Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Y10 Structures Auscur Portfolio
Загружено:
api-261796940Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Y10 Structures Auscur Portfolio
Загружено:
api-261796940Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
STRUCTUR
ES
CHAPTER
9
Course: Australian Curriculum Year 10 Science
Definition of Force A push or a
pull
SI unit to measure force
newton (N) in a given direction
Remember Force is a vector!!
The effects of a Force
a) Change the motion of a body
(a change in speed and/or direction)
b) Changes shape of a body
(squash or extend)
The addition of Force vectors
If you consider a number of forces acting on an
object
the net force is the overall effect of these forces
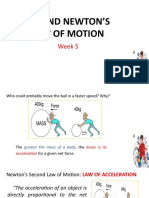
Example a boy and a girl pull a Controller with
equal force in opposite directions.
The sum of the forces or net force is zero
80 N
80 N
The addition of Force vectors
If the girl increases her force to 100 N
the sum of the forces or net force changes
The net force is 20 N right
100 N
80 N
Balanced Forces
When the net force acting on an
object is zero
In terms of motion this means the
object will not accelerate
It can stay at a constant speed in a
straight line
OR it can stay at rest
Balanced Forces
Example balanced forces on a car at rest
Weight Force
20 000 N down
Reaction Force
20 000 N up
Balanced Forces
Example balanced forces on a car
moving at a constant velocity
Weight Force
20 000 N down
Reaction Force
20 000 N up
Driving Force
3000 N right
Friction
3000 N left
Unbalanced Forces
When the net force acting on an
object is NOT zero
In terms of motion this means the
object will accelerate
Within a building or structure this will
cause Failure
Unbalanced Forces
Example unbalanced forces on a car that
is accelerating
Weight Force
20 000 N down
Reaction Force
20 000 N up
Driving Force
7000 N right
Friction
3000 N left
What is the net force on the
balloon?
Weight Force
1 N down
Lift Force
5 N up
Wind Force
5 N right
Friction
2 N left
The net forces are:
Net force =
5 N up + right
(53.1)
4 N up
3 N right
Vector addition
Vector addition: Example
Show the resultant force F for the vector diagram below
Vector addition: Example
There are many variations that will result in the same net force
Vector addition: Example
Work out the net force and direction on the
game control (remember to give an angle for
direction).
75N @ N 180
degrees
330N @ N 270
degrees
0 Degrees North
Vector addition: Example
Work out the net force and direction on the
game control (remember to give an angle for
direction).
220N @ N 45
degrees
75N @ N 180
degrees
330N @ N 270
degrees
0 Degrees North
Forces in structures
Structures are designed so that all forces acting
within them are always balanced.
If any forces become unbalanced this can lead to
Failure
Minor Failure examples doors jam, windows
stick, cracks appear in tile, brickwork, plaster.
Major Failure examples parts of the structure or
the entire structure will collapse.
Examples of minor failure
Examples of minor failure
Examples of minor failure
Geological structures
Geological structures
Geological structures
Major failures
Gravity
Gravity is the attractive force that acts between
masses.
Any 2 masses are attracted to each other with
an equal force
The bigger the masses the bigger the force
The closer they are the bigger the force
Newtons universal law of
gravity
G = Gravitational constant = 6.67 x 10 ^ -11
What does this
mean for a man on
the moon?
The man is being
attracted to the moon and
the moon is also being
attracted to the man.
This attraction between
the two bodies is less
than if the man were on
Earth because the mass
of the Moon and the man
is less than the mass of
Earth and the man.
Gravity Application
Gravity Application Mineral
discovery
The discovery of many
hidden mineral
deposits are found
using geophysics. One
technique of
geophysics is to
analyse gravity data.
Mass
Mass (m) is a measure of the amount of a
substance measured in kilograms (kg)
How many kg is a car with a mass of 2.2
tonnes?
Ans: 2200 kg
How many kg is a can of coke 375 grams ?
Ans 0.375 kg
A dose of medicine has a mass of 5 grams,
how many kg is this?
Ans: 0.005 kg
Weight
Weight (W) is the force acting on a mass
placed in a gravitational field and measured in
newtons (N)
W = m.g
g = gravitational field strength (N per kg)
g (Earth) = 9.8 N per kg
g (moon) = 1.62 N per kg
m = mass (kg)
Example Calculation
The mass of bricks and mortar
used to make a wall is 250 kg
Calculate the Weight Force of
the wall pressing down into the
ground
W = m.g
W = 250 x 9.8 = 2450 N into the ground
Calculate the weight force if the wall was
constructed on the moon
W = m.g
W = 250 x 1.62 = 405 N into the moon
Example Calculation 2
What is the combined weight of the 4 skydivers
travelling towards earth if each had a mass of
75kg?
The Reaction Force
Any mass has weight, even a skydiver in free-fall
When a mass is placed on firm ground the weight
causes an action force that pushes into the
ground.
The ground pushes back with the same force
perpendicular to the surface a normal reaction
force
How many forces acting on the brick?
= 2, Weight and Reaction Force
What is the net force on the brick?
= zero, the forces are balanced
Weight of brick
Reaction Force from
ground into brick
Action Force from
brick into ground
The Reaction Force Example
2
(a) What is the weight
of the 20kg box (on
Earth)?
(b) Determine the
Normal force the table
exhibits on the 20kg
box.
(c) Determine the
Normal force the 20kg
box exhibits on the
10kg box.
Compression
If forces are acting on a component that tend to
squash it, then it is in Compression.
If a Rhino is placed
on top of a marble
column.
The action force from
the Rhinos weight
pushes down on the
column
The reaction force
from the brick base
pushes up on the
column
Compression
Example 2
The legs of the
water tower are
compressed by the
weight of the water
acting down and the
reaction force from
the ground acting up
Tension
if forces are acting on a component that tend to
stretch it, then it is in Tension
A Gorilla is hanging from
a rope attached to the
ceiling
The action force from the
Gorillas weight pulls
down on the rope
The reaction force from
the ceiling pulls up on
the rope
Example 2
The cables of a suspension bridge are in
tension supporting the weight of the
roadway
Example 3
Label the sketch to indicate
what members are in
tension and what are in
compression
A
B
C
Tension
Tension
Compressi
on
Substances used in Structures
When building structures it is important to select the
best materials for the job.
Some materials are very strong in compression but
are weak in tension:
Examples: Concrete, Brick, Marble
Some materials are good in tension but weak in
compression.
Examples: Carbon Fibre, Nylon, Kevlar
Some materials are good in both compression and
tension
Examples: Steel, Aluminium, Timber, Bone
Concrete testing
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QrcRABenT
BE
Slow motion
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gg_bIMJ7I0
M
Concrete example
Concrete strong under compression weak under
tension
UNLESS it is reinforced.examples.
Other Factors to consider
Weight
Cost
Availability
Ease of construction
Ability to repair
Fire protection
Material safety
etc. etc.
Stress
Stress
Which footwear is best suited to walk across
the beach?
Both support the same Weight but the thongs
spread the load over a greater surface area.
Stress example
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vo2iE94iAoA
Stress
=
Force
Cross sectional surface area
(
2
)
Symbols: =
(
2
)
Units
mega newton per m
2
= 1 million N/m
2
= 1
MN/m
2
Stress
Cross sectional surface area:
Consider 2 columns supporting the weight of a
gorilla
The Cross-sectional surface area is the area that
supports the load
Think of a slice through the component
Compressive Stress
Calculate the stress on a rectangular concrete
column with a square cross section measuring 35
cm 35 cm supporting a tank of mass 188 tonnes.
Force = Weight = m.g
Force = 188 000 x 9.8
Force = 1 842 400 N
Compressive Stress
Area = 0.35
2
Area = 0.1225 m
2
=
=
1 842 400
0.1225
= 15 040 000
2
(convert to mega newtons per
m
2
)
15.04 MN/m
2
Compare with maximum compressive stress table
9.1.1 on page 297. Will this concrete support the
tank?
Concrete = 20 MN/m
2
so YES it will support the
tank!!
Tension and necking
If there is a weakness in the material under
tension then necking may occur depending on
the type of material.
A weakness can be a scratch or a slight dint in
the material which causes the forces to
become unbalanced at that point (like our
paper towers).
What is necking?
Read the paragraph on p297 explain and
draw diagrams
Вам также может понравиться
- B - Energy and Momentum 2008Документ152 страницыB - Energy and Momentum 2008Mielle Grace CarballoОценок пока нет
- Force and Friction Work Energy Power o Level 1Документ25 страницForce and Friction Work Energy Power o Level 1kasumbaashraf3Оценок пока нет
- 1 Law of Acceleration Law of InteractionДокумент25 страниц1 Law of Acceleration Law of InteractionIah VergaraОценок пока нет
- SheeeshhhhhhДокумент21 страницаSheeeshhhhhhEXTREME GAMERS SQUADОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент9 страницIGCSE Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionKasunDilshanОценок пока нет
- Year 11 Term 1 Notes: Introduction To Engineering Statics and Engineering DrawingДокумент45 страницYear 11 Term 1 Notes: Introduction To Engineering Statics and Engineering DrawingFrankie TamОценок пока нет
- 3.1 ForceДокумент80 страниц3.1 ForceMuhd AfifОценок пока нет
- Newton's Second Law of Motion - Force and AccelerationДокумент31 страницаNewton's Second Law of Motion - Force and AccelerationJayhia Malaga JarlegaОценок пока нет
- Ding Thethe Effects of A ForceДокумент18 страницDing Thethe Effects of A Forcenik mohamad solehinОценок пока нет
- Loadings and Aspects of Structural Theory Relating To BuildingsДокумент9 страницLoadings and Aspects of Structural Theory Relating To Buildingspkimani10098Оценок пока нет
- 2 Force and AccelerationДокумент22 страницы2 Force and AccelerationMohd Harris IdrisОценок пока нет
- Force and Motion IIДокумент10 страницForce and Motion IIShubham ParabОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Newton's Second Law of MotionДокумент35 страницCH 5 Newton's Second Law of MotionMalik Nazim ChannarОценок пока нет
- Physics 122 Problem SetДокумент86 страницPhysics 122 Problem SetCarmen DraghiaОценок пока нет
- Delhi Public School, Udaipur SESSION (2020-21) Chapter 11: Force and Pressure (Notes)Документ6 страницDelhi Public School, Udaipur SESSION (2020-21) Chapter 11: Force and Pressure (Notes)Shilpa GoyalОценок пока нет
- Physics Notes Chapter No 4: Force and MotionДокумент6 страницPhysics Notes Chapter No 4: Force and Motionmohsin ali khanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 (A)Документ18 страницChapter 1 (A)Izzat AsyraafОценок пока нет
- 17.1.1 Assignment No. 1: Task 1Документ3 страницы17.1.1 Assignment No. 1: Task 1chami8082084Оценок пока нет
- Notes - Mech Energy and Momentum - ExpandedДокумент9 страницNotes - Mech Energy and Momentum - ExpandedAndy HeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7: Dynamic: Types of ForceДокумент54 страницыChapter 7: Dynamic: Types of ForceNur Azila ZabidiОценок пока нет
- ForceДокумент10 страницForceengmun80Оценок пока нет
- Nota FizikДокумент12 страницNota Fizikmoshi_nemo100% (1)
- Frictional ForceДокумент18 страницFrictional ForcemohammadrashikzamanОценок пока нет
- 2 (1) .Physics MechanicsДокумент35 страниц2 (1) .Physics MechanicsNo PainОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Physics NotesДокумент7 страницIGCSE Physics NotesRhea AgrawalОценок пока нет
- As 21c Motion&ForceДокумент40 страницAs 21c Motion&ForceHany ElGezawyОценок пока нет
- AssignДокумент10 страницAssignkakaОценок пока нет
- Week 5Документ54 страницыWeek 5christinereponte160Оценок пока нет
- Newton'S Law of MotionДокумент44 страницыNewton'S Law of MotionRussel SalvacionОценок пока нет
- L16 FrictionДокумент7 страницL16 Frictioni5piritiОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Part 1 - No RecordДокумент34 страницыUnit 2 Part 1 - No RecordRaed JahshanОценок пока нет
- AP Physics Notes - Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент9 страницAP Physics Notes - Newton's Laws of MotionAndy HeОценок пока нет
- Science Physics NotesДокумент46 страницScience Physics Noteshenry bhoneОценок пока нет
- Physics 101 Chapter 4 New Sec Law Term VelДокумент39 страницPhysics 101 Chapter 4 New Sec Law Term VelAndrew GoolsbyОценок пока нет
- Forces and MotionДокумент37 страницForces and MotionpjpanisОценок пока нет
- CH 8 - Energy & WorkДокумент23 страницыCH 8 - Energy & WorkJonni Maruli Tua SitorusОценок пока нет
- Physics Notes Chapter 3-7Документ16 страницPhysics Notes Chapter 3-7Esther Chua100% (1)
- JJ310 STRENGTH OF MATERIAL Chapter 1 (A) Forces On MaterialДокумент18 страницJJ310 STRENGTH OF MATERIAL Chapter 1 (A) Forces On MaterialAh Tiang100% (1)
- Work 2Документ18 страницWork 2elenaОценок пока нет
- Tut Test 4 MemoДокумент8 страницTut Test 4 MemoVogelОценок пока нет
- Apparent Weight. Example PDFДокумент5 страницApparent Weight. Example PDFShamoon WahedОценок пока нет
- Y9 Forces 1 Booklet 1 - Newton and Hookes Laws STW HuxleyДокумент43 страницыY9 Forces 1 Booklet 1 - Newton and Hookes Laws STW HuxleyhuxleymcentireОценок пока нет
- PM TB Solutions C03Документ5 страницPM TB Solutions C03Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (5)
- Work Energy and PowerДокумент42 страницыWork Energy and PowerKryschan CaditeОценок пока нет
- General Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionДокумент87 страницGeneral Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionPortia Egken100% (1)
- Chapter 3 DynamicsДокумент45 страницChapter 3 DynamicsEshaal MaryamОценок пока нет
- Forces and EquilibriumДокумент36 страницForces and EquilibriumSalmanОценок пока нет
- Physics of BridgesДокумент64 страницыPhysics of Bridgesthe-spirit50% (2)
- 3.3 Using Newton's LawsДокумент29 страниц3.3 Using Newton's LawsCeline JamalОценок пока нет
- Science 9 - Week 25Документ5 страницScience 9 - Week 25Mira VeranoОценок пока нет
- Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion: Phys101 Lectures 4 & 5Документ25 страницDynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion: Phys101 Lectures 4 & 5Anonymous m8oCtJBОценок пока нет
- Physics Forces Secondary3Документ23 страницыPhysics Forces Secondary3SoniaAlexОценок пока нет
- Effects of ForceДокумент38 страницEffects of ForceAz MY100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionДокумент61 страницаChapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionMUHAMMAD MAHMMOUD EL-QUDAFFYОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Science - 210614 - 104559Документ14 страницChapter 4 Science - 210614 - 104559Fatin AmirОценок пока нет
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstДокумент34 страницыPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaОценок пока нет
- Physics A Unit 4 Equilibrium ForcesДокумент12 страницPhysics A Unit 4 Equilibrium ForcesAli Ahmad AliОценок пока нет
- Lakhmir Singh Science Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 11Документ15 страницLakhmir Singh Science Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 11k l pandeyОценок пока нет
- Vortex - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент8 страницVortex - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSheikh Zakir100% (1)
- CVE 303 Fluid MechanicsДокумент8 страницCVE 303 Fluid MechanicsSamuel Oluwaseun OlatunjiОценок пока нет
- Chemical Engineering Lab I Manual - SP15Документ66 страницChemical Engineering Lab I Manual - SP15MohammedAliMohammed100% (2)
- Experiment # 7Документ4 страницыExperiment # 7Maro VioОценок пока нет
- ENG 102 Syllabus PDFДокумент4 страницыENG 102 Syllabus PDFSteelcover100% (1)
- Impact of Jet On VanesДокумент5 страницImpact of Jet On Vanesanil chejara100% (7)
- Vorticity and CirculationДокумент18 страницVorticity and CirculationShweta NagpalОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Oxygen As It Flows Through A NozzleДокумент5 страницThermodynamic Analysis of Oxygen As It Flows Through A NozzleEmmanuel AnakorОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3 Fanno FlowДокумент3 страницыAssignment 3 Fanno FlowABHI THAKKAR0% (1)
- Topic Required Tools Reference Books No. of Period Required Date Students RemarkДокумент3 страницыTopic Required Tools Reference Books No. of Period Required Date Students RemarkjeetОценок пока нет
- Problems FluidsДокумент7 страницProblems FluidsSameer SamaraОценок пока нет
- 3.2 - Gravitational Acceleration WorksheetДокумент1 страница3.2 - Gravitational Acceleration WorksheetAlvin Cajipo SagubanОценок пока нет
- A Coriolis Tutorial: Part 2: A Rotating Shallow Water Model, Potential Vorticity and Geostrophic AdjustmentДокумент59 страницA Coriolis Tutorial: Part 2: A Rotating Shallow Water Model, Potential Vorticity and Geostrophic Adjustmenttagne simo rodrigueОценок пока нет
- Forces Acting On An AircraftДокумент11 страницForces Acting On An AircraftRajesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Line Sizing MainДокумент10 страницLine Sizing MainNitin KurupОценок пока нет
- Assign 1Документ2 страницыAssign 1Waleed Bin KhalidОценок пока нет
- Predict Friction Lossin Slurry Pipes Darbyetal 1992Документ5 страницPredict Friction Lossin Slurry Pipes Darbyetal 1992Baris YeltekinОценок пока нет
- Proportional Directional Valves: Series LVS08 and LVS12 - Preferred Products ProgrammeДокумент66 страницProportional Directional Valves: Series LVS08 and LVS12 - Preferred Products ProgrammealeksandrОценок пока нет
- MA3006 Introduction Sem. 2, 2020-21Документ3 страницыMA3006 Introduction Sem. 2, 2020-21ZenОценок пока нет
- Physics Paper PDFДокумент18 страницPhysics Paper PDFRana IrfanОценок пока нет
- 4647 - EME2066 Tutorial 4, Trim.3,2014-15Документ1 страница4647 - EME2066 Tutorial 4, Trim.3,2014-15Ong Teck ChongОценок пока нет
- ME 4953.009 Gas Dynamics Syllabus Spring 2015, Rev. BДокумент7 страницME 4953.009 Gas Dynamics Syllabus Spring 2015, Rev. Bxxxtoyaxxx0% (1)
- IHD602 Assignment RVF1 HydraulicJump 20161011yimДокумент2 страницыIHD602 Assignment RVF1 HydraulicJump 20161011yimAshafОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ52 страницыChapter 2Manamno BezaОценок пока нет
- Rotational Kinetic Energy: Learning OutcomeДокумент10 страницRotational Kinetic Energy: Learning OutcomeBouatake HedstromОценок пока нет
- Pump Part 2Документ35 страницPump Part 2Amit KhadkaОценок пока нет
- PLUMBING Booster Pump (AS PER IPC) - 13Документ55 страницPLUMBING Booster Pump (AS PER IPC) - 13Mohsin ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Ijer 2014 406Документ4 страницыIjer 2014 406Innovative Research PublicationsОценок пока нет
- Maria Pascu DissertationДокумент138 страницMaria Pascu DissertationVigiiОценок пока нет
- The Friction Factor It Is Denoted by F and Defined As The Ratio of The Wall Shear Stress To The Product of The Velocity Head (VДокумент2 страницыThe Friction Factor It Is Denoted by F and Defined As The Ratio of The Wall Shear Stress To The Product of The Velocity Head (VJHuvieCLaireОценок пока нет