TV,
FM
AM
Radio Waves
Long Radio Waves
Visible Light
(not to scale)
Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red
7
.
6
9
1
0
1
4
6
.
5
9
1
0
1
4
6
.
1
0
1
0
1
4
5
.
2
0
1
0
1
4
5
.
0
3
1
0
1
4
4
.
8
2
1
0
1
4
3
.
8
4
1
0
1
4
Wavelength in a vacuum (m)
Frequency (Hz)
10
13
10
12
10
11
10
10
10
9
10
8
10
7
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
10
2
10
1
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
4
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Absolute Indices of Refraction
(f = 5.09 10
14
Hz)
Air 1.00
Corn oil 1.47
Diamond 2.42
Ethyl alcohol 1.36
Glass, crown 1.52
Glass, flint 1.66
Glycerol 1.47
Lucite 1.50
Quartz, fused 1.46
Sodium chloride 1.54
Water 1.33
Zircon 1.92
Energy Level Diagrams
Classification of Matter Particles of the Standard Model
Hydrogen
Energy Levels for the Hydrogen Atom
Ground State
Ionization
13.60 n = 1
n = 2
n = 3
n = 4
n = 5
n = 6
n =
3.40
1.51
0.85
0.54
0.38
0.00
Level Energy (eV)
A Few Energy Levels for the Mercury Atom
Mercury
Ground State
Ionization
10.38 a
b
c
d
e
f
g
j
5.74
5.52
4.95
3.71
2.68
2.48
0.00
Level Energy (eV)
h
i
1.57
1.56
Quarks
Name up charm top
Symbol u c t
Charge + e + e + e
down strange bottom
d s b
e e e
Leptons
electron muon tau
e
1e 1e 1e
electron muon tau
neutrino neutrino neutrino
0 0 0
Note: For each particle, there is a corresponding antiparticle with a
charge opposite that of its associated particle.
1
3
1
3
1
3
2
3
2
3
2
3
Matter
Hadrons Leptons
Baryons Mesons
three quark and
quarks antiquark
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 Edition Page 3
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 Edition Page 4
Resistivities at 20C
Material Resistivity (m)
Aluminum 2.82 10
8
Copper 1.72 10
8
Gold 2.44 10
8
Nichrome 150. 10
8
Silver 1.59 10
8
Tungsten 5.60 10
8
Circuit Symbols
cell
battery
switch
voltmeter
ammeter
resistor
variable resistor
lamp
Series Circuits
I = I
1
= I
2
= I
3
= . . .
V = V
1
+ V
2
+ V
3
+ . . .
R
eq
= R
1
+ R
2
+ R
3
+ . . .
Parallel Circuits
I = I
1
+ I
2
+ I
3
+ . . .
V = V
1
= V
2
= V
3
= . . .
= + + + . . .
1
R
3
1
R
2
1
R
1
1
R
eq
Electricity
A = cross-sectional area
E = electric field strength
F
e
= electrostatic force
I = current
k = electrostatic constant
L = length of conductor
P = electrical power
q = charge
R = resistance
R
eq
= equivalent resistance
r = distance between centers
t = time
V = potential difference
W= work (electrical energy)
= change
= resistivity
F
e
=
E =
V =
I =
R =
R =
P = VI = I
2
R =
W= Pt = VIt = I
2
Rt =
V
2
t
R
V
2
R
L
A
V
I
q
t
W
q
F
e
q
kq
1
q
2
r
2
V
A
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 Edition Page 5
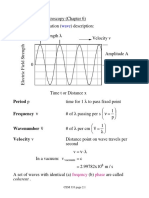
Waves
v = f
T =
i
=
r
n =
n
1
sin
1
= n
2
sin
2
= =
Modern Physics
E
photon
= hf =
E
photon
= E
i
E
f
E = mc
2
Geometry and Trigonometry
Rectangle
A = bh
Triangle
A = bh
Circle
A = r
2
C = 2r
Right Triangle
c
2
= a
2
+ b
2
sin =
cos =
tan =
a
b
b
c
a
c
1
2
hc
2
v
1
v
2
n
2
n
1
c
v
1
f
c = speed of light in a vacuum
f = frequency
n = absolute index of refraction
T = period
v = velocity or speed
= wavelength
= angle
i
= angle of incidence
r
= angle of reflection
c = speed of light in a vacuum
E = energy
f = frequency
h = Plancks constant
m = mass
= wavelength
A = area
b = base
C = circumference
h = height
r = radius
a
b
c
90
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 Edition Page 6
=
a =
v
f
= v
i
+ at
d = v
i
t + at
2
v
f
2
= v
i
2
+ 2ad
A
y
= A sin
A
x
= A cos
a =
F
f
= F
N
F
g
=
g =
p = mv
p
before
= p
after
J = F
net
t = p
F
s
= kx
PE
s
= kx
2
F
c
= ma
c
a
c
=
PE = mgh
KE = mv
2
W= Fd = E
T
E
T
= PE + KE + Q
P = = = F
a = acceleration
a
c
= centripetal acceleration
A = any vector quantity
d = displacement or distance
E
T
= total energy
F = force
F
c
= centripetal force
F
f
= force of friction
F
g
= weight or force due to gravity
F
N
= normal force
F
net
= net force
F
s
= force on a spring
g = acceleration due to gravity or
gravitational field strength
G = universal gravitational constant
h = height
J = impulse
k = spring constant
KE = kinetic energy
m = mass
p = momentum
P = power
PE = potential energy
PE
s
= potential energy stored in a spring
Q = internal energy
r = radius or distance between centers
t = time interval
v = velocity or speed
= average velocity or average speed
W= work
x = change in spring length from the
equilibrium position
= change
= angle
= coefficient of friction
v
v
Fd
t
W
t
1
2
v
2
r
1
2
F
g
m
Gm
1
m
2
r
2
F
net
m
1
2
v
t
d
t
v
DET 615 96-05540 96-040 CDC
Mechanics
Вам также может понравиться
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОт EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Оценок пока нет
- Adapted Reference TablesДокумент4 страницыAdapted Reference Tablesapi-327660250Оценок пока нет
- Physics Reference TableДокумент4 страницыPhysics Reference Tablegoncstate93Оценок пока нет
- M e M M C N G R G K: Table of Information For 2010 and 2011Документ3 страницыM e M M C N G R G K: Table of Information For 2010 and 2011mys85Оценок пока нет
- 2 PDFДокумент5 страниц2 PDFDre ParkerОценок пока нет
- IB Physics Data and FormulasДокумент5 страницIB Physics Data and FormulasfossacecaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaДокумент48 страницChapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaYew Keong Ng100% (3)
- Unit 1 - Task 1 - Electromagnetic Waves in Open Media - Andres QuinteroДокумент11 страницUnit 1 - Task 1 - Electromagnetic Waves in Open Media - Andres QuinteroAndresОценок пока нет
- Physical Constants PDFДокумент13 страницPhysical Constants PDFYasin ŞaleОценок пока нет
- Appendix: Data SheetДокумент3 страницыAppendix: Data SheetbreezeinthewindОценок пока нет
- Current and Resistance: Answers To QuestionsДокумент20 страницCurrent and Resistance: Answers To QuestionsSamuel González MoralesОценок пока нет
- MPP 2Документ3 страницыMPP 2Lian ChiОценок пока нет
- The Following List of Data, Formulae and Relationships Will Be Provided in The Question Papers For Candidates' ReferenceДокумент3 страницыThe Following List of Data, Formulae and Relationships Will Be Provided in The Question Papers For Candidates' ReferenceLian ChiОценок пока нет
- Physics Formula Sheet-By Er Rammohan MudgalДокумент8 страницPhysics Formula Sheet-By Er Rammohan MudgalRammohan Mudgal0% (1)
- Chapter 42 Photoelectric Effect and Wave-Particle DualityДокумент8 страницChapter 42 Photoelectric Effect and Wave-Particle Dualityabbh07Оценок пока нет
- Solutions To Chapter27Документ18 страницSolutions To Chapter27AladdinSultanAlTamimiОценок пока нет
- Formule Iz FizikeДокумент5 страницFormule Iz FizikeАлександар ДимитријевићОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaДокумент54 страницыChapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDesmond Kuek100% (2)
- Lecture12 EDMДокумент13 страницLecture12 EDMOmar Adnan AhmadОценок пока нет
- Science Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыScience Formula Sheetrhemaksha78% (9)
- Astronomy Masters - Midterm TestДокумент7 страницAstronomy Masters - Midterm TestE. F.Оценок пока нет
- Physics Formulas & SI UnitДокумент14 страницPhysics Formulas & SI Unitönemsiz biriОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Physical Constants - Physico-Chemical ConstantsДокумент1 страницаFundamental Physical Constants - Physico-Chemical ConstantsmexcesОценок пока нет
- Conceptual Physics Equation SheetДокумент2 страницыConceptual Physics Equation SheetjeremytimmonsОценок пока нет
- Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыCheat SheetPeter KoszoОценок пока нет
- Physics 1 Honors Formula SheetДокумент11 страницPhysics 1 Honors Formula SheetCody JohnsonОценок пока нет
- 2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionsДокумент2 страницы2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionspappadutОценок пока нет
- High-Field Laser Physics: ETH Zürich Spring Semester 2010 H. R. ReissДокумент18 страницHigh-Field Laser Physics: ETH Zürich Spring Semester 2010 H. R. ReissjasmonОценок пока нет
- Jee Main 2014 Solution Code E EnglishДокумент23 страницыJee Main 2014 Solution Code E Englishsaneer123Оценок пока нет
- Allen Neetug2013 Phy-With SolutionДокумент8 страницAllen Neetug2013 Phy-With SolutionrnsseturajОценок пока нет
- Mycollegebag - In: X - RaysДокумент5 страницMycollegebag - In: X - RaysManjeet BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Week 02Документ10 страницWeek 02Marina Rosa AnggraeniОценок пока нет
- Answer (Paper 1) Answer Explanation 1. 2Документ6 страницAnswer (Paper 1) Answer Explanation 1. 2suhailieliasОценок пока нет
- Oliver ElectronicsДокумент35 страницOliver Electronicsprem_singh_nepal100% (1)
- Quantum Quest KeyДокумент4 страницыQuantum Quest KeyAnonymous 7CxwuBUJz3Оценок пока нет
- Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)Документ20 страницElectrostatic Precipitator (ESP)Muhammad JunaidОценок пока нет
- Detectors and Energy Deposition in Media: (Thanks To J.Thomas (LBNL) )Документ44 страницыDetectors and Energy Deposition in Media: (Thanks To J.Thomas (LBNL) )NenkIndahLestariОценок пока нет
- InvolutДокумент24 страницыInvolutal_mmDОценок пока нет
- Unit ConversionДокумент21 страницаUnit ConversioninsidereaderОценок пока нет
- HKDSE Physics Formulae List (English Version)Документ5 страницHKDSE Physics Formulae List (English Version)flowerinsnowОценок пока нет
- Activity Questions: (Write With Your Own Words)Документ9 страницActivity Questions: (Write With Your Own Words)oswaldo perciaОценок пока нет
- Nelson Thornes Answers To Assessment QuestionsДокумент11 страницNelson Thornes Answers To Assessment QuestionsMitul KaziОценок пока нет
- Welcome To 3.091: September 16, 2009Документ26 страницWelcome To 3.091: September 16, 2009Karla Araojo MatienzoОценок пока нет
- List of Physical Constants: K R/ N N RДокумент2 страницыList of Physical Constants: K R/ N N RszscccccccОценок пока нет
- Physics Rules 5Документ10 страницPhysics Rules 5Chris_Barber09100% (6)
- Jee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilДокумент22 страницыJee Main 2017 Question Paper Solutions Physics 2nd AprilAmit SharmaОценок пока нет
- 2015 Bookmatter AtomsMoleculesAndOpticalPhysic PDFДокумент135 страниц2015 Bookmatter AtomsMoleculesAndOpticalPhysic PDFxxxnomenxneutrumОценок пока нет
- Electron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3Документ63 страницыElectron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3younessinaОценок пока нет
- Four Probe MethodДокумент5 страницFour Probe MethodSubhrajit SamantaОценок пока нет
- Physics Class 9 FormulasДокумент13 страницPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- CHP 2Документ38 страницCHP 2NK NKОценок пока нет
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksОт EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Particles, Fields and Forces: A Conceptual Guide to Quantum Field Theory and the Standard ModelОт EverandParticles, Fields and Forces: A Conceptual Guide to Quantum Field Theory and the Standard ModelОценок пока нет
- Optics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyОт EverandOptics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesОт EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- TANCET ME (Basic Engineering & Sciences) - Basic - Engg - and - SciencesДокумент4 страницыTANCET ME (Basic Engineering & Sciences) - Basic - Engg - and - Sciencesrameshdurairaj81% (16)
- Project State of MatterДокумент6 страницProject State of Matterpaloma silvaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Fluid Pressure and Its Measurement PDFДокумент52 страницыChapter 2 - Fluid Pressure and Its Measurement PDFrohit sharma100% (1)
- LECTURE - FoundationsДокумент6 страницLECTURE - FoundationsFazelah YakubОценок пока нет
- Shear Moment DiagramsДокумент23 страницыShear Moment DiagramsmoisesramosОценок пока нет
- 01 Test-1 (CH # 1-6) Final PDFДокумент4 страницы01 Test-1 (CH # 1-6) Final PDFMeher AdeelОценок пока нет
- GRABSUM School Inc. Name: Grade Level and Section: 12 - STEMДокумент6 страницGRABSUM School Inc. Name: Grade Level and Section: 12 - STEMWendell CapiliОценок пока нет
- Gas Turbine MetersДокумент3 страницыGas Turbine Meterssubhadip33coolОценок пока нет
- ProblemsДокумент3 страницыProblemsRangaОценок пока нет
- 2 2Документ121 страница2 2Marina DavidovicОценок пока нет
- Table 5.1. Nominal Strength Per Unit Area of BoltsДокумент1 страницаTable 5.1. Nominal Strength Per Unit Area of BoltsNwe OoОценок пока нет
- A First Course On Variational Methods in Structural Mechanics and EngineeringДокумент223 страницыA First Course On Variational Methods in Structural Mechanics and EngineeringPablo A. Domínguez L.Оценок пока нет
- Irreversible ThermodynamicsДокумент2 страницыIrreversible ThermodynamicsManoj PrakashОценок пока нет
- Buckling of ColumnsДокумент47 страницBuckling of ColumnsMuhamad Khairudin AwangОценок пока нет
- AH Physics 2012Документ24 страницыAH Physics 2012pixelhoboОценок пока нет
- Mass Distribution of 30 Particles CorrectДокумент6 страницMass Distribution of 30 Particles Correctvishwas gaurОценок пока нет
- Seminar Nr.5: Llogaritja e Themeleve Te Tipit Pilota Nen Vibrime VertikaleДокумент5 страницSeminar Nr.5: Llogaritja e Themeleve Te Tipit Pilota Nen Vibrime VertikaleTEОценок пока нет
- All Physics Formulae Panorama FrazMallick PDFДокумент57 страницAll Physics Formulae Panorama FrazMallick PDFSiyar AhmadОценок пока нет
- Just What Did Archimedes Say About Buoyancy?: Erlend H. GrafДокумент4 страницыJust What Did Archimedes Say About Buoyancy?: Erlend H. GrafAnonymous 0pBRsQXfnxОценок пока нет
- MEE Avoiding Bolt FailuresДокумент2 страницыMEE Avoiding Bolt Failuresridwan347Оценок пока нет
- LS DYNA Glass ModelДокумент14 страницLS DYNA Glass ModelalexremОценок пока нет
- 3d Radii ManipulationДокумент3 страницы3d Radii Manipulationk6mdes22shraynitapaliwalaОценок пока нет
- Applied Mathematics and Computation: M. Cermák, S. Sysala, J. ValdmanДокумент20 страницApplied Mathematics and Computation: M. Cermák, S. Sysala, J. ValdmanLuis Saavedra Santa MariaОценок пока нет
- Calculation For Water Pressure TestingДокумент7 страницCalculation For Water Pressure TestingRaj MaОценок пока нет
- Lab Report BalloonДокумент5 страницLab Report Balloonapi-385691949Оценок пока нет
- Stress Predictions at Elbow Ends Under Internal Pressure and System MomentsДокумент9 страницStress Predictions at Elbow Ends Under Internal Pressure and System MomentsGaurav BedseОценок пока нет
- Dom Lab Manual NewДокумент44 страницыDom Lab Manual NewjeyashrirangamОценок пока нет
- Einstein and Planck On Mass-EnergyДокумент16 страницEinstein and Planck On Mass-EnergyLuis GPОценок пока нет
- Lec 2Документ38 страницLec 2Nathaniel CruelОценок пока нет