Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit 2 3 Lesson 6 - Market Equilibrium
Загружено:
api-260512563Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 2 3 Lesson 6 - Market Equilibrium
Загружено:
api-260512563Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Market Equilibrium &
Efficiency
Where Demand meets Supply
Learning outcomes:
Explain the interaction of supply & demand
to produce market equilibrium.
Analyze using diagrams how changes in the
non-price determinants of supply/demand
change market equilibrium.
Identify using diagrams, excess supply &
demand in a market.
Market Equilibrium
Market Equilibrium:
the price where the
quantity demanded is
equal to the quantity
supplied.
Also called market
clearing price
Excess Supply
Market disequilibrium
where the market is not
efficient.
Occurs when the price is
set above the market
clearing price such that
Quantity Supplied >
Quantity Demanded
Excess Demand
Market disequilibrium
where the market is not
efficient.
Occurs when the price is
set below the market
clearing price.
Quantity Demanded >
Quantity Supplied
http://www.amosweb.com/images/ExDm001w.gif
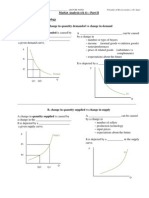
Function of Price
1. Price is the system used to organize the
allocation of our scarce resources. Answers:
How & What...
2. Decrease supply (S-S1) causes excess
demand at price P : Qd (e) > Qs (e1).
3. Incentive for firms to increase Price from P-
P1. Movement along the supply curve from
e1 - e2 decreasing Quantity supplied.
4. As Price increases, the Rationing effect of
consumers to decrease Qd moving along the
Demand curve from e - e2.
5. Market eventually reaches clearing price &
quantity at e2.
Changes in Demand
1. Increase in Demand (D1-D2).
2. At Price P1 - Qd2 >Qs1 creating
excess demand at P1.
3. Signal to the market to increase
price from P1 - P2 thus increasing
the Qs.
4. Therefore, an increase in Demand
from D1 - D2 due to a change in a
non-price determinant of Demand
leads to an increase in Price from
P1 - P2 and an increase in
Quantity Supplied from Q1 - Q2.
http://www.personal.psu.edu/~dxl31/econ2/Spring_2006/demand_increase.png
Decrease in Demand
1. Decrease in Demand (D-Dnew).
2. At Price P1 - Qs > Qdnew creating
excess supply at P1.
3. Signal to the market to decrease
price from P1 - P2 thus decreasing
the Qs.
4. Therefore, a decrease in Demand
from D - Dnew due to a change in a
non-price determinant of Demand
leads to an decrease in Price from
P1 - P2 and a decrease in Quantity
Supplied from Q1 - Q2.
http://www.raybromley.com/notes/noteimages/equilibrium/decrdemandeq.jpg
Increase Supply
1. Increase in Supply (S - S1).
2. At Price P - Qs1 >Qd creating
excess supply at P.
3. Signal to the market to decrease
price from P - P1 thus increasing
the Qd from Q - Q1.
4. Therefore, an increase in Supply
from S - S1 due to a change in a
non-price determinant of Supply
leads to an decrease in Price from
P - P1 and an increase in Quantity
Demanded from Q - Q1.
Decrease Supply
1. Decrease in Supply (S - S1).
2. At Price P - Qd > Qs1 creating
excess demand at P.
3. Signal to the market to increase price
from P - P1 thus decreasing the Qd
from Q - Q1.
4. Therefore, an decrease in Supply
from S - S1 due to a change in a non-
price determinant of Supply leads to
an increase in Price from P - P1 and
an decrease in Quantity Demanded
from Q - Q1
Вам также может понравиться
- Group8-Baldwin Bicycle CompanyДокумент9 страницGroup8-Baldwin Bicycle CompanyChandrachuda SharmaОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1Документ2 страницыProblem Set 1Cooper Greenfield0% (1)
- Marketing Management MCQ Pune UniДокумент32 страницыMarketing Management MCQ Pune UniABHIJIT S. SARKAR80% (5)
- Kodak Case AnalysisДокумент11 страницKodak Case AnalysisShree Nayak50% (2)
- MicroeconomicsДокумент1 страницаMicroeconomicsJoy Angelique JavierОценок пока нет
- Resource Allocation and Price ControlsДокумент28 страницResource Allocation and Price ControlsAlexander Betz100% (1)
- Role of CCMДокумент5 страницRole of CCMdeepa parbooОценок пока нет
- International Marketing Communication StrategiesДокумент60 страницInternational Marketing Communication Strategiessumantsmriti100% (1)
- Product Most People Can Buy Only Every Couple of Years?Документ2 страницыProduct Most People Can Buy Only Every Couple of Years?Avijit Chakraborty100% (1)
- Conflicts in Governments Objectives (Economics)Документ15 страницConflicts in Governments Objectives (Economics)MarcosОценок пока нет
- Production Possibility CurvesДокумент6 страницProduction Possibility CurvesFari AliОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Demand-Supply Practice WorksheetДокумент1 страницаAggregate Demand-Supply Practice WorksheetRoberto Velasco MabulacОценок пока нет
- IBDP Economic HL Chapter 5 NotesДокумент9 страницIBDP Economic HL Chapter 5 NotesAditya RathiОценок пока нет
- Econ 002 Midterm Review by Craig Mclaren KEYДокумент16 страницEcon 002 Midterm Review by Craig Mclaren KEYaslator100% (1)
- Page 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandДокумент4 страницыPage 35 Answer Key Student Booklet - Classwork - 2: - Definitions of DemandRumana AliОценок пока нет
- Economics Midterm ReviewДокумент5 страницEconomics Midterm ReviewAmyОценок пока нет
- EC 102 Revisions Lectures - Macro - 2015Документ54 страницыEC 102 Revisions Lectures - Macro - 2015TylerTangTengYangОценок пока нет
- Elasticity Exam Paper Model AnswersДокумент5 страницElasticity Exam Paper Model AnswersNicole BostanОценок пока нет
- Basic Economic Ideas: Opportunity Cost.Документ37 страницBasic Economic Ideas: Opportunity Cost.huzaifathe007100% (2)
- IGCSE Economics Scheme of Work and TopicsДокумент47 страницIGCSE Economics Scheme of Work and TopicsunrealkenОценок пока нет
- Economics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics GlossaryДокумент7 страницEconomics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics Glossarymarcodl18Оценок пока нет
- Economics Unit OutlineДокумент8 страницEconomics Unit OutlineHaris AОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - Economics - Supply and DemandДокумент4 страницыWorksheet - Economics - Supply and DemandAwais UR RehmanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The CourseДокумент7 страницIntroduction To The Courseapi-217192353Оценок пока нет
- Indifference Curves and Budget LinesДокумент9 страницIndifference Curves and Budget LinesRanaОценок пока нет
- Kinked Demand CurveДокумент8 страницKinked Demand CurvepriyankaОценок пока нет
- Supply and Demand Ii: Markets and WelfareДокумент48 страницSupply and Demand Ii: Markets and Welfarejoebob1230Оценок пока нет
- Price Elasticity of Demand WorksheetДокумент2 страницыPrice Elasticity of Demand WorksheetAzizul KirosakiОценок пока нет
- 2017-Economics: Instructor: Chang LiДокумент60 страниц2017-Economics: Instructor: Chang LiYiran CaoОценок пока нет
- IB Economics DefinitionsДокумент21 страницаIB Economics DefinitionsYokesh ProОценок пока нет
- ECN 2215 - Topic - 2 PDFДокумент54 страницыECN 2215 - Topic - 2 PDFKalenga AlexОценок пока нет
- Tutor2u - Fixed and Floating Exchange RatesДокумент4 страницыTutor2u - Fixed and Floating Exchange RatesSumanth KumarОценок пока нет
- EQUI Marginal Concept-WordДокумент4 страницыEQUI Marginal Concept-Wordnithinsdn100% (2)
- Punjab University College of Information Technology Assignment01 Economics Demand PracticeДокумент5 страницPunjab University College of Information Technology Assignment01 Economics Demand PracticeAhmad NuttОценок пока нет
- 02 Scalars and VectorsДокумент3 страницы02 Scalars and VectorsomОценок пока нет
- Answering Paper 2 Questions: Economics For The IB DiplomaДокумент9 страницAnswering Paper 2 Questions: Economics For The IB Diploma정우창Оценок пока нет
- Economics Answers MankiwДокумент3 страницыEconomics Answers MankiwDaniella RodriguezОценок пока нет
- GDP WorksheetДокумент2 страницыGDP WorksheetClosu100% (1)
- Managerial Economics:: Perfect CompetitionДокумент43 страницыManagerial Economics:: Perfect CompetitionPhong VũОценок пока нет
- Demand and Supply - Concepts and Applications (2) (1) (Compatibility Mode)Документ11 страницDemand and Supply - Concepts and Applications (2) (1) (Compatibility Mode)Aminul Islam AminОценок пока нет
- Market Equilibrium and ForcesДокумент6 страницMarket Equilibrium and ForcesThais HernandezОценок пока нет
- IAS Economics - Student Book Answers - Unit2Документ88 страницIAS Economics - Student Book Answers - Unit2temwaniОценок пока нет
- Consumer Surplus and Price Elasticity of DemandДокумент8 страницConsumer Surplus and Price Elasticity of Demandsweetice79Оценок пока нет
- Unit 10 - Lesson 5 - Demand-Pull and Cost-Push InflationДокумент21 страницаUnit 10 - Lesson 5 - Demand-Pull and Cost-Push Inflationapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- MICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Документ6 страницMICROECONOMICS - Revison Notes 2013 S1 Ques Set 2Imelda WongОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics Assignment 2Документ4 страницыMacroeconomics Assignment 2reddygaru1Оценок пока нет
- IB Econ Chap 16 Macro EQДокумент11 страницIB Econ Chap 16 Macro EQsweetlunaticОценок пока нет
- Commercial Studies 7101 Sow Year 9 For SPN 21 Express Track - 2 YearsДокумент41 страницаCommercial Studies 7101 Sow Year 9 For SPN 21 Express Track - 2 YearsYenny TigaОценок пока нет
- Commercial Studies 7101 SPN 21 Year 10 Normal Track - 3 YearsДокумент22 страницыCommercial Studies 7101 SPN 21 Year 10 Normal Track - 3 YearsYenny TigaОценок пока нет
- Group 3 Command TermsДокумент1 страницаGroup 3 Command Termsmgupta72Оценок пока нет
- Economic Growth (Main Macro Objective) Essay (Edexcel)Документ3 страницыEconomic Growth (Main Macro Objective) Essay (Edexcel)Atom SonicОценок пока нет
- Demand Supply Equilibrium WorksheetДокумент2 страницыDemand Supply Equilibrium Worksheethuhu4545Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - Lesson 6 - Critique of Maximizing Behaviour of Consumers ProducersДокумент24 страницыUnit 2 - Lesson 6 - Critique of Maximizing Behaviour of Consumers Producersapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unemployment InflationДокумент50 страницUnemployment Inflationshelou_domantayОценок пока нет
- Price Cielings and Price FloorДокумент54 страницыPrice Cielings and Price FloorKrish KumarОценок пока нет
- A2 OligopolyДокумент6 страницA2 Oligopolypunte77Оценок пока нет
- Microeconomics Quiz 1 Study GuideДокумент8 страницMicroeconomics Quiz 1 Study GuideeinsteinspyОценок пока нет
- Measuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewДокумент4 страницыMeasuring A Nation'S Income: Questions For ReviewNoman MustafaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 4 - UncertaintyДокумент3 страницыTutorial 4 - UncertaintyCarine TeeОценок пока нет
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Документ4 страницыPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerОценок пока нет
- Economicsslide C10Документ41 страницаEconomicsslide C10Tamara JacobsОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Economics conceptsДокумент16 страницIntroduction to Economics conceptsAbhi Agarwal100% (1)
- Macro 95 Ex 2Документ17 страницMacro 95 Ex 2Engr Fizza AkbarОценок пока нет
- B 7006 Part 1 - Intro & Demand & SupplyДокумент70 страницB 7006 Part 1 - Intro & Demand & SupplySanjay DeshpandeОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - Lesson 4 - Competitive Market Equilibrium Demand SupplyДокумент19 страницUnit 2 - Lesson 4 - Competitive Market Equilibrium Demand Supplyapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Lecture03 D&S BДокумент34 страницыLecture03 D&S BMirza Wajahat BaigОценок пока нет
- Unit 12 - Lesson 4 - Impact of Income and Wealth InequalityДокумент9 страницUnit 12 - Lesson 4 - Impact of Income and Wealth Inequalityapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 12 - Lesson 5 - Policies To Reduce Income and Wealth Inequalities and Poverty 1Документ17 страницUnit 12 - Lesson 5 - Policies To Reduce Income and Wealth Inequalities and Poverty 1api-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 12 - Lesson 3 - Causes of Economic Inequality PovertyДокумент10 страницUnit 12 - Lesson 3 - Causes of Economic Inequality Povertyapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 12 - Lesson 6 - Calculations of Direct and Indirect TaxesДокумент8 страницUnit 12 - Lesson 6 - Calculations of Direct and Indirect Taxesapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 12 - Lesson 1 - InequalityДокумент14 страницUnit 12 - Lesson 1 - Inequalityapi-260512563100% (1)
- Unit 10 - Lesson 6 - Phillips Curve Higher LevelДокумент19 страницUnit 10 - Lesson 6 - Phillips Curve Higher Levelapi-260512563100% (2)
- Unit 11 - Lesson 3 - Sustainable Level of Government DebtДокумент20 страницUnit 11 - Lesson 3 - Sustainable Level of Government Debtapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 11 - Lesson 4 - Potential Conflict Between Macroeconomic ObjectivesДокумент8 страницUnit 11 - Lesson 4 - Potential Conflict Between Macroeconomic Objectivesapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 10 - Lesson 2 - Types and Causes of Unemployment 1Документ20 страницUnit 10 - Lesson 2 - Types and Causes of Unemployment 1api-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 12 - Lesson 2 - PovertyДокумент17 страницUnit 12 - Lesson 2 - Povertyapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 11 - Lesson 1 - Economic GrowthДокумент16 страницUnit 11 - Lesson 1 - Economic Growthapi-260512563100% (1)
- Unit 11 - Lesson 2 - Why Economic Growth OccursДокумент25 страницUnit 11 - Lesson 2 - Why Economic Growth Occursapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 10 - Lesson 5 - Demand-Pull and Cost-Push InflationДокумент21 страницаUnit 10 - Lesson 5 - Demand-Pull and Cost-Push Inflationapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 9 - Lesson 6 - Shifting Aggregate Supply Curve Over The Long-RunДокумент12 страницUnit 9 - Lesson 6 - Shifting Aggregate Supply Curve Over The Long-Runapi-260512563100% (1)
- Unit 10 - Lesson 3 - InflationДокумент28 страницUnit 10 - Lesson 3 - Inflationapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 10 - Lesson 1 - Macroeconomic Objective 1 Low UnemploymentДокумент15 страницUnit 10 - Lesson 1 - Macroeconomic Objective 1 Low Unemploymentapi-260512563100% (1)
- Unit 8 - Lesson 3 - Calculations Based On National Income StatisticsДокумент15 страницUnit 8 - Lesson 3 - Calculations Based On National Income Statisticsapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 10 - Lesson 4 - Constructing A Weighted Price IndexДокумент17 страницUnit 10 - Lesson 4 - Constructing A Weighted Price Indexapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 9 - Lesson 3 - Short-Run Equilibrium in The Ad - As ModelДокумент19 страницUnit 9 - Lesson 3 - Short-Run Equilibrium in The Ad - As Modelapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 9 - Lesson 4 - Long-Run Aggregate Supply Monetarist New Classical ModelДокумент20 страницUnit 9 - Lesson 4 - Long-Run Aggregate Supply Monetarist New Classical Modelapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 9 - Lesson 5 - Keynesian ModelДокумент20 страницUnit 9 - Lesson 5 - Keynesian Modelapi-260512563100% (1)
- Unit 8 - Lesson 4 - Business CycleДокумент18 страницUnit 8 - Lesson 4 - Business Cycleapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 8 - Lesson 2 - Measuring Economic ActivityДокумент20 страницUnit 8 - Lesson 2 - Measuring Economic Activityapi-260512563100% (1)
- Unit 5 - Lesson 7 - Methods To Correct Negative Consumption Externalities 1Документ15 страницUnit 5 - Lesson 7 - Methods To Correct Negative Consumption Externalities 1api-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 9 - Lesson 2 - Short-Run Aggregate SupplyДокумент10 страницUnit 9 - Lesson 2 - Short-Run Aggregate Supplyapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 8 - Lesson 5 - National Income Statistics and Alternative MeasuresДокумент19 страницUnit 8 - Lesson 5 - National Income Statistics and Alternative Measuresapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 9 - Lesson 1 - Aggregate DemandДокумент26 страницUnit 9 - Lesson 1 - Aggregate Demandapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 7 - Lesson 13 - Government Intervention in Response To Abuse of Market PowerДокумент12 страницUnit 7 - Lesson 13 - Government Intervention in Response To Abuse of Market Powerapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 7 - Lesson 11 - OligopolyДокумент37 страницUnit 7 - Lesson 11 - Oligopolyapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- Unit 7 - Lesson 12 - Evaluating OligopolyДокумент6 страницUnit 7 - Lesson 12 - Evaluating Oligopolyapi-260512563Оценок пока нет
- 02Документ16 страниц02Paran GuptaОценок пока нет
- Investing 101 Types of InvestmentsДокумент4 страницыInvesting 101 Types of InvestmentsNatasha SaqibОценок пока нет
- Distridution and Channel MemberДокумент6 страницDistridution and Channel Memberabdulhaq4Оценок пока нет
- Awesome Oscillator IndicatorДокумент17 страницAwesome Oscillator IndicatorInfoterminalОценок пока нет
- Implementing Merchandising Plan LogisticsДокумент12 страницImplementing Merchandising Plan LogisticsrvaraprasadОценок пока нет
- Implications of Pricing Decisions in the Luxury Sector: The Mulberry CaseДокумент13 страницImplications of Pricing Decisions in the Luxury Sector: The Mulberry Casenurhuda majidОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Retail in India: Shoppers Stop Case StudyДокумент33 страницыEvolution of Retail in India: Shoppers Stop Case StudyNishant Shekhar100% (1)
- Marketing and New Product DevelopmentДокумент67 страницMarketing and New Product DevelopmentAnonymous KXfZdVuIp100% (1)
- SNS College of Technology: Coimbatore - 35Документ16 страницSNS College of Technology: Coimbatore - 35ARUN KUMARОценок пока нет
- Advertising Mid Term Assignment PDFДокумент7 страницAdvertising Mid Term Assignment PDFRehan MalikОценок пока нет
- Portfolio Management ServicesДокумент24 страницыPortfolio Management ServicesASHI100% (5)
- 7 Chart Patterns That Consistently Make Money - Ed Downs - Page 16 To 30Документ15 страниц7 Chart Patterns That Consistently Make Money - Ed Downs - Page 16 To 30YapKJОценок пока нет
- BibliographyДокумент3 страницыBibliographyandes vilmaОценок пока нет
- Revenue ManagementДокумент3 страницыRevenue ManagementMichael FabonОценок пока нет
- MARKETINGДокумент10 страницMARKETINGJyothimol JoyОценок пока нет
- Omni-Channel Management in The New Retailing Era: A Systematic Review and Future Research AgendaДокумент1 страницаOmni-Channel Management in The New Retailing Era: A Systematic Review and Future Research AgendaNISHANT SINGHОценок пока нет
- Harvard Economics Course on Capital MarketsДокумент11 страницHarvard Economics Course on Capital MarketsauctmetuОценок пока нет
- Fixed Income Fundamentals: Interest Rate CalculationsДокумент167 страницFixed Income Fundamentals: Interest Rate CalculationsRavi KumarОценок пока нет
- EconomicsДокумент15 страницEconomicsSania AnsariОценок пока нет
- Managerial Economics For ImtДокумент24 страницыManagerial Economics For Imtsukanya_mistuОценок пока нет
- Rangkuman Bab 12 Market EfficiencyДокумент4 страницыRangkuman Bab 12 Market Efficiencyindah oliviaОценок пока нет
- Brochure Derivatives Trading & StrategiesДокумент14 страницBrochure Derivatives Trading & StrategiesGokulesh DanapalОценок пока нет
- APEUni Summarize Written Text TemplateДокумент1 страницаAPEUni Summarize Written Text TemplateMihiraj Kodithuwakku100% (1)
- Case 26-2: Forner Carpet CompanyДокумент3 страницыCase 26-2: Forner Carpet CompanyCarlosCaballeroОценок пока нет