Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Curriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 7 2014
Загружено:
api-263902873Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Curriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 7 2014
Загружено:
api-263902873Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
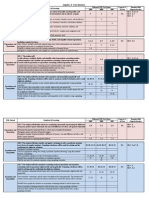
Curriculum Outcomes for Mathematics 7
Strand
Number Sense and
Number Concepts
GCO A: Students
will demonstrate
number sense and
apply number theory
concepts
A1 model and use power, base, and exponent to represent repeated multiplication
A2 rename numbers among exponential, standard, and expanded forms
A rewrite large numbers from standard form to scientific notation and !ice !ersa
A" sol!e and create problems in!ol!ing common factors and greatest common
factors #GC$%
A& sol!e and create problems in!ol!ing common multiples and least common
multiples #'C(%
A) de!elop and apply di!isibility rules for , ", ), and *
A+ apply patterning in renaming numbers from fractions and mixed numbers to
decimal numbers
A, rename single-digit and double-digit repeating decimals to fractions through the
use of patterns, and use these patterns to ma.e predictions
A* compare and order proper and improper fractions, mixed numbers, and decimal
numbers
A1/ illustrate, explain, and express ratios, fractions, decimals, and percents in
alternati!e forms
A11 demonstrate number sense for percent
A12 represent integers #including 0ero% concretely, pictorially, and symbolically, using a
!ariety of models
A1 compare and order integers
Operation Sense
and Number
Operations
GCO 1: Students
will demonstrate
operation sense and
apply operation
principles and
procedures in both
numeric and
algebraic situations
11 use estimation strategies to assess and 2ustify the reasonableness of calculation
results for integers and decimal numbers
12 use mental math strategies for calculations in!ol!ing integers and decimal
numbers
1 demonstrate an understanding of the properties of operations with decimal
numbers and integers
1" determine and use the most appropriate computational method in problem
situations in!ol!ing whole numbers and3or decimals
1& apply the order of operations for problems in!ol!ing whole and decimal numbers
1) estimate the sum or difference of fractions when appropriate
1+ multiply mentally a fraction by a whole number and !ice !ersa
45C6 + 5/& demonstrates an understanding of adding and subtracting positi!e
fractions and mixed numbers, with li.e and unli.e denominators, concretely,
pictorially, symbolically #limited to positi!e sums and differences%
1, estimate and determine percent when gi!en the part and the whole
1* estimate and determine the percent of a number
11/ create and sol!e problems that in!ol!e the use of percent
111 add and subtract integers concretely, pictorially, and symbolically to sol!e
problems
11" sol!e and pose problems which utili0e addition and subtraction of integers
45C6 + 67/ demonstrate an understanding of preser!ation of e8uality by modelling
preser!ation of e8uality, concretely, pictorially, and symbolically
45C6 67/& e!aluate an expression, gi!en the !alue of the !ariable#s%
Strand
Patterns and
Relations
GCO C: Students
will explore,
recogni0e, represent
and apply patterns
and relationships,
both informally and
formally
C1 describe a pattern, using written and spo.en language and tables and graphs
C2 summari0e simple patterns, using constants, !ariables, algebraic expression, and
e8uations, and use them in ma.ing predictions
C explain the difference between algebraic expressions and algebraic e8uations
45C6 +67/" explain the difference between an expression and an e8uation
C" sol!e one- and two-step single-!ariable linear e8uations, using systematic trial
C& illustrate the solution for one- and two-step single-!ariable linear e8uations, using
concrete materials and diagrams
C) graph linear e8uations, using a table of !alues
C+ interpolate and extrapolate number !alues from a gi!en graph
C, determine if an ordered pair is a solution to a linear e8uation
C* construct and analyse graphs to show how change in one 8uantity affects a
related 8uantity
Measurement
GCO 9: Students
will demonstrate an
understanding of
and apply concepts
and s.ills associated
with measurement
91 identify, use, and con!ert among the S: units of measure, estimate, and sol!e
problems that relate to length, area, !olume, mass, and capacity
92 apply concepts and s.ills related to time in problem situations
9 de!elop and use rate as a tool for sol!ing indirect measurement problems in a
!ariety of contexts
9" construct and analyse graphs of rates to show how change in one 8uantity affects
a related 8uantity
45C6 +(/1 demonstrate an understanding of circles by
; describing the relationships among radius, diameter and circumference
; relating circumference to pi
; determining the sum of the central angles
; constructing circles with a gi!en radius or diameter
; sol!ing problems in!ol!ing the radii, diameters and circumferences of circles
45C6 +(/2 de!elop and apply a formula for determining the area of triangles,
parallelograms, and circles
Geometry
GCO <: Students
will demonstrate
spatial sense and
apply geometric
concepts, properties
and relationships
<1 recogni0e, name, describe, and construct polygons
<2 predict and generate polygons that can be formed with a transformation or
composition of transformations of a gi!en polygon
< ma.e and apply generali0ations about the properties of regular polygons
<" ma.e and apply generali0ations about tessellations of polygons
45C6 + G/1 perform geometric constructions, including
perpendicular line segments
parallel line segments
perpendicular bisectors
angle bisectors
45C6 + G/2 identify and plot points in the four 8uadrants of a Cartesian plane, using
integral ordered pairs
45C6 + G/ perform and describe transformation#translations, rotations or reflections%
of a 2-9 shape in all four 8uadrants of a Cartesian plane #limited to integral number
!ertices%
<, ma.e and apply generali0ations about the commutati!ity of transformations
Data Management
GCO $: Students
will sol!e problems
in!ol!ing the
collection, display
and analysis of data
$1 communicate through example the distinction between biassed and unbiassed
sampling, and first- and second-hand data
$2 formulate 8uestions for in!estigation from rele!ant contexts
$ select, defend, and use appropriate data collection methods and e!aluate issues
to be considered when collecting data
45C6 +S6/ construct, label and interpret circle graphs to sol!e problems
$& construct appropriate data displays, grouping data where appropriate and ta.ing
into consideration the nature of data
$) read and ma.e inferences for grouped and ungrouped data displays
$, determine measures of central tendency and how they are affected by data
presentations and fluctuations
Strand
Data Management
GCO $: Students
will sol!e problems
in!ol!ing the
collection, display
and analysis of data
$* draw inferences and ma.e predictions based on the !ariability of data sets, using
range and the examination of outliers, gaps, and clusters
Probability
GCO G: Students
will represent and
sol!e problems
in!ol!ing uncertainty
G1 identify situations for which the probability would be near /, =, >, ?, and 1
G2 sol!e probability problems, using simulations and by conducting experiments
G identify all possible outcomes of two independent e!ents, using tree diagrams and
area models
G" create and sol!e problems, using the numerical definition of probability
G& compare experimental results with theoretical results
G) use fractions, decimals, and percents as numerical expressions to describe
probability
Вам также может понравиться
- Curriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 8 2014Документ2 страницыCurriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 8 2014api-263902873Оценок пока нет
- 8 ThgradecurriculumДокумент5 страниц8 Thgradecurriculumapi-254290621Оценок пока нет
- Common Core MathДокумент3 страницыCommon Core Mathapi-268879403Оценок пока нет
- CCSSI Math Standards 7Документ6 страницCCSSI Math Standards 7establoid1169Оценок пока нет
- Stage 9 Maths Curriculum Framework 2018 (Checkpoint)Документ4 страницыStage 9 Maths Curriculum Framework 2018 (Checkpoint)Mahmoud SalaheldinОценок пока нет
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5Документ20 страницAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5establoid1169Оценок пока нет
- Sixth Math StandardsДокумент3 страницыSixth Math Standardsapi-233655908Оценок пока нет
- Seventh Math StandardsДокумент3 страницыSeventh Math Standardsapi-233655908Оценок пока нет
- Iskl Grade 7 MathsДокумент5 страницIskl Grade 7 MathsMathiarasu MuthumanickamОценок пока нет
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenДокумент7 страницMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenestabloid1169Оценок пока нет
- Syllabus BBA Entry Test Math PortionДокумент6 страницSyllabus BBA Entry Test Math PortionSyedMaazAliОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 8 - Unit 6 - Linear Equations and GraphingДокумент23 страницыMathematics 8 - Unit 6 - Linear Equations and GraphingReal Estate ForumОценок пока нет
- Algebra 2 Equations & FunctionsДокумент6 страницAlgebra 2 Equations & FunctionsHarish MulevaОценок пока нет
- Calculating Means and PercentagesДокумент7 страницCalculating Means and PercentagesRida SnobОценок пока нет
- KS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapДокумент20 страницKS3 Mathematics: Curriculum MapGrace TabfОценок пока нет
- CcssДокумент10 страницCcssapi-2372294750% (1)
- Unit A4: Index - SHTMLДокумент9 страницUnit A4: Index - SHTMLmstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- Math StandardsДокумент28 страницMath Standardsapi-312297693Оценок пока нет
- Stds Math6Документ2 страницыStds Math6api-262305377Оценок пока нет
- Grade 6 MathДокумент12 страницGrade 6 Mathapi-264682510Оценок пока нет
- S.Y 2022-2023 Mathematics 5 Course Outline: I. DescriptionДокумент11 страницS.Y 2022-2023 Mathematics 5 Course Outline: I. DescriptionPrincess Mae LumawagОценок пока нет
- Math 7 Commom Core Syllabus 2014-2015Документ8 страницMath 7 Commom Core Syllabus 2014-2015api-261815606Оценок пока нет
- Math Grade 4 08 11Документ7 страницMath Grade 4 08 11api-246939068Оценок пока нет
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014Документ4 страницыGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 1 1 2013-2014api-233707670Оценок пока нет
- Tnready Blueprint g6 MathДокумент9 страницTnready Blueprint g6 Mathapi-282869532Оценок пока нет
- Math 7 Syllabus 2014-2015Документ5 страницMath 7 Syllabus 2014-2015api-266524097Оценок пока нет
- 7 Grade Math Instructional GuideДокумент7 страниц7 Grade Math Instructional Guideapi-323730622Оценок пока нет
- Ac Maths Yr5 Overviewauscrc Term4Документ3 страницыAc Maths Yr5 Overviewauscrc Term4api-242936990Оценок пока нет
- 8 Grade Mathematics Unpacked Content: What Is The Purpose of This Document?Документ42 страницы8 Grade Mathematics Unpacked Content: What Is The Purpose of This Document?baboosabОценок пока нет
- Mathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships BetweenДокумент7 страницMathematics - Grade 6: X Y) To Describe Relationships Betweenapi-365969613Оценок пока нет
- Unit A2: Ax + AyДокумент7 страницUnit A2: Ax + Aymstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- 6thgrade Math I Can StatementsДокумент155 страниц6thgrade Math I Can StatementsRhonda GrossОценок пока нет
- Annual Learning Targets: MathsДокумент5 страницAnnual Learning Targets: MathsAnkur UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- 4024 Y04 SW 6Документ6 страниц4024 Y04 SW 6mstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- Fourth Grade Syllabus 2015Документ8 страницFourth Grade Syllabus 2015api-274977607Оценок пока нет
- Grade 7 Sorico Math Unit 2 3 2013-2014Документ4 страницыGrade 7 Sorico Math Unit 2 3 2013-2014api-233707670Оценок пока нет
- CSEC Add Maths Study GuideДокумент4 страницыCSEC Add Maths Study Guider6hОценок пока нет
- Ccgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit4seДокумент28 страницCcgps Math 6 6thgrade Unit4seapi-239312188Оценок пока нет
- Teks 4TH-8TH GradeДокумент20 страницTeks 4TH-8TH GradeFreddy Reyes FalckОценок пока нет
- Chapter 111. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills For Mathematics Subchapter C. High SchoolДокумент17 страницChapter 111. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills For Mathematics Subchapter C. High Schoolascap85Оценок пока нет
- Using Definitions and Geometric Properties: Geometry, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1Документ4 страницыUsing Definitions and Geometric Properties: Geometry, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1rmullen82Оценок пока нет
- Secondary Math Standards by Strand - Achieve - May 2008Документ59 страницSecondary Math Standards by Strand - Achieve - May 2008Dennis AshendorfОценок пока нет
- Math Grade 5 08 11Документ6 страницMath Grade 5 08 11api-246939068Оценок пока нет
- Math 8 Commom Core SyllabusДокумент6 страницMath 8 Commom Core Syllabusapi-261815606Оценок пока нет
- CCSSI Math Standards 5Документ6 страницCCSSI Math Standards 5establoid1169Оценок пока нет
- CPM Ebooks - CC Course 1 Overview PDFДокумент1 страницаCPM Ebooks - CC Course 1 Overview PDFnayana_ksОценок пока нет
- Rules of Exponents and Scientific Notation: Grade 8 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1Документ4 страницыRules of Exponents and Scientific Notation: Grade 8 Mathematics, Quarter 1, Unit 1.1api-270891801Оценок пока нет
- 6th Grade CBEДокумент3 страницы6th Grade CBEAneetha Trikur0% (1)
- Math 10c Long Range PlanДокумент6 страницMath 10c Long Range Planapi-266460789Оценок пока нет
- Fourth Math StandardsДокумент3 страницыFourth Math Standardsapi-233655908Оценок пока нет
- Grade Six Indicators For The Mathematics Standard Course of StudyДокумент56 страницGrade Six Indicators For The Mathematics Standard Course of StudyNeha SinghОценок пока нет
- NCTM Statement of Beliefs: M A T H E M A T I C SДокумент6 страницNCTM Statement of Beliefs: M A T H E M A T I C SFreddy Reyes FalckОценок пока нет
- Articulated by Grade LevelДокумент45 страницArticulated by Grade LevelForrest FlenerОценок пока нет
- Algebra IaДокумент2 страницыAlgebra Iaapi-246939068Оценок пока нет
- CCSSI Math Standards 4Документ6 страницCCSSI Math Standards 4establoid1169Оценок пока нет
- Standard Eight: No Plastic PleaseДокумент130 страницStandard Eight: No Plastic PleaseSana SohoniОценок пока нет
- CCSS Unpacking Template ExampleДокумент7 страницCCSS Unpacking Template Examplechardz10Оценок пока нет
- Grade 6 Sorico Math Unit 1 2 2013-2014Документ5 страницGrade 6 Sorico Math Unit 1 2 2013-2014api-233707670Оценок пока нет
- Scheme of Work Maths Stage 7Документ18 страницScheme of Work Maths Stage 7Sue Adames de Velasco100% (7)
- Wanted Poster Exemplar BariumДокумент2 страницыWanted Poster Exemplar Bariumapi-263902873Оценок пока нет
- Science 9 Course Outline 2015Документ2 страницыScience 9 Course Outline 2015api-263902873Оценок пока нет
- New Grade 9 Specific Curriculum OutcomesДокумент9 страницNew Grade 9 Specific Curriculum Outcomesapi-263902873Оценок пока нет
- Healthy Living 9 OutcomesДокумент2 страницыHealthy Living 9 Outcomesapi-263902873Оценок пока нет
- Math 9 Course Outline 2015Документ2 страницыMath 9 Course Outline 2015api-263902873Оценок пока нет
- Math 8 Course Outline 2014 v2Документ2 страницыMath 8 Course Outline 2014 v2api-263902873Оценок пока нет
- Science 9 OutcomesДокумент3 страницыScience 9 Outcomesapi-263902873Оценок пока нет
- Math 8 Course Outline 2014 v2Документ2 страницыMath 8 Course Outline 2014 v2api-263902873Оценок пока нет
- Exam Ref AZ 305 Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Sol 2023Документ285 страницExam Ref AZ 305 Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Sol 2023maniОценок пока нет
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week - 01 Module - 01 Lecture - 01Документ8 страницDesign and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week - 01 Module - 01 Lecture - 01SwatiОценок пока нет
- Obat LasaДокумент3 страницыObat Lasaibnunanda29Оценок пока нет
- Call SANROCCO 11 HappybirthdayBramanteДокумент8 страницCall SANROCCO 11 HappybirthdayBramanterod57Оценок пока нет
- City of Brescia - Map - WWW - Bresciatourism.itДокумент1 страницаCity of Brescia - Map - WWW - Bresciatourism.itBrescia TourismОценок пока нет
- Mesopotamia CivilizationДокумент56 страницMesopotamia CivilizationYashika TharwaniОценок пока нет
- HP 5973 Quick ReferenceДокумент28 страницHP 5973 Quick ReferenceDavid ruizОценок пока нет
- Merchandise Floor Ready Standards - Supplier InformationДокумент46 страницMerchandise Floor Ready Standards - Supplier InformationGarmentLearner100% (1)
- Done by Akansha Bharti Harshitha K.N. Ishika Sunil Rajput Rashmi NaikДокумент12 страницDone by Akansha Bharti Harshitha K.N. Ishika Sunil Rajput Rashmi NaikRamya BalanОценок пока нет
- AJK Newslet-1Документ28 страницAJK Newslet-1Syed Raza Ali RazaОценок пока нет
- Body Scan AnalysisДокумент9 страницBody Scan AnalysisAmaury CosmeОценок пока нет
- The Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeДокумент44 страницыThe Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeYiğit KılıçОценок пока нет
- STERNOL Specification ToolДокумент15 страницSTERNOL Specification ToolMahdyZargarОценок пока нет
- Legal Research MethodsДокумент10 страницLegal Research MethodsCol Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Center of Gravity and Shear Center of Thin-Walled Open-Section Composite BeamsДокумент6 страницCenter of Gravity and Shear Center of Thin-Walled Open-Section Composite Beamsredz00100% (1)
- Ipo Exam Revised SyllabusДокумент1 страницаIpo Exam Revised Syllabusজ্যোতিৰ্ময় বসুমতাৰীОценок пока нет
- StsДокумент10 страницStsSamonte, KimОценок пока нет
- LLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety TrendsДокумент23 страницыLLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety Trendssuvabrata_das01100% (1)
- Keberhasilan Aklimatisasi Dan Pembesaran Bibit Kompot Anggrek Bulan (Phalaenopsis) Pada Beberapa Kombinasi Media TanamДокумент6 страницKeberhasilan Aklimatisasi Dan Pembesaran Bibit Kompot Anggrek Bulan (Phalaenopsis) Pada Beberapa Kombinasi Media TanamSihonoОценок пока нет
- Policies and Regulations On EV Charging in India PPT KrishnaДокумент9 страницPolicies and Regulations On EV Charging in India PPT KrishnaSonal ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- BỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO ĐỀ THI HỌC PHẦN KINH TẾ VĨ MÔДокумент5 страницBỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO ĐỀ THI HỌC PHẦN KINH TẾ VĨ MÔPhạm Thu NgaОценок пока нет
- Desarme Del ConvertidorpdfДокумент7 страницDesarme Del ConvertidorpdfDiego Orlando Santos BuitragoОценок пока нет
- Eudragit ReviewДокумент16 страницEudragit ReviewlichenresearchОценок пока нет
- Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsДокумент8 страницAddition and Subtraction of PolynomialsPearl AdamosОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5 CMAДокумент10 страницLesson 5 CMAAssma SabriОценок пока нет
- Assessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistДокумент7 страницAssessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistNicole NipasОценок пока нет
- Flexible AC Transmission SystemsДокумент51 страницаFlexible AC Transmission SystemsPriyanka VedulaОценок пока нет
- Application Programming InterfaceДокумент12 страницApplication Programming InterfacesorinproiecteОценок пока нет
- January 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Документ2 страницыJanuary 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Rizwanur RahmanОценок пока нет